Guide to electrical materials for all. Part 11
Continuing guidance on electrical materials. Almost the final part, about tapes and tubes. About Blue Tape, too, have a couple of words.

Welcome to CAT (TRAFFIC)
')
When it comes to electrical tape - the first thought that comes to mind is blue PVC electrical tape from the USSR. It is blue insulating tape that is a reason for jokes and writing comments that have no value in some communities. But electrical tape is not only available on the basis of PVC film, there are many other types of electrical tape and below is a list of the most popular electrical tape. The type of electrical tape is selected on the basis of tasks, operating conditions, requirements for operation.
UPD: This is version 1.0, in version 1.4 this section has been significantly expanded. Download links are in the 12th part.
The artifact of the Soviet era is still being produced and sold - fabric duct tape (GOST 2162-97) - cotton fabric impregnated with rubber. Of the advantages - when heated, it does not melt, but is charred. This is where her merits end. Despite the impregnation, it is still partially hygroscopic, dries out over time, losing stickiness. Enjoys special love from the Oldfags.

Fabric rubberized electrical tape modern production.
Rubberized HB tape should not be confused with modern fabric tapes like Coroplast, they are a synthetic fabric cloth (or non-woven cloth) with an impregnation and adhesive layer (sometimes specially combed to "hairiness"). Used for wiring harnesses in cars. In contrast to PVC tape, such a harness does not “thunder” during vibration, as the fabric well damps vibrations.
Represent a thick (0.5-1 mm) rubber tape with a protective layer. At isolation of connection the protective tape is removed, the insulating tape with a tension is reeled overlapped. From contact with air, the overlap places are self-welded, forming a monolithic layer. Then do not unwind this winding, just cut it.
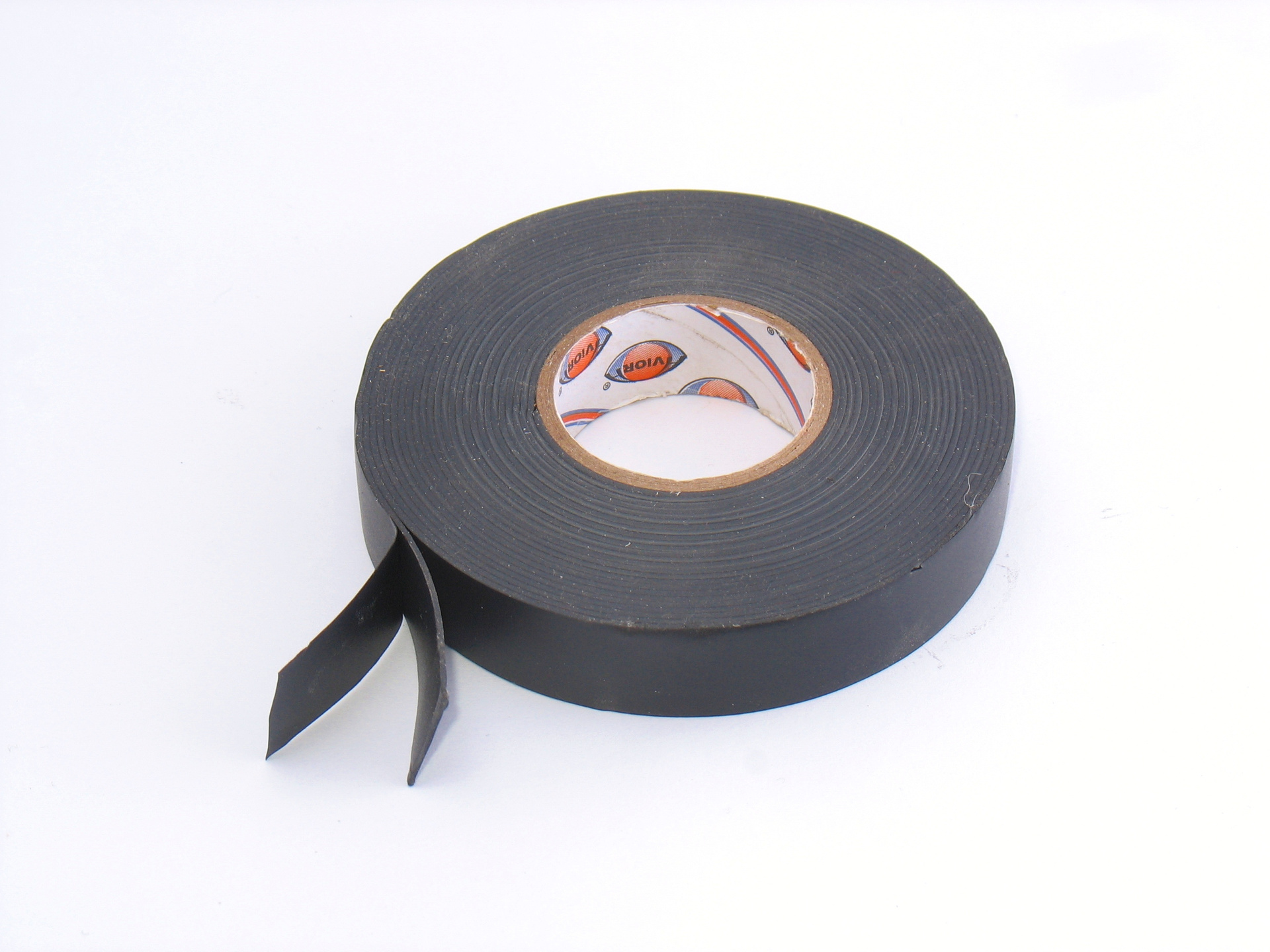

A roll of self-sticking (self-curing) electrical tape. The protective thin layer is removed during winding, and the tape itself is stretched tightly wrapping around the joint.
Similar to rubber, but from silicone polymer. These are tapes LETSAR (RET-SAR - with a reinforcing layer of fiberglass). After winding overlap in a couple of days, they stick together tightly. Silicones, unlike rubber, are more heat-resistant, resistant to chemical attack, retain elasticity in the cold.
Also known as “thermoscratch”, “Kapton tape”. (Kapton - as well as Teflon - is a registered trademark, which has become a household name.) Yellow transparent heat-resistant tape, can often be seen in phones, laptops - loops and wires are fixed to it.
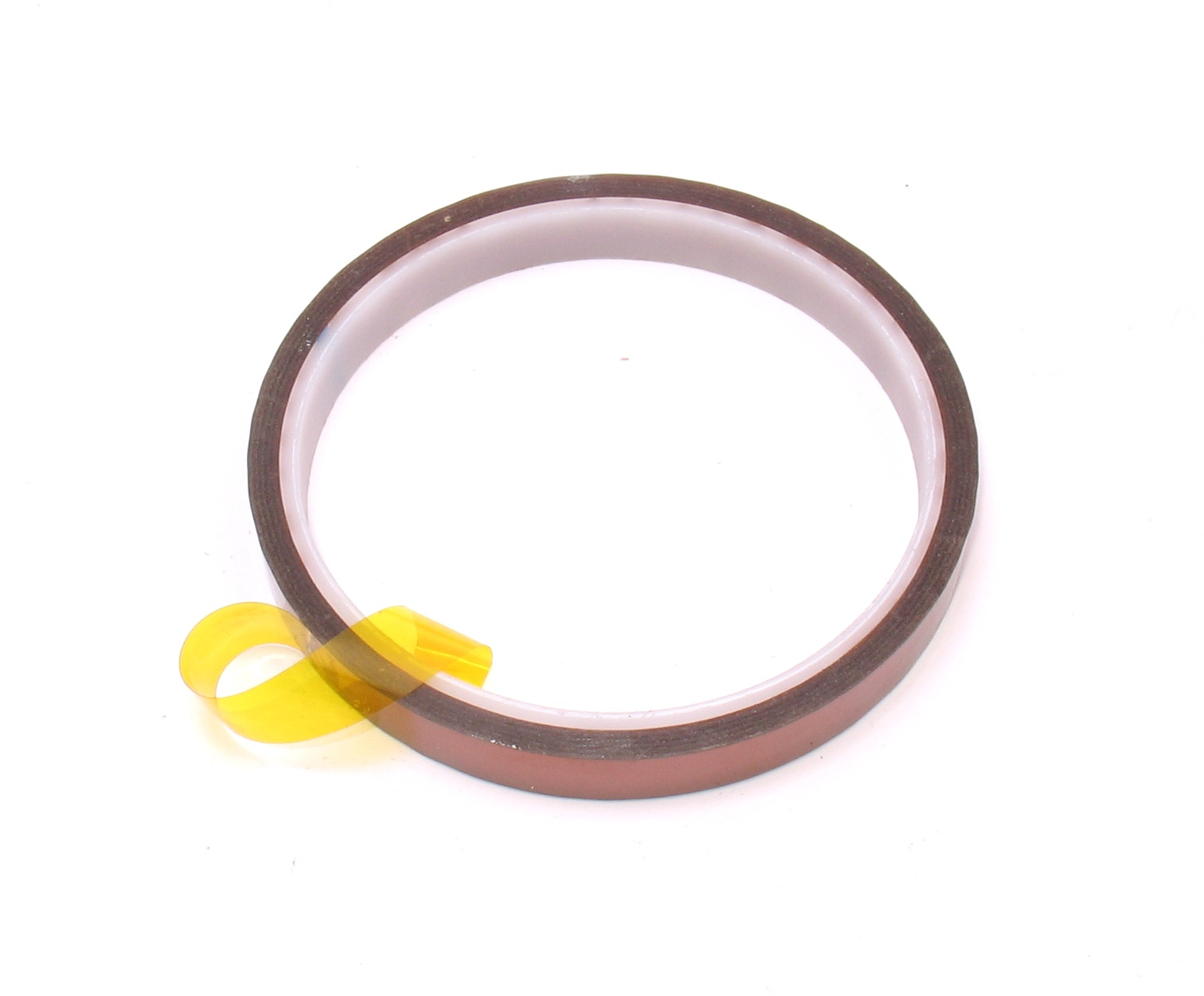

A roll of self-adhesive heat-resistant insulation tape.
Heat resistant (does not melt with a soldering iron), does not stretch, in the cold does not dubet as PVC. For
Electronic affairs are rare. Used in the repair of equipment, with
soldering a hair dryer with such a tape you can glue the elements that are not to be soldered so as not to blow off
them by chance.
The most common type of electrical tape. We say “insulating tape” - blue PVC insulating tape is immediately on your mind. Plasticized PVC tape with adhesive layer. Not afraid of moisture, the connection is insulated with such tape is not afraid of bends. The quality of electrical tape varies from "not sticky" in poorly kept old domestic ones, to "it is a pleasure to work" with 3M or Tesa branded products.

Different colors electrical tape.
The only electrical tape with a wide palette of colors - black, green, red, brown, gray ... for any color and taste, and to order there is even pink, purple and orange.
There is also a striped yellow-green - all for the color marking of conductors according to the EMP. And only a clinical idiot rolls all the connections with yellow-green tape for PE conductors.
It stretches well - it is possible to insulate complex joints without folds and bubbles.
It is afraid of heating. When overheating drains, though in the wake of the insulation wires. With prolonged low heat (80 - 100 ° C) loses elasticity and crumbles.
Afraid of the sun. The sun loses color and elasticity.
Crawling. This is the disadvantage of all electrical tape with non-dry sticky layer. If the tape is wound with great effort, it gradually "crawls" on the adhesive layer.
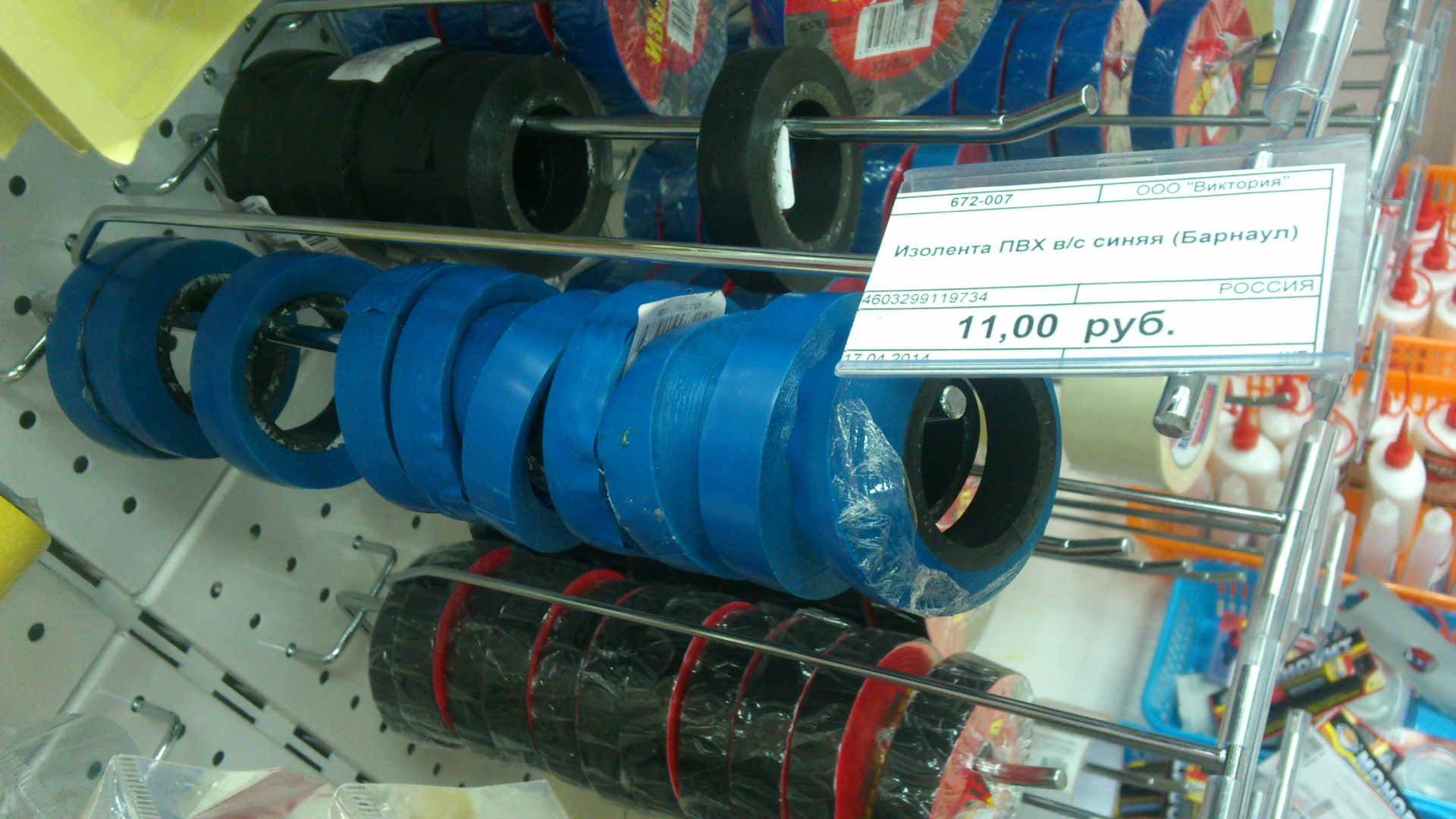

Deformed rolls of electrical tape. The tape on the roll was wound with effort and tape "crept" on the adhesive layer.
In the cold dubeet. The disadvantage of PVC, if you try to wind up the connection at an outdoor temperature of -5 ° C, you may encounter the fact that the tape does not stick, and when
Severe Ural frosts at -35 ° C electrical tape can fall out of your hand and break. Some manufacturers produce special cold-resistant tape that can work at low temperatures.
Scotch is a trademark, but like a thermos, copier, scuba and other brands has become a common name for transparent adhesive tape. Although such adhesive tape is not used in electrical engineering it is worth talking about it.
It is made most often from BOPP - Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene. The tape is transparent, strong enough and is a good dielectric. Unfortunately, such an adhesive tape is prone to the "effect of an unbuttoned zipper" and the presence of cuts allows the tape to burst with minimal effort.
One layer of adhesive tape can withstand a voltage of about 1000 V AC, so if you need to insulate the connection, and there is nothing else at hand, you can do it with adhesive tape, although the quality and reliability of such insulation will be low.
Sometimes the use of pipes as dielectric is preferable to electrical tape - due to
the complexity of use in the mass assembly of equipment, for guaranteed tightness, with difficulties in the availability of the connection for wet tape. The slang name insulating tubes - " cambric ."
It was widespread in the USSR to isolate the connections of wires to the terminals, the connections of wires between themselves, wherever shrinkable materials are now used.
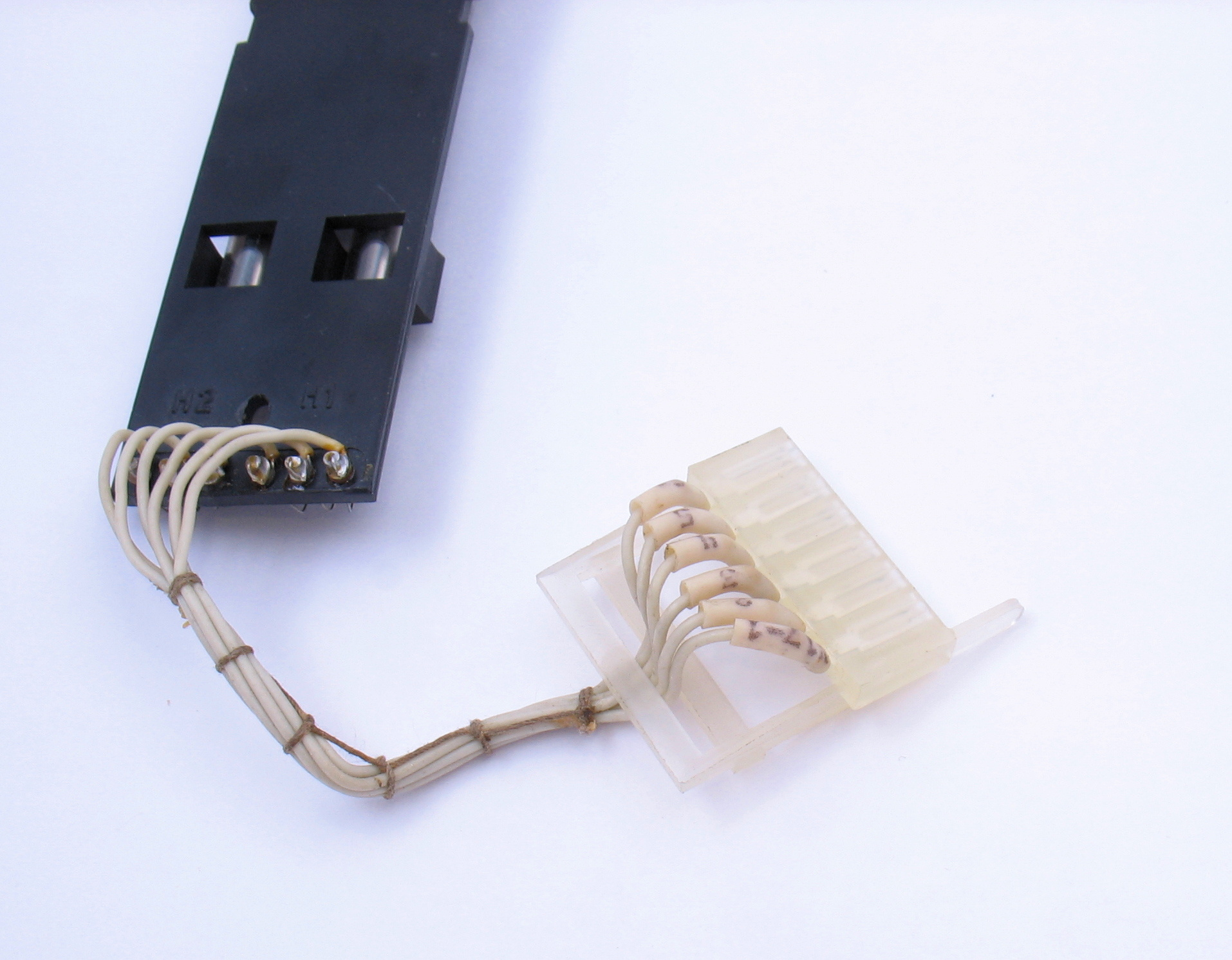
The soldering points of the wire to the connector are covered with a shaker.
It is still sold and used. It has a low elasticity, so you need to take measures so that the tube does not jump off or slide along the wire.
In some cases, it is quite possible to use various PVC hoses as an insulating tube, including for compressors, aquariums, etc. All the advantages and disadvantages of polyvinyl chloride remain the same and are described in the section above on PVC.
It is used as heat-resistant insulation, especially when paired with MGTF wire. As well as the fluoroplastic does not like long mechanical loads, but it keeps quite a high temperature. Slippery and non-elastic.
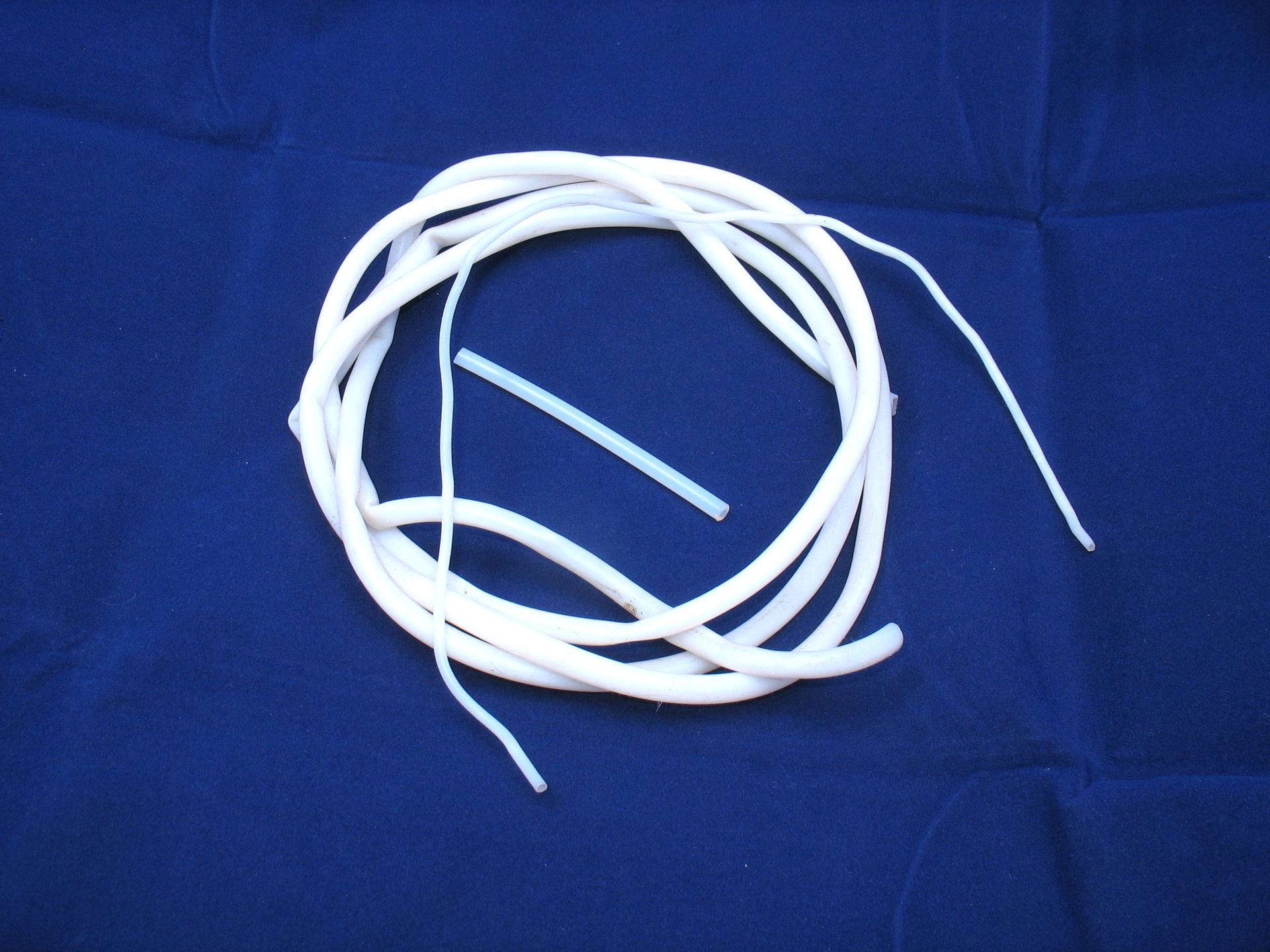
PTFE insulation tube. In the center is a piece of pneumatic fluoroplastic tube.
In the plastic supply mechanisms of 3D printers, a fluoroplastic tube for pneumatic systems is used as a thermal barrier (outer diameter 4 mm, internal 2 mm). When filing a plastic filament through such a tube into an extruder, the slipperiness of the fluoroplastic plays an important role.
There are several types, depending on the material of reinforcement. (Details can be found in GOST 17675-87).
A tube made of cotton stocking impregnated with varnish is called "linoxin
tube "(type 110 according to GOST 17675-87).," Insulating tube TLV "," insulating lacquer tube ", and has a characteristic yellow color with a visible weave texture. Used to isolate the joints of windings of electrical machines with stranded wires.
Where there is a constant heater - kettles, irons, fan heaters, thermopots, etc., a more heat-resistant version is used - “glass-reinforced insulation tube”. It is a silicone tube, covered outside with a glass cloth stocking, or the stocking itself is impregnated with silicone. Silicone itself is heat-resistant and sufficient for insulation, but fiberglass adds strength and prevents adhesion. However, non-reinforced silicone tubes are sometimes found as insulating.
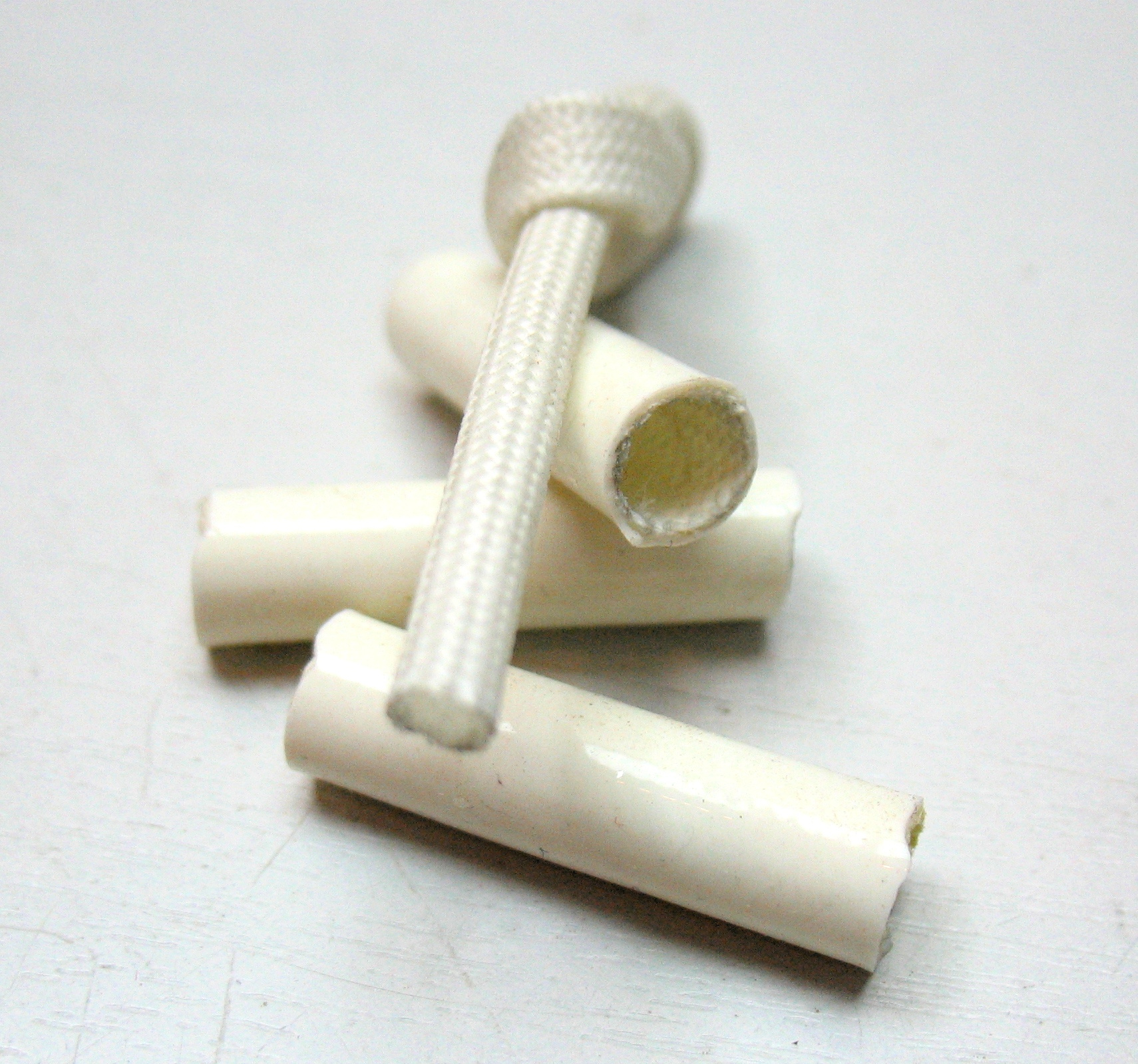

Fiberglass-silicone heat-resistant insulation tube. Glass cloth reinforcing layer can be both inside the tube and outside.
It is worth noting that when using such tubes, it is necessary to take into account their fixation in place; if the arrangement is unsuccessful, such a tube can “come off” over the wire and expose the connection.
It is widely used for insulation of compounds and almost completely ousted from their positions PVC cambric, as it is convenient to use. It is a polymer (The specific type of polymer depends on the manufacturer, unfortunately it is impossible to unequivocally indicate that it is only polyethylene for example.) A tube with shape memory - the tube stretches in a cold one after manufacturing (In fact, the temperature regimes in manufacturing are somewhat more complicated, but for convenience we’ll assume that in a cold state) condition that creates internal stress. When heated to the softening temperature, (but not melting), the polymer tends to regain its shape and the tube "shrinks", decreasing in diameter very significantly. The heat shrink tubing tightly wraps around the connections, ensuring that the tube does not slip off and does not dislodge.
Available in a variety of colors, diameters, types.
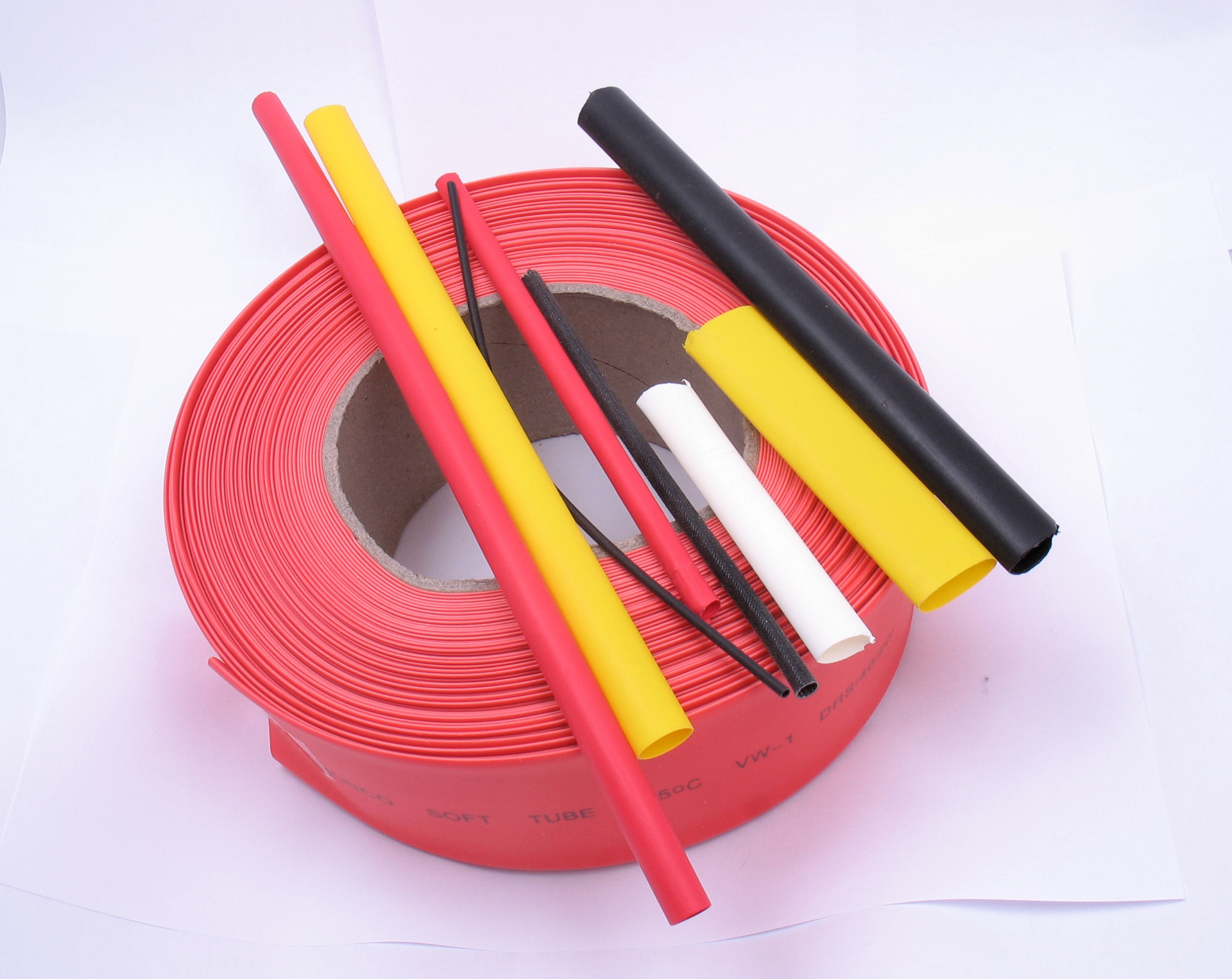

Various pieces of heat shrink tubing.
Work with shrinking is simple - cut, wear, heat.

Solder connection, we push the heat shrinkable tube of suitable diameter and heat it. After shrinking the tube is securely fixed.
To ensure a tight connection, heat shrinkable tubes with an adhesive layer are produced - they are coated on the inside with a layer of glue, which, when heated and settled, firmly sticks the tube to the surface of the wire. Such a connection may be necessary, for example, when extending the wire of a submersible pump.
Sometimes the body of the device generally consists of a single heat shrink.
Thermal shrinking in the presence of dexterity is quite realistic to stretch to an additional millimeter in diameter when there is no suitable one at hand, and the one that exists does not fit very well.
If the heat shrink tube is heated up strongly and “pinned” the end, it will stick together, thus it is possible to plug the ends of the cables from moisture ingress.
At this point, a link to the full pdf version of the manual was planned, and a part was conceived as final. But thanks to your comments formed a large list of improvements. Therefore, I take a break for revision of the manual, and the last, 12th part will be devoted to improvements + bonus chapter. Write in the comments about what else you would like to know?
1 : Conductors: Silver, Copper, Aluminum.
2 : Conductors: Iron, Gold, Nickel, Tungsten, Mercury.
3 : Conductors: Carbon, nichrome, thermostable alloys, solders, transparent conductors.
4 : Inorganic dielectrics: Porcelain, glass, mica, ceramics, asbestos, gas and water.
5 : Organic semi-synthetic dielectrics: Paper, click, paraffin, oil and wood.
6 : Synthetic dielectrics based on phenol-formaldehyde resins: carbolite (bakelite), getinax, textolite.
7 : Dielectrics: Glass fiber (FR-4), varnished cloth, rubber and ebonite.
8 : Plastics: polyethylene, polypropylene and polystyrene.
9 : Plastics: polytetrafluoroethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene terephthalate and silicones.
10 : Plastics: polyamides, polyimides, polymethyl methacrylate and polycarbonate. History of the use of plastics.
11 : Insulating tapes and tubes.
12 : Final

Welcome to CAT (TRAFFIC)
')
Electrical tape
When it comes to electrical tape - the first thought that comes to mind is blue PVC electrical tape from the USSR. It is blue insulating tape that is a reason for jokes and writing comments that have no value in some communities. But electrical tape is not only available on the basis of PVC film, there are many other types of electrical tape and below is a list of the most popular electrical tape. The type of electrical tape is selected on the basis of tasks, operating conditions, requirements for operation.
UPD: This is version 1.0, in version 1.4 this section has been significantly expanded. Download links are in the 12th part.
Rubberized fabric electrical tape
The artifact of the Soviet era is still being produced and sold - fabric duct tape (GOST 2162-97) - cotton fabric impregnated with rubber. Of the advantages - when heated, it does not melt, but is charred. This is where her merits end. Despite the impregnation, it is still partially hygroscopic, dries out over time, losing stickiness. Enjoys special love from the Oldfags.

Fabric rubberized electrical tape modern production.
Fabric tapes
Rubberized HB tape should not be confused with modern fabric tapes like Coroplast, they are a synthetic fabric cloth (or non-woven cloth) with an impregnation and adhesive layer (sometimes specially combed to "hairiness"). Used for wiring harnesses in cars. In contrast to PVC tape, such a harness does not “thunder” during vibration, as the fabric well damps vibrations.
Rubber self vulcanizing tape
Represent a thick (0.5-1 mm) rubber tape with a protective layer. At isolation of connection the protective tape is removed, the insulating tape with a tension is reeled overlapped. From contact with air, the overlap places are self-welded, forming a monolithic layer. Then do not unwind this winding, just cut it.

A roll of self-sticking (self-curing) electrical tape. The protective thin layer is removed during winding, and the tape itself is stretched tightly wrapping around the joint.
Silicone Self-Adhesive Tapes
Similar to rubber, but from silicone polymer. These are tapes LETSAR (RET-SAR - with a reinforcing layer of fiberglass). After winding overlap in a couple of days, they stick together tightly. Silicones, unlike rubber, are more heat-resistant, resistant to chemical attack, retain elasticity in the cold.
Polyimide tape
Also known as “thermoscratch”, “Kapton tape”. (Kapton - as well as Teflon - is a registered trademark, which has become a household name.) Yellow transparent heat-resistant tape, can often be seen in phones, laptops - loops and wires are fixed to it.

A roll of self-adhesive heat-resistant insulation tape.
Heat resistant (does not melt with a soldering iron), does not stretch, in the cold does not dubet as PVC. For
Electronic affairs are rare. Used in the repair of equipment, with
soldering a hair dryer with such a tape you can glue the elements that are not to be soldered so as not to blow off
them by chance.
PVC electrical tape
The most common type of electrical tape. We say “insulating tape” - blue PVC insulating tape is immediately on your mind. Plasticized PVC tape with adhesive layer. Not afraid of moisture, the connection is insulated with such tape is not afraid of bends. The quality of electrical tape varies from "not sticky" in poorly kept old domestic ones, to "it is a pleasure to work" with 3M or Tesa branded products.

Different colors electrical tape.
Buns
The only electrical tape with a wide palette of colors - black, green, red, brown, gray ... for any color and taste, and to order there is even pink, purple and orange.
There is also a striped yellow-green - all for the color marking of conductors according to the EMP. And only a clinical idiot rolls all the connections with yellow-green tape for PE conductors.
It stretches well - it is possible to insulate complex joints without folds and bubbles.
disadvantages
It is afraid of heating. When overheating drains, though in the wake of the insulation wires. With prolonged low heat (80 - 100 ° C) loses elasticity and crumbles.
Afraid of the sun. The sun loses color and elasticity.
Crawling. This is the disadvantage of all electrical tape with non-dry sticky layer. If the tape is wound with great effort, it gradually "crawls" on the adhesive layer.

Deformed rolls of electrical tape. The tape on the roll was wound with effort and tape "crept" on the adhesive layer.
In the cold dubeet. The disadvantage of PVC, if you try to wind up the connection at an outdoor temperature of -5 ° C, you may encounter the fact that the tape does not stick, and when
Severe Ural frosts at -35 ° C electrical tape can fall out of your hand and break. Some manufacturers produce special cold-resistant tape that can work at low temperatures.
Office adhesive tape "tape"
Scotch is a trademark, but like a thermos, copier, scuba and other brands has become a common name for transparent adhesive tape. Although such adhesive tape is not used in electrical engineering it is worth talking about it.
It is made most often from BOPP - Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene. The tape is transparent, strong enough and is a good dielectric. Unfortunately, such an adhesive tape is prone to the "effect of an unbuttoned zipper" and the presence of cuts allows the tape to burst with minimal effort.
One layer of adhesive tape can withstand a voltage of about 1000 V AC, so if you need to insulate the connection, and there is nothing else at hand, you can do it with adhesive tape, although the quality and reliability of such insulation will be low.
Insulating tubes
Sometimes the use of pipes as dielectric is preferable to electrical tape - due to
the complexity of use in the mass assembly of equipment, for guaranteed tightness, with difficulties in the availability of the connection for wet tape. The slang name insulating tubes - " cambric ."
PVC tube
It was widespread in the USSR to isolate the connections of wires to the terminals, the connections of wires between themselves, wherever shrinkable materials are now used.

The soldering points of the wire to the connector are covered with a shaker.
It is still sold and used. It has a low elasticity, so you need to take measures so that the tube does not jump off or slide along the wire.
In some cases, it is quite possible to use various PVC hoses as an insulating tube, including for compressors, aquariums, etc. All the advantages and disadvantages of polyvinyl chloride remain the same and are described in the section above on PVC.
PTFE tube
It is used as heat-resistant insulation, especially when paired with MGTF wire. As well as the fluoroplastic does not like long mechanical loads, but it keeps quite a high temperature. Slippery and non-elastic.

PTFE insulation tube. In the center is a piece of pneumatic fluoroplastic tube.
In the plastic supply mechanisms of 3D printers, a fluoroplastic tube for pneumatic systems is used as a thermal barrier (outer diameter 4 mm, internal 2 mm). When filing a plastic filament through such a tube into an extruder, the slipperiness of the fluoroplastic plays an important role.
Reinforced tubes
There are several types, depending on the material of reinforcement. (Details can be found in GOST 17675-87).
A tube made of cotton stocking impregnated with varnish is called "linoxin
tube "(type 110 according to GOST 17675-87).," Insulating tube TLV "," insulating lacquer tube ", and has a characteristic yellow color with a visible weave texture. Used to isolate the joints of windings of electrical machines with stranded wires.
Where there is a constant heater - kettles, irons, fan heaters, thermopots, etc., a more heat-resistant version is used - “glass-reinforced insulation tube”. It is a silicone tube, covered outside with a glass cloth stocking, or the stocking itself is impregnated with silicone. Silicone itself is heat-resistant and sufficient for insulation, but fiberglass adds strength and prevents adhesion. However, non-reinforced silicone tubes are sometimes found as insulating.

Fiberglass-silicone heat-resistant insulation tube. Glass cloth reinforcing layer can be both inside the tube and outside.
It is worth noting that when using such tubes, it is necessary to take into account their fixation in place; if the arrangement is unsuccessful, such a tube can “come off” over the wire and expose the connection.
Heat-shrink tubing
It is widely used for insulation of compounds and almost completely ousted from their positions PVC cambric, as it is convenient to use. It is a polymer (The specific type of polymer depends on the manufacturer, unfortunately it is impossible to unequivocally indicate that it is only polyethylene for example.) A tube with shape memory - the tube stretches in a cold one after manufacturing (In fact, the temperature regimes in manufacturing are somewhat more complicated, but for convenience we’ll assume that in a cold state) condition that creates internal stress. When heated to the softening temperature, (but not melting), the polymer tends to regain its shape and the tube "shrinks", decreasing in diameter very significantly. The heat shrink tubing tightly wraps around the connections, ensuring that the tube does not slip off and does not dislodge.
Available in a variety of colors, diameters, types.

Various pieces of heat shrink tubing.
Work with shrinking is simple - cut, wear, heat.

Solder connection, we push the heat shrinkable tube of suitable diameter and heat it. After shrinking the tube is securely fixed.
To ensure a tight connection, heat shrinkable tubes with an adhesive layer are produced - they are coated on the inside with a layer of glue, which, when heated and settled, firmly sticks the tube to the surface of the wire. Such a connection may be necessary, for example, when extending the wire of a submersible pump.
Sometimes the body of the device generally consists of a single heat shrink.
Thermal shrinking in the presence of dexterity is quite realistic to stretch to an additional millimeter in diameter when there is no suitable one at hand, and the one that exists does not fit very well.
If the heat shrink tube is heated up strongly and “pinned” the end, it will stick together, thus it is possible to plug the ends of the cables from moisture ingress.
At this point, a link to the full pdf version of the manual was planned, and a part was conceived as final. But thanks to your comments formed a large list of improvements. Therefore, I take a break for revision of the manual, and the last, 12th part will be devoted to improvements + bonus chapter. Write in the comments about what else you would like to know?
Links to parts of the manual:
1 : Conductors: Silver, Copper, Aluminum.
2 : Conductors: Iron, Gold, Nickel, Tungsten, Mercury.
3 : Conductors: Carbon, nichrome, thermostable alloys, solders, transparent conductors.
4 : Inorganic dielectrics: Porcelain, glass, mica, ceramics, asbestos, gas and water.
5 : Organic semi-synthetic dielectrics: Paper, click, paraffin, oil and wood.
6 : Synthetic dielectrics based on phenol-formaldehyde resins: carbolite (bakelite), getinax, textolite.
7 : Dielectrics: Glass fiber (FR-4), varnished cloth, rubber and ebonite.
8 : Plastics: polyethylene, polypropylene and polystyrene.
9 : Plastics: polytetrafluoroethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene terephthalate and silicones.
10 : Plastics: polyamides, polyimides, polymethyl methacrylate and polycarbonate. History of the use of plastics.
11 : Insulating tapes and tubes.
12 : Final
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/370795/
All Articles