Made in USSR: Werther, Lunokhod, and other robots
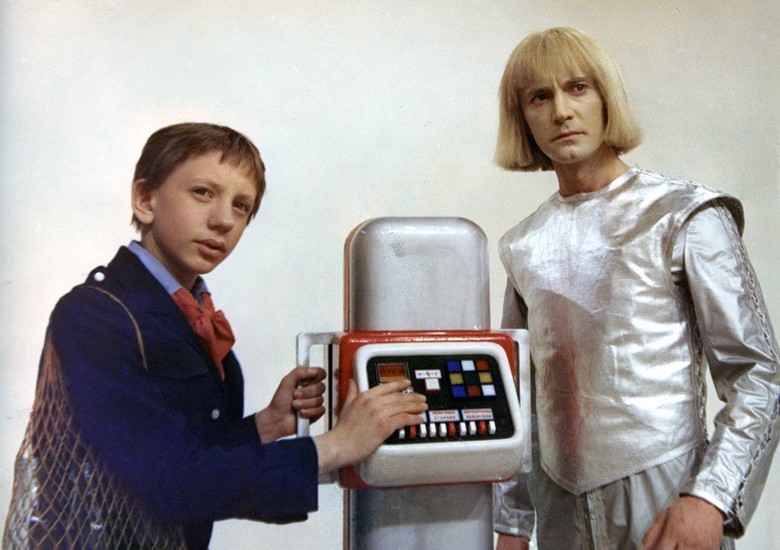

Recently, we talked about domestic combat robots , and today we want to somewhat expand this topic and recall the bright representatives of Soviet robotics.
Those who are from the USSR do not need to explain who is depicted in the title picture. In fact, the robot Werther in the second half of the 1980s personified not only the future for the whole country, but also all robotics in general. What was the situation with robots in the Soviet Union?
Immediately, we want to clarify: in this article, robots do not mean self-propelled devices, but a much wider range of automatic devices “designed to carry out production and other operations that operate on a pre-programmed program and receive information about the outside world from sensors. At the same time, a robot can either have a connection with an operator (receive commands from it) or act autonomously . ”
As we have already told , first of all, experiments with robotization in the USSR began in the army, when several light-weight remote-controlled tanks were created before the war (TT-26 and TU-26). By the way, before the war, experiments were carried out on the territory of the Karelian fortified area with automatic opening of fire from machine guns when infrared photosensors are triggered (at night and in smoke conditions). True, this probably refers to automation rather than robotization.
And then it became not a high-tech.
After the war, cosmonautics became one of the main trends in the development of high technologies. In addition, the army needed a qualitatively new models of weapons. Therefore, in 1951 in MSTU. Bauman opened the department SM-7 "Special robotics and mechatronics." The country is actively developing the theory of computers and automation of programming, creating an element base, putting computers into operation that are not inferior to the best world models (MESM, Setun, AVM MN-10, SVM 5E89 Kurs, Dnipro), creating new teams of scientists and engineers robotics.
Space robots
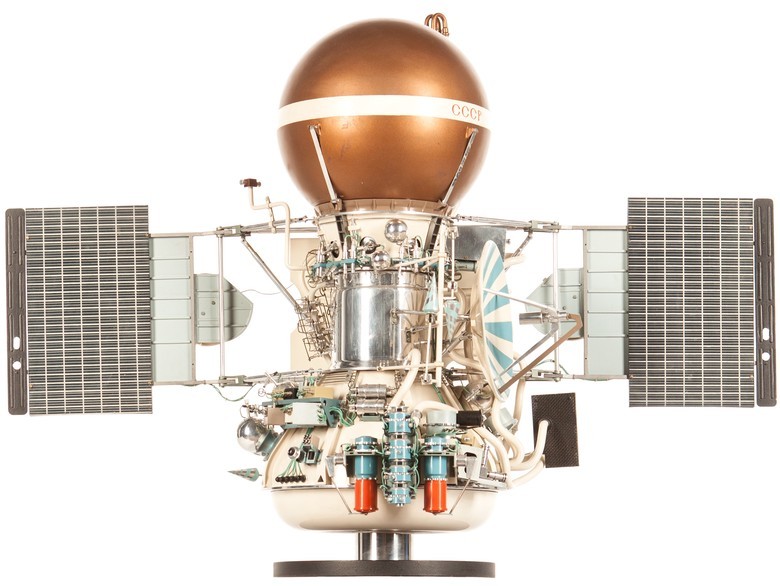
In 1959, the USSR launched the world's first automatic interplanetary station "Luna-1". In 1961, the automatic station Venera-1 was launched, but it didn’t reach Venus. But this was done in five years by Venus-3. And in 1975, for the first time, it was possible to relay data from the surface of the planet: the descent modules of the automatic stations Venera-9 and Venera-10 sent information to the orbital modules, and they transmitted it to Earth.
In 1963, the world's first external space manipulator was developed at the above-mentioned SM-7 department in Baumanka.
In 1970, the USSR took a new frontier: the automatic station Luna-16 delivered soil samples from the moon. Two months later, we opened the era of use of planetary rovers.
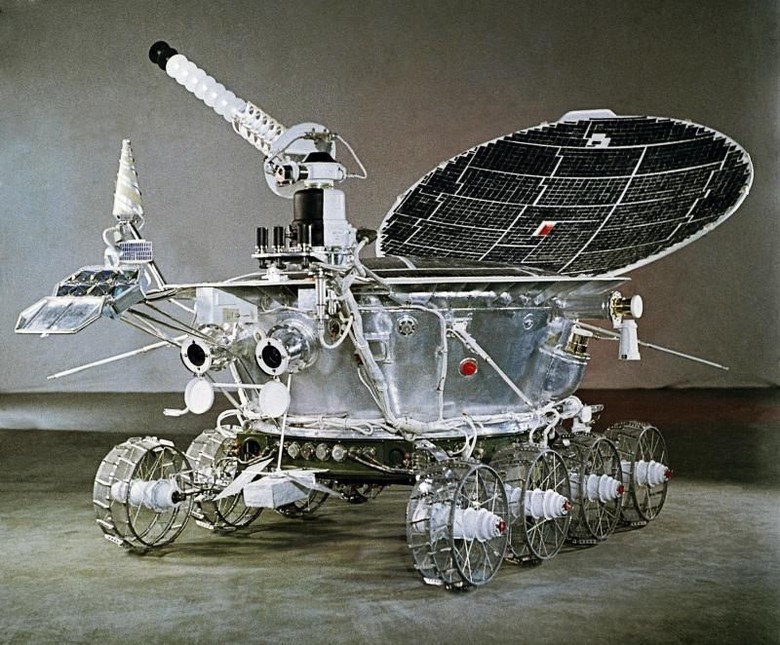
By the way, it should have happened almost two years earlier, but the rocket with the first Lunokhod collapsed in the air shortly after launch. But in 1973, the Lunokhod-2 arrived on the moon, which together covered 42 kilometers - more than its predecessor.
In 1971, Soviet robotics made a new breakthrough - the Mars-3 automatic interplanetary station made the world's first soft landing on Mars.
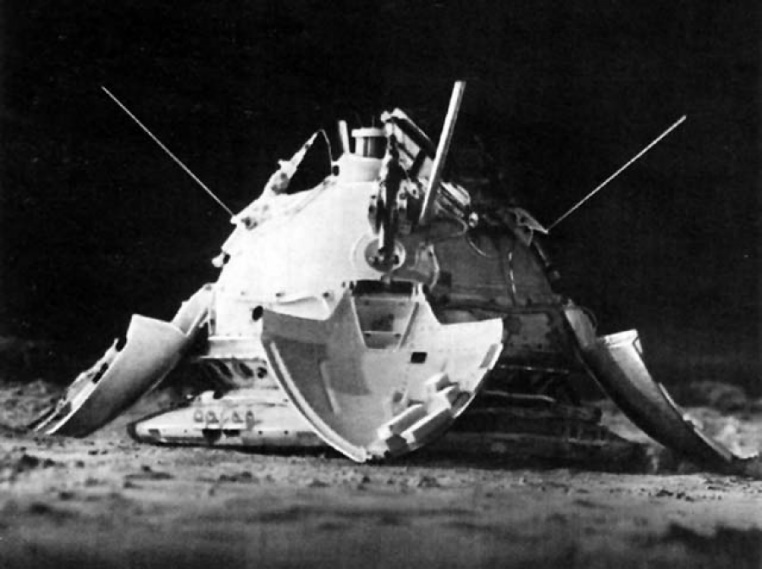
Alas, but on this our achievements in the study of the Red Planet ended. Although then no one could have known that subsequent projects sending research vehicles to Mars would fail for a variety of reasons. In 1977, an experimental model of the rover was created, an integrated all-wheel-drive robot "Centaur" , designed to test the algorithms of the autonomous motion control system, check mathematical and engineering calculations.
The navigation and control system for the Energia-Buran space complex became one of the masterpieces of domestic robotics: the entire flight, from take-off to landing, was carried out fully in automatic mode. This has become a unique event in the world space program! “Buran” entered the atmosphere at a speed of about 30,000 km / h, ideally landed at a speed of 300 km / h in strong crosswind conditions, while ahead of the estimated landing time by just one second. One second, Karl! And the deviation from the central axis of the runway is only 1.5 m.
UAV
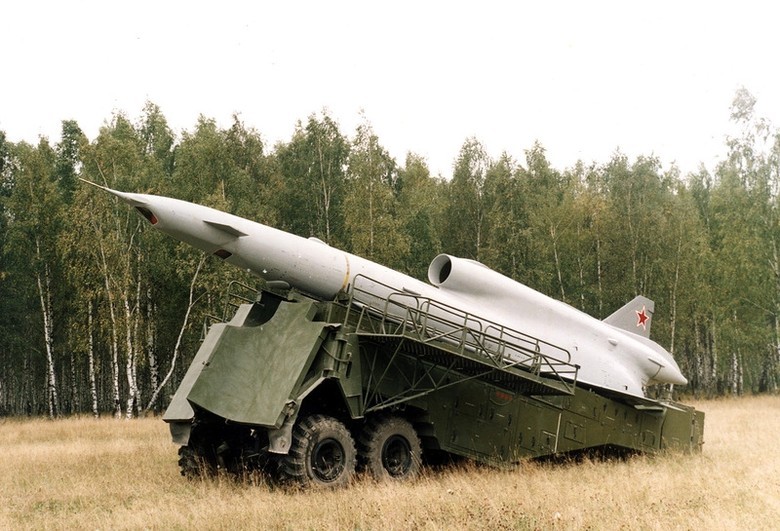
In 1961, the first Soviet-made supersonic reconnaissance drone Tu-123, which had a maximum speed of 2700 km / hour, was created. The drone was moving along the route program, the photographing was done automatically, when approaching the landing site, the radio transmission system to the airfield automatically turned on.
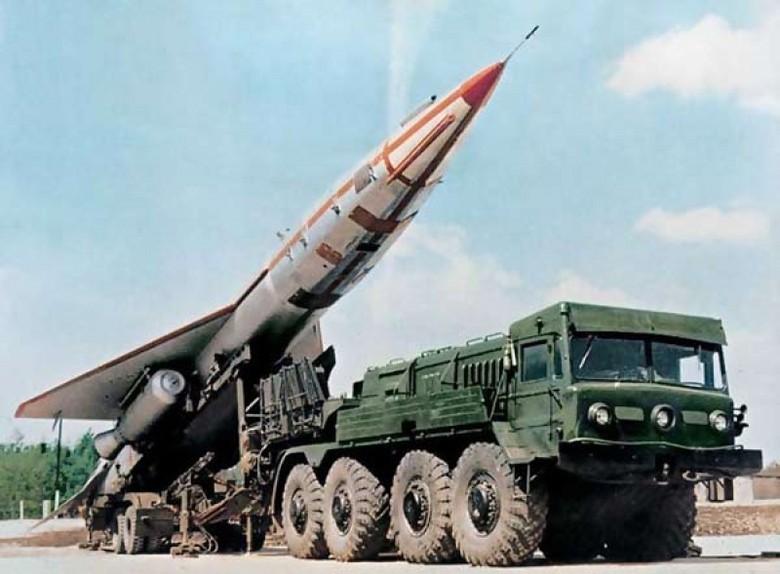

In 1970, the Tu-143 appeared, intended for conducting photo, tele- and radiation reconnaissance in the front-line zone. Cruising speed - 950 km / h, range - 180 km.

In 1974, the drone of the operational and tactical level of the Tu-141 flew. The maximum speed is 1000 km / h, the range is 1000 km.

"Chernobyl"
In 1986, for the elimination of the consequences of the explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, urgent development of all kinds of robots began. First of all, they were needed for reconnaissance on the premises and on the roof of the reactor block, as well as for clearing debris that had an insane amount of x-rays.
Many lives and health preserved developed in MSTU. Bauman robots "Mobot-H-HV" and "Mobot-H-HV2."
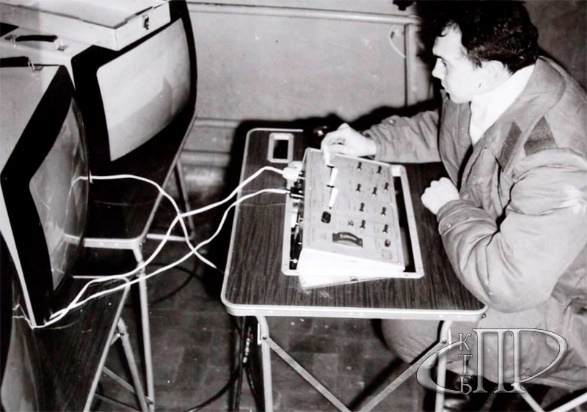
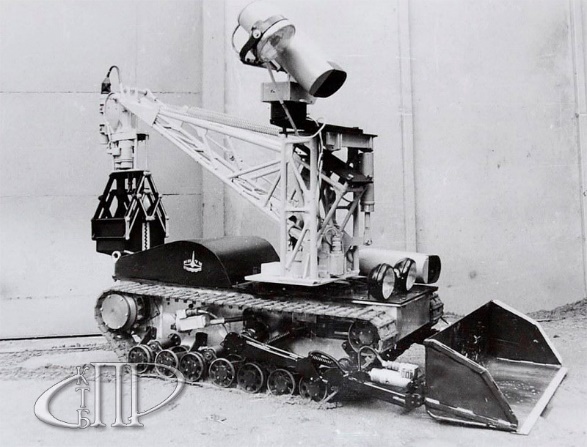
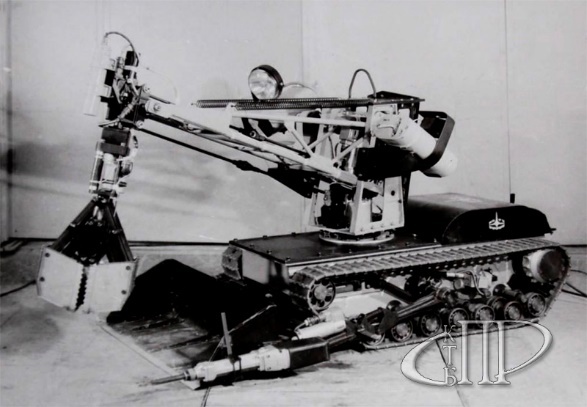

For the same purposes, the STR-1 robot (a special transport robot ) was urgently developed. Its weight is 1100 kg, the maximum speed is 1 km / h, the power is silver-zinc batteries.

After the completion of work on the roof of the reactor block, the STR-1, like many other equipment, was moved to the storage site - due to the wild level of radiation, it was dangerous to get closer than a few meters.
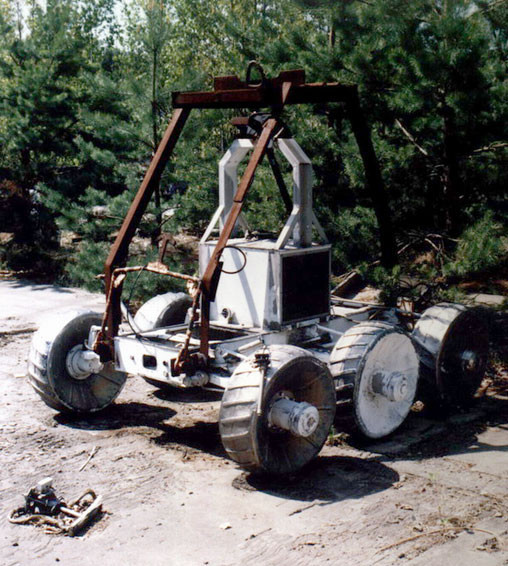

However, other robots were operating on the territory of the Chernobyl NPP, including reconnaissance machines of the ultra-light class:
Robot bulldozer raking radioactive debris:

Small DUSA robots (Remote-Controlled Self-Propelled Units) were used to reduce indoor dusting, reconnaissance, sample collection, clearance. The advantage of these kids was in their size - they could drive there, where larger robots got stuck.
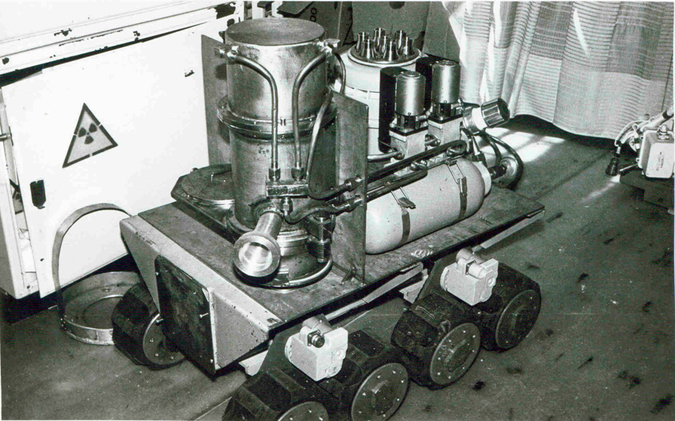

Air filtration robot.
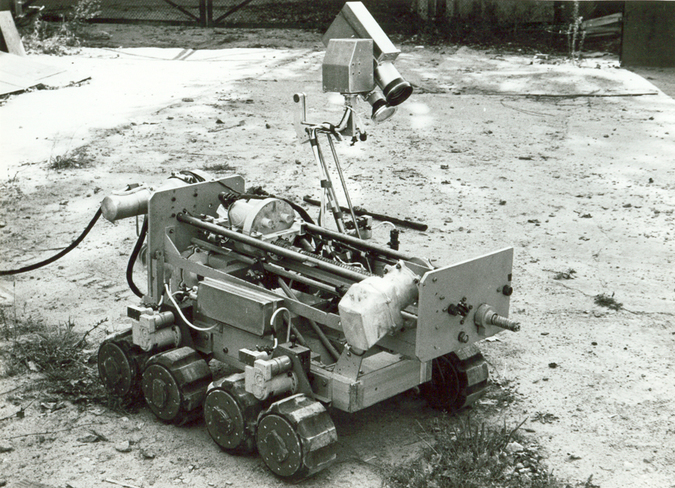
TR-4 robot with a drilling rig for collecting samples.
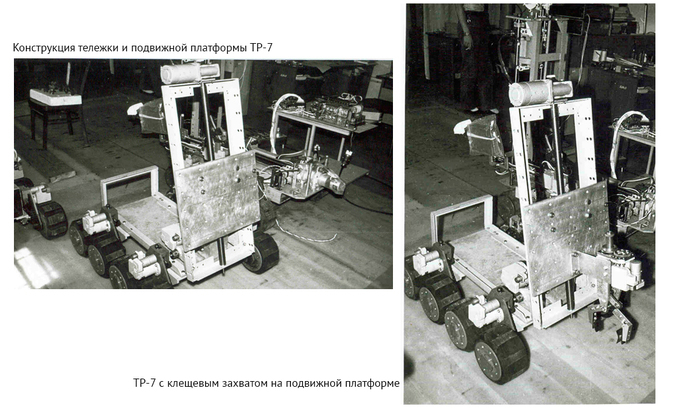

Scout robot. Note the extra spotlight behind the camera module.
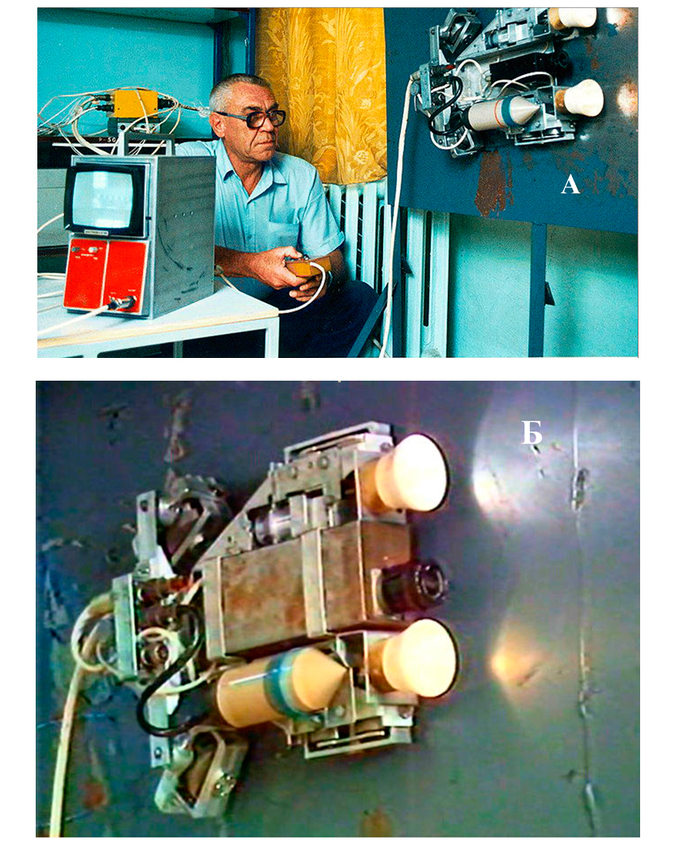
Robot magnetocooler, who was able to move on metal surfaces thanks to powerful rare-earth magnets.
Industrial robots
Achievements in space and military technology is great, but still the foundation is peaceful constructive work. In 1966, the first Soviet industrial robotic arm, developed at the Voronezh Institute of Enikmash, appeared. From 1972 the first Soviet UM-1 numerical control robots began to be produced.
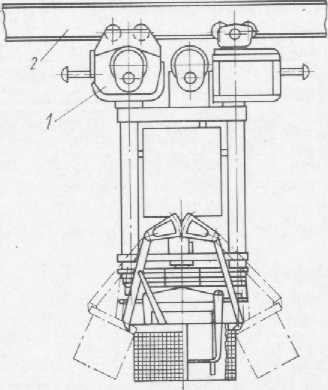
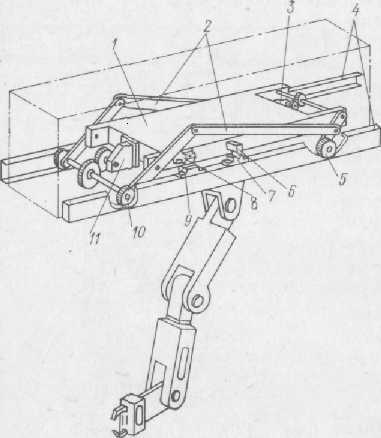
In 1973, the first mobile industrial robots in the USSR were created:
- transport robot "Sprut-1", moving along the monorail guide:
- and the MP-1 robotic arm, which was a mechanical “arm” on a trolley:
In the 1970s, the Petrodvorets Watch Factory was the first in the world to switch to a robotized assembly line of watch movements - the so-called post scheme. This allowed in the 1980s to increase production to 4.5 million hours per year.
By the early 1980s in the USSR, several dozen models of industrial robots were developed, which in thousands worked at various enterprises in a huge country. At the time of the collapse of the USSR, we developed over 200 models of industrial robots.
And at the end of our selection, the novelty of the domestic - Russian - robotics: Android Fedor:
The future is near.

')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/370371/
All Articles