The future is no longer what it used to be: the virtual becomes real
 Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (Augmented Reality, AR) have been confronted with technical limitations for more than a decade, and until recently, these technologies were presented in workstations mainly by experimental solutions. Meanwhile, they are increasingly being used in the entertainment industry. The global virtual reality market is emerging. Its leading players offer more VR options for PCs, virtual reality helmets, etc.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (Augmented Reality, AR) have been confronted with technical limitations for more than a decade, and until recently, these technologies were presented in workstations mainly by experimental solutions. Meanwhile, they are increasingly being used in the entertainment industry. The global virtual reality market is emerging. Its leading players offer more VR options for PCs, virtual reality helmets, etc.With the advent of more and more VR equipment and the development of software, tremendous opportunities are opening up for the creators of AR / VR systems. Accordingly, the demand is growing. Commercial products for professionals are starting to appear.
VR / AR is a collective concept uniting a multitude of related and unrelated technologies, therefore it is more correct to speak from different markets, vertical applications and VR / AR application scenarios.
What is virtual reality?
Wikipedia defines it as a world created by technical means (objects and subjects), transmitted to a person through his sensations: sight, hearing, smell, touch, and others. Virtual reality imitates both impact and reaction to impact. To create a convincing complex of sensations of reality, computer-aided synthesis of VR properties and reactions is carried out in real time.
')
Augmented reality , unlike virtual reality, is a combination of real objects and virtual reality. AR allows you to place virtual text or an image on top of objects from the real world that a person observes (usually using mobile devices). Virtual objects can be superimposed on selected real objects, and, as a rule, are directly related to the object in the real world.
That is, augmented reality combines various information, but its foundation is physical reality - what the user actually sees. AR helps to get useful information about the location and objects, allows you to interact with virtual content in the real world. At the same time, AR users are able to distinguish virtual content from a real object, and can also turn on and off selected AR functions that can be associated with specific objects.

CAD new generation: the use of the tablet and augmented reality technology. Virtual content is superimposed over the image of an object in the real world that the user sees.
If in virtual reality the device completely immerses the user into the world created by the developers, which is difficult to distinguish from the real, then the devices of augmented reality only in some way change the picture of the world visible to the user.
 According to Gartner Emerging Technologies Hype Cycle 2015, AR / VR technologies can become mainstream in 3-4 years.
According to Gartner Emerging Technologies Hype Cycle 2015, AR / VR technologies can become mainstream in 3-4 years.In particular, there are many solutions for smartphones that allow using the augmented reality to get the necessary information about the environment. For example, back in 2010, AlterGeo released an application with augmented reality for the iPhone. The product allowed to look through the camera of the smartphone, in which side and at what distance from the user are the city sights and places. For constant contact with the medium of augmented reality, part of the solutions in this area is embodied in the form of glasses.
It is not excluded that the announcement of Apple's augmented reality glasses may take place in the fall, simultaneously with the new iPhone 8 or during the opening of the campus of the Apple corporation in Cupertino. According to the developers of Apple, as well as the CEO of the company Tim Cook, in the future, the augmented rather than virtual reality will be in demand.

A striking example of augmented reality is the game Pokemon Go. The user sees on the screen of his smartphone the surrounding environment, complemented by virtual objects - pokemon.
Although virtual and augmented reality are technically very different, they are often referred to together. In both cases, this is a completely new experience for the user, but in augmented reality, he remains in contact with the physical world and interacts with virtual objects, and in virtual reality is in a fully modeled space. At the same time, these technologies can complement each other, they use similar development tools used, 3D-modeling engines.

According to Digi-Capital analysts, the main driver of the global VR / AR market, the volume of which may reach $ 108 billion by 2021, will be an augmented reality on mobile devices, and in general the share of AR will prevail - $ 83 billion against $ 25 billion . dollars from VR. The example of Pokémon GO is indicative - $ 600 million on mobile augmented reality in the first three months only.
What is important is not so much the sales of VR / AR products as the impact on the “market trajectory” of this new reality. Many well-known brands in the IT market are currently working in this area, including Microsoft, Apple, Google, Facebook, Sony, Samsung and a number of others.
Due to the development of computer games, VR has become consumerized. Virtual reality devices and software have become available to consumers, many startups have appeared, offering all sorts of products. VR / AR applications are booming, primarily on mobile platforms. However, for the time being, for a high-quality VR application, it is still preferable to have the VR helmet connected to a powerful desktop computer. Over time, this restriction will be able to cope.
In order for AR technologies to become able to win a mass audience, you need a device that can be a sales hit; battery for a whole day of battery life; mobile networks; application ecosystem; participation of telecom companies.
Solving these problems is not easy, but it is already obvious that the future of many areas of entertainment is somehow connected with the use of augmented or virtual reality technologies. In the meantime, VR / AR technologies are already finding quite wide practical applications besides the entertainment industry.
VR / AR in practice
The virtual and augmented reality technology market is just beginning to develop. It is difficult to say in which directions he will continue to grow. Experts are confident that this will not only be a movie and video games, that the scope of AR / VR will also extend to many other segments. So far, the most promising areas of AR / VR are mobile platforms, where there are a large number of potential users, and highly specialized solutions.
Meanwhile, there are quite a few practical examples. Thus, virtual reality has been used for a long time and successfully for teaching professions where the operation of real devices and mechanisms is associated with an increased risk or is associated with high costs (an airplane pilot, a train driver, a dispatcher, a driver, a mine rescuer, etc.).
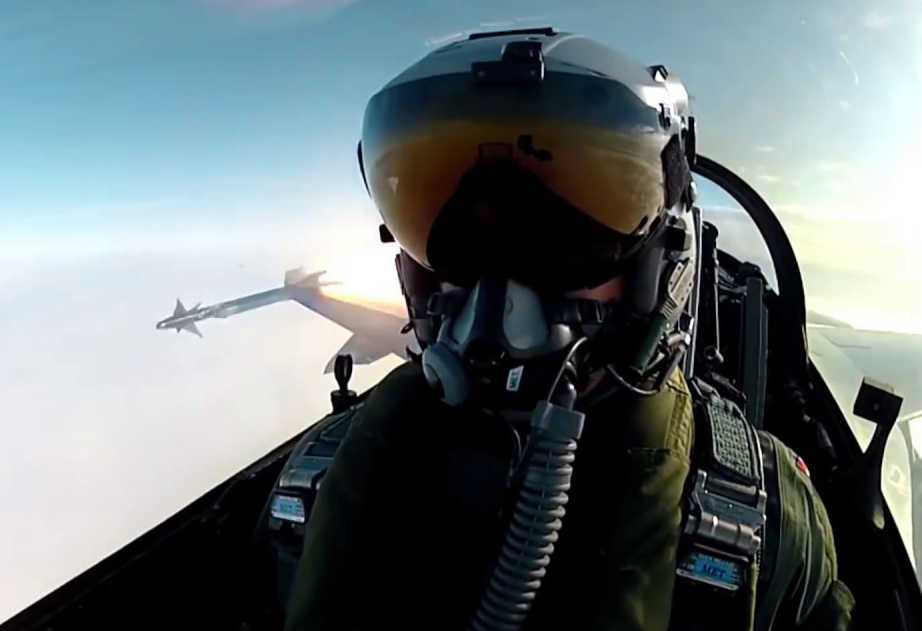

Modern military aircraft and helicopters often use a helmet-mounted display system. It allows the pilot to obtain the most important information directly against the background of the situation he observes, without being distracted by the main dashboard. This helps save seconds, for example, during agile air combat. Also, many such systems allow target designation by turning the head or eyeball movements.
Augmented reality is gradually being introduced into the educational process. For example, some US universities have agreed to introduce Microsoft's augmented reality technology into student learning.
These technologies provide a real opportunity to the designer to try out various concepts - consider them in detail and select the best one. At NASA, virtual reality technology was used to design a helicopter project, and Boeing used them to create the latest model aircraft.
In medicine, attempts are being made to use VR technology for analyzing images and treating various phobias. It is assumed that the use of such practices will allow patients to overcome their fears over time. Therapy in the virtual space requires only the presence of the equipment itself. You can gradually increase the level of stressful situation.
Interesting prospects are opened in the Internet-trade: the buyer will be able to test all the functions of the product, touch or try on it. Such virtual shops are considered as potential as a replacement for real boutiques or salons.
The media are already using virtual reality technology in their reports, in covering events. Some experts believe that the virtual space is an ideal medium for broadcasting news publications.
Microsoft representatives predict the replacement of conventional monitors with virtual and augmented reality systems. The user will not need to sit for hours at the screen. All the necessary management functions will be right in front of him.
Microsoft devices (HoloLens) and Meta have the function of making calls in the virtual space. The image of the interlocutor appears right in front of the user. Such technology will simplify the process of communication, conducting for business meetings, online trainings and events.

With the help of the Intel RealSense camera, you can control the content on the screen: scroll through the pages with gestures, rotate objects, change the scale. Intel RealSense allows you to scan three-dimensional objects without the help of a special scanner. In 2017, the company will open its software and hardware for developers.
VR and workstations
For the development of such technologies will not take much time. In the near future, technologies of augmented and virtual reality will have an impact on any business, assure analysts of Gartner.
Workstation manufacturers are actively preparing for this. In 2017, VR and AR systems may appear, targeting not only the education market and the entertainment industry, but also methods of computer design and modeling, content creation. As these platforms become more mature, that is, in the middle or at the end of 2017, VR workstations will begin to appear on the market in increasing numbers.

In 2016, Dell introduced the Dell Precision T5810 and T7810 workstations to work with VR, whether it's consumption or content creation. Dell currently offers a large number of VR options for PCs, including support for Oculus helmets and HTC in XPS PCs, Alienware, and Precision workstations.
The new workstations with virtual reality support (VR-Ready) combine high performance of the processor, memory and graphics for optimal viewing of VR, have special graphics drivers and are tested for compatibility with VR helmets and software products.
 Dell's new Precision 7720 is Dell’s first mobile workstation designed specifically for creating virtual reality content. This is Dell’s most powerful mobile workstation: it is equipped with the latest 7th generation Intel Core processors and Intel Xeon, NVIDIA Pascal Quadro professional graphics, and since it’s a mobile workstation, VR content creators can work on it anywhere - will find inspiration.
Dell's new Precision 7720 is Dell’s first mobile workstation designed specifically for creating virtual reality content. This is Dell’s most powerful mobile workstation: it is equipped with the latest 7th generation Intel Core processors and Intel Xeon, NVIDIA Pascal Quadro professional graphics, and since it’s a mobile workstation, VR content creators can work on it anywhere - will find inspiration. NVIDIA is actively working with vendors to bring professional NVIDIA VR Ready workstations to the market. Dell Precision T5810, T7810, T7910, R7910 models with NVIDIA-recommended configurations meet the requirements for working with VR content and allow working with the VRWorks package, which includes tools and technologies for application developers.
NVIDIA is actively working with vendors to bring professional NVIDIA VR Ready workstations to the market. Dell Precision T5810, T7810, T7910, R7910 models with NVIDIA-recommended configurations meet the requirements for working with VR content and allow working with the VRWorks package, which includes tools and technologies for application developers.NVIDIA VR Ready professional mobile workstations allow designers, engineers and other professionals to launch VR projects anywhere, which speeds up work on a project and improves its quality. You can train remote employees, immersing them in the workflow, visualize concepts and models, provide customers with the opportunity to walk among virtual buildings.
For all of its Precision line of workstations, Dell has developed a set of configurations that are guaranteed to work with virtual reality systems and applications — gaming (HTC Vive or Oculus Rift VR) and professional. The latter are already actively promoted today by independent suppliers of engineering software as a toolkit for building the most accurate three-dimensional models of complex objects, as well as for 3D prototyping.

Experimental development company 8Ninths - Holographic Workstation based on Microsoft technologies. This is the workplace of a trader with visualization of the results of financial applications.
VR can lead to revolutionary changes in the architecture of workstations and how to use them. For example, the development of the company 8Ninths is designed to complement the traditional tools of the trader. 8Ninths has created its own design patterns and language to study how Microsoft's HoloLens glasses can be used to convert 2D data into 3D holography. This is how Holographic Workstation was born, which optimizes the work of the trader in interacting with data in a multi-level system. This allows you to quickly delve into the essence of the data and accurately process them.
Through glasses HoloLens, a trader can monitor the financial market, whose indicators are presented in the form of “floating” in the space of colored objects - their value depends on trading activity. Holographic Workstation can work with existing financial applications. In the near future, the developers intend to apply this principle in solutions for other industries.
Epic is going to introduce VR functionality into a future version of the editor, which is used to create games based on the Unreal Engine 4. By connecting a virtual reality helmet to the workstation, the developer will be able to see the game scene the same as the players see it, and to use the tool window applications, it will be enough to turn your head.

It can be expected that new technologies will begin to be even more widely applied in the household PC segment. Microsoft announced that in 2017, Windows 10 will receive a Windows Holographic shell. The shell API will allow applications in the 3D-interface mode to be adapted for this purpose along with standard programs. Virtual reality is not just the beginning of a new stage in the development of the entertainment industry. It becomes a big, serious business, opens up new opportunities for professionals.
Hardware and software aspects of AR / VR
One of the obstacles to virtual reality is the high cost of devices. This year can be a turning point, as many companies are working on the price reduction. In addition, bulky and imposing a number of other restrictions VR-gadgets continue to decrease in size. Along with this, the number of augmented reality devices is increasing on the market.
For application developers, this may mean that serious efforts and skills will be required: virtual software development must combine design skills in 2D and in 3D. You will need to design interfaces that work uniformly both in a virtual environment and outside of it. This is a serious problem in terms of application architecture. Another unresolved problem: setting up elements of VR systems such as position tracking sensors for fixing head and eye movements, for controlling applications.
The task of writing applications is complicated by binding to proprietary software and hardware of a particular VR device. Standardization of hardware specifications will help simplify it.
Along with hardware platforms, software is also being improved. For example, PTC has released the Vuforia Studio Enterprise corporate toolkit for developing AR applications. Previously known by the code name Project ThingX, the Vuforia Studio Enterprise package is now offered under the Vuforia Studio Pilot Program. It is integrated with PTC Creo 3D CAD visualization software and the ThingWorx Internet of Things (IoT) platform to add augmented reality elements to “connected things”.
According to the developers, Vuforia Studio Enterprise does not require programming and allows you to create applications of augmented reality without deep knowledge in this area.

By integrating 3D CAD data from tools like Creo and IoT data from ThingWorx, Vuforia Studio gives organizations the ability to use augmented reality elements to more effectively create and maintain their connected products.
PTC believes that the lack of tools for preparing and creating content hinders the introduction of augmented reality in enterprises. Vuforia Studio software is designed to solve this problem.
Developers can test this innovative technology through the ThingWorx Studio pilot program: create augmented reality industrial environments that allow them to develop concept justification projects, build augmented reality environments in a simple, drag-and-drop-free environment, and use existing content through integration 3D CAD, , .
The developed environment can be quickly published for iOS and Android devices. You can get acquainted with augmented reality by installing one of special browsers on your mobile device, which allow you to see digital content that complements the physical world. Such browsers have long been known - one of the first was Junaio from Metaio, which was later acquired by Apple.
For example, Layar's popular augmented reality browser is designed to animate static pages of newspapers and magazines, billboards, booklets and other printed materials. In addition to browsers, more and more different applications of augmented reality appear.
In such solutions, models of search and localization of specific points of real-world objects are usually used, in turn, these models are trained inhigh-performance equipment - this requires a huge amount of data. The methods of image classification, search and localization of objects, semantic segmentation are applied. Various methods have been developed for training classifiers .
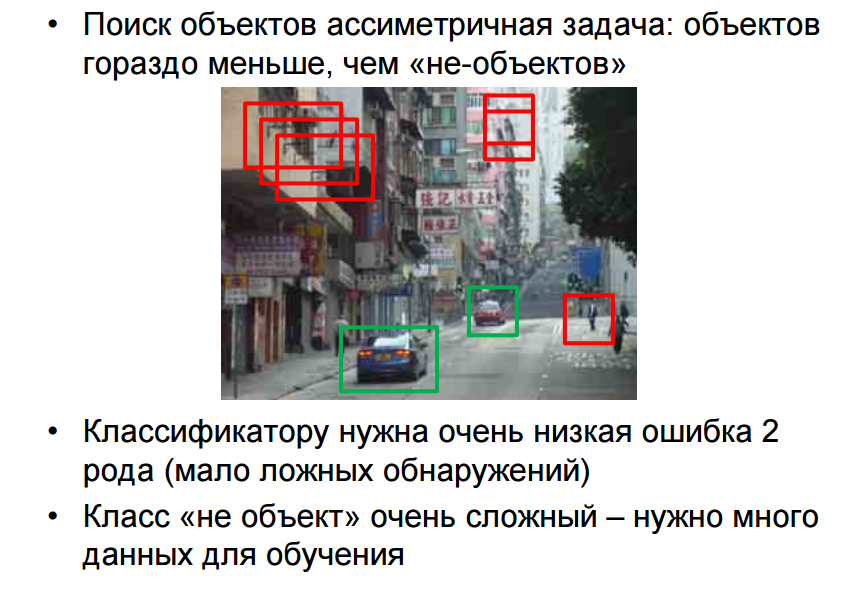
The task of " learning classifier ." It is extremely difficult to build a class model of an object, so you have to train a model / algorithm on a large set of examples of object images.
The main modern approach to the detection of objects in the scene is the recognition of a set of selected signs. The main methods used are HOG, Edgelet and a group of local pattern methods (Local Binary Patterns, LBP; Local Ternary Patterns, LTP; Scale Invariant LBP, SILBP; Scale Invariant LTP, SILTP). The method in which the histogram of oriented gradients (Histogram of Oriented Gradients, HOG) is used, is based on the contour of the object and the construction of gradients, which allows us to distinguish one object from other objects. The Edgelet is designed specifically for detecting objects: using the filters, an object's contour is constructed, a histogram-oriented gradient is extracted from this contour, then histograms are normalized and used to create a feature vector.
However, HOG in poorly contrasting scenes does not work well. In this situation, three-dimensional marking of a scene with segmentation comes to the rescue, which helps to identify objects in specific areas. Improving the quality of HOG's work can be achieved by learning the recognition system — for example, recognizing a person by individual body parts (arms, legs, body, head), which reduces the number of false positives.

An example of learning the system to recognize a person.
Edgelet-based methods (Edgelet - a segment of a straight or curved line) also use training, which, when recognizing people, is performed on the humeral girdle and body. Edgelets of 4–12 pixels in size — segments of straight lines, arcs of circles, symmetrical segments of straight lines, and symmetric arcs of circles — are compared with the contours in the image. With proper training, sufficiently good recognition results are provided. To improve the accuracy, a modification of LBP-based EJLT is used, allowing to expand the feature vector. As a result, the probability of recognizing a person in his shoulder girdle increases by 20–25%. These methods continue to be improved.
Summary
Both virtual reality and augmented reality have been actively developing lately. It can be said that VR / AR technologies will have a serious impact on how business problems are solved. Technologies of virtual and augmented reality have already emerged from the embryonic state, but the most interesting is waiting for us ahead.
How will the application of visualization change in the design in the era of virtual and augmented reality:
→ Part 1
→ Part 2
→ Part 3
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/370237/
All Articles