On the role of sigmoids in the life of an individual
A sigmoid is a smooth monotone increasing non-linear function, having the shape of the letter "S". Is a special case of the so-called. S-shaped curves (this is no longer a mathematical term, but a kind of general designation for all curves resembling the writing of a Latin letter).
The formula of the variety of this function, which we are going to talk about, looks like this (see Wikipedia for more details about it):
F (x) = 1 / (1 + exp (-Kx))
Where K is a constant.
The family of curves for different values of K (2.5 and 10 for black, red and blue, respectively) is shown in the figure below:
')
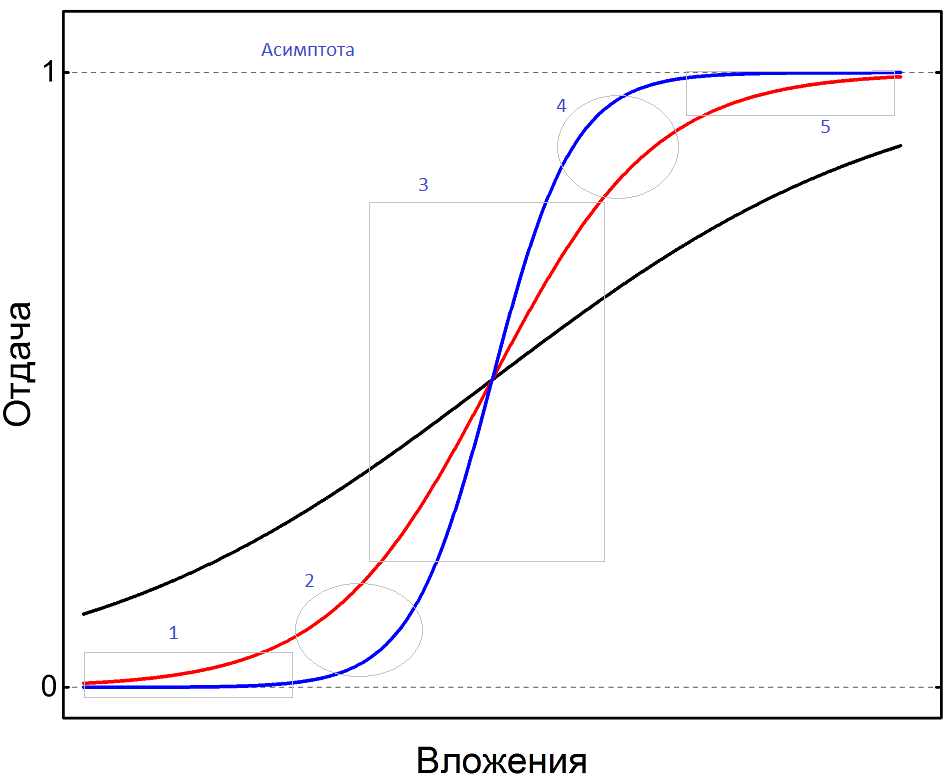
The smaller the K coefficient, the flatter the line. The curves are divided into 5 areas, which we will discuss in this material.
But first, I want to explain why, at the beginning, we are talking about a sigmoid, and not just some kind of S-shaped curve. The chip here is the presence of asymptotes - by definition, it is a straight line, with the property that the distance from the sigmoid point to this straight line tends to zero as the point moves along the branch to infinity.
Actually, it can be clearly seen from the formula. For the function to reach the value 1, it is necessary that the exponent becomes zero. But mathematically this is impossible, for any value of "x" its value will be different from zero. And, therefore, we will inevitably divide 1 by a value, a little more than 1. A unit is unattainable.
From the point of view of the individual, this means that the ideal / perfection is unattainable. More precisely, to achieve them requires an infinite amount of investment / effort - which is physically impossible for an individual because of the finiteness of his existence.
This is an infinitely important philosophical conclusion. Including it implies the complete futility of perfectionism. The same property illustrates a purely everyday and practical conclusion, which most adults know well from personal experience. Namely - the repair in the house can not be completed, it can only be interrupted by willpower.
Now separately about the curve sections. For clarity, we take as an example the occupation of any hobby, say, photography.
Then area 1 is the stage where those who did not have time to acquire the motivation necessary to overcome the difficulties of the first stage are eliminated. And all the rest invest almost without return. Those. in order to survive this period, you need patience and perseverance. Obviously, in the case of a hobby (rather than hateful work), this requires positive motivation. At the starting point, at the beginning of the path, the individual already wants to take pictures better (by the way, according to the same property of sigmoids, it turns out that a person never starts from scratch).
As you understand from your experience, it is difficult to endure in a situation where everything develops along a blue sigmoid. You stick - and you still feel like a helpless newcomer who is not doing anything.
There is a great desire to “jump over” to the red trajectory, where the return is somehow more palpable. It is possible - you need to enroll in photography courses. Then instead of the “spear method” in the course of self-education you will be assisted by qualified people.
Naturally, for people of different degrees of endowments, the length and slope of the sections (including the first), and their length will differ.
Separately, it is necessary to say about the situation when you are not moving along this sigmoid - but teach someone. Student progress will be similar. And the art of a teacher / coach is the ability to intuitively understand whether the evolution curve of this particular student will break away from the zero line. Or a person is hopeless and we waste time on him. The difficulty is that the blue curve after a long ineffectual period promises us a rapid jump. Those. a student moving in a blue path will give a really high result faster than a student moving in red. The only question is whether it will give in principle.
In the following figure, along with the original S-shaped curve, the dependences of the volume of investments, the volume of new knowledge / skills and profits are shown.
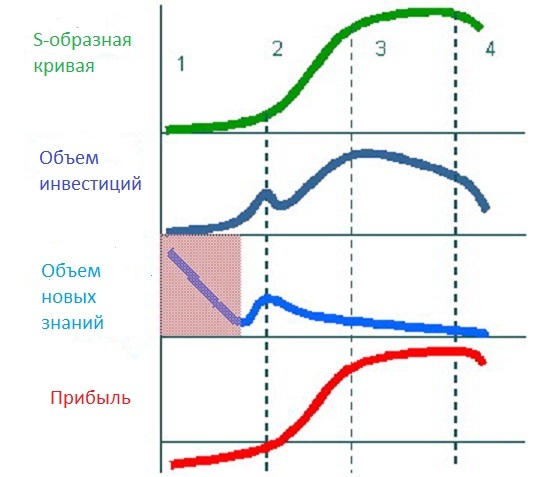
It can be seen that there is no financial profit, you are in the "minus". But the volume of new knowledge is the highest, especially at the beginning, when you are only “getting into the topic.” And this is the main "bonus" of the first stage.
There are many people for whom this prize is the main one. And I understand them well, since I myself am largely one of them.
The main charm (and, at the same time, the main difficulty) of the S-shaped curve is that it is not a graphic image of a certain analytical equation, a pattern (unlike sigmoid). This means, firstly, that - being in section 1 - we do not know when section 2 will begin, what slope will be at the growth curve in section 3, etc. Secondly, this means that only the general form of display of various processes. Those. we know from experience that the course of evolution will be similar to the letter S.
But from this we have no information about the factors influencing and determining the course and parameters of this particular process. It is only obvious that during the evolution of the photographer and during the home repair these factors are different. Those. no analogies and far-reaching conclusions can be done. In general, no conclusions about the existing forces from the shape of the curve does not follow.
Let me remind you of the classic example of erroneous conclusions. A small town in the wild West at the beginning of the 19th century. According to statistical data there is 1 church and 3 brothels. After 20 years, statistics showed the presence of 5 churches and 15 brothels. There are people who try to conclude on this basis that the more churches in the city, the more popular is prostitution. In fact, in the town, the population just grew 5 times. And there is no correlation between temples and brothels. Those. before drawing conclusions, it is not bad to begin with correctly to prove the existence of a causal connection between the factors.
However, one should not underestimate the importance of the fact that we obviously know about the evolution curve of this process!
Let's return to our S-shaped curve (the first figure). Section 2 subjectively looks weird. You have been “cutting a topic” for quite some time now with almost zero returns. And suddenly the results for no apparent reason begin to grow, and with increasing speed. (By the way, this is a concrete expression of the law of transition of the amount of effort into the quality of the result.)
From the point of view of photography as a hobby, this is a turning point, because profit (with some effort on the part of the individual) is a plus (see the second figure). Those. a person notices that his photo is not worse than the average for this sample. And, if desired, he can start working as a wedding photographer.
Naturally, the specific choice depends on the real life situation. I had a friend who was fascinated by photography in the army, being an officer. And then, during the cuts, he was fired from the army. And suddenly it turned out that a hobby that is quite expensive for the family budget can become the main source of income. If the amateur photographer has a good job, and in the course of taking a photo, he gets the main pleasure from the process (shooting and discussing new photos with colleagues in a warm company with a glass of tea) - then what is the point for him to turn pleasure into an “obligatory” one?
From the history of photography it is known that many famous professional photographers are so annoyed with what they do for money, day after day - that they began to photograph bricks or curls of exfoliated paint on the old walls. Or cigarette butts.
Here is an example when the famous English photographer Cecil Beaton gave vent to emotions. For money, he shot these portraits like this:

This is the English princess Margaret. He filmed the coronation of the current English queen, all her relatives. And also a sea of glamor for fashion magazines. But from time to time he made shots like this:
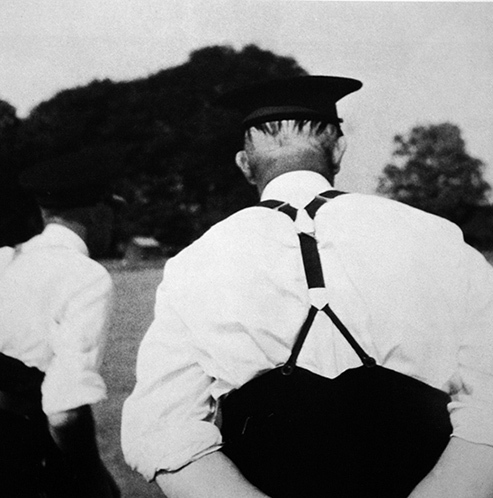

He called it simply and unpretentiously - "England" (England).
Let's go back to the curve. Section 3 describes rapid growth. The amateur makes all the big and big successes. And a colleague who has gone into commerce gets more and more income:

At the same time, economic efficiency sharply increases as investments decline.
From the point of view of the psychology of creativity, at this stage, many people “grab a star”. Those. they have a bias in the assessment of their own personality and creativity. This changes attitudes towards others. Otherwise, it is called the “test of copper pipes” (if you recall the phrase “fire, water and copper pipes”).
Fortunately, and at the same time, unfortunately, life quickly puts the "stars" in place. In terms of the curve, we do not know the angle of inclination of the curve in section 3. And its duration is unknown (level of achievements along the ordinate axis). This is another consequence of the fact that the S-shaped curve only describes the general course of the process.
As a matter of fact, according to the angle of inclination and the level of people reached at the end of stage 3, people can be divided into gifted, talented and ingenious. The main thing here is not to rush to the labels. Because the development of a genius can occur rather slowly (angle of inclination) - but it remains in principle unclear whether he reaches section 4 or not. Being already at an incredibly high level, when more fierce competitors, who initially demonstrated their “steepness” (in the direct sense, the slope of the curve in section 3), have long been far below.
The overwhelming majority of people reach the highest possible level for themselves in the data of specific living conditions - and goes to section 4. The psychological section is the hardest, the most critical. In fact, you seem to be almost a master, you have been praised more and more - and suddenly everything “disappears” somewhere. The speed drops, there is a feeling of trampling on the spot. And then it turns out that this is not a feeling at all - but a real fact.
There are many options for further action. If a person is pleased to be cut into something new, then after the third stage of “skimming” it is time, as they say, “to make legs”. Those. start another project to go through again, catch those sensations that are so attractive. At stage 4, such people are extremely uncomfortable.
But I specifically chose a photo as an example. This is not a hobby that is easy to just quit and get carried away with something else. For many reasons. Therefore, the 4 stage turns for the photographer into a painful, but extremely useful for the development of personality. Deeper knowledge of yourself, the acquisition of skills of patience and endurance, the development of new qualities.
I will give an example from another area. It is known that football academies in our country produce a fairly large number of young football players. However, in the media, groans about how few young talents grow to the level of the Premier League teams and the national team do not subside. In terms of technical skills, a graduate of a football academy is in zone 4. That is, perform technical activities in training, he knows how great. And he really has nowhere to grow on this scale. A mature master differs from a graduate in that he is able to perform the most complex technical and tactical actions not only in training, but in the match of the World Cup final. Note that, formally, according to a curve, the quantitative difference in the level of technical equipment between a novice and a master is minimal. Essentially, the gap is infinite (i.e. it is qualitative).
Here we stick to another feature of the S-shaped curves. The fact is that you need to make a lot of effort to understand the coordinates in which we build it in this particular case. And the real processes in life are always multidimensional. They are usually described on many scales (as in the multifactorial / multidimensional personal MMPI questionnaire in personality psychology). A person, like a real life phenomenon, cannot be described by one scale as “fool-clever”, for example.
Thus, being on plot 4, it makes sense to think about which of the S-shaped family of curves we are now. If this is the ability to build a frame composition, then it is desirable to remember that the level of a photo is not exhausted only by composition. There are more color and other factors. In addition, as it is endlessly not tired of repeating on forums on a photo, the photographer always takes pictures, not the camera. In particular, the level of photos directly depends on the level of personal development of the master.
Those. We continue to develop the ability to build interesting compositions - but we are mainly focusing on the development of other personality traits and abilities of the photographer.
If we interpret the coordinate system extremely globally, it is “efforts - the result”, then at stage 4 the photographer begins (and at stage 5 completes) reconfiguring, nuancing his feelings and emotions from taking photographs. Simply put, learns to find pleasure in thinking about the place and time of shooting, in preparing the tools for the photo shoot. From the feeling of anticipation of a successful frame. From the process of processing photos on the computer. Ie pleasure, satisfaction from hobbies is not lost anywhere. It is located in those places that we did not even know about at stage 1, but at stages 2 and 3 we simply did not think, did not understand their place and meaning in the overall picture.
In a sense, this can be called an attempt to break the deadlock by shifting the focus of attention to detail. This is if the pessimist judges. An optimist will call it expanding the range of available ideas and emotions, sensations. There is no “correct” solution; this is a classic question: “is the glass half empty - or half full?” However, to successfully continue the passion for photography, it is advisable to think and act positively. Those. Amateurs who are incapable of this are eliminated at stage 4.
The fifth, the final stage of the S-shaped curve. Area of stability. If all is well, then this is the time to get the most complete satisfaction from your favorite hobby. At the same time sadly more and more complete awareness of the fact that reached the ceiling.
Just do not think that the curve in the 5th section will automatically go up. Of course, “mastering is not lost” - but even maintaining a constant level requires constant effort. Graphically, it looks like this:
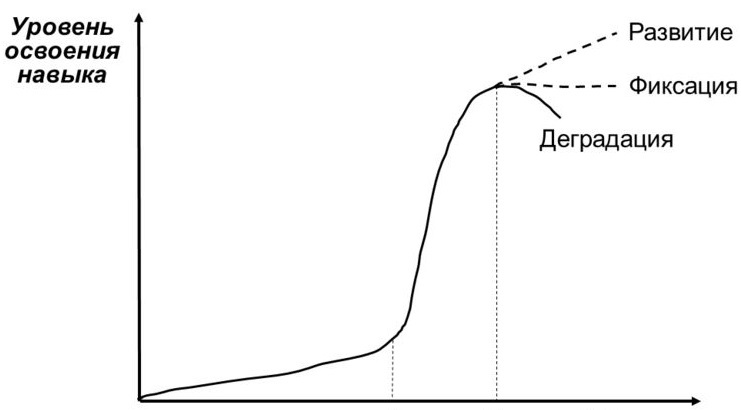
If the conditions are not applied, then the curve is bent "at half past six" (as men sometimes joke with each other).
Of course, in a good way, if possible, it is better not to climb into the 5th stage in most life processes at the 5th stage. Including and therefore, for example, there is a recommendation to change jobs once every 3-5 years.
But many processes do not leave us such a choice. That is why it is important to find strength and additional motivation for life and development in this finishing segment.
By the way, to choose a point when it is time to “jump off” from this curve is very difficult. Especially when it comes to the essential things for a person like money or power. If you leave earlier, you will not get yours. You will be late with leaving - you will start to lose faster and faster.
Some other S-curve applications
I thought that the most important thing in this material was to draw attention to the need to take into account and reflect on the fact of development along a S-shaped trajectory of many processes in the life of an individual. However, the applicability of this curve to various processes in nature and society has been known for a long time. In particular, there is a point of view that the model of an S-shaped curve was first proposed by the French mathematician Pierre Verhulst back in 1838.
For example, if several pairs of fighting hamsters are brought to Easter Island, then the evolution of their population is described by this kind of S-shaped curve:
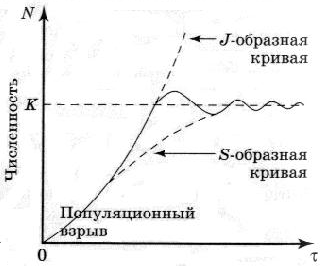
Extremely popular is the curve among people engaged in innovation, the development of new technologies (including in the framework of start-up):

Including There is a lot of material about when to switch to another curve (steps 4-5) and what this is fraught with. Graphically, this is usually depicted as:
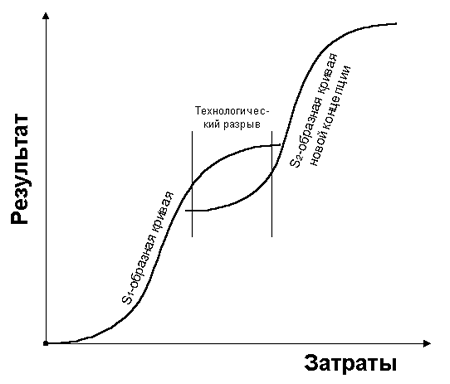
Obviously, the transition to a new curve is always painful and costly. And always jump into the unknown with no guarantee of a positive result.
Amusingly, the totality of qualitative jumps can be finally considered as a continuous evolutionary development (if we imagine the envelope of the following sequence of S-shaped curves):
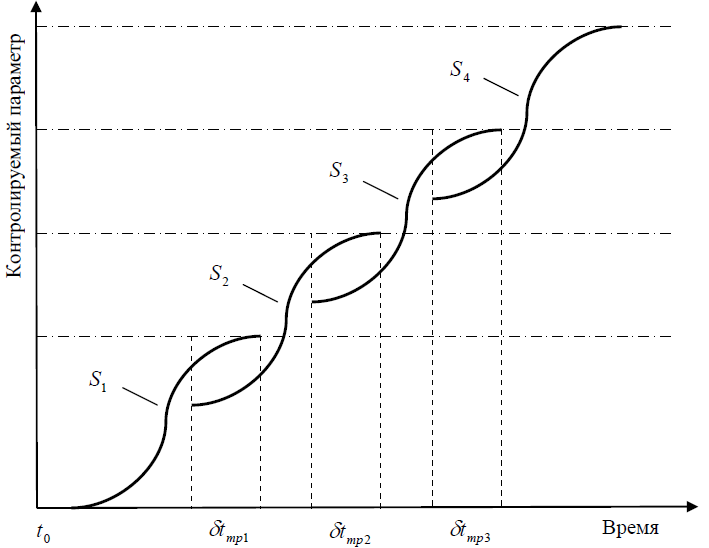
The development of whole areas of technology can be described by an S-shaped curve. Here is an interesting graph of the growth of speed records:
Separately, I will explain how the S-shaped curve differs radically from sigmoid in life. For the latter, achievement 1 is impossible by definition. But a significant part of serious projects requires the implementation of the plan that was approved and for which funding was allocated. Therefore, formally, some curves reach 1 (at least from the point of view of higher superiors, investigative bodies and prosecutors). Although, honestly, I do not believe it. Not because of the shortcomings of individuals and organizations. But in principle - well, it is impossible to perform exactly 100%, in life there are always differences and deviations (another thing is that they may be considered as a blessing or mistake within the limits of the permissible error).
In general, on the net you can independently find a lot of interesting things (see the “Sources” section below).
I want to emphasize one important thing, which is always desirable to remember. Science-based reasoning and graphics, universities, dissertation councils, journals and other attributes are designed to create the impression of the scientific character of a given area of human activity (for example, management, sociology). This is a question of status, it is important for the individual, so the temptation to associate oneself with science is very great. In reality, there is no management science, for example, innovation. /.
, .
The formula of the variety of this function, which we are going to talk about, looks like this (see Wikipedia for more details about it):
F (x) = 1 / (1 + exp (-Kx))
Where K is a constant.
The family of curves for different values of K (2.5 and 10 for black, red and blue, respectively) is shown in the figure below:
')

The smaller the K coefficient, the flatter the line. The curves are divided into 5 areas, which we will discuss in this material.
But first, I want to explain why, at the beginning, we are talking about a sigmoid, and not just some kind of S-shaped curve. The chip here is the presence of asymptotes - by definition, it is a straight line, with the property that the distance from the sigmoid point to this straight line tends to zero as the point moves along the branch to infinity.
Actually, it can be clearly seen from the formula. For the function to reach the value 1, it is necessary that the exponent becomes zero. But mathematically this is impossible, for any value of "x" its value will be different from zero. And, therefore, we will inevitably divide 1 by a value, a little more than 1. A unit is unattainable.
From the point of view of the individual, this means that the ideal / perfection is unattainable. More precisely, to achieve them requires an infinite amount of investment / effort - which is physically impossible for an individual because of the finiteness of his existence.
This is an infinitely important philosophical conclusion. Including it implies the complete futility of perfectionism. The same property illustrates a purely everyday and practical conclusion, which most adults know well from personal experience. Namely - the repair in the house can not be completed, it can only be interrupted by willpower.
Now separately about the curve sections. For clarity, we take as an example the occupation of any hobby, say, photography.
Then area 1 is the stage where those who did not have time to acquire the motivation necessary to overcome the difficulties of the first stage are eliminated. And all the rest invest almost without return. Those. in order to survive this period, you need patience and perseverance. Obviously, in the case of a hobby (rather than hateful work), this requires positive motivation. At the starting point, at the beginning of the path, the individual already wants to take pictures better (by the way, according to the same property of sigmoids, it turns out that a person never starts from scratch).
As you understand from your experience, it is difficult to endure in a situation where everything develops along a blue sigmoid. You stick - and you still feel like a helpless newcomer who is not doing anything.
There is a great desire to “jump over” to the red trajectory, where the return is somehow more palpable. It is possible - you need to enroll in photography courses. Then instead of the “spear method” in the course of self-education you will be assisted by qualified people.
Naturally, for people of different degrees of endowments, the length and slope of the sections (including the first), and their length will differ.
Separately, it is necessary to say about the situation when you are not moving along this sigmoid - but teach someone. Student progress will be similar. And the art of a teacher / coach is the ability to intuitively understand whether the evolution curve of this particular student will break away from the zero line. Or a person is hopeless and we waste time on him. The difficulty is that the blue curve after a long ineffectual period promises us a rapid jump. Those. a student moving in a blue path will give a really high result faster than a student moving in red. The only question is whether it will give in principle.
In the following figure, along with the original S-shaped curve, the dependences of the volume of investments, the volume of new knowledge / skills and profits are shown.

It can be seen that there is no financial profit, you are in the "minus". But the volume of new knowledge is the highest, especially at the beginning, when you are only “getting into the topic.” And this is the main "bonus" of the first stage.
There are many people for whom this prize is the main one. And I understand them well, since I myself am largely one of them.
The main charm (and, at the same time, the main difficulty) of the S-shaped curve is that it is not a graphic image of a certain analytical equation, a pattern (unlike sigmoid). This means, firstly, that - being in section 1 - we do not know when section 2 will begin, what slope will be at the growth curve in section 3, etc. Secondly, this means that only the general form of display of various processes. Those. we know from experience that the course of evolution will be similar to the letter S.
But from this we have no information about the factors influencing and determining the course and parameters of this particular process. It is only obvious that during the evolution of the photographer and during the home repair these factors are different. Those. no analogies and far-reaching conclusions can be done. In general, no conclusions about the existing forces from the shape of the curve does not follow.
Let me remind you of the classic example of erroneous conclusions. A small town in the wild West at the beginning of the 19th century. According to statistical data there is 1 church and 3 brothels. After 20 years, statistics showed the presence of 5 churches and 15 brothels. There are people who try to conclude on this basis that the more churches in the city, the more popular is prostitution. In fact, in the town, the population just grew 5 times. And there is no correlation between temples and brothels. Those. before drawing conclusions, it is not bad to begin with correctly to prove the existence of a causal connection between the factors.
However, one should not underestimate the importance of the fact that we obviously know about the evolution curve of this process!
Let's return to our S-shaped curve (the first figure). Section 2 subjectively looks weird. You have been “cutting a topic” for quite some time now with almost zero returns. And suddenly the results for no apparent reason begin to grow, and with increasing speed. (By the way, this is a concrete expression of the law of transition of the amount of effort into the quality of the result.)
From the point of view of photography as a hobby, this is a turning point, because profit (with some effort on the part of the individual) is a plus (see the second figure). Those. a person notices that his photo is not worse than the average for this sample. And, if desired, he can start working as a wedding photographer.
Naturally, the specific choice depends on the real life situation. I had a friend who was fascinated by photography in the army, being an officer. And then, during the cuts, he was fired from the army. And suddenly it turned out that a hobby that is quite expensive for the family budget can become the main source of income. If the amateur photographer has a good job, and in the course of taking a photo, he gets the main pleasure from the process (shooting and discussing new photos with colleagues in a warm company with a glass of tea) - then what is the point for him to turn pleasure into an “obligatory” one?
From the history of photography it is known that many famous professional photographers are so annoyed with what they do for money, day after day - that they began to photograph bricks or curls of exfoliated paint on the old walls. Or cigarette butts.
Here is an example when the famous English photographer Cecil Beaton gave vent to emotions. For money, he shot these portraits like this:

This is the English princess Margaret. He filmed the coronation of the current English queen, all her relatives. And also a sea of glamor for fashion magazines. But from time to time he made shots like this:

He called it simply and unpretentiously - "England" (England).
Let's go back to the curve. Section 3 describes rapid growth. The amateur makes all the big and big successes. And a colleague who has gone into commerce gets more and more income:

At the same time, economic efficiency sharply increases as investments decline.
From the point of view of the psychology of creativity, at this stage, many people “grab a star”. Those. they have a bias in the assessment of their own personality and creativity. This changes attitudes towards others. Otherwise, it is called the “test of copper pipes” (if you recall the phrase “fire, water and copper pipes”).
Fortunately, and at the same time, unfortunately, life quickly puts the "stars" in place. In terms of the curve, we do not know the angle of inclination of the curve in section 3. And its duration is unknown (level of achievements along the ordinate axis). This is another consequence of the fact that the S-shaped curve only describes the general course of the process.
As a matter of fact, according to the angle of inclination and the level of people reached at the end of stage 3, people can be divided into gifted, talented and ingenious. The main thing here is not to rush to the labels. Because the development of a genius can occur rather slowly (angle of inclination) - but it remains in principle unclear whether he reaches section 4 or not. Being already at an incredibly high level, when more fierce competitors, who initially demonstrated their “steepness” (in the direct sense, the slope of the curve in section 3), have long been far below.
The overwhelming majority of people reach the highest possible level for themselves in the data of specific living conditions - and goes to section 4. The psychological section is the hardest, the most critical. In fact, you seem to be almost a master, you have been praised more and more - and suddenly everything “disappears” somewhere. The speed drops, there is a feeling of trampling on the spot. And then it turns out that this is not a feeling at all - but a real fact.
There are many options for further action. If a person is pleased to be cut into something new, then after the third stage of “skimming” it is time, as they say, “to make legs”. Those. start another project to go through again, catch those sensations that are so attractive. At stage 4, such people are extremely uncomfortable.
But I specifically chose a photo as an example. This is not a hobby that is easy to just quit and get carried away with something else. For many reasons. Therefore, the 4 stage turns for the photographer into a painful, but extremely useful for the development of personality. Deeper knowledge of yourself, the acquisition of skills of patience and endurance, the development of new qualities.
I will give an example from another area. It is known that football academies in our country produce a fairly large number of young football players. However, in the media, groans about how few young talents grow to the level of the Premier League teams and the national team do not subside. In terms of technical skills, a graduate of a football academy is in zone 4. That is, perform technical activities in training, he knows how great. And he really has nowhere to grow on this scale. A mature master differs from a graduate in that he is able to perform the most complex technical and tactical actions not only in training, but in the match of the World Cup final. Note that, formally, according to a curve, the quantitative difference in the level of technical equipment between a novice and a master is minimal. Essentially, the gap is infinite (i.e. it is qualitative).
Here we stick to another feature of the S-shaped curves. The fact is that you need to make a lot of effort to understand the coordinates in which we build it in this particular case. And the real processes in life are always multidimensional. They are usually described on many scales (as in the multifactorial / multidimensional personal MMPI questionnaire in personality psychology). A person, like a real life phenomenon, cannot be described by one scale as “fool-clever”, for example.
Thus, being on plot 4, it makes sense to think about which of the S-shaped family of curves we are now. If this is the ability to build a frame composition, then it is desirable to remember that the level of a photo is not exhausted only by composition. There are more color and other factors. In addition, as it is endlessly not tired of repeating on forums on a photo, the photographer always takes pictures, not the camera. In particular, the level of photos directly depends on the level of personal development of the master.
Those. We continue to develop the ability to build interesting compositions - but we are mainly focusing on the development of other personality traits and abilities of the photographer.
If we interpret the coordinate system extremely globally, it is “efforts - the result”, then at stage 4 the photographer begins (and at stage 5 completes) reconfiguring, nuancing his feelings and emotions from taking photographs. Simply put, learns to find pleasure in thinking about the place and time of shooting, in preparing the tools for the photo shoot. From the feeling of anticipation of a successful frame. From the process of processing photos on the computer. Ie pleasure, satisfaction from hobbies is not lost anywhere. It is located in those places that we did not even know about at stage 1, but at stages 2 and 3 we simply did not think, did not understand their place and meaning in the overall picture.
In a sense, this can be called an attempt to break the deadlock by shifting the focus of attention to detail. This is if the pessimist judges. An optimist will call it expanding the range of available ideas and emotions, sensations. There is no “correct” solution; this is a classic question: “is the glass half empty - or half full?” However, to successfully continue the passion for photography, it is advisable to think and act positively. Those. Amateurs who are incapable of this are eliminated at stage 4.
The fifth, the final stage of the S-shaped curve. Area of stability. If all is well, then this is the time to get the most complete satisfaction from your favorite hobby. At the same time sadly more and more complete awareness of the fact that reached the ceiling.
Just do not think that the curve in the 5th section will automatically go up. Of course, “mastering is not lost” - but even maintaining a constant level requires constant effort. Graphically, it looks like this:

If the conditions are not applied, then the curve is bent "at half past six" (as men sometimes joke with each other).
Of course, in a good way, if possible, it is better not to climb into the 5th stage in most life processes at the 5th stage. Including and therefore, for example, there is a recommendation to change jobs once every 3-5 years.
But many processes do not leave us such a choice. That is why it is important to find strength and additional motivation for life and development in this finishing segment.
By the way, to choose a point when it is time to “jump off” from this curve is very difficult. Especially when it comes to the essential things for a person like money or power. If you leave earlier, you will not get yours. You will be late with leaving - you will start to lose faster and faster.
Some other S-curve applications
I thought that the most important thing in this material was to draw attention to the need to take into account and reflect on the fact of development along a S-shaped trajectory of many processes in the life of an individual. However, the applicability of this curve to various processes in nature and society has been known for a long time. In particular, there is a point of view that the model of an S-shaped curve was first proposed by the French mathematician Pierre Verhulst back in 1838.
For example, if several pairs of fighting hamsters are brought to Easter Island, then the evolution of their population is described by this kind of S-shaped curve:

Extremely popular is the curve among people engaged in innovation, the development of new technologies (including in the framework of start-up):

Including There is a lot of material about when to switch to another curve (steps 4-5) and what this is fraught with. Graphically, this is usually depicted as:

Obviously, the transition to a new curve is always painful and costly. And always jump into the unknown with no guarantee of a positive result.
Amusingly, the totality of qualitative jumps can be finally considered as a continuous evolutionary development (if we imagine the envelope of the following sequence of S-shaped curves):

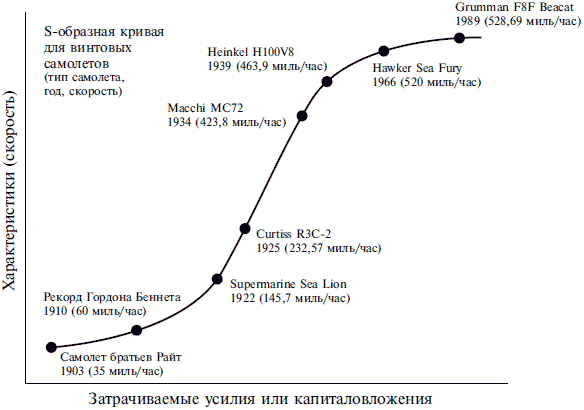
The development of whole areas of technology can be described by an S-shaped curve. Here is an interesting graph of the growth of speed records:

Separately, I will explain how the S-shaped curve differs radically from sigmoid in life. For the latter, achievement 1 is impossible by definition. But a significant part of serious projects requires the implementation of the plan that was approved and for which funding was allocated. Therefore, formally, some curves reach 1 (at least from the point of view of higher superiors, investigative bodies and prosecutors). Although, honestly, I do not believe it. Not because of the shortcomings of individuals and organizations. But in principle - well, it is impossible to perform exactly 100%, in life there are always differences and deviations (another thing is that they may be considered as a blessing or mistake within the limits of the permissible error).
In general, on the net you can independently find a lot of interesting things (see the “Sources” section below).
I want to emphasize one important thing, which is always desirable to remember. Science-based reasoning and graphics, universities, dissertation councils, journals and other attributes are designed to create the impression of the scientific character of a given area of human activity (for example, management, sociology). This is a question of status, it is important for the individual, so the temptation to associate oneself with science is very great. In reality, there is no management science, for example, innovation. /.
, .
Sources
1. www.metodolog.ru/00767/00767.html
2. ibcm.biz/%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%8F-s-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%8F-%D0%BA%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%8F-%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%8F
3. www.integro.ru/system/ots/evolution/s_curve.htm
4. milutin-school.livejournal.com/13287.html
5. tech.wikireading.ru/9422
6. bezogr.ru/byurokraticheskij-socializm-ruhnul-potomu-chto-ne-pozvolyal-ce.html?page=3
2. ibcm.biz/%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%8F-s-%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%8F-%D0%BA%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%8F-%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%8F
3. www.integro.ru/system/ots/evolution/s_curve.htm
4. milutin-school.livejournal.com/13287.html
5. tech.wikireading.ru/9422
6. bezogr.ru/byurokraticheskij-socializm-ruhnul-potomu-chto-ne-pozvolyal-ce.html?page=3
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/370211/
All Articles