A history of rare neurodegenerative diseases: Peak's disease, Hallervorden-Spatz disease

Today we will talk about two rare neurodegenerative diseases - Pick's disease and Gallervorden-Spatz disease. Both diseases are named after their discoverers, each of whom has lived a difficult but rich life.
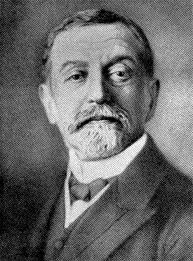 Pick's disease is a rare chronic progressive disease of the central nervous system. Named after Arnold Pick, professor of psychiatry at Charles University in Prague . Like many medical researchers of that time, at the very beginning of his way he studied a wide range of disciplines: clinical neuroscience, psychiatry and neuropathology, which is now quite difficult to imagine. Contemporaries spoke of him as an intelligent, modest and principled man who made a significant contribution in the field of psychiatry and neurology: more than 350 publications in German and English are proof of this.
Pick's disease is a rare chronic progressive disease of the central nervous system. Named after Arnold Pick, professor of psychiatry at Charles University in Prague . Like many medical researchers of that time, at the very beginning of his way he studied a wide range of disciplines: clinical neuroscience, psychiatry and neuropathology, which is now quite difficult to imagine. Contemporaries spoke of him as an intelligent, modest and principled man who made a significant contribution in the field of psychiatry and neurology: more than 350 publications in German and English are proof of this.')
During his work at Charles University, he encountered many problems associated with academic teaching in German and Czech under the control of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Often, the scientist did not have enough basic tools, he was faced with hostility and resentment, which prevented him from performing his duty. Despite this, his ability to communicate with patients with psychosis and aphasia was admired, and his contribution to medicine later turned out to be legendary.
Cases of patients with various forms of frontotemporal dementia and its symptoms began to be described for the first time in the late XIX - early XX century. In 1892, Arnold Pick studied the clinical symptoms of a patient named Augustus H., who suffered from severe aphasia - speech loss and dementia. It was later thought that it was Peak who first recorded the case of primary progressive aphasia.
In the following paper, a German doctor studied the case of a patient named Anna H., whose symptoms included behavioral abnormalities and loss of cognitive function, which also correlated with frontal dementia. The third study described the problem of a patient named Anna D. - a 75-year-old woman with weakened speech skills and a loss of conceptual knowledge: Anna occasionally forgot how to use familiar household items.
All three cases formed the basis of Pick's hypothesis that dementia is the result of localized deterioration in specific areas of the brain, and not a general dysfunction of the brain. Subsequently, Alois Alzheimer , in whose honor the German psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin (Emill Kraepelin) would later name one of the types of senile dementia, identified protein tangles that settled inside the nerve cells in the damaged parts of the brain - Pick's Taurus.
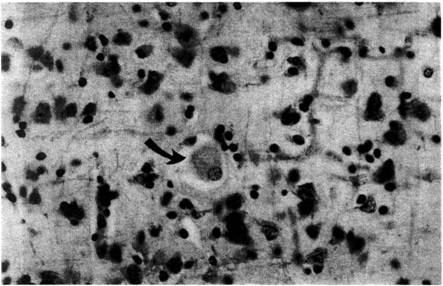
Pick Cell
Pick's Taurus and Peak's cells contain an abnormal form of tau protein - organic matter that is present in all nerve cells, but for some reason produced in abnormal amounts or changed form. During numerous studies, scientists were able to establish the cause of the abnormal amount of this protein in nerve cells: it’s all a matter of mutations affecting chromosome number 17. But it is still unknown to science why the form of tau proteins is changing.
Pick's disease could easily be confused with Alzheimer's disease, if not for the fact that the former only affects certain parts of the brain, because it is often called frontotemporal dementia. The frontal lobe of the brain controls such important aspects of vital activity as emotions, verbal communication, behavior, inhibition, as well as some forms of movement. Obviously, any change in the cells of this part of the brain can lead to irreversible consequences.
Pick's disease is a rare disease that causes progressive and irreversible dementia. A person with this diagnosis has difficulty controlling speech, behavior, thinking, judgment, and memory. As with patients with other types of dementia, sudden personality changes may occur. Most often, this disorder is diagnosed in people between the ages of 40 and 60, but is sometimes found in 20-year-olds.
Universal test that determines the fronto-temporal dementia, no. Doctors can conduct a number of indirect studies: to study the history of the disease, to conduct tests for oral and written speech, to appoint a detailed neurological examination, as well as to examine the brain tissue using MRI and computed tomography.
How is Pick's disease treated? There are no known treatments that effectively slow the progression of the fronto-temporal dementia, but some drugs can alleviate the symptoms. For example, a doctor may prescribe antidepressants or antipsychotics to inhibit emotional and behavioral changes.
The prognosis for people with frontotemporal dementia is disappointing. According to the University of California, the disorder progresses over a period of 8-10 years. In this case, it may take several years from the onset of the first symptoms to the diagnosis of the disease. As a result, the time interval between diagnosis and death is about 5 years.
Pick's disease occurs only in three cases per million, but claimed enough lives of famous people. Robert Floyd , known for his contribution to the Floyd-Vorschall algorithm, David Rumelhart , an American scientist, famous for his studies of learning and memory in semantic neural networks, fought this disorder at various times. poet, writer, musician and revolutionary Kazi Nazrul Islam , bass guitarist, composer and artist, famous for his work with the Van der Graaf Generator Nick Potter and others.

David Rumelhart
Neurodegeneration with iron deposition in the brain of the first type, or Hallervorden-Spatz disease
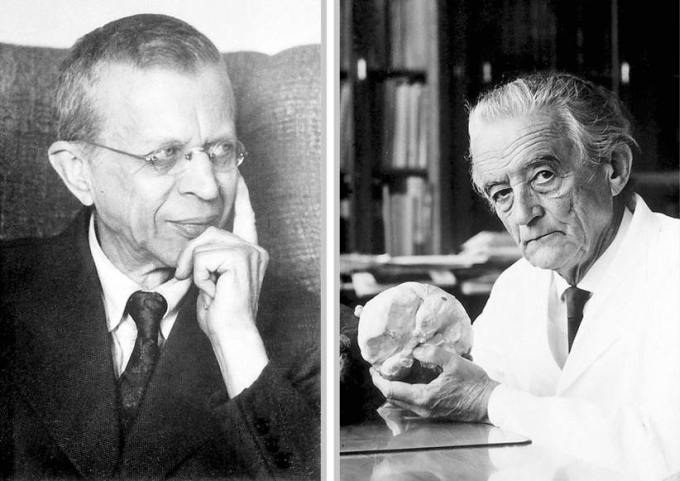

Julius Gallervorden (left) and Hugo Spatz (right)
Julius Hallervorden, whose name is associated with this disease, made an important contribution to neurology. Despite this, his work during the Second World War raises serious questions about the moral obligations of medical science. There was no law obliging to participate in the “ T-4 Killing Program ” and “put to sleep”, however some German doctors agreed to this almost voluntarily. Among them was Julius Gallervorden.
Some believe that the name of this German neuropathologist should be removed from the name of the disease. Scientists proposed renaming the disease to “Marfa-Alma’s disease”, in honor of two sisters, whose brain tissues were first investigated by Julius Hallervorden and Hugo Spatz. In 1996, Todd Taylor (Todd Taylor) suggested that this disorder can be described as neurodegenerative with an accumulation of iron in the brain (NBIA1), in order to avoid the unwanted eponym "Gallervorden-Spatz." Today, the Taylor variant is widespread throughout the world.
Neurodegeneration with iron deposition in the brain was first described by two German neuropathologists, Julius Gallervorden and Hugo Spatz in 1922. At the discovery of a new non-degenerative disease, they were prompted by the case of one family, in which five sisters at once showed signs of dementia and dysarthria - difficulty in pronouncing words. After the death of the sisters at the autopsy, doctors discovered brown spots in various areas of the brain. They were found in particularly large quantities in the pale ball and the substantia nigra — components of the basal ganglia . These mysterious spots were iron deposits.
Further research and descriptions produced Meyer in 1958, which diagnosed 30 individual cases of NBIA1. Meyer's followers described the five affected family members and hypothesized that the disease first appeared in central Europe. Thus, they supported the issue of clinical genetic analysis.
Gallervorden-Spatz disease is a genetic neurological disorder that causes problems with movement. Usually develops in childhood and increases over time. In each patient, the symptoms may vary, but a general group of symptoms is distinguished: distortions in muscle contraction and difficulty in coordinating movement.
About a quarter of all people suffering from this type of neurodegeneration experience an atypical form of NBIA1, which develops after reaching 10 years of age. In this case, the disease progresses slowly and gradually, in contrast to the situation when the disease manifests itself at an earlier age. At the same time, adult patients are more likely to experience a significant impairment of speech, as well as serious mental and behavioral disorders.
Unintended, intermittent muscle contractions on the face, body or limbs are also a signal for the occurrence of a neurodegenerative disease. Such cuts may subsequently change the postures that are familiar to humans. Other symptoms accompanying patients include muscle hardening, problems with movement coordination, seizures, disorientation, difficulty swallowing, dementia, and some others.
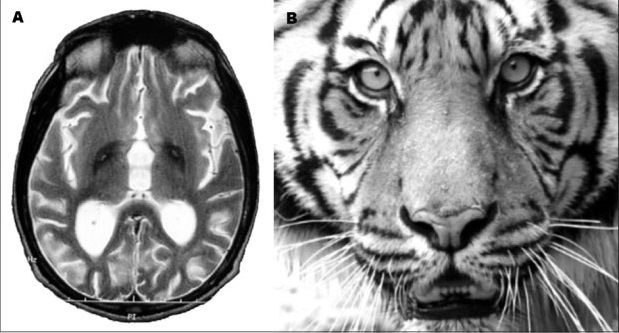
The disease is considered rare: up to 3 patients per 1 million people. Most often these are members of the same family. After the first symptoms are detected, the doctors check the patients with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The main marker of the disorder is the presence in the image of the so-called “tiger's eye” - the hyperintensive oval zone located in the region of the pale ball, surrounded by an even larger hypointense zone. The latter is, in fact, the “eye”, and the hyperintensive is its “pupil”. This effect is usually due to excessive accumulation of iron.
The cause of the disease lies in an inherited defect in the pantothenate kinase 2 (PANK2) gene. Protein PANK2 in the human body controls the production of coenzyme A , which, in turn, helps to convert fats, some amino acids and carbohydrates into energy.
In medical practice, there are cases when neurodegeneration with iron deposition in the brain is not caused by a mutation of the PANK2 gene. Scientists suggest that in such cases, the cause of the disease are defects in one or more other genes that are not yet identified.
Currently, NBIA1 is not treatable, and doctors are only struggling with its symptoms. Depending on the case, doctors prescribe physiotherapy, medication, or both. Physical therapy reduces and prevents muscle stiffness, cramps, and other muscle problems. One of the successful methods of dealing with the symptoms of the disorder is also occupational therapy. With its help, patients develop skills for everyday life and retain their current abilities. Patients seeking a speech therapist can manage swallowing disorders or speech disorders.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/370045/
All Articles