Tectonics of the Russian population
Russia is a quilt sewn from pieces of fabric of different colors, texture and materials. The Russian Federation is not just the largest country in the world in terms of its territory, it is also a huge melting pot, which included representatives of various ethnic groups (the population census of 2010 totals more than 200). Who or what unites all these pieces together? Lomonosov and Tatishchev said that the name of the Varyags was that they got their nickname, “Rus”, and before that they were Slavs. Miller and Schlötzer, German historians, had said earlier that the Normans had founded the Kiev dynasty. In the 20th century, linguists formulated the theory of the ascend of the ethnonym “Rus” to Iranian-speaking roots, increasing the number of questions. Does the term “Russian population” apply to the population of Russia and what is behind it in the new material Genotek.

In science, there is the term population, which describes a group of individuals of one species, living for a long time together in a certain area. Therefore, from a biological point of view, the term “Russian population” has the right to exist, but it is puzzling from the point of view of a person who is amazed at the number of nationalities in the census results. Indeed, the composition of our state, as well as the distribution of the population throughout its territory, is very heterogeneous. If we consider the results of the 2010 census as a reliable source, it can be found that Russians make up almost 80% of the population of Russia. However, in addition to the Russians, there are 6 large national groups: Tatars, Ukrainians, Bashkirs, Chuvash, Chechens, making up a total of 10% of the population. Still, the Russian population exists.
This is not about language, not about culture and not about the broad Russian soul. Let's look at and dissect a group of people who live on the territory of Russia using population genetics methods. Human population genetics studies the history of mankind, its attention is focused on the fate of the great alleles (variants of genes). The most interesting patterns that researchers are trying to figure out are the distribution of allele frequencies in populations and their change in the course of evolution. How exactly this happens, why, and not otherwise, and who will win - the same historical science, only more humane. One of the key concepts in this area of research is haplotype and haplogroup.
')
A haplotype is an abbreviation for the haploid genotype, a set of alleles of those parts of the chromosome that are usually inherited together. As a rule, human sex cells contain unique combinations of variants of genes that our parents mixed together, not having the right and opportunity to choose what we get. Haplogroup - a group of similar haplotypes that have a common ancestor, in which the same mutation took place in both haplotypes - single nucleotide polymorphism, as a rule, the haplotypes of Y-chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (from father and mother, respectively) are considered. The choice of these sequences, on the one hand, is connected with the fact that it is necessary to know for sure that the selected genes are a set from one parent, and not a mixture. On the other hand, mutations in these sequences accumulate and these chromosomes do not exchange portions with any other parts of the genome. Thanks to this, one can track the migration paths and talk about the degree of kinship of certain national groups.
Let us recall the map of the settlement of nations on the territory of modern Russia. In the West since ancient times lived the Finno-Ugric tribes of Eastern Europe. The ancestors of the Saami, Estonians, Komi, Mari and Mordovians lived there. The Central European part of modern Russia was occupied by Slavic tribes, just to the north - the Baltic tribes. Deeper to the northeast: Nenets, Enets, Nganasans, Selkups, Khanty and Mansi. More east: Evenki, Lamut, Udege, Nanai, Orochi, Orok and Ulchi, as well as Chukchi, Eskimos, Koryaks, Itelmens, Chuvans, Aleuts and Nivkhs. In the south were the Iranian-speaking Mongol tribes. In addition to large national groups, many small nations live in Russia. Some even have their own language, but this is another story. They are unique, their peculiarity is that there was little mixing with the general population. Our goal is to create a general image. For this you need to remember the history of the whole nation.
The ups and downs of empires, invasions, slavery, commerce, wars, migrations - throughout history, different human groups have had many reasons to communicate. Any such interactions caused a sudden or sequential transfer of genetic material, creating populations with impurities. In most cases, the genetic heritage of the events of the past millennia is unknown to us, and information from history does not provide a description of the full picture. I want to know more. Let's return to the history of the Russian people. If you recall the moments of “large-scale confusion”, the vocation of the Varangians and the Tatar-Mongol invasion come to mind. These events, of course, influenced the composition of the genome of the modern Russian man. However, we will try to rewind the story several thousand years ago to see something fundamental. So, if you look at the map of ancient cultures, you can get a general idea of how it all was then. Under the picture - deciphering which haplogroups are most characteristic of which culture. The world then seems simple and interesting, like playing with soldiers. Each culture has certain characteristic artifacts, by the name of which it is named (Culture of bell-shaped cups, Culture of corded stoneware), and then they are settled on the map. Now you can also classify them in terms of haplogroups.
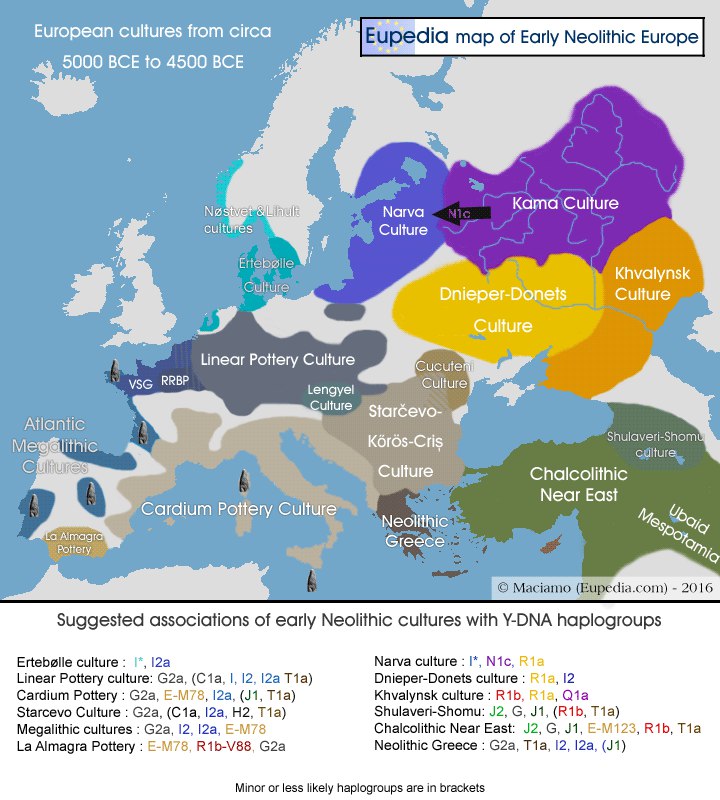
We have compiled a description of haplogroups characteristic of representatives of the Russian population. It includes the most common: R1a, R1b, N, G, I.
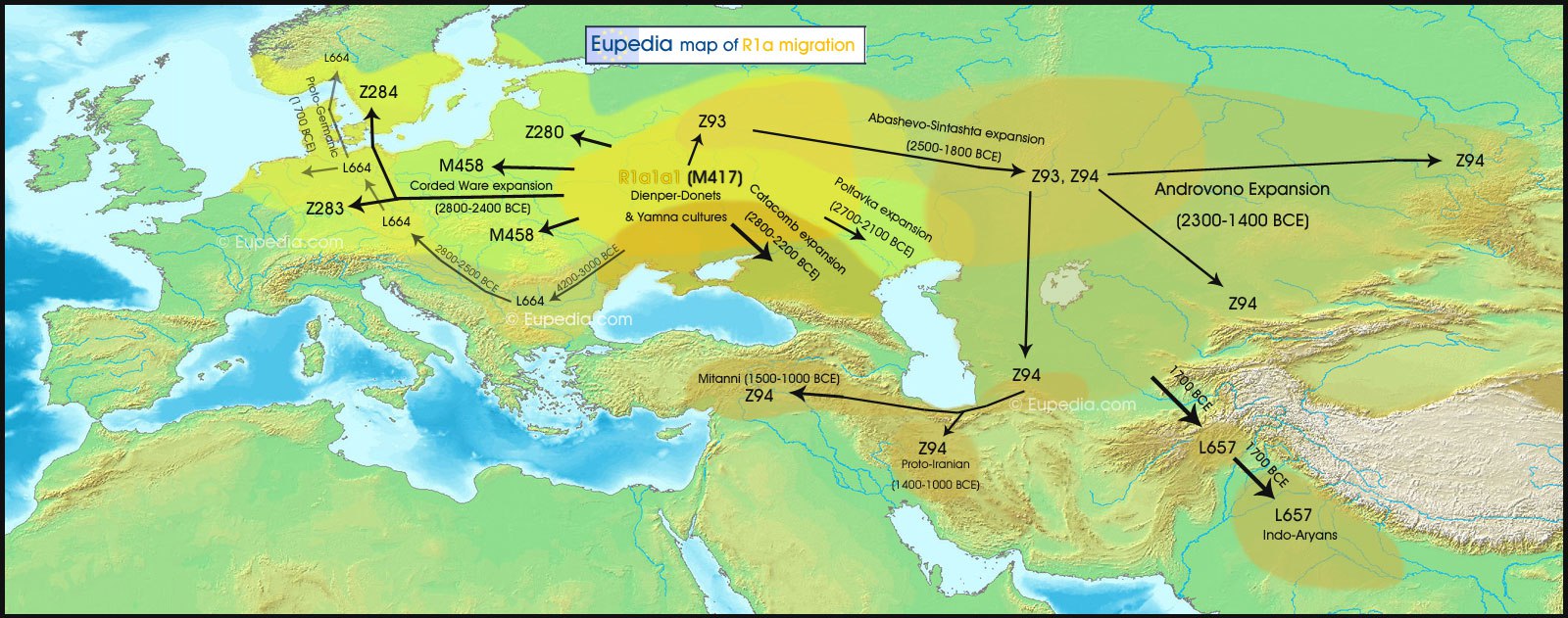
In 2013, a paper was published on the Boy from Malta (emphasis on the last syllable), to the west of Lake Baikal. This boy lived 24,000 years ago in a tribe of mammoth hunters. Genetic analysis showed that his tribe gave rise to many modern Europeans. Haplogroup found remains was called R *. R1a is considered a haplogroup, dominant among the speakers of Proto-Indo-European languages. This language group is divided into Indo-Iranian, Thracian, Baltic and Slavic branches. Today, the haplogroup R1a is most common in Eastern Europe, as well as Central and South Asia, and the R1b group is in Western Europe. Representatives of the haplogroup R1 * are generally characterized by bright eyes, blond hair and fair skin, which is associated with a mutation in our gene SLC24A5. Haplogroups of both R1a and R1b are common in Russia. Among Genotek clients, haplogroup R1a was detected in 38%, and R1b in 9% of men. Initially, there was a hypothesis that the last common ancestor lived in the Balkans or in the south of Siberia due to the strong genetic heterogeneity of these regions, and then a branching occurred - the nomads moved to Eastern Europe. The most likely scenario for R1a is shown in the picture.
Representatives of this haplogroup are descendants of the East Asian branch of the macro-haplogroup that formed in Indochina about 20,000 years ago. It is curious that this haplogroup prevails among the Finns, Balts, Yakuts, Udmurts, and Buryats. Representatives of haplogroup N are found everywhere in Russia, often meeting around Altai, Sayan, Mongolia, and Northern China. They passed from the east through the whole of Russia, spreading the Uralic languages, and stopped in Europe. Yaroslav the Wise belonged to this haplogroup. 13% of male Genotek clients are representatives of this haplogroup.
Today, haplogroup G can be found everywhere from Western Europe and North-West Africa to Central Asia and India. The frequency of occurrence in the population is rather low - from 1 to 10%, with the exception of 2 regions - the Caucasus and Central and Southern Italy (along with Sardinia). There, the frequencies range from 15 to 30%. Haplogroup G dates back to the branch associated with the second major migration of Homo sapiens from Africa about 60,000 years ago. Haplogroups of earlier migrants are found in the population of island South Asia and Oceania, but the path of the second migration through the Arabian Peninsula went to the Middle East. The main branch of this haplogroup is considered to be an ancestral state for 80% of modern Eurasians. Haplogroup G was formed about 50,000 years ago as a branch from the main one. The evolution of representatives of this haplogroup proceeded independently; DNA analysis shows that the descendants who inherited this haplogroup were significantly influenced by the effect of the bottleneck . It is curious that Joseph Stalin belonged to the haplogroup G2a1a, this conclusion was made on the basis of his grandson's DNA data. 5% of Genotek customers are also representatives of haplogroup G.
Haplogroup I is the oldest haplogroup in Europe, and, most likely, the only one formed on this territory. Its carriers came from the Middle East, an independent haplogroup formed about 40,000 years ago. It was one of the haplogroups common among Cro-Magnons. In Europe, it breaks down into many branches. Among the descendants of its various branches - Nikola Tesla, Leo Tolstoy, Warren Buffett, Bill Clinton, as well as 17% of men who completed the study in Genotek.
These haplogroups are most common among representatives of the Russian population. Notice, not a word about ethnicity and Russian. Ethnicity is not a biological concept. Self-consciousness, mentality, culture - these are things that depend on the genome only partly. You can react violently to what is happening and have a hot temper, due to the nature of the work of neurotransmitters, but your world view and attitude depends on your upbringing. You can find out your origin by passing the Genealogy DNA test with a 10% discount on the GeekAncestry promo code . However, if in your heart you are a Tatar / Bashkir / Pole or Mexican, then so be it.

Russian population
In science, there is the term population, which describes a group of individuals of one species, living for a long time together in a certain area. Therefore, from a biological point of view, the term “Russian population” has the right to exist, but it is puzzling from the point of view of a person who is amazed at the number of nationalities in the census results. Indeed, the composition of our state, as well as the distribution of the population throughout its territory, is very heterogeneous. If we consider the results of the 2010 census as a reliable source, it can be found that Russians make up almost 80% of the population of Russia. However, in addition to the Russians, there are 6 large national groups: Tatars, Ukrainians, Bashkirs, Chuvash, Chechens, making up a total of 10% of the population. Still, the Russian population exists.
Brilliance and poverty of alleles
This is not about language, not about culture and not about the broad Russian soul. Let's look at and dissect a group of people who live on the territory of Russia using population genetics methods. Human population genetics studies the history of mankind, its attention is focused on the fate of the great alleles (variants of genes). The most interesting patterns that researchers are trying to figure out are the distribution of allele frequencies in populations and their change in the course of evolution. How exactly this happens, why, and not otherwise, and who will win - the same historical science, only more humane. One of the key concepts in this area of research is haplotype and haplogroup.
')
Pop genetics
A haplotype is an abbreviation for the haploid genotype, a set of alleles of those parts of the chromosome that are usually inherited together. As a rule, human sex cells contain unique combinations of variants of genes that our parents mixed together, not having the right and opportunity to choose what we get. Haplogroup - a group of similar haplotypes that have a common ancestor, in which the same mutation took place in both haplotypes - single nucleotide polymorphism, as a rule, the haplotypes of Y-chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (from father and mother, respectively) are considered. The choice of these sequences, on the one hand, is connected with the fact that it is necessary to know for sure that the selected genes are a set from one parent, and not a mixture. On the other hand, mutations in these sequences accumulate and these chromosomes do not exchange portions with any other parts of the genome. Thanks to this, one can track the migration paths and talk about the degree of kinship of certain national groups.
Check the landmarks
Let us recall the map of the settlement of nations on the territory of modern Russia. In the West since ancient times lived the Finno-Ugric tribes of Eastern Europe. The ancestors of the Saami, Estonians, Komi, Mari and Mordovians lived there. The Central European part of modern Russia was occupied by Slavic tribes, just to the north - the Baltic tribes. Deeper to the northeast: Nenets, Enets, Nganasans, Selkups, Khanty and Mansi. More east: Evenki, Lamut, Udege, Nanai, Orochi, Orok and Ulchi, as well as Chukchi, Eskimos, Koryaks, Itelmens, Chuvans, Aleuts and Nivkhs. In the south were the Iranian-speaking Mongol tribes. In addition to large national groups, many small nations live in Russia. Some even have their own language, but this is another story. They are unique, their peculiarity is that there was little mixing with the general population. Our goal is to create a general image. For this you need to remember the history of the whole nation.
Inherit in the genome
The ups and downs of empires, invasions, slavery, commerce, wars, migrations - throughout history, different human groups have had many reasons to communicate. Any such interactions caused a sudden or sequential transfer of genetic material, creating populations with impurities. In most cases, the genetic heritage of the events of the past millennia is unknown to us, and information from history does not provide a description of the full picture. I want to know more. Let's return to the history of the Russian people. If you recall the moments of “large-scale confusion”, the vocation of the Varangians and the Tatar-Mongol invasion come to mind. These events, of course, influenced the composition of the genome of the modern Russian man. However, we will try to rewind the story several thousand years ago to see something fundamental. So, if you look at the map of ancient cultures, you can get a general idea of how it all was then. Under the picture - deciphering which haplogroups are most characteristic of which culture. The world then seems simple and interesting, like playing with soldiers. Each culture has certain characteristic artifacts, by the name of which it is named (Culture of bell-shaped cups, Culture of corded stoneware), and then they are settled on the map. Now you can also classify them in terms of haplogroups.

We have compiled a description of haplogroups characteristic of representatives of the Russian population. It includes the most common: R1a, R1b, N, G, I.
R *
In 2013, a paper was published on the Boy from Malta (emphasis on the last syllable), to the west of Lake Baikal. This boy lived 24,000 years ago in a tribe of mammoth hunters. Genetic analysis showed that his tribe gave rise to many modern Europeans. Haplogroup found remains was called R *. R1a is considered a haplogroup, dominant among the speakers of Proto-Indo-European languages. This language group is divided into Indo-Iranian, Thracian, Baltic and Slavic branches. Today, the haplogroup R1a is most common in Eastern Europe, as well as Central and South Asia, and the R1b group is in Western Europe. Representatives of the haplogroup R1 * are generally characterized by bright eyes, blond hair and fair skin, which is associated with a mutation in our gene SLC24A5. Haplogroups of both R1a and R1b are common in Russia. Among Genotek clients, haplogroup R1a was detected in 38%, and R1b in 9% of men. Initially, there was a hypothesis that the last common ancestor lived in the Balkans or in the south of Siberia due to the strong genetic heterogeneity of these regions, and then a branching occurred - the nomads moved to Eastern Europe. The most likely scenario for R1a is shown in the picture.

N
Representatives of this haplogroup are descendants of the East Asian branch of the macro-haplogroup that formed in Indochina about 20,000 years ago. It is curious that this haplogroup prevails among the Finns, Balts, Yakuts, Udmurts, and Buryats. Representatives of haplogroup N are found everywhere in Russia, often meeting around Altai, Sayan, Mongolia, and Northern China. They passed from the east through the whole of Russia, spreading the Uralic languages, and stopped in Europe. Yaroslav the Wise belonged to this haplogroup. 13% of male Genotek clients are representatives of this haplogroup.
G
Today, haplogroup G can be found everywhere from Western Europe and North-West Africa to Central Asia and India. The frequency of occurrence in the population is rather low - from 1 to 10%, with the exception of 2 regions - the Caucasus and Central and Southern Italy (along with Sardinia). There, the frequencies range from 15 to 30%. Haplogroup G dates back to the branch associated with the second major migration of Homo sapiens from Africa about 60,000 years ago. Haplogroups of earlier migrants are found in the population of island South Asia and Oceania, but the path of the second migration through the Arabian Peninsula went to the Middle East. The main branch of this haplogroup is considered to be an ancestral state for 80% of modern Eurasians. Haplogroup G was formed about 50,000 years ago as a branch from the main one. The evolution of representatives of this haplogroup proceeded independently; DNA analysis shows that the descendants who inherited this haplogroup were significantly influenced by the effect of the bottleneck . It is curious that Joseph Stalin belonged to the haplogroup G2a1a, this conclusion was made on the basis of his grandson's DNA data. 5% of Genotek customers are also representatives of haplogroup G.
I
Haplogroup I is the oldest haplogroup in Europe, and, most likely, the only one formed on this territory. Its carriers came from the Middle East, an independent haplogroup formed about 40,000 years ago. It was one of the haplogroups common among Cro-Magnons. In Europe, it breaks down into many branches. Among the descendants of its various branches - Nikola Tesla, Leo Tolstoy, Warren Buffett, Bill Clinton, as well as 17% of men who completed the study in Genotek.
These haplogroups are most common among representatives of the Russian population. Notice, not a word about ethnicity and Russian. Ethnicity is not a biological concept. Self-consciousness, mentality, culture - these are things that depend on the genome only partly. You can react violently to what is happening and have a hot temper, due to the nature of the work of neurotransmitters, but your world view and attitude depends on your upbringing. You can find out your origin by passing the Genealogy DNA test with a 10% discount on the GeekAncestry promo code . However, if in your heart you are a Tatar / Bashkir / Pole or Mexican, then so be it.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/369979/
All Articles