History of world epidemics, part 4
If in the case of tuberculosis and influenza, the percentage of deaths and the number of people infected over the years is reduced, then the death rate from malaria, according to scientists, will double in the next twenty years due to a decrease in susceptibility to drugs. The second terrible disease we are talking about today is leprosy. In medieval France, lepers were condemned to death, served over the funeral service over the living, threw a couple of shovels of land at the cemetery and after such a funeral were taken to a special house - the leper colony.
Leprechaun on the image from the manuscript of the XIV century
Malaria, or, as it used to be called, “swamp fever,” is caused by unicellular parasites of the genus Plasmodium, which are transmitted to humans through the bite of anopic mosquitoes. Perhaps mankind has known this disease for more than fifty thousand years. Plasmodium could previously be the simplest, capable of photosynthesis, but then adapted to life in the intestines of aquatic invertebrates and became a parasite. And he moved to live in the larvae of the first blood-sucking insects.
According to the latest data, twenty million years ago, Plasmodium used mosquitoes to infect victims. Analysis of the plasmodium controversy allowed scientists to suggest that cold-blooded creatures could also be sick with malaria. For example, dinosaurs. Later, with the advent of man, the parasites adapted to him and began to use us to spread among bloodsucking insects.
')
Malaria was first described around 2700 BC in the Chinese Chronicle. But the first epidemic could have happened much earlier, from 8 to 15 thousand years ago, malaria could cause a sharp reduction in the number of people on Earth.
Doctors have learned that unicellular organisms cause malaria in the 1880s. French doctor Churl Louis Alphonse Laveran discovered a parasite in the patient’s blood, for which he won the Nobel Prize. In 1894, for the first time, it was suggested that mosquitoes transmit malaria. This method was confirmed by Giovanni Battista Grassi with the help of volunteers. Another method of transmission is now known: from person to person through the blood. Malaria can cause a baby in the womb.
There are different types of plasmodia. A person may suffer from five of them. Infection occurs when a mosquito injects parasites at one of their developmental stages into human blood. From the blood they enter the liver, where they begin to multiply. After a few weeks or months, the disease begins to manifest itself because the plasmodia re-enters the circulatory system. The incubation period depends on the type of plasmodia.
The patient begins to hurt the joints, fever and chills, cramps. A person becomes a lure for mosquitoes - begins to smell delicious to them. It is necessary that the Plasmodia again fall to their beloved master, since for them man is only a means of propagation.
Not so long ago, namely in the 1980s, scientists discovered another stage in the existence of the parasite — the resting one. Because of this stage, people became ill with malaria even years after their blood was completely purified from plasmodia.
Children and people with HIV / AIDS are most at risk. The disease for them can be fatal.
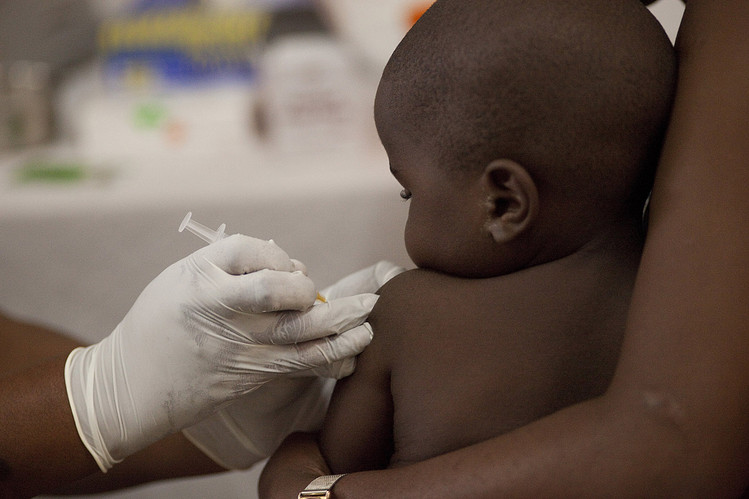
Tanzania, child vaccination against malaria. A source
Malaria seems to be some kind of distant African disease. Malaria mosquitoes themselves live in almost all climatic zones. But for the risk of infection you need a large number of these insects and their rapid reproduction. Malaria used to be called “swamp fever” precisely because it is common in places where there are no low temperatures, there are swamps and a lot of precipitation falls. The risk of infection is highest in the equatorial and subequatorial zones. In Russia, such mosquitoes exist throughout the European part of the country.
Malaria in Russia and the USSR was widespread until the 1950s. In order to cope with this disease in the resort area, swamps were drained in Sochi, as well as oil reservoirs: they were covered with a layer of oil in order to exterminate the mosquito larvae.
The largest number of cases in the history of the USSR was recorded in the years 1934-1935 - then 9 million people became infected. In 1962, malaria was won in the USSR. Isolated cases of infection were possible after that. During the war in Afghanistan in 1986-1990, the USSR recorded an increase in the number of infected - 1314 cases.
Malaria covers 97 countries. Although nearly half of the world's population was at risk of having malaria in 2015 — 3.2 billion people — most of the cases are in sub-Saharan Africa. It is there that 88% of cases of illness and 90% of deaths from malaria occur.
In 2015, 214 million people became infected with malaria, and 438 thousand of them died. Bill Gates and the British Chancellor George Osborne in January 2016 promised to give 4.3 billion dollars to fight the disease. This money is planned to spend on the study of the disease and the search for drugs .

Mark of the USSR, 1962
Hundreds of years ago, American Indians used cinchona bark as a febrifuge. Spanish naturalist Bernab Cobo brought it to Europe in 1632. After curing the wife of the Viceroy of Peru from malaria, they learned about the wonderful properties of the medicine throughout the country, then the bark was transported to Spain and Italy, and it began to be used throughout Europe. It took almost two hundred years to extract quinine directly from the cortex, which was used as a powder. It is still used to treat a disease.
For decades (or even hundreds), people have been trying to create a vaccine against malaria. Unfortunately, vaccines still do not have a 100% guarantee against the disease. In July 2015, the Moskirix vaccine was approved in Europe, which was tested on 15,000 children. The effectiveness of this vaccine is up to 40% when administered four times from 0 to 20 months. Vaccine use will begin in 2017.
In October 2015, the Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded to Youyou Tu for discoveries in the field of malaria control. The scientist extracted artemisinin, an extract of the herb Artemisia annua, the use of which significantly reduces the death rate from malaria. It is interesting that she found the recipe of the alchemist Ge Hoon in the book “Prescriptions for emergency care” of 340 AD. He advised to squeeze the juice of the leaves of wormwood in plenty of cold water. Yuyu Tuu achieved stable results in the case of cold extraction.

Ge Hong "Prescriptions for emergency care." 340 year
In 2015, scientists from the University of California created genetically modified mosquitoes that can quickly introduce a malaria-blocking gene into a population of ordinary mosquitoes. In addition, after introducing the gene, the eyes of mosquitoes begin to fluoresce, which increases the chance of their detection in the dark.
Entomologist Bart Nols almost every year comes up with new ways to kill mosquitoes , more and more “innovative”. He simply hates these insects, so he uses human odor simulations to trap, trains dogs to recognize larvae to identify mosquito breeding sites, fills the blood with medicine that kills insects on bites, uses drones and a special fungus.
One of the effective means to combat malaria is an insecticide-impregnated mosquito net. Cheap and angry. Saves lives. Now Bart Nols tests homes that are insect traps themselves.

Lepra, or Hansen's disease, is a chronic granulomatosis: it affects the human skin, peripheral nervous system, eyes, respiratory tract, testicles, hands and feet. The outdated name of this disease is leprosy, it was mentioned in the Bible, it was known in ancient India and was common in Medieval Europe. It is so widespread that at the beginning of the XIII century there were 19 thousand leprosariums in Europe, special houses for lepers.
 In 503, a decree was issued in France obliging all leprosy patients to live in leprosariums. A person with such a diagnosis was taken to the church in a coffin, served as a requiem service, was carried to the cemetery in the same coffin, and there they were lowered into the grave. Then they dumped a few shovels of the earth, saying, "You are not alive, you are dead to all of us . " Then the person was taken to the leprosarium. A person could go for a walk, but only wearing a gray cloak with a hood and a bell around his neck to warn others about the approach of the "dead".
In 503, a decree was issued in France obliging all leprosy patients to live in leprosariums. A person with such a diagnosis was taken to the church in a coffin, served as a requiem service, was carried to the cemetery in the same coffin, and there they were lowered into the grave. Then they dumped a few shovels of the earth, saying, "You are not alive, you are dead to all of us . " Then the person was taken to the leprosarium. A person could go for a walk, but only wearing a gray cloak with a hood and a bell around his neck to warn others about the approach of the "dead".
The disease is associated with the word "hospital". The knights of the Order of St. Lazarus took lepers. And they took care of other patients. Housed the Order on the island of Lazaretto in Italy.
Until the 16th century, there was an epidemic of leprosy in Europe, but the number of patients for unknown reasons decreased. Scientists in 2013 recovered the DNA of bacteria from 1300, removing it from the teeth of people who died at that time in leprosariums. It turned out that for seven hundred years the bacterium has not changed much. This suggests that people simply developed a relative immunity to the disease.
In 1873, a Norwegian physician, Gerhard Hansen, isolated the first bacterium, the causative agent of leprosy, Mycobacterium leprae. In 2008, Mycobacterium lepromatosis was isolated, these bacteria are common in Mexico and the Caribbean. Until recently, it was believed that only people are ill with leprosy. But it turned out that armadillos and proteins can transmit the disease to us. Moreover, the squirrels themselves suffer from leprosy - they develop ulcers and growths on the head and paws. Sick animals were discovered in the UK in 2016.

Lazaretto Island
The incubation period of the disease can last 5 years, and the symptoms in a person can appear only 20 years after infection. Doctors distinguish three types of the course of the disease: lepromatous, tuberculoid and borderline.
When lepromatous on the skin appear bumps or nodes in the size of a pea, which can merge into the formation of large sizes. Then on these bumps open ulcers filled with a large number of bacteria that cause the disease. These ulcers ultimately affect not only the skin, but reach the joints and bones of the person, after which the limbs can be amputated.
The tuberculoid type is characterized by lesions of the skin and the peripheral nervous system only. Disturbed perception of temperature, touch.
An unidentifiable type of leprosy can go to any of the previous types. If it is possible damage to the nervous system, deformation of the feet and hands.
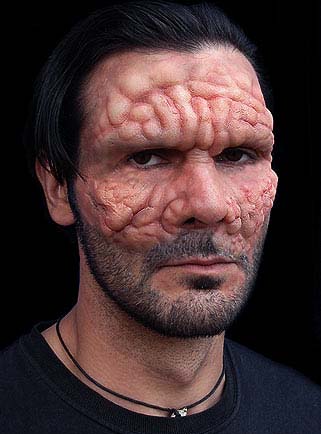
The appearance of a patient with leprosy. A source
Lepra is transmitted through drops from the nose and mouth with frequent contact with people who do not receive treatment. In other words, the shouts of “unclean, unclean” and the bell on the neck of the patients were too powerful a means of prevention. Today it is known that leprosy is not transmitted when touched to a person and does not always lead to death. Previously, it was incurable and really led to imminent disability. The point is in the means and methods: bloodletting against leprosy is not the best method of treatment, as well as cleansing the stomach.
A person may not get sick at all even if he is in too close contact with infected flesh. Norwegian physician Daniel Cornelius Danielelsen experimented on himself: he injected the patient's blood with leprosy, rubbed the pus of patients in the scratches on his skin, injected under his skin pieces of leprous tubercle from the patient. But he never got sick. Now scientists have suggested that the disease also depends on the DNA of a particular person.
A breakthrough in treatment occurred in the 1940s when dapson was developed. The drug has an antibacterial effect not only against Mycobacterium leprae, but also kills Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The disease is closely related to social status. For 2000, the World Health Organization named 91 countries with endemic leprosy foci. In 70% of cases, leprosy occurs in India, Burma and Nepal. In the risk group, those people who have weakened immunity, who drink polluted water, eat little and live below the poverty line.
The number of patients has decreased over time, although this figure is not always decreasing on a year scale. In 1999, 640,000 new cases of infection were recorded worldwide, in 2000 - 738,000, and in 2001 - 775,000. But in 2015, several times fewer people got sick - 211 thousand.
In Russia in 2007 there were 600 patients with leprosy, of which only 35% were hospitalized, while the rest were on outpatient treatment and under observation. In the USSR, there were 16 leprosariums, and four of them remained in Russia. Patients can go to their relatives, but remain under observation. In the Terek leper colony in the Stavropol region, some patients live for about 70 years . And they die not from the disease itself, but from old age.
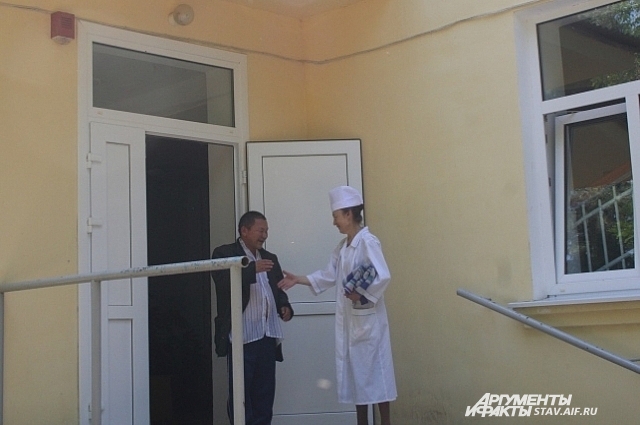

Communication between the patient and the doctor in the Terek leprosarium. No masks and gloves
As the World Health Organization notes, over 20 years, more than 16 million patients with leprosy have been cured. This disease has been defeated almost all over the world. Fortunately, the causative bacterium has hardly changed, and it does not have drug resistance. The most important thing is to diagnose the disease as early as possible and begin its treatment. People with weak immunity and poor living conditions are still at risk.
In the case of malaria, things are not so rosy. In some countries, it poses a serious threat to people's lives. A cure is more likely when a disease is detected within 24 hours. If you do not get into this period of time - the outcome can be the death of the patient. The fight against the disease is complicated by the fact that there is still no vaccine with a high percentage of efficacy. Therefore, the best option is not to give the anopheles mosquitoes to bite people. For example, using a mosquito net or some other insect trap.

Leprechaun on the image from the manuscript of the XIV century
Malaria
Malaria, or, as it used to be called, “swamp fever,” is caused by unicellular parasites of the genus Plasmodium, which are transmitted to humans through the bite of anopic mosquitoes. Perhaps mankind has known this disease for more than fifty thousand years. Plasmodium could previously be the simplest, capable of photosynthesis, but then adapted to life in the intestines of aquatic invertebrates and became a parasite. And he moved to live in the larvae of the first blood-sucking insects.
According to the latest data, twenty million years ago, Plasmodium used mosquitoes to infect victims. Analysis of the plasmodium controversy allowed scientists to suggest that cold-blooded creatures could also be sick with malaria. For example, dinosaurs. Later, with the advent of man, the parasites adapted to him and began to use us to spread among bloodsucking insects.
')
Malaria was first described around 2700 BC in the Chinese Chronicle. But the first epidemic could have happened much earlier, from 8 to 15 thousand years ago, malaria could cause a sharp reduction in the number of people on Earth.
Doctors have learned that unicellular organisms cause malaria in the 1880s. French doctor Churl Louis Alphonse Laveran discovered a parasite in the patient’s blood, for which he won the Nobel Prize. In 1894, for the first time, it was suggested that mosquitoes transmit malaria. This method was confirmed by Giovanni Battista Grassi with the help of volunteers. Another method of transmission is now known: from person to person through the blood. Malaria can cause a baby in the womb.
There are different types of plasmodia. A person may suffer from five of them. Infection occurs when a mosquito injects parasites at one of their developmental stages into human blood. From the blood they enter the liver, where they begin to multiply. After a few weeks or months, the disease begins to manifest itself because the plasmodia re-enters the circulatory system. The incubation period depends on the type of plasmodia.
The patient begins to hurt the joints, fever and chills, cramps. A person becomes a lure for mosquitoes - begins to smell delicious to them. It is necessary that the Plasmodia again fall to their beloved master, since for them man is only a means of propagation.
Not so long ago, namely in the 1980s, scientists discovered another stage in the existence of the parasite — the resting one. Because of this stage, people became ill with malaria even years after their blood was completely purified from plasmodia.
Children and people with HIV / AIDS are most at risk. The disease for them can be fatal.

Tanzania, child vaccination against malaria. A source
Malaria seems to be some kind of distant African disease. Malaria mosquitoes themselves live in almost all climatic zones. But for the risk of infection you need a large number of these insects and their rapid reproduction. Malaria used to be called “swamp fever” precisely because it is common in places where there are no low temperatures, there are swamps and a lot of precipitation falls. The risk of infection is highest in the equatorial and subequatorial zones. In Russia, such mosquitoes exist throughout the European part of the country.
Malaria in Russia and the USSR was widespread until the 1950s. In order to cope with this disease in the resort area, swamps were drained in Sochi, as well as oil reservoirs: they were covered with a layer of oil in order to exterminate the mosquito larvae.
The largest number of cases in the history of the USSR was recorded in the years 1934-1935 - then 9 million people became infected. In 1962, malaria was won in the USSR. Isolated cases of infection were possible after that. During the war in Afghanistan in 1986-1990, the USSR recorded an increase in the number of infected - 1314 cases.
Malaria covers 97 countries. Although nearly half of the world's population was at risk of having malaria in 2015 — 3.2 billion people — most of the cases are in sub-Saharan Africa. It is there that 88% of cases of illness and 90% of deaths from malaria occur.
In 2015, 214 million people became infected with malaria, and 438 thousand of them died. Bill Gates and the British Chancellor George Osborne in January 2016 promised to give 4.3 billion dollars to fight the disease. This money is planned to spend on the study of the disease and the search for drugs .

Mark of the USSR, 1962
Hundreds of years ago, American Indians used cinchona bark as a febrifuge. Spanish naturalist Bernab Cobo brought it to Europe in 1632. After curing the wife of the Viceroy of Peru from malaria, they learned about the wonderful properties of the medicine throughout the country, then the bark was transported to Spain and Italy, and it began to be used throughout Europe. It took almost two hundred years to extract quinine directly from the cortex, which was used as a powder. It is still used to treat a disease.
For decades (or even hundreds), people have been trying to create a vaccine against malaria. Unfortunately, vaccines still do not have a 100% guarantee against the disease. In July 2015, the Moskirix vaccine was approved in Europe, which was tested on 15,000 children. The effectiveness of this vaccine is up to 40% when administered four times from 0 to 20 months. Vaccine use will begin in 2017.
In October 2015, the Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded to Youyou Tu for discoveries in the field of malaria control. The scientist extracted artemisinin, an extract of the herb Artemisia annua, the use of which significantly reduces the death rate from malaria. It is interesting that she found the recipe of the alchemist Ge Hoon in the book “Prescriptions for emergency care” of 340 AD. He advised to squeeze the juice of the leaves of wormwood in plenty of cold water. Yuyu Tuu achieved stable results in the case of cold extraction.

Ge Hong "Prescriptions for emergency care." 340 year
In 2015, scientists from the University of California created genetically modified mosquitoes that can quickly introduce a malaria-blocking gene into a population of ordinary mosquitoes. In addition, after introducing the gene, the eyes of mosquitoes begin to fluoresce, which increases the chance of their detection in the dark.
Entomologist Bart Nols almost every year comes up with new ways to kill mosquitoes , more and more “innovative”. He simply hates these insects, so he uses human odor simulations to trap, trains dogs to recognize larvae to identify mosquito breeding sites, fills the blood with medicine that kills insects on bites, uses drones and a special fungus.
One of the effective means to combat malaria is an insecticide-impregnated mosquito net. Cheap and angry. Saves lives. Now Bart Nols tests homes that are insect traps themselves.

Leprosy
Lepra, or Hansen's disease, is a chronic granulomatosis: it affects the human skin, peripheral nervous system, eyes, respiratory tract, testicles, hands and feet. The outdated name of this disease is leprosy, it was mentioned in the Bible, it was known in ancient India and was common in Medieval Europe. It is so widespread that at the beginning of the XIII century there were 19 thousand leprosariums in Europe, special houses for lepers.
 In 503, a decree was issued in France obliging all leprosy patients to live in leprosariums. A person with such a diagnosis was taken to the church in a coffin, served as a requiem service, was carried to the cemetery in the same coffin, and there they were lowered into the grave. Then they dumped a few shovels of the earth, saying, "You are not alive, you are dead to all of us . " Then the person was taken to the leprosarium. A person could go for a walk, but only wearing a gray cloak with a hood and a bell around his neck to warn others about the approach of the "dead".
In 503, a decree was issued in France obliging all leprosy patients to live in leprosariums. A person with such a diagnosis was taken to the church in a coffin, served as a requiem service, was carried to the cemetery in the same coffin, and there they were lowered into the grave. Then they dumped a few shovels of the earth, saying, "You are not alive, you are dead to all of us . " Then the person was taken to the leprosarium. A person could go for a walk, but only wearing a gray cloak with a hood and a bell around his neck to warn others about the approach of the "dead".The disease is associated with the word "hospital". The knights of the Order of St. Lazarus took lepers. And they took care of other patients. Housed the Order on the island of Lazaretto in Italy.
Until the 16th century, there was an epidemic of leprosy in Europe, but the number of patients for unknown reasons decreased. Scientists in 2013 recovered the DNA of bacteria from 1300, removing it from the teeth of people who died at that time in leprosariums. It turned out that for seven hundred years the bacterium has not changed much. This suggests that people simply developed a relative immunity to the disease.
In 1873, a Norwegian physician, Gerhard Hansen, isolated the first bacterium, the causative agent of leprosy, Mycobacterium leprae. In 2008, Mycobacterium lepromatosis was isolated, these bacteria are common in Mexico and the Caribbean. Until recently, it was believed that only people are ill with leprosy. But it turned out that armadillos and proteins can transmit the disease to us. Moreover, the squirrels themselves suffer from leprosy - they develop ulcers and growths on the head and paws. Sick animals were discovered in the UK in 2016.

Lazaretto Island
The incubation period of the disease can last 5 years, and the symptoms in a person can appear only 20 years after infection. Doctors distinguish three types of the course of the disease: lepromatous, tuberculoid and borderline.
When lepromatous on the skin appear bumps or nodes in the size of a pea, which can merge into the formation of large sizes. Then on these bumps open ulcers filled with a large number of bacteria that cause the disease. These ulcers ultimately affect not only the skin, but reach the joints and bones of the person, after which the limbs can be amputated.
The tuberculoid type is characterized by lesions of the skin and the peripheral nervous system only. Disturbed perception of temperature, touch.
An unidentifiable type of leprosy can go to any of the previous types. If it is possible damage to the nervous system, deformation of the feet and hands.

The appearance of a patient with leprosy. A source
Lepra is transmitted through drops from the nose and mouth with frequent contact with people who do not receive treatment. In other words, the shouts of “unclean, unclean” and the bell on the neck of the patients were too powerful a means of prevention. Today it is known that leprosy is not transmitted when touched to a person and does not always lead to death. Previously, it was incurable and really led to imminent disability. The point is in the means and methods: bloodletting against leprosy is not the best method of treatment, as well as cleansing the stomach.
A person may not get sick at all even if he is in too close contact with infected flesh. Norwegian physician Daniel Cornelius Danielelsen experimented on himself: he injected the patient's blood with leprosy, rubbed the pus of patients in the scratches on his skin, injected under his skin pieces of leprous tubercle from the patient. But he never got sick. Now scientists have suggested that the disease also depends on the DNA of a particular person.
A breakthrough in treatment occurred in the 1940s when dapson was developed. The drug has an antibacterial effect not only against Mycobacterium leprae, but also kills Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The disease is closely related to social status. For 2000, the World Health Organization named 91 countries with endemic leprosy foci. In 70% of cases, leprosy occurs in India, Burma and Nepal. In the risk group, those people who have weakened immunity, who drink polluted water, eat little and live below the poverty line.
The number of patients has decreased over time, although this figure is not always decreasing on a year scale. In 1999, 640,000 new cases of infection were recorded worldwide, in 2000 - 738,000, and in 2001 - 775,000. But in 2015, several times fewer people got sick - 211 thousand.
In Russia in 2007 there were 600 patients with leprosy, of which only 35% were hospitalized, while the rest were on outpatient treatment and under observation. In the USSR, there were 16 leprosariums, and four of them remained in Russia. Patients can go to their relatives, but remain under observation. In the Terek leper colony in the Stavropol region, some patients live for about 70 years . And they die not from the disease itself, but from old age.

Communication between the patient and the doctor in the Terek leprosarium. No masks and gloves
As the World Health Organization notes, over 20 years, more than 16 million patients with leprosy have been cured. This disease has been defeated almost all over the world. Fortunately, the causative bacterium has hardly changed, and it does not have drug resistance. The most important thing is to diagnose the disease as early as possible and begin its treatment. People with weak immunity and poor living conditions are still at risk.
In the case of malaria, things are not so rosy. In some countries, it poses a serious threat to people's lives. A cure is more likely when a disease is detected within 24 hours. If you do not get into this period of time - the outcome can be the death of the patient. The fight against the disease is complicated by the fact that there is still no vaccine with a high percentage of efficacy. Therefore, the best option is not to give the anopheles mosquitoes to bite people. For example, using a mosquito net or some other insect trap.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/369929/
All Articles