Neural network Google Translate has made a single database of meanings of human words
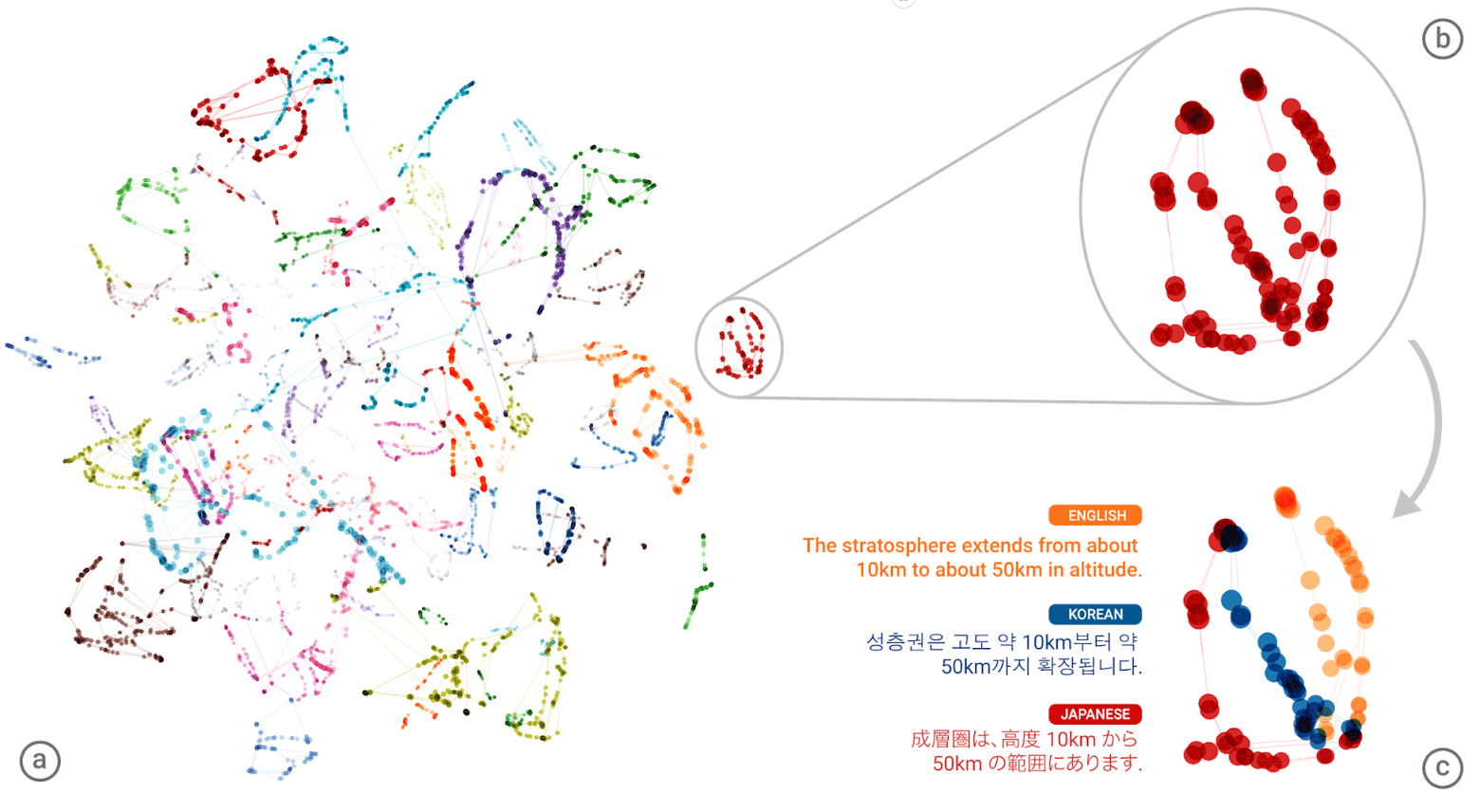
The “universal language” of the Google Neural Machine Translation Neural Network (GNMT). In the left illustration, different colors show clusters of the meanings of each word, on the lower right - the meanings of the word obtained for it from different human languages: English, Korean and Japanese.
Over the past ten years, Google Translate has grown from several languages to 103, and now it translates 140 billion words a day. In September, it was reported that the developers decided to fully translate the Google Translate service into in-depth training. There are many advantages to this approach. Translation is getting much better. Moreover, the system can translate texts into languages for which I have never seen translations, that is, I did not study specifically for this language pair.
The Google neural network for machine translation is called Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT) . From the very beginning to the end, the translation of the text now fully performs the neural network. Traditionally, AI has been used on Google Translate in limited mode, for some supporting tasks. For example, to compare texts available in several languages, such as official documents of the United Nations or the European Parliament. In this mode, the translation of each word in the texts was compared.
NMTS neural network works on a fundamentally new level. It not only analyzes the existing translation options in the learning process, but also performs intellectual analysis of the sentences, breaking them up into “vocabulary segments”. In a certain representation within the network, these “vocabulary segments” correspond to the meanings of words .
')
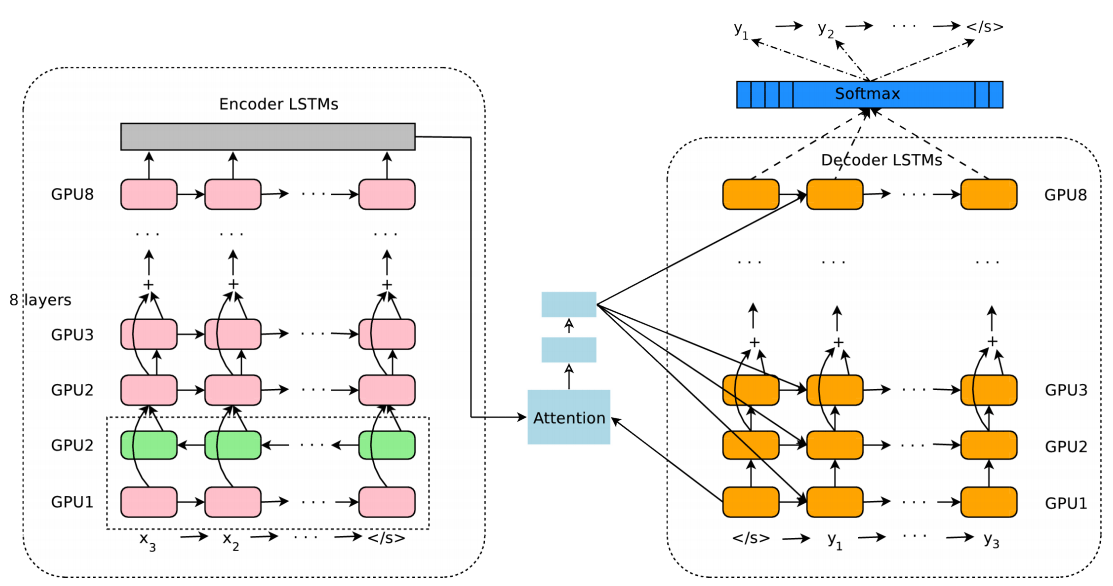
GNMT (Google's Neural Machine Translation) architecture model. Encoder network on the left, decoder on the right, attention module in the middle. The bottom layer of the encoder is two-sided: the pink modules collect information from left to right, and the green ones - in the opposite direction
This internal representation within the network is in some way the universal language of humanity. Unfortunately, people will not be able to speak this universal language. It is a machine code with which work is performed at the internal intermediate level of the neural network. It is an intermediary machine language between any language pairs of all human languages supported by the system. Nevertheless, the existence of such a universal base of meanings, which unites all the languages of the world, will impress any linguist. Generally speaking, the development of such a base with all the connotations , a thorough description of all possible meanings of each word, is like a Grail in linguistics. We dreamed about it for decades. Thanks to Google's neural network, this dream is gradually being realized. The neural network already has a de facto base of meaning inside the “black box”, with an indication of the possible meanings of each word. The only problem is that so far only she herself can work with this base, this neural network. For human understanding the base of meanings in machine codes is inaccessible just like that, it requires special processing.
New GNMT universal architecture that translates any language pairs.
What is most interesting, thanks to the universal base of meanings of all human words, the neural network of translation can work even for those language pairs on which it was not trained. Take an example on animation. The system is trained for language pairs "Japanese-English" and "Korean-English." After that, the neural network will also be able to translate the Japanese-Korean language pair through a universal base of meanings, although it did not train on it.
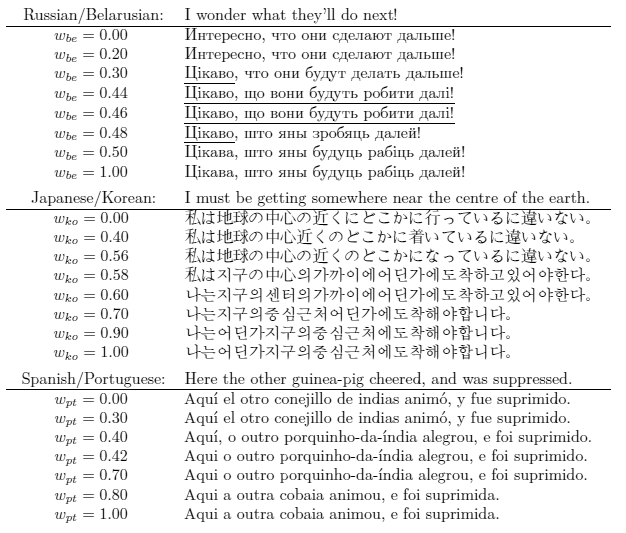
Some examples of mixing target languages in a multilingual model.
The journalists immediately seized upon this topic and called the service system with the base of meanings “the new universal language of mankind”. For example, the well-known Russian marketer Andrei Sebrant writes : “The representation of meanings in a universal form, not tied to a specific existing language, is, in fact, the creation of a new universal language. That's just not the fact that accessible to man. "
Indeed, the “new universal language” - it sounds very beautiful and mysterious. Although in reality it is just a single multidimensional space, compiled using the t-SNE technique , that is, using a non-linear dimension reduction and visualization of multidimensional variables (t-distributed stochastic and neighbor embedding).
Visualization of multidimensional data space in a neural network
If we talk about the practical use of the neural network, then independent experts admit that Google’s development shows a “stunning” result and clearly demonstrates that neural translation with the help of AI can far surpass the classical methods of machine translation in quality. Google's neural network clearly improves translation quality in many ways.
The authors of the new scientific work add that the universal architecture, which translates any language pairs, in reality shows a higher efficiency than the neural network, trained in only one language pair. For some reason, knowledge of foreign languages helps neural networks to better translate from this particular language.
At the intuitive level, this effect is clear: a person also begins to better understand a foreign language, if he knows other languages of the same group. In this way, he expands the space of meanings in his brain. He is aware of the meanings with which not a single word in his native language corresponds.
The new method of universal translation, called the developers "Zero-Shot Translation", does not require any changes in the architecture of the neural network Google Neural Machine Translation.
The scientific work describing the Neural Machine Translation System multilingual machine translation system based on the neural network authorship by Melvin Johnson, Maxim Krikun and other Google employees was published on November 14, 2016 in open access.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/369913/
All Articles