Scanning the physical structure of the brain establishes a person’s identity with accuracy close to 100%
 Researchers have received "prints" of the white matter of the human brain. Using the diffusion MRI method, they modeled the most detailed map of neural connections ever created. Scientists have confirmed: structural compounds in the brain are unique to each individual. The study revealed that the structure of the nervous system can identify a person with an accuracy close to 100%
Researchers have received "prints" of the white matter of the human brain. Using the diffusion MRI method, they modeled the most detailed map of neural connections ever created. Scientists have confirmed: structural compounds in the brain are unique to each individual. The study revealed that the structure of the nervous system can identify a person with an accuracy close to 100% A team of scientists led by Timothy Verstinen, an associate professor at the Department of Psychology at Carnegie Mellon University, studied 699 neural-connection maps — a connection . Connectomes show detailed connections in a region of the central nervous system consisting of axons. All axons in this area are covered with a white shell, so it is called white matter .
The architecture of the white matter is an individual thing, so it is suitable for determining the differences between the “imprints” of the brain. The structure of neural connections is partially determined by genetic factors, but most of it changes under the influence of time.
')
Specific features of the brain that help identify a person are encoded by a unique pattern of connections between neurons. To compare two connections of different people and to express this difference by some quantitative indicator is a rather difficult task. Analysis requires an accurate map of the white matter architecture. In order to build the most detailed map of neural connections, in their research, scientists used diffusion MRI data. It measures the diffusion of water molecules along the white matter fibers in the brain. This method gives scientists the opportunity to trace the directions of axons and determine the structure of the neural connection from one site to another, but it is not accurate enough. Therefore, researchers abandoned it in favor of a local connectome.
Local connection is the degree of connectivity between adjacent elements in white matter beams. It is measured by the water diffusion tensor. If you combine these measurements, you get a vector that describes the set of features that corresponds to the connection of a particular person.

The uniqueness of the structure of the local connection: A - the distribution function of the spins, showing the diffusion of the liquid; B - demonstration of the differences of each object with the help of fractional anisotropy; C - definition of uniqueness using diffusion coefficient.
Scientists were able to evaluate the effectiveness of the approach with the help of four sets of data of repeated scans, which they received at different time intervals. This is the main feature of the study - scientists analyzed the information already collected once. Then they figured out whether it was possible to determine if a connection was human. To do this, they compared the information with fingerprints. Subsequent analysis showed that a local connectom can determine the quantitative similarity between genetically related people.
Measurements have shown that each person’s connection is unique, as are fingerprints. Such a detailed map can be used for personal identification along with fingerprinting, and 17 thousand identification tests have confirmed this assumption. With almost 100% accuracy, they could determine whether two connectoms belong to the same person or not. The probability of an error of this technology is a thousand times less than that of dactyloscopy. But even this method does not give a full guarantee.
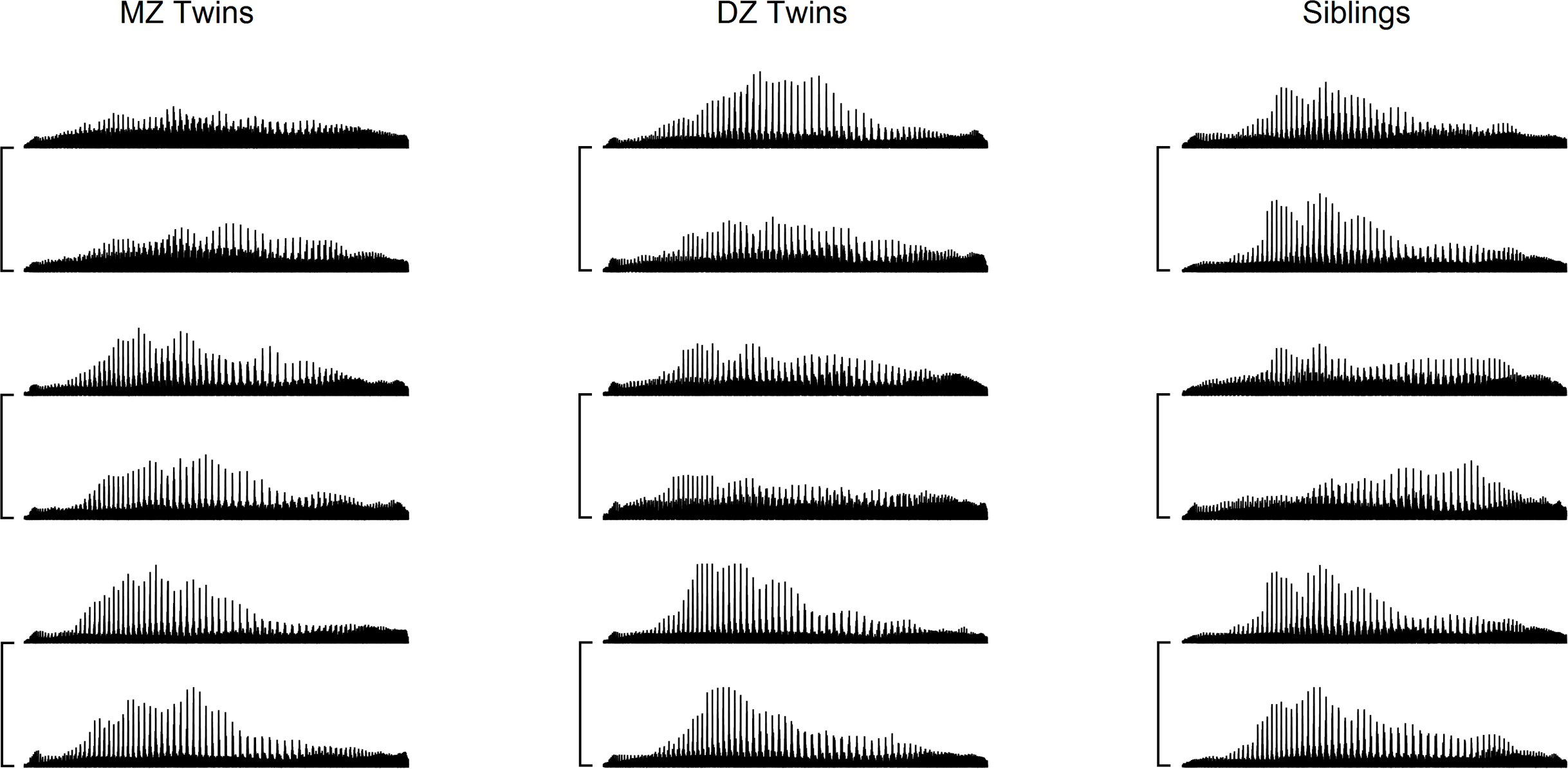
Connectomas of homozygous (MZ), heterozygous (DZ) twins and siblings (Siblings)
Connect can be used as a marker of human phenotype. Scientists have found that homozygous twins match 12.51% of structural bonds. In heterozygous, the total part is even smaller, only 5.4%. For brothers and sisters who were born alternately, the similarity is 4.51%. Over time, this proportion decreases by an average of 12.79% every 100 days.

Similarities and differences between twins and siblings
“The most exciting part of this study is that now we can apply the new method to the data that were collected earlier and reveal new information that nobody has interpreted before. The higher accuracy of this method allows us to reliably determine how inherited factors and environmental features affect the human brain over time. In this way, we can better understand the functions and dysfunctions of the brain, ”notes Fan-Chen Ye, an assistant professor of neurological surgery at the University of Pittsburgh and one of the authors of the study.
In this way, we can see how events that unite people affect the work of the brain. The diffusion MRI method provides researchers with useful biomarkers. They will help determine how diseases, the environment, hereditary and social factors affect the brain and its changes over time. This means that all life shocks somehow affect the connections of the human brain. The uniqueness of the “fingerprints” of the brain is comparable to the fingerprints and it is possible that someday the neuron map will complement or completely replace fingerprinting.
Recently, scientists are increasingly using MRI data in various fields. In their work, scientists from the University of Pennsylvania compared the accuracy of the fMRI and polygraph in determining lies. It turned out that even neurologists with no experience in lie detection have a 24% higher chance of detecting deception than professional polygraph examiners. In the spring, a group of neuroscientists from the University of California at Berkeley created a “semantic atlas” of the cerebral cortex. It shows which areas of the brain are responsible for processing words related to numbers, visual images, geographic objects, emotions and other factors. In addition, according to the atlas, you can approximately understand what a person is reading and what he is thinking about.
Scientific work published in the journal PLoS Computational Biology November 15, 2016
DOI: 10.1371 / journal.pcbi.1005203
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/369899/
All Articles