NASA approved new Mars InSight launch date
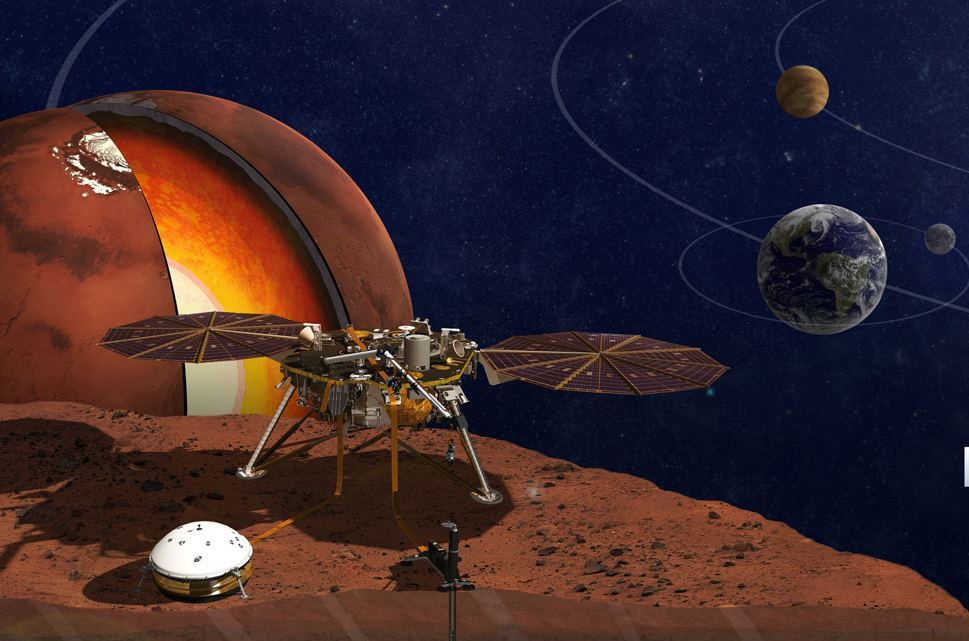
Mars Insight (source: NASA)
In early September, NASA announced the approval of the launch date of the Mars InSight spacecraft to Mars. The full name of the mission is The Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) . Initially, the launch was scheduled for March of this year. But due to technical problems with the main scientific instrument of the SEIS apparatus, the launch date had to be postponed. The agency plans to send InSight to the red planet on May 5, 2018. If everything goes as planned, the system will fall to the surface of Mars on November 26, 2018.
"Our robotic probes, such as InSight, pave the way to the red planet for humans," said Geoff Yoder, a NASA administration spokesman. According to the NASA plan, the device must work on Mars for at least 720 days. The basis for InSight served as the construction of the landing probe Phoenix , which had previously worked on the red planet.
NASA previously submitted several scientific targets for InSight:
')
1. Study of the geological evolution of Mars. The red planet belongs to the terrestrial planets of the solar system. The apparatus will study the internal structure and processes that occur in the thickness of the Martian soil;
1.2 Insight will determine the size, composition and state of aggregation of the planet’s core;
1.3 Also, the device will be able to obtain data on the thickness and structure of the crust of Mars;
1.4 Mars Insight will determine the composition and structure of the mantle;
1.5 All these data, in turn, allow us to determine the temperature of the inner layers of Mars.
2. Determination of the level of tectonic activity and frequency of meteorites falling on the surface of the red planet.
“We believe that the new mission, which will start in 2018, will allow to fulfill all the goals,” said Jim Green, director of NASA's planetary sciences department.
The device will receive energy from solar panels, as well as a number of other Martian vehicles. The device will not be able to move on the surface of Mars, it is a fixed system equipped with a drill with a depth of 6 m. InSight is equipped with the following tools:
- Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS). This is a seismometer that is planned to be used to accurately measure the tectonic activity of the red planet. As mentioned above, the problems with this tool influenced the postponement of the launch of the device. The instrument was developed by the French National Space Research Center with the participation of a number of scientific organizations in this country. Its cost is $ 42 million. The fact that the tool is still unsuitable for use (depressurization has occurred) became known in early December of last year. At the same time, representatives of NASA announced that the launch date of the probe was postponed for two years;
- Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3) - this tool is designed to measure the heat flux over the surface of Mars. During the study, the tool must drill a well down to 6 meters deep. If this task is completed, InSight will set an absolute record in the depth of drilling of the surface of an extraterrestrial object. A well is needed to determine the amount of heat emanating from the inner layers of Mars. The tool was developed by the Germans;
- Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment (RISE) is a highly accurate tool for conducting an experiment to accurately measure the oscillations of Mars under the influence of the Sun. The obtained data, according to scientists, will allow to determine the internal structure of Mars. Developed the instrument NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory;
- A camera that is installed on a robotic manipulator system. It will be used for black-and-white shooting of instruments onboard the apparatus with the creation of three-dimensional images of the surface. The obtained data will help determine the optimal location for installing a SEIS seismometer and a heat flow probe. As in the case of Curiosity, this camera will help to create panoramic images of the Red Planet;
- A second camera mounted on the bottom of Mars Insight. It will provide additional control over the work of the scientific instruments of the probe.
The project budget initially was $ 675 million. But solving technical problems with the scientific instrument Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) and postponing the start date led to an increase in the budget by $ 153.8 million. NASA representatives say that the budget increase did not negatively affect missions
“The approval of the launch date of the Insight probe to Mars is great news for us, and a unique opportunity to get more information about the structural features of the inner layers of Mars. This is one of the main tasks for planetary science, ”said Jean-Yves Le Gall, President of the French National Space Research Center (CNES).
Now scientists need to have time to correct problems with the device, so that it is suitable for the mission. If the specialists do not have time, then the launch date will have to be postponed again or it will be canceled. The fact is that the amount of fuel in a launch vehicle cannot be more than a certain amount. The launch window is open from the 5th to the 30th of May, 2018. After this period, Mars and Earth will diverge by a distance that cannot be covered with the current fuel supply using the trajectory calculated for launch during the May window.
Besides the Mars Insight probe, NASA is currently developing a solar-powered helicopter drone. Drone will help to study the features of a number of regions of the Red Planet. The agency has already created a full-scale drone model and is testing it.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/369639/
All Articles