Artificial Intelligence helps diagnose cancer
Scientists from the University of California, Los Angeles have developed a method for non-invasive study of blood samples and cancer diagnostics
In order to determine the presence of special cells, markers of cancer, it is necessary to conduct complex analyzes. Quite often, physicians use chemical preparations that make cancer cells clearly visible. This is a good method, but such a sample can be used only once, after which it becomes impossible to study.
')
There are other technologies, among which stands out the method of analyzing the structure of the cells of tissues. Usually, the structure of cancer cells is different from the structure of normal, healthy cells, and therefore it becomes possible to diagnose cancer. But it takes a lot of time to prepare the cells, plus the method itself cannot be called sufficiently accurate. And what if you use the capabilities of artificial intelligence to diagnose cancer? That is what scientists from the University of California, Los Angeles decided to do.
Experts have decided that the cognitive system will be able to determine the presence or absence of cancer cells faster than a person, and this will be done with higher accuracy. The results of the work are published in the authoritative edition - the journal Scientific Reports .
The method developed by scientists has two significant differences from the methods that are used everywhere. The first is the use of a new type of photon microscope. The second is the work with artificial intelligence, which analyzes the entire received data array.
As for the microscope, nanosecond laser pulses are used to capture images of hundreds of thousands of blood cells per second. Conventional technology does not allow to analyze more than 2000 cells per second using a flow cytometer and standard digital cameras. With a more dense stream of cells, the images are blurry, the study of such images is impossible. Specialists from the University of California developed a technology for non-invasive image acquisition using an ADC (analog-to-digital converter). Laser pulses illuminate individual cells, the image of which is quite clear, without "blurring." At the same time, as mentioned above, hundreds of thousands of cells per second are analyzed.
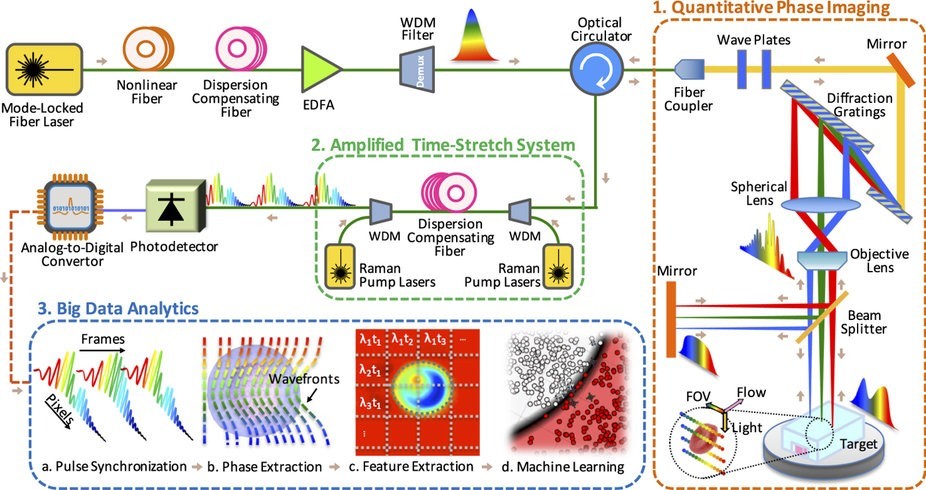
Scheme blood test developed by scientists
The resulting images are then “fed” to a specially created software - an algorithm that analyzes data on 16 different criteria: assessment of diameter, degree of absorption of radiation, roundness and other parameters of cells. In order to detect cancer cells, on average it is necessary to analyze about 100 thousand normal cells. With the standard technique, this takes quite a lot of time (recall that the bandwidth of the standard technique is 2 thousand cells per second, plus people work with the footage). The technology developed in the USA allows analyzing hundreds of thousands of cells per second. Accordingly, the diagnostic accuracy is higher, and the time required for diagnostics is lower than usual.
Initially, experts trained the software created to recognize exactly cancer cells. After conducting trial tests, it turned out that the accuracy of diagnosis using a photon microscope and artificial intelligence is 17% higher than the accuracy of all other methods of analysis.
It is worth noting that cognitive systems have been used for quite some time to fight cancer. For example, IBM Watson helps doctors through the Watson for Oncology program. At the same time, the active block of the system no longer occupies the whole room, the block size is now equal to about three pizza boxes stacked on top of each other. Watson asks questions and makes assumptions using data from recent medical research in the field of oncology, plus information from the patient's medical record and current symptoms are used. As a result, each patient receives an individual approach - after all, the same disease, even the simplest and innocuous, occurs in different people in different ways. What to say about such a complex problem as cancer.
The system is able to analyze huge data arrays (and this is unstructured data), “lay out in folders” and make objective conclusions. In this case, Watson is studying the latest data on a particular disease or group of diseases. An ordinary doctor simply can not study all the necessary information. At best, we are talking about several thematic articles on the results of research. IBM Watson can structure huge amounts of data in seconds, while studying the results of research on a specific topic over the past couple of years.
Already, a number of medical centers and hospitals are participating in the Watson for Oncology project. This, for example, the International Hospital Bumrungrad (Thailand), the New York Center for Human Genome Research and other organizations.
Experts believe that in the near future, cognitive systems will help humanity to more effectively deal with various diseases (not only cancerous). IBM Watson, as mentioned above, is able to effectively analyze huge amounts of information, identifying not too clear links between individual elements. This allows you to study the characteristics of the body of each patient with the further implementation of individual treatment, which greatly increases the likelihood of successful recovery.

In order to determine the presence of special cells, markers of cancer, it is necessary to conduct complex analyzes. Quite often, physicians use chemical preparations that make cancer cells clearly visible. This is a good method, but such a sample can be used only once, after which it becomes impossible to study.
')
There are other technologies, among which stands out the method of analyzing the structure of the cells of tissues. Usually, the structure of cancer cells is different from the structure of normal, healthy cells, and therefore it becomes possible to diagnose cancer. But it takes a lot of time to prepare the cells, plus the method itself cannot be called sufficiently accurate. And what if you use the capabilities of artificial intelligence to diagnose cancer? That is what scientists from the University of California, Los Angeles decided to do.
Experts have decided that the cognitive system will be able to determine the presence or absence of cancer cells faster than a person, and this will be done with higher accuracy. The results of the work are published in the authoritative edition - the journal Scientific Reports .
The method developed by scientists has two significant differences from the methods that are used everywhere. The first is the use of a new type of photon microscope. The second is the work with artificial intelligence, which analyzes the entire received data array.
As for the microscope, nanosecond laser pulses are used to capture images of hundreds of thousands of blood cells per second. Conventional technology does not allow to analyze more than 2000 cells per second using a flow cytometer and standard digital cameras. With a more dense stream of cells, the images are blurry, the study of such images is impossible. Specialists from the University of California developed a technology for non-invasive image acquisition using an ADC (analog-to-digital converter). Laser pulses illuminate individual cells, the image of which is quite clear, without "blurring." At the same time, as mentioned above, hundreds of thousands of cells per second are analyzed.

Scheme blood test developed by scientists
The resulting images are then “fed” to a specially created software - an algorithm that analyzes data on 16 different criteria: assessment of diameter, degree of absorption of radiation, roundness and other parameters of cells. In order to detect cancer cells, on average it is necessary to analyze about 100 thousand normal cells. With the standard technique, this takes quite a lot of time (recall that the bandwidth of the standard technique is 2 thousand cells per second, plus people work with the footage). The technology developed in the USA allows analyzing hundreds of thousands of cells per second. Accordingly, the diagnostic accuracy is higher, and the time required for diagnostics is lower than usual.
Initially, experts trained the software created to recognize exactly cancer cells. After conducting trial tests, it turned out that the accuracy of diagnosis using a photon microscope and artificial intelligence is 17% higher than the accuracy of all other methods of analysis.
It is worth noting that cognitive systems have been used for quite some time to fight cancer. For example, IBM Watson helps doctors through the Watson for Oncology program. At the same time, the active block of the system no longer occupies the whole room, the block size is now equal to about three pizza boxes stacked on top of each other. Watson asks questions and makes assumptions using data from recent medical research in the field of oncology, plus information from the patient's medical record and current symptoms are used. As a result, each patient receives an individual approach - after all, the same disease, even the simplest and innocuous, occurs in different people in different ways. What to say about such a complex problem as cancer.
The system is able to analyze huge data arrays (and this is unstructured data), “lay out in folders” and make objective conclusions. In this case, Watson is studying the latest data on a particular disease or group of diseases. An ordinary doctor simply can not study all the necessary information. At best, we are talking about several thematic articles on the results of research. IBM Watson can structure huge amounts of data in seconds, while studying the results of research on a specific topic over the past couple of years.
Already, a number of medical centers and hospitals are participating in the Watson for Oncology project. This, for example, the International Hospital Bumrungrad (Thailand), the New York Center for Human Genome Research and other organizations.
Experts believe that in the near future, cognitive systems will help humanity to more effectively deal with various diseases (not only cancerous). IBM Watson, as mentioned above, is able to effectively analyze huge amounts of information, identifying not too clear links between individual elements. This allows you to study the characteristics of the body of each patient with the further implementation of individual treatment, which greatly increases the likelihood of successful recovery.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/368911/
All Articles