Mars One fights against criticism and asks for $ 15 million
 In August, the head of Mars One, Bass Lansdorp, discussed with two MIT aerospace engineers the question of how feasible the company's task is. By the end of the dispute, it became clear that Mars One does not have a clear definition of its plans and the concept of "plan" in general. These dates, which have already been shifted twice, are perceived rather as dreams or a source of inspiration. At the moment, Mars One is trying to find funds for additional research and recruitment. The requested amount is 15 million dollars.
In August, the head of Mars One, Bass Lansdorp, discussed with two MIT aerospace engineers the question of how feasible the company's task is. By the end of the dispute, it became clear that Mars One does not have a clear definition of its plans and the concept of "plan" in general. These dates, which have already been shifted twice, are perceived rather as dreams or a source of inspiration. At the moment, Mars One is trying to find funds for additional research and recruitment. The requested amount is 15 million dollars.Mars One is a company that received widespread media attention in 2012 with its ambitious plan to conquer the red planet. This is not just the landing of a small probe or Mars rover on Mars, it is not even the landing of a person, it is the creation of a permanent settlement. It was proposed to create a colony on the basis of volunteers selected from among ordinary people. A feature of the program is fatality: there are no plans for the return of colonists from Mars. For the rest of their lives, the project participants are forced to live on Mars. According to the initial plan, the colony should begin in 2023, when the first people arrive on the planet. It was this closeness and the chance for every person to take part in a historical event that fascinated everyone familiar with the project.
Tiny by the standards of the aerospace industry, the amount for landing on Mars - $ 6 billion - is proposed to be collected by means of a telecast in the format of a reality show and broadcast all stages on television. Data on Mars One contracts with television companies are not available. The colony must be self-sustaining: for example, colonists will eat food grown locally, and oxygen for breathing will be extracted from the soil. Will only send spare parts and equipment. The first four will arrive at the moment in 2027. Like everyone else, this date has already shifted: first from 2023 to 2025, and after to 2027. Delivery is planned using SpaceX missiles, in particular Falcon Heavy. At the moment, there has been no launch of this version of Falcon 9.
In 2013, 202,586 people were obtained during online registration. These are the very 200 thousand participants of Mars One who are often mentioned. In fact, these are just verified email addresses. Later, the fact of overstating the number of participants and the selection process itself were criticized . Only 4227 (according to other data - 2761) paid the registration fee. After that, they were given access to the website in the form of a social networking service, where they were asked to fill out questionnaires and talk about motivation in videos. After passing this stage, only 1058 people remained, with whom the second round of selection began. Within its framework, it was necessary to undergo a medical examination at his own therapist and agree to the publication of a completed profile. Only 660 people followed the interview that followed these two steps. Gradually, the final 100 participants were selected.
')
The project was immediately subjected to harsh criticism because of the unrealistic promise. Back in 2012, Wired magazine gave Mars One 2 points out of 10 on the credibility scale. An independent technical analysis of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology says that colonists will die approximately 68 days after disembarking due to the low oxygen partial pressure. Habitat will also be at risk of fire due to the high molar fraction of oxygen. Even if this does not happen, the burden of maintaining the colony will increase exponentially due to the need to send repair equipment. Mars One notices that although the study contains criticism, the mission is regarded as possible in it. But the researchers refute this statement: "To completely clarify the situation: the plan for the Mars One mission, as described on their website and other places by Mr. Landdorp and others, is not feasible." In an interview with Mars One, Dr. Norbert Kraft, an employee of Mars One, [at 3:50] calls the study “false and fabricated.”
In August, the annual meeting of the Martian Community held a discussion on the realism of the Mars One project. On the one hand were the head of the company Bas Landsorp and aerospace consultant Barry Finger of Paragon Space Development Corporation. The latter recently conducted a life support system research for Mars One. The views of Mars One were disagreed by Sydney Dooe and Andrew Owens, who are the authors of the MIT study mentioned above. Their new analysis uses the declared value of the program ($ 6 billion) from the perspective of the “iron triangle” of project management.
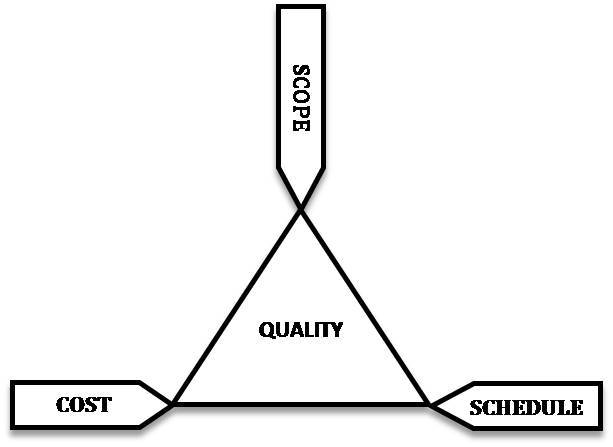
Triple limitation or “iron triangle” describes a balance between the content (goals), cost and time of the project. (Quality is not considered here.) Changing one side of a triangle affects the other sides. An executable project is one in which goals are achieved beyond acceptable limits on cost and lead time. So, Mars One declares : to deliver four people by 2027 (12 years from now) to the surface of Mars, we need 6 billion dollars. For each of the next two years, it is planned to send four more and spend $ 4 billion. The cost is 6 billion dollars and 4 every two years. The goal - the creation of a colony on Mars. Time - 2027 year. The key research question is: can Mars One implement the project with these limitations?
Mars One arguments are well known. Regarding time, Landdorp said: when a man was sent to the moon, NASA had less time. Regarding the goal, it is often mentioned that Mars One plans use existing technologies: there are missiles and landing systems. Landing systems are similar to those used for the Curiosity rover, and life support systems resemble those used on the International Space Station.
However, this is not the case. Large image size is available by click.

Space today is not the lot of only government agencies, so it is easy to find, with which to compare the grand designs of Mars One.

It is doubtful and the argument about the existence and accessibility of technology.

Landing is not so simple. Until that moment, only unmanned vehicles were planted on the surface of the red planet. The largest of these is the Curiosity rover. Its weight is 899 kilograms. The Mars One Mars Smart will weigh 2500 kilograms, another 4200 is the dry weight of the Dragon capsule. In total, this is 6,700 kilograms, 7.5 times more than Curiosity. The rover will prepare a place for the colony. A capsule with a life support system will weigh 7,434 kilograms. This is more than the total mass of all vehicles successfully landing on Mars in history. A real leap is required to implement Mars One plans.
The smart rover and other Mars One systems should also have unprecedented reliability. As a rule, the ISS spends about 3 months without additional supplies. Necessary parts or whole blocks of broken life support systems can be added to the space truck and sent to the station. Mars One equipment will not receive new parts for about 26 months, 8.7 times more. As a result, the situation will resemble a logistic nightmare, in which there is much less than the required supply even in conditions 2 times more reliable equipment. Without a production facility on Mars, a one-way ticket strategy is not feasible.
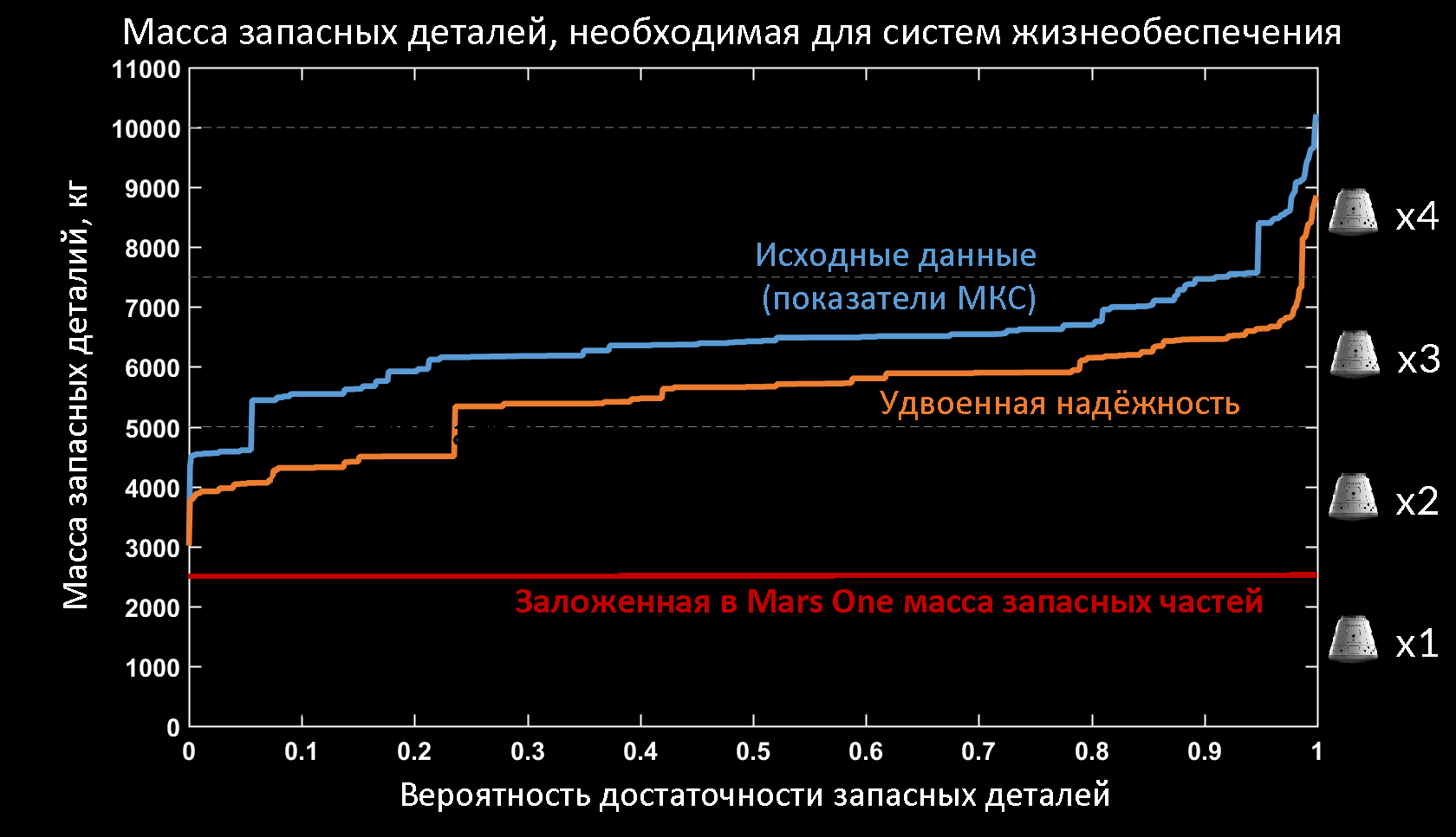
The analysis also touched upon the research of Paragon Corporation: according to the researchers, it affects only the goals, but not the cost and execution time. The researchers also quote direct quotes from the analysis that Barry Finger performed. They say that it will take considerable time to create production facilities. The base for production and there is considered mandatory to achieve permanent settlement.
In response, Landdorp said that the purpose of Mars One is not to send people to Mars in 2027 for $ 6 billion and for 14 launches. The goal is simply to land on Mars. Then he repeated the same mysterious phrase that was said about the previous research: the analysis of Andrew and Sydney, on the contrary, confirms the Mars One plan.
The presentation of Landsdorp contained only one slide, which showed changes in the concepts of Apollo, the apparatus that brought people to the moon. He said that Mars One plans are based on preliminary work and may change over time with the arrival of new data. As an example, Landdorp cited a recent study by Paragon, which states that the mass of the life support system will be higher than expected. Now Mars One is looking for $ 15 million to fund a team building and additional research from Lockheed Martin on the subject of entry, reduction and landing systems. Lansdorp expressed optimism that some billionaire might be announced to finance the whole project, which would speed up the work.
The most frightening argument that Du sounded was not the impracticability of Mars One projects. It was a remark that if the project was blown out loudly, in the future any even the most plausible attempt to conquer Mars would be perceived ambiguously.
Presentation slides with the assessment of Mars One from the perspective of the “iron triangle”
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/368161/
All Articles