Ask Ethan # 3: Expansion of the Universe
“Observations show that the universe is expanding with increasing speed. It will expand forever, and become more empty and dark. "
Stephen Hawking

The reader asks:
And that's what it is about:
')

For each galaxy in the Universe, we can measure the shift of the spectrum of the light emitted by it. Galaxies that approach or move away from us have a shift in the spectral lines (lines absorbed or emitted by the atoms). The amount of shift is directly proportional to the combination of two parameters:
Combine these two parameters, and the result will explain the observed shifts in the light of all galaxies.
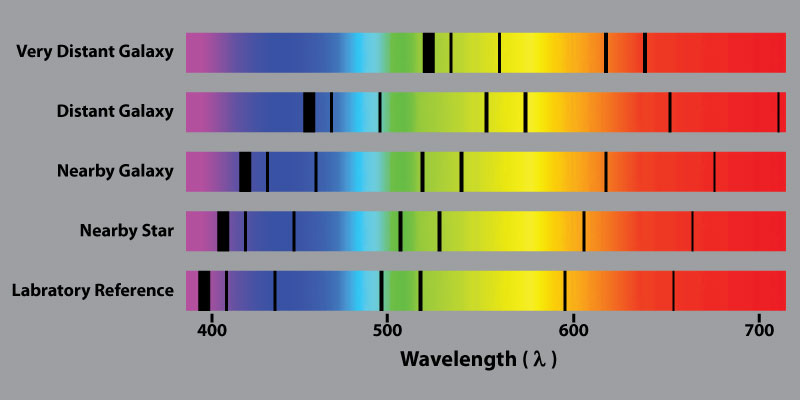
For very distant galaxies, their speed is negligible compared to the expansion of space-time. This light went on for billions of years, therefore, by measuring the red shift of galaxies at different distances, we can calculate how the Universe expanded.
But this is not the only possibility. Recently, an alternative has emerged that has attracted attention.
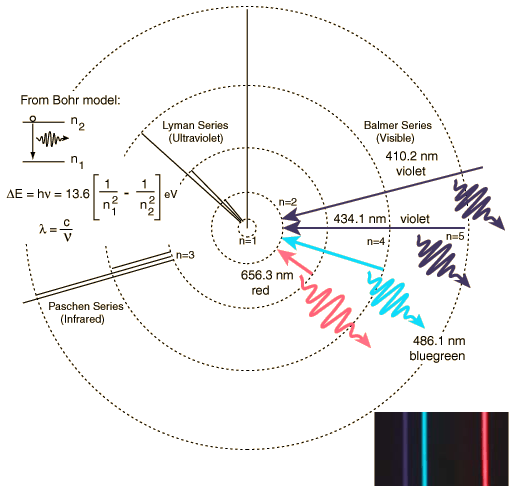
Instead of expanding the universe, which stretches the wavelength of the photons, we can gradually correct the mass of the particles of the universe so that the light emitted many years ago will be redder, because the equations of quantum physics will change.
The idea gave Christoph Wetterich ( work ). It may look unintuitive, but in fact everything is very simple. Consider Newton's gravity.
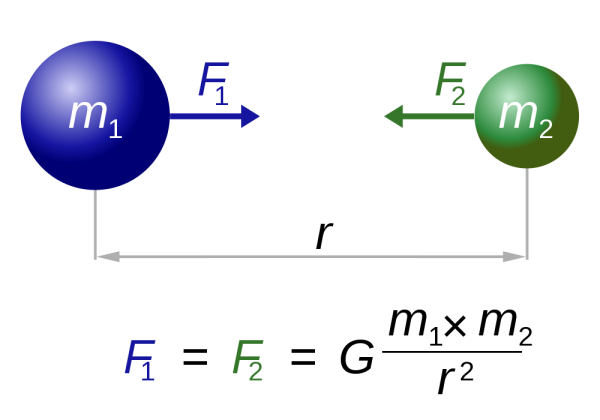
Imagine that there are only two masses in the universe, and they fly apart from each other. All you can measure is the power of their attraction. And what do we see? If r increases, then the force decreases as r -2 .
But is it possible to be sure that r increases, and not G (or both masses) decreases? No, if gravity is all you can measure. So with our galaxies.

Relatively distant galaxies, we can measure only a few parameters - the rest remains to guess. Since our experience and experiments with space-time and mass suggest that the mass of particles does not change, and space-time expands, shrinks and warps, we assume that the universe works on a large scale in the same way - although, there we set up an experiment and can not.
But Vetterich’s idea might work. But that does not tell about it - for it will have to pay something.
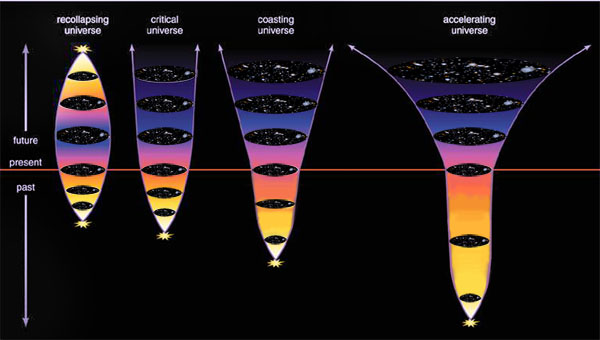
In an expanding universe obeying GTR, one powerful prediction arises: the rate of expansion is determined by a combination of curvature and energy density. All matter in the universe tells us how the universe has expanded, and what redshift the objects should have.

In our universe, we observe how galaxies, at different distances, have different redshifts, determined by a special formula, and this tells us about what our universe is made of.
We can reconstruct everything that, as we know, was in our universe at any given time, predict how the universe evolved, and will evolve, and check it all out.
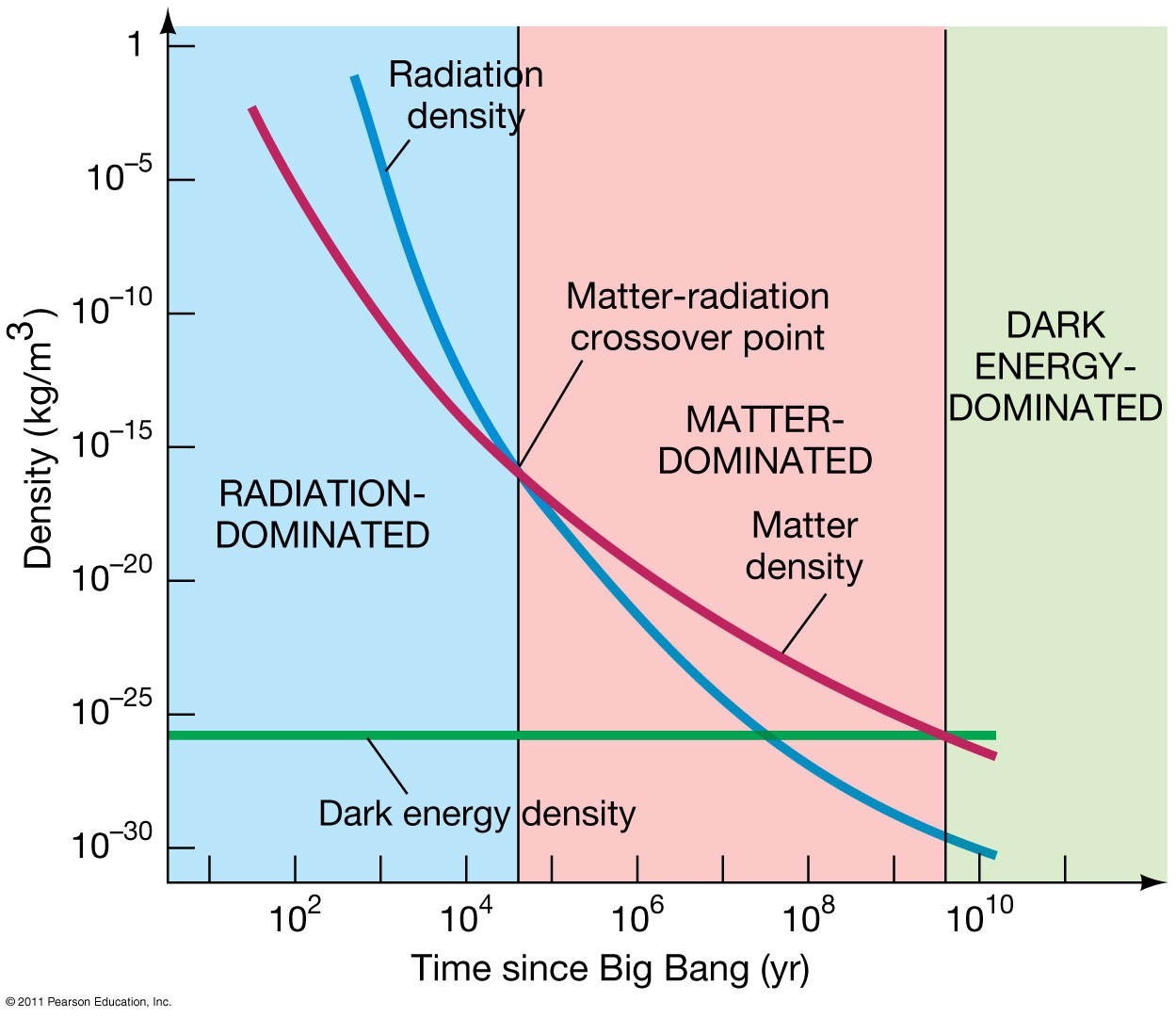
We can compare these predictions with data obtained from cosmic background radiation, the large-scale structure of the universe, and the Big Bang nucleosynthesis, etc. And it all fits very well.
But if the redshift is caused not by the expansion of the universe, but by a change in mass, all this predictive power evaporates.
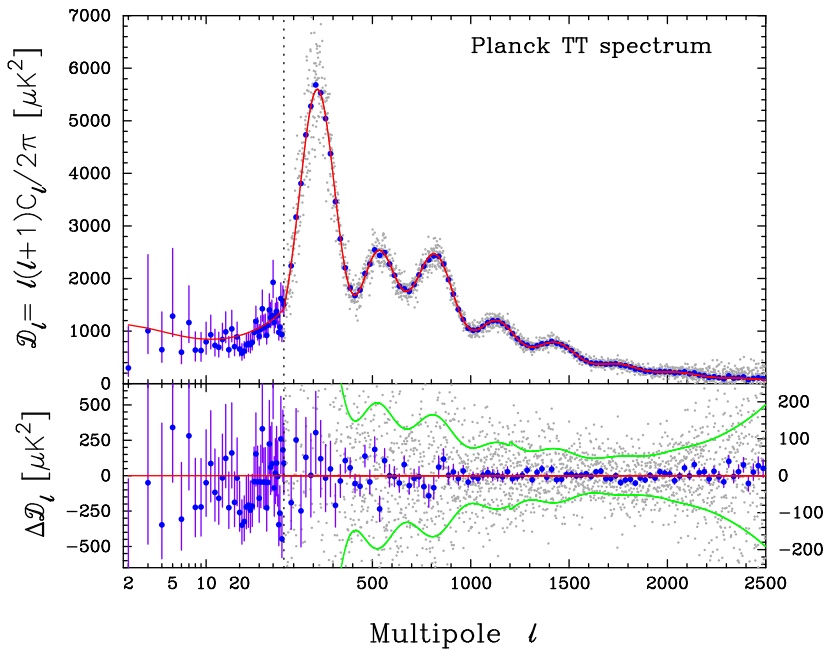
Fluctuations in the background radiation are just that, because the mass has changed so that they turn out to be so - and not because there are powerful physical laws behind it. The Universe is accelerating, not because it has inherent dark energy, but because the mass changes according to such a law. And about the same for all other observations.
But from the news you will not get such nuances.
Stephen Hawking

The reader asks:
I recently read that some researchers are considering the possibility that things are falling in mass, as an alternative explanation for some issues concerning the expansion of the universe. Does this make any sense?
And that's what it is about:
')

For each galaxy in the Universe, we can measure the shift of the spectrum of the light emitted by it. Galaxies that approach or move away from us have a shift in the spectral lines (lines absorbed or emitted by the atoms). The amount of shift is directly proportional to the combination of two parameters:
- how fast the object moves to us (blue offset) or from us (red)
- how much the space-time of the universe has expanded (for redshift) or shrunk (for blue) from the time the light was emitted, until the time it came into our eyes
Combine these two parameters, and the result will explain the observed shifts in the light of all galaxies.

For very distant galaxies, their speed is negligible compared to the expansion of space-time. This light went on for billions of years, therefore, by measuring the red shift of galaxies at different distances, we can calculate how the Universe expanded.

But this is not the only possibility. Recently, an alternative has emerged that has attracted attention.

Instead of expanding the universe, which stretches the wavelength of the photons, we can gradually correct the mass of the particles of the universe so that the light emitted many years ago will be redder, because the equations of quantum physics will change.
The idea gave Christoph Wetterich ( work ). It may look unintuitive, but in fact everything is very simple. Consider Newton's gravity.

Imagine that there are only two masses in the universe, and they fly apart from each other. All you can measure is the power of their attraction. And what do we see? If r increases, then the force decreases as r -2 .
But is it possible to be sure that r increases, and not G (or both masses) decreases? No, if gravity is all you can measure. So with our galaxies.

Relatively distant galaxies, we can measure only a few parameters - the rest remains to guess. Since our experience and experiments with space-time and mass suggest that the mass of particles does not change, and space-time expands, shrinks and warps, we assume that the universe works on a large scale in the same way - although, there we set up an experiment and can not.
But Vetterich’s idea might work. But that does not tell about it - for it will have to pay something.

In an expanding universe obeying GTR, one powerful prediction arises: the rate of expansion is determined by a combination of curvature and energy density. All matter in the universe tells us how the universe has expanded, and what redshift the objects should have.

In our universe, we observe how galaxies, at different distances, have different redshifts, determined by a special formula, and this tells us about what our universe is made of.
We can reconstruct everything that, as we know, was in our universe at any given time, predict how the universe evolved, and will evolve, and check it all out.

We can compare these predictions with data obtained from cosmic background radiation, the large-scale structure of the universe, and the Big Bang nucleosynthesis, etc. And it all fits very well.
But if the redshift is caused not by the expansion of the universe, but by a change in mass, all this predictive power evaporates.

Fluctuations in the background radiation are just that, because the mass has changed so that they turn out to be so - and not because there are powerful physical laws behind it. The Universe is accelerating, not because it has inherent dark energy, but because the mass changes according to such a law. And about the same for all other observations.
But from the news you will not get such nuances.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/367425/
All Articles