PC Buyer's Guide: Choosing a Power Supply
Hi, Geektimes! Today we continue our PC Buyers Guide cycle and talk about that piece of hardware, without which no computer will work at all. About the power supply.

Questions about power supplies are asked a lot and regularly. Of course, the most common question is about how to choose the right power supply and how powerful the power box is for certain types of iron. But besides the calculations of the required power, there are several interesting topics that I would like to highlight today: what is “80+” certification, which marketing “improvers” should be ignored, and which ones to take into account, and, of course, which manufacturer to choose.
In order to better understand some aspects of the power supply industry and to understand more or less why the choice of power supply is more important than at first glance many users (especially those who have not yet lost their glands because of the rotten feeder), it is worth considering the general principles of this thing.
')
In the outlet we have with you (as well as with most of humanity) alternating current, voltage - 220 volts, which change their "direction" 50 times per second. In countries of decaying capitalism, a different standard has been adopted overseas (usually 110 V at 60 Hz, but various other perversions also occur). Modern BP have the opportunity to work both in those and in other networks. Input characteristics are determined automatically or manually (by a switch), depending on the model.

The main voltages inside the computer are 3.3 V, 5 V and 12 V, moreover, we are not talking about any “change”, all the elements operate at a constant current. In order to correctly “straighten” the variables of 220 V and “saw them” into the above indicated voltmeter readings in a computer, a power supply unit is used. So, what does the BP have inside and why are they asking for such big money?
Attention: the description of the part of the intrinsic design is deliberately omitted: those who know electrical engineering / are interested in microelectronics - it is up to date on how the power supply unit is constructed, this section will be fine, and those who have all this new theoretical material are hardly needed now, the rest - Wikipedia to help.
The internal parts of the power supply unit can be divided into three large parts: input circuits, a converter, and output circuits.
In the input circuits, the alternating current, passing through several filters and a power corrector (about it later), is “rectified” by a diode bridge:
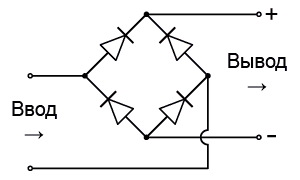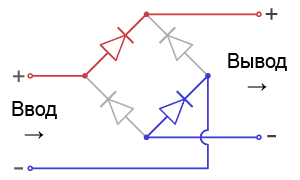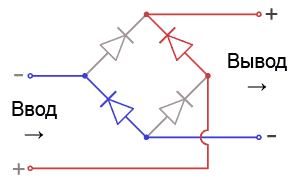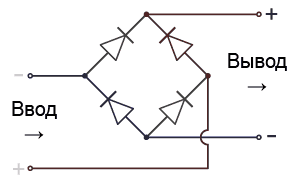
Despite the constant polarity reversal at the input, the mutual orientation of the diodes makes it possible to obtain a fixed output with “plus” and “minus”. After such a transformation, the alternating current is transformed into direct current, albeit with one small unpleasant effect: instead of direct current and constant voltage, we get direct current of alternating voltage:

For normal further DC conversion, it is necessary to apply various filters: capacitors, chokes, voltage stabilizers, which will smooth out the ripple in the voltage to acceptable values.
Further, the current straightened and tamed to constant values enters the conversion unit, which consists of a push-pull converter for bipolar, which is now rare or MOSFET transistors. Next, a pulse transformer is used, which creates the voltages necessary for the computer (+3.3, +5 and +12 Volt). It is also used for the galvanic isolation of the internals of the PSU and PC with the external network. The main magic happens here. Circuitry inside the device is responsible for the stability and efficiency of conversion, and the better it is, the more expensive the device and the less energy is wasted: heating, fan noise and electricity bills. In addition, the better the stuffing, the less likely it is that something will happen to the computer due to unstable power supply.
The output circuits re-filter the received power lines and “feedback” the iron to the PC: an increase in power consumption causes a voltage drop, and it makes it clear to the BP that it is necessary to increase the transformer's performance and restore the required parameters of the PC's internal power supply.
It so happened that almost 95% of the electricity generated by the power supply unit goes to just ... warm the air! No, in fact, all this movement of electrons and holes is involved in switching transistors, settling in the form of "ones" and "zeros" on hard drives and SSD, displaying information on the display and dynamics, but along the way they create only one kind of mechanical work: heat (we already talked about heat removal from the processor in the last PCBG release).
Roughly speaking, it is possible to consider computer consumption of electric power according to the declared TDP (heat packs) of its components, adding some constants for those devices whose TDP are not known to us or not stated: hard drives and optical drives, cooling systems and all peripherals. Video card manufacturers usually do not indicate the TDP of their offspring, but power consumption can be approximately determined by the power connectors used. A standard PCIe x8 / x16 bus delivers up to 75 watts of power for the video adapter. Additional 6-pin plugs add 75 watts each. More powerful video cards can have 8-pin connectors on board that allow you to transfer up to 150 watts. Thus, if your video card (current or planned) has one 6-PIN and 8-PIN connector, then its maximum power consumption will be 75 W from PCIe + 75 W from 6-PIN + 150 W from 8-PIN = 300 watts.
So that you do not get confused in all this variety, we have prepared a convenient sign by which you can estimate the required power of the power supply unit.
Suppose you are collecting a new domestic horse for a couple of years ahead, it remains only to choose the BP. Here is an example of the power consumption calculations:
The motherboard does not belong to the High-End, we will not overclock anything, so we take the average value on the plate: about 50 watts. The processor claims 84 watts, round up to 85. On the video card, there are two six-pin power connectors + there are 75 watts via a PCIe connector, for a total of 3x75 watts, two memory modules of 5 watts each, 1 HDD and 1 SSD, a total of 10 + 5 watts. Let there be a total of 5 fans in the case (along with a processor cooler): another 3x5 watts. Fold in, we get 50 + 85 + 75x3 + 5x2 + 10 + 5 + 5x3 = 400 W!
But wait rejoice. The fact is that the efficiency of the power supply is not equal to 100%, moreover, it depends directly on the load. At the minimum (that is, in the case when your computer is idle) efficiency drops, at the maximum or close to it - the same. The most effective range is 50-60% of the load on the power supply, in this case, the performance of the PSU is at the optimal level. Accordingly, if your wiz-case is a game on weekends, a typewriter on weekdays, then you can limit yourself to a reasonable 15-20% of the calculated power (just in case + for a potential upgrade of RAM and hard drives), since most of the time is “iron” will not load the power supply unit to the limit and the whole system will be in comfortable conditions for it. If the computer at home is also a working tool, it is worth, firstly, to make a margin of power a little higher, and secondly, to deal with one more thing.
When choosing a power supply, you may have noticed that on many models it is either indicated in the description of the product, or there is a sticker on the PSU itself, indicating incomprehensible eighty plus points. In fact, this label is a sign of the certification of efficiency of the PSU. The higher the sticker class, the higher the BP efficiency and the less “extra” power it eats from your wallet every month in electricity bills. In addition, the 80 PLUS sticker has another nice bonus. To achieve such efficiency, using so-so components inside will not work. That is, it is also a banal "certificate of quality" of your BP.

When buying a new computer, even in conditions of austerity, you should not take power supplies from an unknown manufacturer without such a sticker, even a basic, white color. There is a chance to run into a cheap Chinese crafts, and on what they save inside tricky optimizers - it is not known.
Of course, we in Yulmart try to avoid unreliable models and dubious suppliers, but once a year, as they say, the stick shoots
As for saving, here we have to disappoint you. To buy a purchase of a power unit with a class of 80+ Platinum or Titanium, you must at least have a bitcoin farm on video cards, otherwise the exhaust will be minimal. If you are not very constrained by the means, you should pay attention to models with certification above 80+ Bronze, but not to engage in meaningless "improving", the extra two or three thousand in the power supply for the sake of the treasured 80+ Platinum is better to spend on the processor, more capacious SSD or more powerful graphics card - depending on your needs.
One of the most pleasant "chips" of modern power supplies is a modular design: some of the wires (and sometimes all the wires) have connectors at two ends, allowing you to remove unnecessary and unused "braids" from the system unit: it is aesthetically pleasing and it is more convenient to lay cables inside the PC , and less resistance for airflow in the enclosure. Of course, this chip has to pay extra, albeit a bit.
If you collect a computer and your budget is very limited, you can not bother with "modulnikami" and just take an inexpensive high-quality model with "embedded" wires, and there will always be extra 500-600 rubles where to invest.
Many companies are introducing various “unique” technologies with beautiful names into their own BP, trying to justify the high price of their products. Often, all these chips are the usual public achievements of electrical engineering in a beautiful wrapper, however, there are a number of letters and phrases that are worth paying attention to.
The necessary pieces include:
OVP / UVP - overvoltage and undervoltage protection,
OCP / OLP / OPP - protection from excessive current and power supply overload,
OTP / OHP - overheat protection,
NLO - protection from work without load,
SCP - short circuit protection.
Not to say that all these features are necessary when working every second, but it is better to have just turned off the power supply and computer, than smoke and the stench from exploded capacitors or dead iron for many thousand rubles.
Of the simple, reliable and unremarkable power supply units, the FSP ATX-550PNR can be noted. It is inexpensive (less than three thousand rubles), perfectly assembled, does not make noise, has a two-year warranty and rarely happens in service centers. The power supply capacity is 550W, which is quite enough for a completely typical system unit (such as what we “collected” a couple of paragraphs above).
A slightly more expensive model (but already with an efficiency class of 80+) - Chieftec GPS-550A8 , and it looks more pleasant, and does not make noise.
If, after all the calculations, you came to the conclusion that you need a power unit with a capacity of 600-650 W, you should pay attention to the model CoolerMaster G650M . It is certified 80+ Bronze, a good cooling system, supports automatic regulation of the fan speed, a modular cable connection system and costs a little more than five thousand rubles. The model is fresh, but in the “iron” press and among enthusiasts, she enjoys exceptional success. By the way, it also exists in the 750-watt version.

An alternative for Cooler Master in the segment of powerful power supply units for top computers can be called the Corsair CX 750 M. Available - all the same advantages as the CM G650M - modular design, 80+ Bronze certificate and excellent reputation. In addition, the price does not bite much - we “Corsair” costs a little less than seven thousand rubles.

Well, about any monsters, such as the Corsair CP-9020008-EU 1.2 KW, you can safely forget. If you do not have 4 video cards for 30-40 thousand rubles each, then such a monster for ~ 20 thousand rubles is definitely not required for you.
For fans of deathly silence, there are special fanless models that do not make any sounds at all (unless, of course, the manufacturer has supplied normal chokes). All of them are usually indecently expensive due to the certification of 80+ Platinum / Titanium (and without such efficiency passive cooling is hard to get).
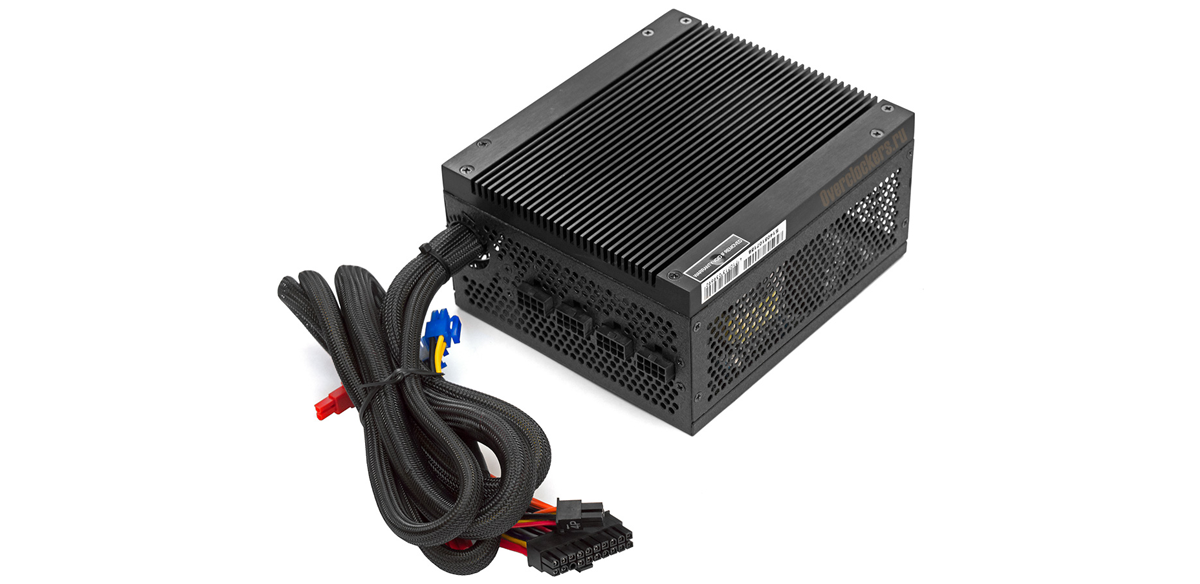

Thanks for the picture for the resource Overclockers.ru
An example is the 500 Watt Chieftec PGS-500C . Price - an impressive 10 and a half thousand rubles. For about the same money, for example, you can get an 850-watt TT Moscow with “golden” certification and a completely silent cooler or a 1000-watt TT Volga with similar characteristics in terms of efficiency and noise.

You can only hear him in a deaf crypt, but ordinary people do not understand these passive people :)
There are a number of frequently encountered questions that I would like to highlight before we sum up.
>> I already have a power supply, I thought it should be enough. Do I need to replace it with a new one or can I leave it as is?
The question is how old your BP is. If you have not changed your computer since the fourth Pentium, and now you decide to install a new Core i3 and a simple video card like nVidia 840, you may be faced with the fact that your PSU simply does not support 24-pin power for modern motherboards. In addition, the old PSUs had an emphasis on the 3.3 and 5 volt lines, and the twelve-volt power lines were mainly focused on connecting hard drives and optical drives. Now the emphasis is shifted just to the voracious 12-volt power supply of video cards. So if you have a frankly old BP, it is worth replacing it with the current one, even if it is not very expensive.
>> Why do some BPs issue a nasty whistle under load?
Lousy whistle or creak is the sound of the filter elements ( chokes ). The fact is that a choke is a banal inductor, and the high-frequency current that passes through it can make it vibrate finely, hence the whistling-hissing-creaking sound. Power supply chokes can be whistled both on the PSU and on the motherboard / video card. If you find such a flaw in the new product - bring and change. Unfortunately, the whistle of chokes is rarely recognized as a warranty case, so in the "old" power supplies either to put up or ... If your hands grow from the shoulders, you can fill the chokes with epoxy, however, this leads to a loss of warranty.
>> Why put the power supply on 1 kW and more?
These PSUs are used in gaming computers with two or more video cards. The urgency of such an assembly for everyday use is a big question, since SLI / Crossfire-X adequately manifests itself only in multi-monitor assemblies with a huge overall resolution, for a single monitor, even with a resolution of 2560x1440 and 3840x2160, just one video card of the R9-290X or nVidia 780Ti type is enough (it is more productive than the 980th, and the 980Ti has not yet come out).
>> How many BPs consume from the network?
The efficiency of a power unit with a good filling floats around 80-90%. Thus, a 600 watt power supply consumes about 660-720 watts from the network under almost full load. In addition, depending on the design of the PSU and the installed power correction unit, it can be consumed from 2 to 30% “from above” into the void and heat. So the old 600-Vattnik of an unknown manufacturer may well consume up to 1 KW under full load under adverse conditions. Intensively working for 4 hours a day, such a computer “nazht” your electricity by about 1x4x30 = 120 kWh. That is about 540 rubles for a single tariff meter in Moscow per month. Replacing a power supply unit with, say, a new one, with a power of 700 W, will make it possible to “beat off” the difference in a couple of years. On the one hand - saving so-so, on the other - who knows how much electricity will cost in 2-3 years?
That's all. In our store, there are always a choice of many models of power supplies for the most diverse ones - a good selection of iron, a high-quality power supply and no knowledge of the road to the service centers :)
Previous publications from the PC Buyer's Guide cycle:
» PC Buyer's Guide: Cooling
» PC Buyer's Guide 2015: Motherboards, Chipsets, and Sockets
» Twist-twirl, I want to confuse. Understanding the HDD lines
What topic do you want to read PCBG in the next issues?

Questions about power supplies are asked a lot and regularly. Of course, the most common question is about how to choose the right power supply and how powerful the power box is for certain types of iron. But besides the calculations of the required power, there are several interesting topics that I would like to highlight today: what is “80+” certification, which marketing “improvers” should be ignored, and which ones to take into account, and, of course, which manufacturer to choose.
Instead of the preface
- Grandfather, and how does the plane fly?
“How-how ... Here's how:“ Ooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooes all bears
In order to better understand some aspects of the power supply industry and to understand more or less why the choice of power supply is more important than at first glance many users (especially those who have not yet lost their glands because of the rotten feeder), it is worth considering the general principles of this thing.
')
In the outlet we have with you (as well as with most of humanity) alternating current, voltage - 220 volts, which change their "direction" 50 times per second. In countries of decaying capitalism, a different standard has been adopted overseas (usually 110 V at 60 Hz, but various other perversions also occur). Modern BP have the opportunity to work both in those and in other networks. Input characteristics are determined automatically or manually (by a switch), depending on the model.

The main voltages inside the computer are 3.3 V, 5 V and 12 V, moreover, we are not talking about any “change”, all the elements operate at a constant current. In order to correctly “straighten” the variables of 220 V and “saw them” into the above indicated voltmeter readings in a computer, a power supply unit is used. So, what does the BP have inside and why are they asking for such big money?
Mene inside, um ... neon!
Attention: the description of the part of the intrinsic design is deliberately omitted: those who know electrical engineering / are interested in microelectronics - it is up to date on how the power supply unit is constructed, this section will be fine, and those who have all this new theoretical material are hardly needed now, the rest - Wikipedia to help.
The internal parts of the power supply unit can be divided into three large parts: input circuits, a converter, and output circuits.
In the input circuits, the alternating current, passing through several filters and a power corrector (about it later), is “rectified” by a diode bridge:

Despite the constant polarity reversal at the input, the mutual orientation of the diodes makes it possible to obtain a fixed output with “plus” and “minus”. After such a transformation, the alternating current is transformed into direct current, albeit with one small unpleasant effect: instead of direct current and constant voltage, we get direct current of alternating voltage:

For normal further DC conversion, it is necessary to apply various filters: capacitors, chokes, voltage stabilizers, which will smooth out the ripple in the voltage to acceptable values.
Further, the current straightened and tamed to constant values enters the conversion unit, which consists of a push-pull converter for bipolar, which is now rare or MOSFET transistors. Next, a pulse transformer is used, which creates the voltages necessary for the computer (+3.3, +5 and +12 Volt). It is also used for the galvanic isolation of the internals of the PSU and PC with the external network. The main magic happens here. Circuitry inside the device is responsible for the stability and efficiency of conversion, and the better it is, the more expensive the device and the less energy is wasted: heating, fan noise and electricity bills. In addition, the better the stuffing, the less likely it is that something will happen to the computer due to unstable power supply.
The output circuits re-filter the received power lines and “feedback” the iron to the PC: an increase in power consumption causes a voltage drop, and it makes it clear to the BP that it is necessary to increase the transformer's performance and restore the required parameters of the PC's internal power supply.
Calculation of the required power
It so happened that almost 95% of the electricity generated by the power supply unit goes to just ... warm the air! No, in fact, all this movement of electrons and holes is involved in switching transistors, settling in the form of "ones" and "zeros" on hard drives and SSD, displaying information on the display and dynamics, but along the way they create only one kind of mechanical work: heat (we already talked about heat removal from the processor in the last PCBG release).
Roughly speaking, it is possible to consider computer consumption of electric power according to the declared TDP (heat packs) of its components, adding some constants for those devices whose TDP are not known to us or not stated: hard drives and optical drives, cooling systems and all peripherals. Video card manufacturers usually do not indicate the TDP of their offspring, but power consumption can be approximately determined by the power connectors used. A standard PCIe x8 / x16 bus delivers up to 75 watts of power for the video adapter. Additional 6-pin plugs add 75 watts each. More powerful video cards can have 8-pin connectors on board that allow you to transfer up to 150 watts. Thus, if your video card (current or planned) has one 6-PIN and 8-PIN connector, then its maximum power consumption will be 75 W from PCIe + 75 W from 6-PIN + 150 W from 8-PIN = 300 watts.
So that you do not get confused in all this variety, we have prepared a convenient sign by which you can estimate the required power of the power supply unit.
| PC components | Power consumption under load |
| CPU | 35 to 150-160 W, see processor TDP |
| Video card | 75 W for PCIe, 75 W for 6-PIN, 150 W for 8-PIN, summarize all connectors |
| Motherboard | 35-65 W |
| DDR memory per module | 4-6 W |
| HDD, optical drive (in recording mode) | 10 W for normal models, 15 W for high-speed HDD or Blu Ray |
| SSD | 5 watts for regular models, 10-15 watts for exotic PCIe with built-in RAID |
| PCI-X devices | 2-5 W |
| Fans | ~ 3 W |
MBo: MSI H97 PC Mate
CPU: Core i5-4460 , TDP 84 W
GPU: MSI nVidia GTX970 (6 + 6 PIN)
RAM: 2x8 GB DDR III Kingston HyperX (1866 MHz)
SSD: 120 GB Kingston HyperX 3K
HDD: 2 TB WD SE
The motherboard does not belong to the High-End, we will not overclock anything, so we take the average value on the plate: about 50 watts. The processor claims 84 watts, round up to 85. On the video card, there are two six-pin power connectors + there are 75 watts via a PCIe connector, for a total of 3x75 watts, two memory modules of 5 watts each, 1 HDD and 1 SSD, a total of 10 + 5 watts. Let there be a total of 5 fans in the case (along with a processor cooler): another 3x5 watts. Fold in, we get 50 + 85 + 75x3 + 5x2 + 10 + 5 + 5x3 = 400 W!
But wait rejoice. The fact is that the efficiency of the power supply is not equal to 100%, moreover, it depends directly on the load. At the minimum (that is, in the case when your computer is idle) efficiency drops, at the maximum or close to it - the same. The most effective range is 50-60% of the load on the power supply, in this case, the performance of the PSU is at the optimal level. Accordingly, if your wiz-case is a game on weekends, a typewriter on weekdays, then you can limit yourself to a reasonable 15-20% of the calculated power (just in case + for a potential upgrade of RAM and hard drives), since most of the time is “iron” will not load the power supply unit to the limit and the whole system will be in comfortable conditions for it. If the computer at home is also a working tool, it is worth, firstly, to make a margin of power a little higher, and secondly, to deal with one more thing.
80+ certification
When choosing a power supply, you may have noticed that on many models it is either indicated in the description of the product, or there is a sticker on the PSU itself, indicating incomprehensible eighty plus points. In fact, this label is a sign of the certification of efficiency of the PSU. The higher the sticker class, the higher the BP efficiency and the less “extra” power it eats from your wallet every month in electricity bills. In addition, the 80 PLUS sticker has another nice bonus. To achieve such efficiency, using so-so components inside will not work. That is, it is also a banal "certificate of quality" of your BP.

When buying a new computer, even in conditions of austerity, you should not take power supplies from an unknown manufacturer without such a sticker, even a basic, white color. There is a chance to run into a cheap Chinese crafts, and on what they save inside tricky optimizers - it is not known.
Of course, we in Yulmart try to avoid unreliable models and dubious suppliers, but once a year, as they say, the stick shoots
As for saving, here we have to disappoint you. To buy a purchase of a power unit with a class of 80+ Platinum or Titanium, you must at least have a bitcoin farm on video cards, otherwise the exhaust will be minimal. If you are not very constrained by the means, you should pay attention to models with certification above 80+ Bronze, but not to engage in meaningless "improving", the extra two or three thousand in the power supply for the sake of the treasured 80+ Platinum is better to spend on the processor, more capacious SSD or more powerful graphics card - depending on your needs.
Nice bonuses
One of the most pleasant "chips" of modern power supplies is a modular design: some of the wires (and sometimes all the wires) have connectors at two ends, allowing you to remove unnecessary and unused "braids" from the system unit: it is aesthetically pleasing and it is more convenient to lay cables inside the PC , and less resistance for airflow in the enclosure. Of course, this chip has to pay extra, albeit a bit.
If you collect a computer and your budget is very limited, you can not bother with "modulnikami" and just take an inexpensive high-quality model with "embedded" wires, and there will always be extra 500-600 rubles where to invest.
Marketing husks
Many companies are introducing various “unique” technologies with beautiful names into their own BP, trying to justify the high price of their products. Often, all these chips are the usual public achievements of electrical engineering in a beautiful wrapper, however, there are a number of letters and phrases that are worth paying attention to.
The necessary pieces include:
OVP / UVP - overvoltage and undervoltage protection,
OCP / OLP / OPP - protection from excessive current and power supply overload,
OTP / OHP - overheat protection,
NLO - protection from work without load,
SCP - short circuit protection.
Not to say that all these features are necessary when working every second, but it is better to have just turned off the power supply and computer, than smoke and the stench from exploded capacitors or dead iron for many thousand rubles.
Recommended models
Of the simple, reliable and unremarkable power supply units, the FSP ATX-550PNR can be noted. It is inexpensive (less than three thousand rubles), perfectly assembled, does not make noise, has a two-year warranty and rarely happens in service centers. The power supply capacity is 550W, which is quite enough for a completely typical system unit (such as what we “collected” a couple of paragraphs above).
A slightly more expensive model (but already with an efficiency class of 80+) - Chieftec GPS-550A8 , and it looks more pleasant, and does not make noise.
If, after all the calculations, you came to the conclusion that you need a power unit with a capacity of 600-650 W, you should pay attention to the model CoolerMaster G650M . It is certified 80+ Bronze, a good cooling system, supports automatic regulation of the fan speed, a modular cable connection system and costs a little more than five thousand rubles. The model is fresh, but in the “iron” press and among enthusiasts, she enjoys exceptional success. By the way, it also exists in the 750-watt version.

An alternative for Cooler Master in the segment of powerful power supply units for top computers can be called the Corsair CX 750 M. Available - all the same advantages as the CM G650M - modular design, 80+ Bronze certificate and excellent reputation. In addition, the price does not bite much - we “Corsair” costs a little less than seven thousand rubles.

Well, about any monsters, such as the Corsair CP-9020008-EU 1.2 KW, you can safely forget. If you do not have 4 video cards for 30-40 thousand rubles each, then such a monster for ~ 20 thousand rubles is definitely not required for you.
Passive cooling
For fans of deathly silence, there are special fanless models that do not make any sounds at all (unless, of course, the manufacturer has supplied normal chokes). All of them are usually indecently expensive due to the certification of 80+ Platinum / Titanium (and without such efficiency passive cooling is hard to get).

Thanks for the picture for the resource Overclockers.ru
An example is the 500 Watt Chieftec PGS-500C . Price - an impressive 10 and a half thousand rubles. For about the same money, for example, you can get an 850-watt TT Moscow with “golden” certification and a completely silent cooler or a 1000-watt TT Volga with similar characteristics in terms of efficiency and noise.

You can only hear him in a deaf crypt, but ordinary people do not understand these passive people :)
FAQ
There are a number of frequently encountered questions that I would like to highlight before we sum up.
>> I already have a power supply, I thought it should be enough. Do I need to replace it with a new one or can I leave it as is?
The question is how old your BP is. If you have not changed your computer since the fourth Pentium, and now you decide to install a new Core i3 and a simple video card like nVidia 840, you may be faced with the fact that your PSU simply does not support 24-pin power for modern motherboards. In addition, the old PSUs had an emphasis on the 3.3 and 5 volt lines, and the twelve-volt power lines were mainly focused on connecting hard drives and optical drives. Now the emphasis is shifted just to the voracious 12-volt power supply of video cards. So if you have a frankly old BP, it is worth replacing it with the current one, even if it is not very expensive.
>> Why do some BPs issue a nasty whistle under load?
Lousy whistle or creak is the sound of the filter elements ( chokes ). The fact is that a choke is a banal inductor, and the high-frequency current that passes through it can make it vibrate finely, hence the whistling-hissing-creaking sound. Power supply chokes can be whistled both on the PSU and on the motherboard / video card. If you find such a flaw in the new product - bring and change. Unfortunately, the whistle of chokes is rarely recognized as a warranty case, so in the "old" power supplies either to put up or ... If your hands grow from the shoulders, you can fill the chokes with epoxy, however, this leads to a loss of warranty.
>> Why put the power supply on 1 kW and more?
These PSUs are used in gaming computers with two or more video cards. The urgency of such an assembly for everyday use is a big question, since SLI / Crossfire-X adequately manifests itself only in multi-monitor assemblies with a huge overall resolution, for a single monitor, even with a resolution of 2560x1440 and 3840x2160, just one video card of the R9-290X or nVidia 780Ti type is enough (it is more productive than the 980th, and the 980Ti has not yet come out).
>> How many BPs consume from the network?
The efficiency of a power unit with a good filling floats around 80-90%. Thus, a 600 watt power supply consumes about 660-720 watts from the network under almost full load. In addition, depending on the design of the PSU and the installed power correction unit, it can be consumed from 2 to 30% “from above” into the void and heat. So the old 600-Vattnik of an unknown manufacturer may well consume up to 1 KW under full load under adverse conditions. Intensively working for 4 hours a day, such a computer “nazht” your electricity by about 1x4x30 = 120 kWh. That is about 540 rubles for a single tariff meter in Moscow per month. Replacing a power supply unit with, say, a new one, with a power of 700 W, will make it possible to “beat off” the difference in a couple of years. On the one hand - saving so-so, on the other - who knows how much electricity will cost in 2-3 years?
Total
That's all. In our store, there are always a choice of many models of power supplies for the most diverse ones - a good selection of iron, a high-quality power supply and no knowledge of the road to the service centers :)
Previous publications from the PC Buyer's Guide cycle:
» PC Buyer's Guide: Cooling
» PC Buyer's Guide 2015: Motherboards, Chipsets, and Sockets
» Twist-twirl, I want to confuse. Understanding the HDD lines
What topic do you want to read PCBG in the next issues?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/365243/
All Articles