A Century of Experiments 2 or the Future of Car Electronics
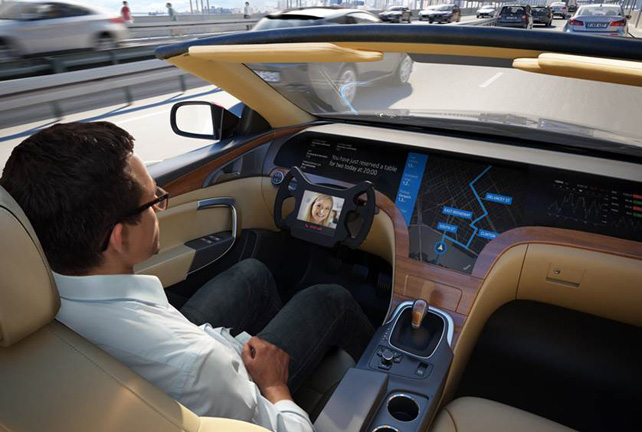

As we promised, after the history of car electronics it is time to find out which electronics should be expected in cars in the near future. Let's try to imagine what other gadgets and technologies may become as familiar as car radios or DVRs.
Wireless networks in the car

Manufacturers of semiconductor solutions for communications already produce special versions of chips for cars designed for automotive information and entertainment systems. Depending on the need, using a Wi-Fi + Bluetooth connection, the media center of the car can communicate with the wearable electronics of the owner (after all, we are talking about the future, where the options of wearable electronics can be even more than modern smart watches) and depending on the information received, unlock the car or warn of danger.
')

An even more interesting application of various combinations of wireless networks will be to become systems like V2X - involving the exchange of data between the car and the surrounding infrastructure. Vehicular communication systems are automotive communication systems that provide for the exchange of information between vehicles (data about accidents, traffic situations, traffic jams, etc.), providing for the ability to more effectively manage the traffic situation as a whole, by providing information to all participants. There are already several options for implementing such short-range communication networks (DRSC). Technically, they should work in the frequency range 5.9 GHz (5.85-5.925 GHz), with an approximate range of up to 1000 meters. This standard was named IEEE 802.11p (WAVE), and was approved in 2010.
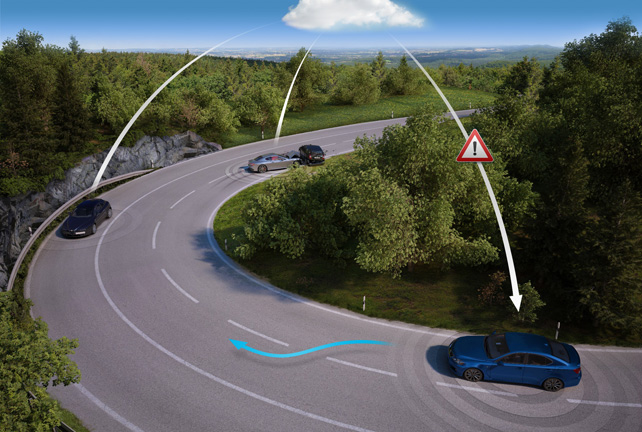

In 1999, this frequency in the United States was assigned to create an intelligent transport system (ITS). ITS of the future can be considered as a system in which information and communication technologies are applied in the field of motor transport (including infrastructure, vehicles, system participants, as well as road traffic regulation), and having the ability to interact with other modes of transport. For the operation of such systems, traditional WiMAX, GSM, 3G or 4G / 5G technologies can also be used. Considering the current solutions for wireless networks in cars, it is safe to assume that the connection or the “connection” of the car to the global network, in one form or another, is almost inevitable.
Mobile operating systems for cars

Modern motorists are no longer surprised by a media center running Android OS. Most often, you can find Android on the head unit of the car (in case you use a modern DVR, then Android can be found even ... in the rearview mirror CANSONIC SKY ).

However, in fact, the plans of the companies extend much further, and Android Auto, presented by Google in 2014, is an example of such solutions for the future. With the support of twenty-eight car manufacturers and Nvidia, a mobile-optimized mobile operating system is fighting for the right to revolutionize the zoo of various proprietary operating systems in media centers. Somewhere we have already seen it, right? Just as Android on smartphones eventually pressed its own operating systems of various manufacturers, you can rely on the repetition of this scenario on cars. In its current form, the system already has good functionality - it supports GPS navigation, music playback, SMS, telephony, web search, touch screens and the ability to control hardware switches and buttons, along with voice control. At the moment, Android Auto relies on the presence (and connection to the car) of the main Android device driver, speaking more like an interface for easy integration of the usual functions of a smartphone into a car. This approach has its advantages - taking into account the speed of updating and the increasing power of modern mobile platforms, the absence of its own built-in (and therefore deliberately becoming outdated with each passing year) electronics will make it possible to obtain new functions simply by connecting a new smartphone. The car acts as a “regular” docking station - perhaps now it sounds strange, but in the future such a scenario is not at all excluded.
Pilotless cars and electric cars
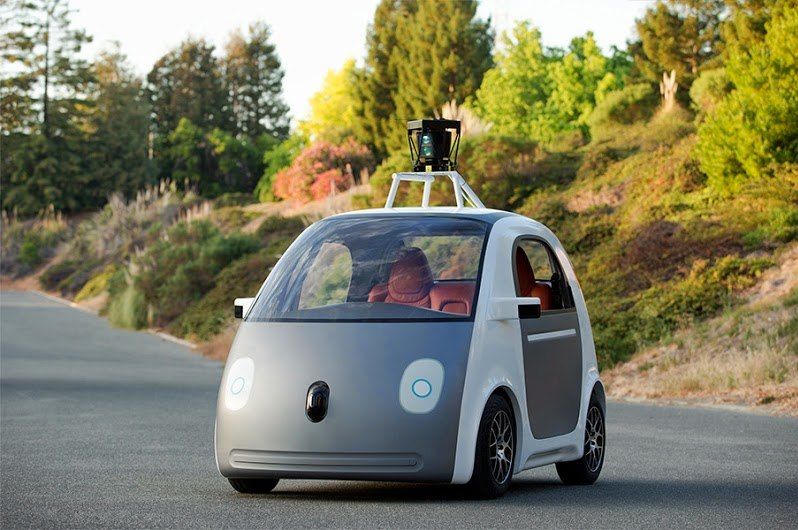

Of course, what is the future without self-driving cars! However, almost everyone who imagines self-driving cars that are seriously different from classic manual cars will be a little disappointed. The only modern concept of the car "without steering and pedals" became self-driving cars from Google. Most self-managed concepts (including those that have been granted the right to drive on public roads in some US states) suggest the possibility of returning to manual control at any time. Thus, for the driver and passengers, the use of self-government does not bring external serious changes to the interior of the car. Modern self-driving cars achieve significant success, for example, this year the self-driving car managed to overtake the driver-rider, however, the advantage was very small - only 0.4 seconds.
A similar situation is repeated for electric vehicles and hybrids. If you do not take into account the Tesla company, which stands alone, automakers are striving in every way to unify the experience of using electric vehicles, hybrids and cars with ICE. So in many cases, it is possible to distinguish an electric car from a regular car (except for the sound of a motor) except for additional charge indicators on the dashboard and the presence of a charging socket instead of the fuel tank neck.
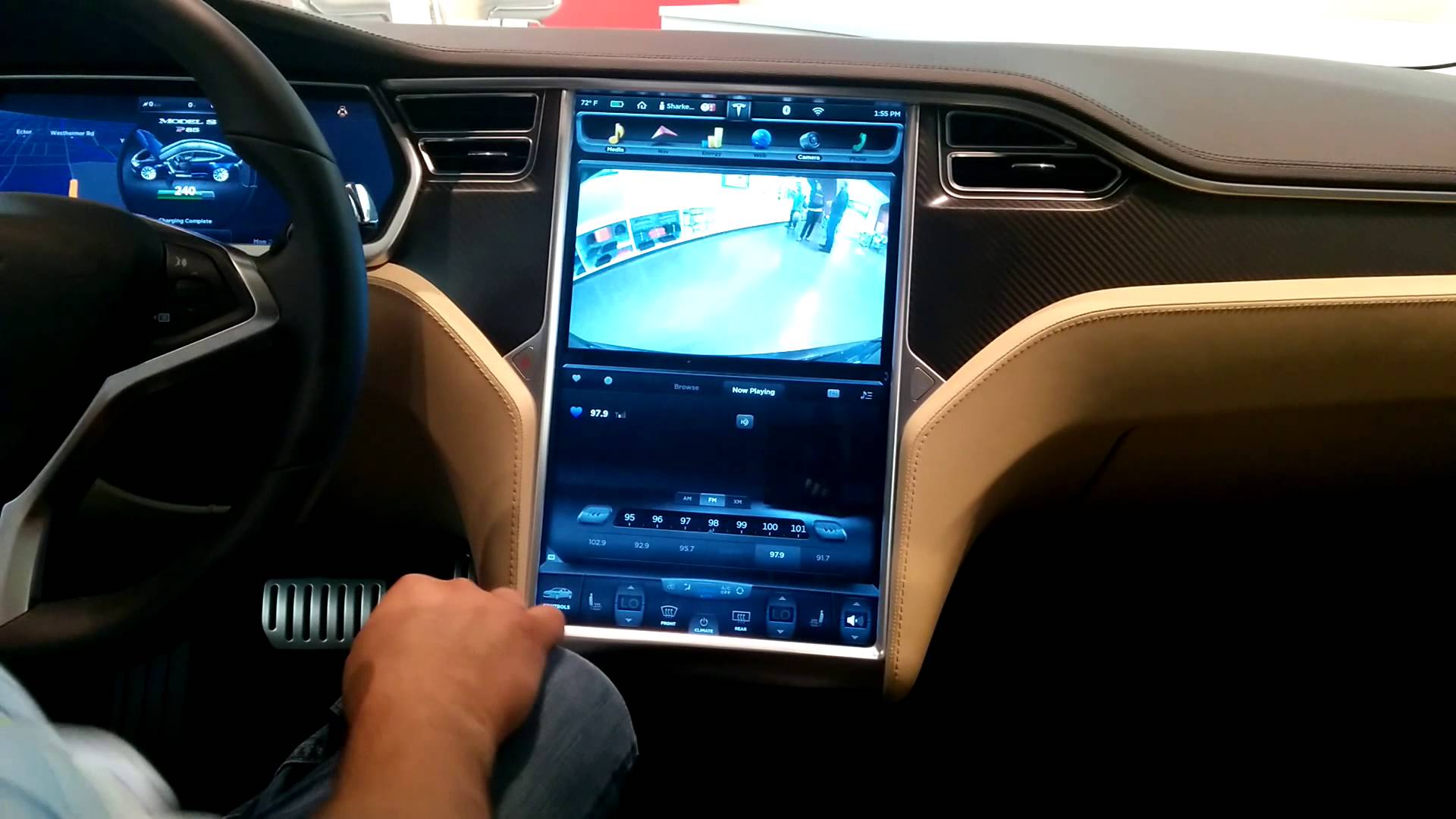
But there are reverse examples. Manufacturers such as Tesla Motors (as well as many prototypes at the auto shows 2014-2015) allow you to rethink possible options for head units. Until now, the record has not been surpassed, the 17 "touchscreen with a resolution of 1920x1080 in Tesla cars replaces the driver and the control panel and media center. Let's not dwell on it in too much detail, because you can read a detailed overview of this system on Habrahabr'e .
Holographic HUD Displays

Back in 2006, the company Light Blue Optics Ltd announced the acquisition of a license to manufacture full-color holographic laser projectors. The technology itself was invented by Edward Buckley and Adrian Cable in 2003 at the University of Cambridge. Since 2009, this system began to be adapted for use in displays that do not require driver distraction from the road (head-up display, HUD). There are plenty of options for projecting the image onto the windshield of the car - these are full-color laser holograms and much simpler solutions (a reflection of the bright image of a bright monochrome display from the glass). So far, automakers are not in a hurry to equip all new HUD models with displays, but there are such examples - in 2014, the Range Rover Evoque received such a system, and Ford relied on the MISHOR 3D system, with similar functions. HUD displays have securely won the windshields of aircraft (primarily military), but in future cars (especially self-driving ones) such a system for displaying information will look more than appropriate.
Augmented Reality in Cars
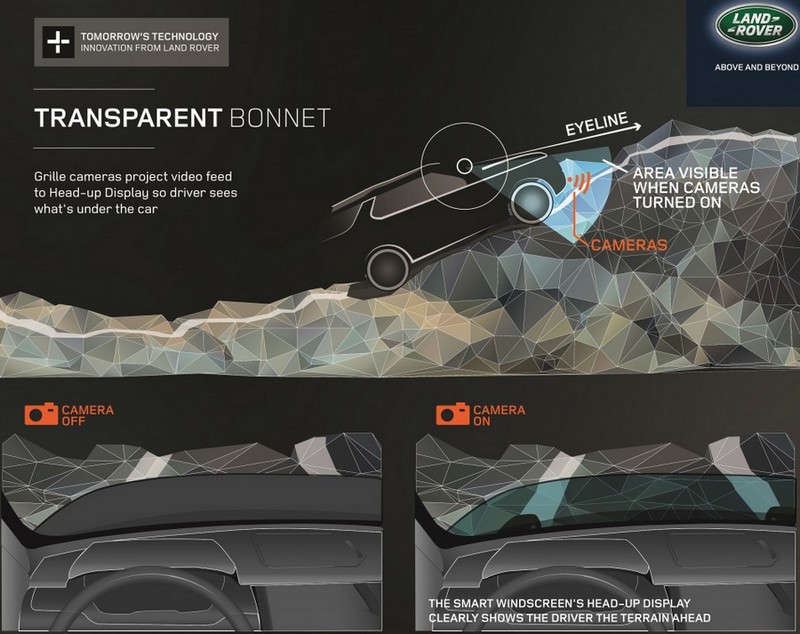
Why limit the scope of the possible projection of the windshield? Approximately such reasoning was guided by the authors of modern concepts of augmented reality systems. This is the “transparent hood” system in Land Rover cars (the system allows the driver to see the road surface, which is hidden under normal conditions, implemented with the help of cameras and projectors inside the car) and the concept of a virtual screen with “hints” regarding the required trajectory of movement (exactly like in the NFS Shift game series).
A more extravagant solution is the concept of a completely transparent car of Japanese University Keio. In it, the back seat of the car becomes transparent, so as not to block the driver's view when driving in reverse. Behind the car is a projector that projects the image onto a reflective screen located between the two front seats and slightly behind them.

When the driver turns back over his shoulder, he sees almost a real view from the back of the car, but only through augmented reality. The concept is certainly interesting, but obviously does not take into account the presence of passengers in the car. Most likely, such systems will still conquer the cars of the future, projecting the image in the form of augmented reality in one form or another.
Alternative management methods
In addition to voice control or entering the desired route through the touch screen (in a hypothetical self-driving car of the future), automakers are experimenting with more exotic methods of control - including gesture control. Back in 2012, Mercedes-Benz, presented the concept of the cabin called DICE (Dynamic & Intuitive Control Experience).
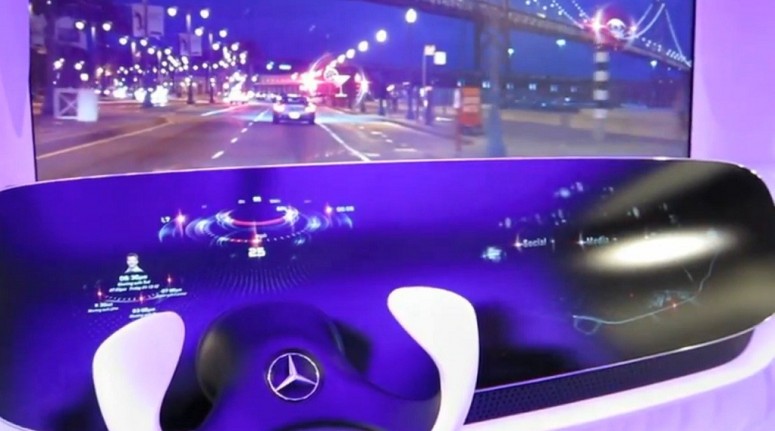

Instead of the windshield, it was proposed to use the display, and using sensors to track the position of the hand of the driver or front passenger in space and monitor its movements to adjust and adjust the functions of the car. Even with super-high resolution screens, drivers are unlikely to soon agree to use them instead of a windshield. Audi also demonstrated the gesture control system in the same year, but there it was used to change the HUD display modes. So, apart from sensors that monitor a seatbelt or passengers in the cabin, in the cabin of the future one can expect a much larger number of different “tracking systems”, like Leap Motion.
Social networks of the future and cars
Even today, social networks and services "for motorists" can significantly influence the traffic situation. There are many examples of this - such applications as Waze (a crowdsourcing project based on user data, with the help of which project participants learn about problems on the roads) even the police point out, speaking both with criticism and with approval. The possibility of notifications about the location of patrols has caused law enforcement concerns for the safety of police officers. Examples of social interactions at the level of “car-car” or “car-infrastructure” can take different forms - these are loyalty programs from gas stations, free electric stations for electric vehicles, optimization of parking places in the city depending on occupancy, taxi call system without a dispatcher, “gamification "And" achievements "(for example, scoring for a safe ride) when using a car. Most of these functions are not surprising in their own right, but they will undoubtedly be developed in future cars.
Afterword
Of course, it’s almost impossible to guess what cars or their electronics will be after several decades. Obviously, car electronics expects a qualitative leap, because every year the concepts at car shows begin to resemble real “cars from the future”, which we presented only in fantastic works. It remains only to wait a bit and we will see what other technologies of the future will seem to us as familiar as a car stereo or DVR.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/365121/
All Articles