Crowd mapping open-source solution: Nextgis Crowd
A couple of days ago, Maxim Dubinin and Ivan Kovalev officially released their long-term construction project - Nextgis Crowd - open source geodata editor.
github.com/nextgis/nextgiscrowd
')
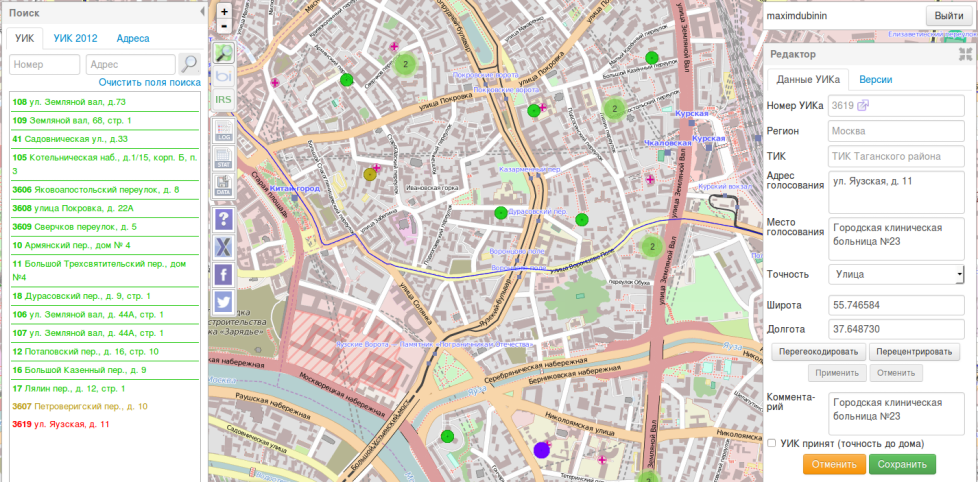
NextGIS Crowd (NGC) allows you to jointly edit the location and description of points with any set of attributes. For the past few years, NGC has been successfully used in the PEC GEO crowdsourcing project to collect information on precinct election commissions (remember, then there were elections?) - hundreds of users contributed tens of thousands of PECs with a description (not without the help of some automation;)
1. Initialize virtualenv
2. Clone the repository
3. We put packages
4. Create and copy the file to the root directory.
5. Edit the config.json see template
6. Run the demon
You need to collect and mark on the map 1000dachas xxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx deleted by the censor xxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx objects of increased public interest that are not on any finished map. You raise a copy of NGC on your server, throw a cry in a popular blog, attract users, crowds of users register on your site and begin to add and edit points and their description. Once a day (or more often) the collected data is automatically uploaded to .CSV files accessible to everyone. Profit!
Search and any filter samples included in the standard delivery.
The code is written in Python (server) and JavaScript (client part) and published under the open license of GNU GPLv2. System requirements: Python 2.7+, spatialite, GEOS, PROJ.4, Virtualenv.
The code is provided “as is”, send your pull-requests.
The project was implemented with the support of the Greenhouses of social technologies .

github.com/nextgis/nextgiscrowd
')
NextGIS Crowd (NGC) allows you to jointly edit the location and description of points with any set of attributes. For the past few years, NGC has been successfully used in the PEC GEO crowdsourcing project to collect information on precinct election commissions (remember, then there were elections?) - hundreds of users contributed tens of thousands of PECs with a description (not without the help of some automation;)
How to put?
1. Initialize virtualenv
virtualenv ngcrowd 2. Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/nextgis/nextgiscrowd.git 3. We put packages
cd <PATH_TO_YOUR_VIRTUAL_ENV>/nextgiscrowd ../bin/python setup.py develop 4. Create and copy the file to the root directory.
development.ini and fill in based on an example5. Edit the config.json see template
6. Run the demon
cd <PATH_TO_YOUR_VIRTUAL_ENV>/nextgiscrowd ../bin/pserve development.ini --daemon start Use case
You need to collect and mark on the map 1000
Search and any filter samples included in the standard delivery.
Under the hood:
The code is written in Python (server) and JavaScript (client part) and published under the open license of GNU GPLv2. System requirements: Python 2.7+, spatialite, GEOS, PROJ.4, Virtualenv.
The code is provided “as is”, send your pull-requests.
The project was implemented with the support of the Greenhouses of social technologies .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/364651/
All Articles