Chinese space program: own rover, space station by the end of the next five-year plan + heavy launch vehicle

China is very actively developing its own space program, not limited to flights to the moon and plans to select a little lunar soil for study. On the contrary, the more successfully the various stages of the Chinese space program are implemented, the more new stages are planned by the Chinese.
The other day, Li Fanpay, the head of the Chinese Space Science and Technology Corporation, shared some of the details of China’s future space program.
')
Mars rover in 2020

The Chinese plan to send their own rover to Mars to explore the Red Planet. Now specifically for this mission, a Long March-5 launch vehicle is being developed, which will take the lander with the Mars rover to Mars.
After the successful landing of the Chinese lunar rover, the Celestial experts decided to use the design of the "Yuytu" as the basis for the Martian ground vehicle. The model of such a device has already been described at Geektimes .
Orbital station in 2022
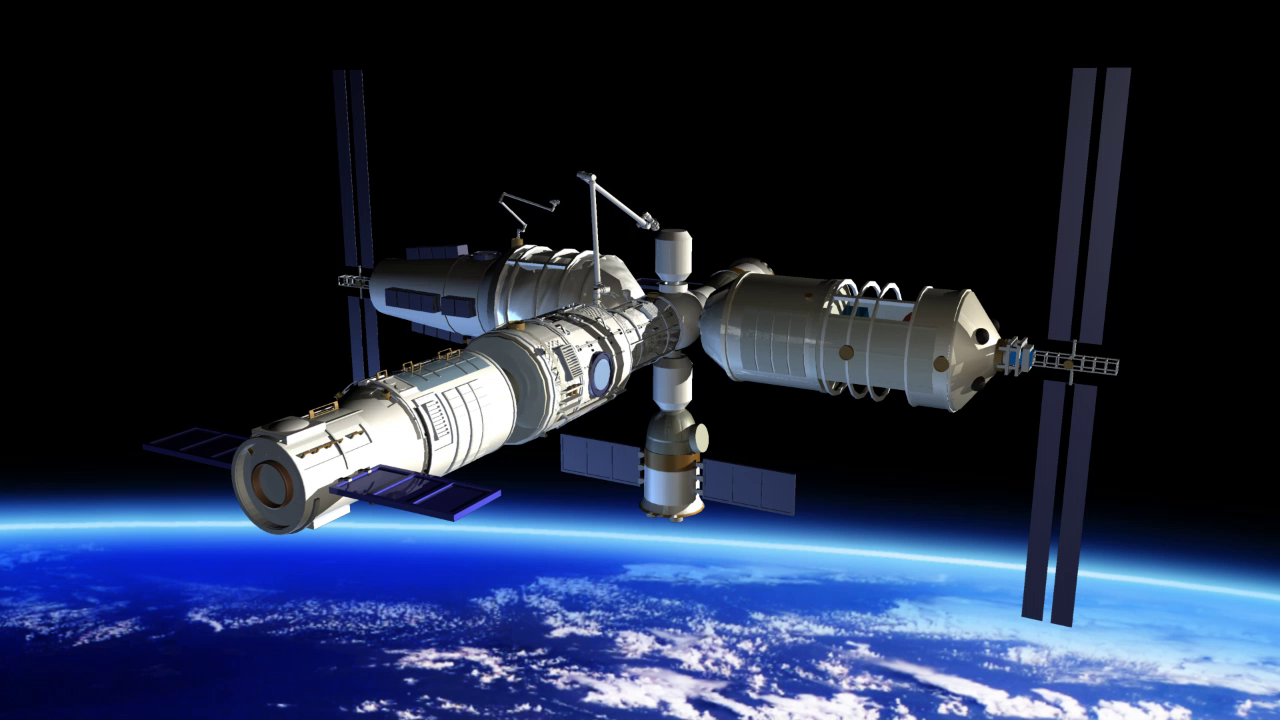
China plans to create a habitable orbital Chinese station. These plans have been implemented for quite some time, and now some stages of the project have already been completed. So, many modules, mechanisms and elements of the station are ready.
The development and production of other elements is also at the stage of re-deployment, including the Tiangong-2 space laboratory, the Tianzhou-1 cargo ship, the Long March-7 rocket and the Shenzhou-11 spacecraft. Two main modules and two space laboratories will soon be tested for "professional suitability."
Almost ready and the Hainan Cosmodrome - this is the fourth cosmodrome in China. It is located in 19 degrees north of the equator, which opens up opportunities for Chinese experts. This spaceport will be used to launch heavy space rockets, deep-space research vehicles, launch vehicles for sending space station modules.
The Tiangong-2 space laboratory will be tested as early as 2016, along with the ship Shenzhou-11 and the Tianzhou-1 truck. And in 2018, the main module of the space station will be sent into space.
By 2022, the orbital space station of China should be fully prepared ... It will consist of three parts: the main module and two laboratories. Each module will weigh about 20 tons.
Tiangong-1 was launched in September 2011. In June 2012, Shenzhou-9 performed the first guided docking operation with Tiangong-1.
Heavy booster
A powerful carrier rocket is needed by the country to complete the key stages of space exploration, including landing on the moon (with human participation). The development of a 460-ton oxygen-kerosene engine and a 220-ton liquid hydrogen engine are underway.
The creation of a heavy carrier rocket is planned for 15 years, so such a rocket will go into space no earlier than 2030 At the same time, it will be possible to take about 130 tons of payload (to a low orbit). The main load will be performed by a rocket in the years 2030-2050.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/364063/
All Articles