Satellite - it's very simple - 2
In the publication “Satellite - it is very simple” it was told how easy it is to hear satellites in near-earth orbits now and about the ability to decipher the received signals of some satellites. Unfortunately, this telemetric information remains inaccessible to interested parties.
And althoughspace ships plow the vastness of the Bolshoi Theater, satellites are successfully placed into orbit and transmit information about the experiments being conducted, but their owners can “hear” only a few minutes. Therefore, the owners of various CubeSat publish instructions and software for receiving their satellites, hoping to get as much telemetric information from enthusiasts as possible. For example, for the Manfred Memorial Moon Mission (4M) , a contest was held among enthusiasts who sent the highest amount of received telemetry.
A possible solution to this issue could be the SatNOGS project , which is a project for mass construction and deployment of amateur tracking stations around the world based on open source technologies and open standards.
')
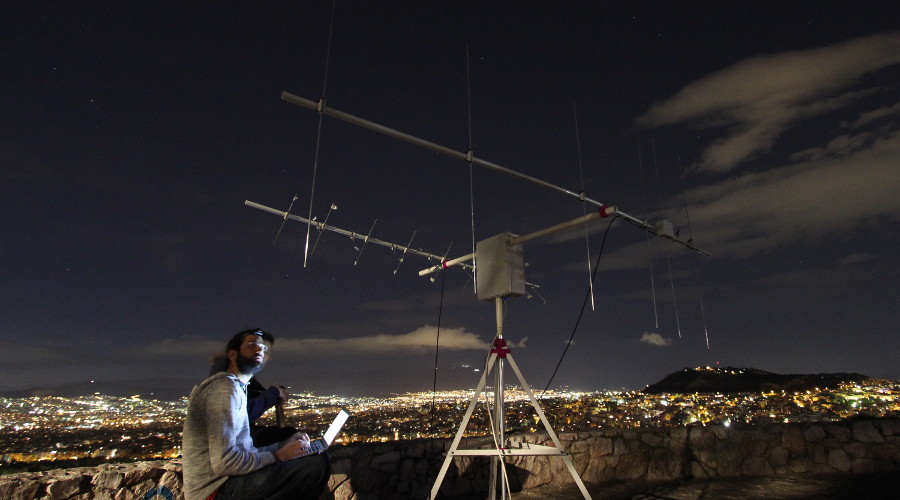

The SatNOGS station is modular and can be easily modified. The station connects to the Internet and is fully automated.
The following diagram shows the essence of the project:
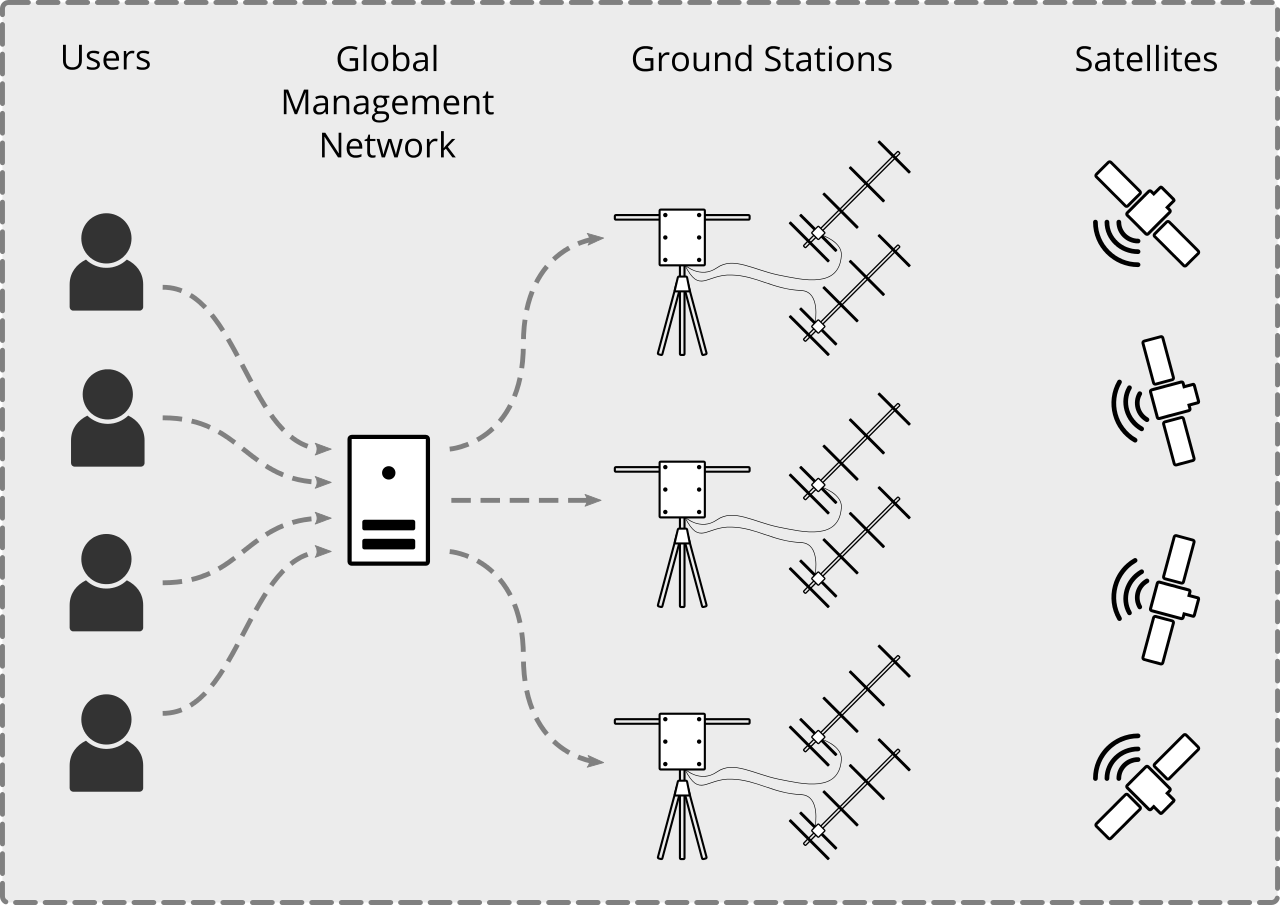
Through the Global Management Network, observers interact with several tracking stations. The collected data will be available to the public through its own website.
The SatNOGS tracking station is an azimuth-turning device, antennas, LNAs and an embedded system that receives scheduled operations from the Global Management Network, records the observations and sends them back to the Global Management Network.
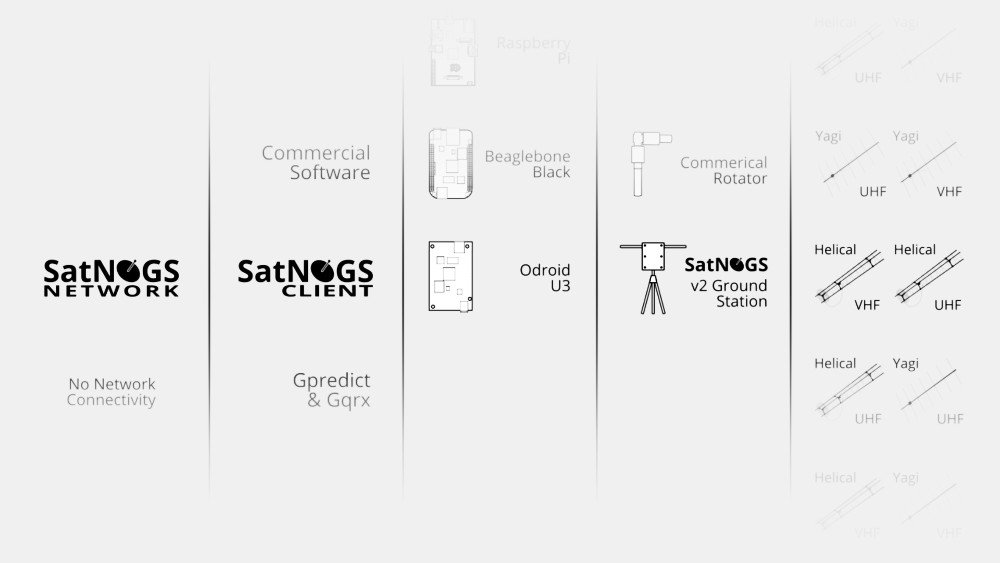
The station configuration can be modified - factory or homemade azimuth-rotary device, different types of antennas:
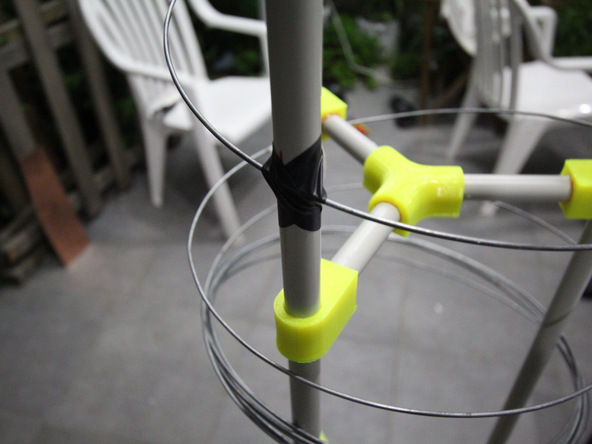
The independent production of the rotator and antennas is well illustrated , and the design uses readily available and cheap materials. For example, plumbing PVC pipes:
The station consists of three parts:
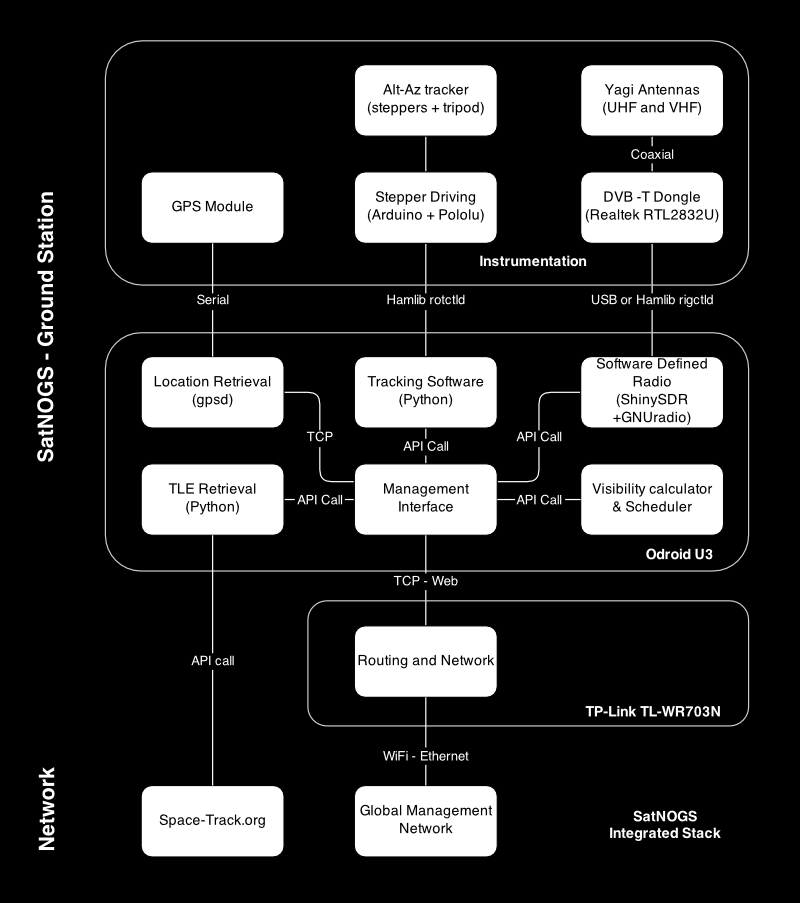
Instrumentation - this antenna, diplexer, amplifier, receiver RTL-SDR, GPS, turning device.
Odroid U3 - station computer to which the functions of antenna control, processing of the work queue, reception and decoding of the signal are assigned.
TP-Link TL-WR-703N - for accessing the Internet via WiFi.
The station is built from the following components:
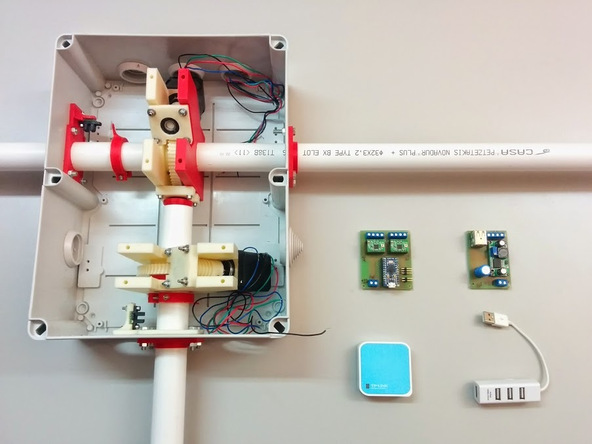
All components are placed inside an easily purchased electrical box:

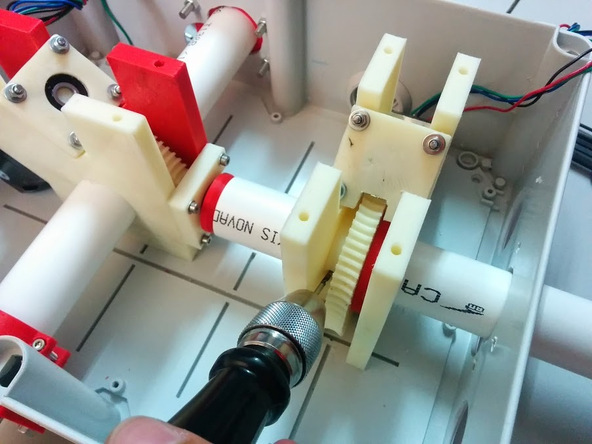
In which mechanical assemblies made on a 3D printer and stepper motors are first mounted:
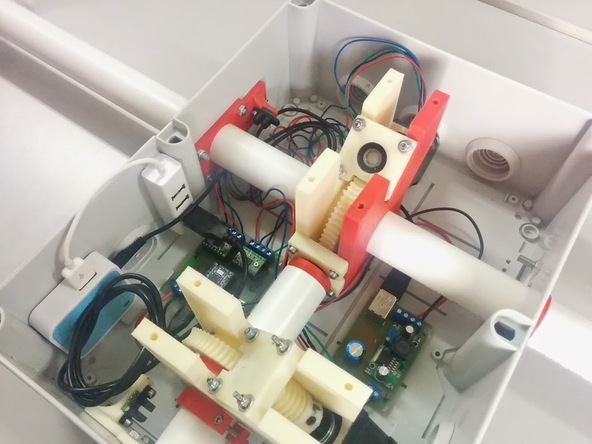
Then electronic components are mounted there:
It remains to proceed to the installation of software for hardware .
Satellites are waiting!
And although
A possible solution to this issue could be the SatNOGS project , which is a project for mass construction and deployment of amateur tracking stations around the world based on open source technologies and open standards.
')

The SatNOGS station is modular and can be easily modified. The station connects to the Internet and is fully automated.
The following diagram shows the essence of the project:

Through the Global Management Network, observers interact with several tracking stations. The collected data will be available to the public through its own website.
The SatNOGS tracking station is an azimuth-turning device, antennas, LNAs and an embedded system that receives scheduled operations from the Global Management Network, records the observations and sends them back to the Global Management Network.
The station configuration can be modified - factory or homemade azimuth-rotary device, different types of antennas:

The independent production of the rotator and antennas is well illustrated , and the design uses readily available and cheap materials. For example, plumbing PVC pipes:

The station consists of three parts:

- Instrumentation
- Odroid u3
- TP-Link TL-WR-703N
Instrumentation - this antenna, diplexer, amplifier, receiver RTL-SDR, GPS, turning device.
Odroid U3 - station computer to which the functions of antenna control, processing of the work queue, reception and decoding of the signal are assigned.
TP-Link TL-WR-703N - for accessing the Internet via WiFi.
The station is built from the following components:
- 2 stepper motors
- 2 drivers A4988 stepper motors
- Arduino Micro (controls the engines on commands Odroid U3)
- TP-Link WR703N
- DVB-T receiver based on RTL2832U
- One directional antenna for 2 meter and 70 cm ranges
- ODROID U3
All components are placed inside an easily purchased electrical box:

In which mechanical assemblies made on a 3D printer and stepper motors are first mounted:

Then electronic components are mounted there:


It remains to proceed to the installation of software for hardware .
Satellites are waiting!

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/363341/
All Articles