Electric Dawn: 19th Century
At the end of the 19th century, electric cars and taxis rolled around the cities of France and England, in 1889 a Russian engineer built a two-seat electric car with a power reserve of 1 km. And in the Soviet Union, on electric NAMI-751 with a carrying capacity of one and a half tons in 1948, mail was transported, but that is another story. Under the cut - a brief excursion into the history of electric vehicles of the last century.
The whole cycle of articles:
Electric Dawn: 19th Century
Dawn and sunset of electric vehicles: the first half of the XX century
Electric car strikes back: the second half of the XX century
Revenge of the electric car: the beginning of the XXI century
')

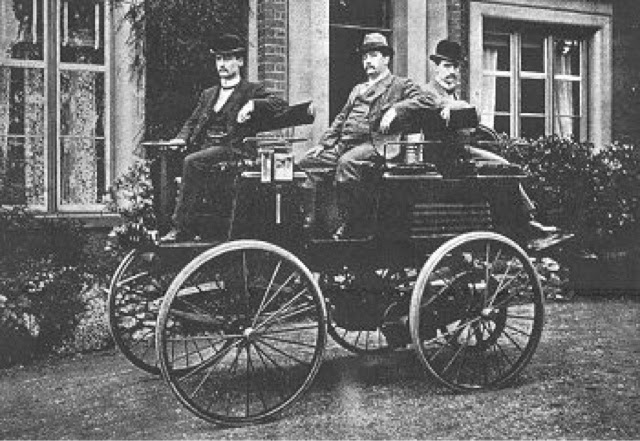
The first internal combustion engine, suitable for use, was designed by the French inventor of Belgian origin, Etienne Lenoir, in 1860. The power of this engine was 12 horsepower, it worked on a mixture of air and light gas with electric spark ignition. The electric motor appeared earlier: in 1841 it was equipped with a trolley. Even earlier, in 1828, Hungarian Agnos Dzhedlik used an electric motor for a tiny, skateboard-like car.
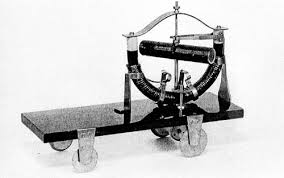
In 1888, a three-wheeled vehicle was introduced in the USA. The ten lead-acid batteries manufactured by the Electrical Accumulator Company weighed about forty kilograms. The maximum construction speed was eight miles per hour. Engine power - 0.5 horsepower. It was rather a three-wheeled electric bike.
The lead battery was invented by Gaston Plante in 1859-1860, and in 1878 Camille Faure improved its design. Today, these batteries are used in automotive or moto transport as starter batteries.
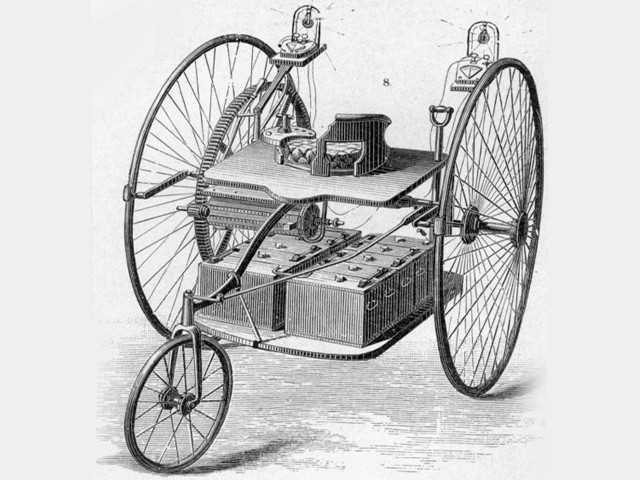
Thomas Perker was responsible for the electrification of the London Underground. And he designed and built this electric car in 1884. In addition, he himself developed a battery for his vehicle.

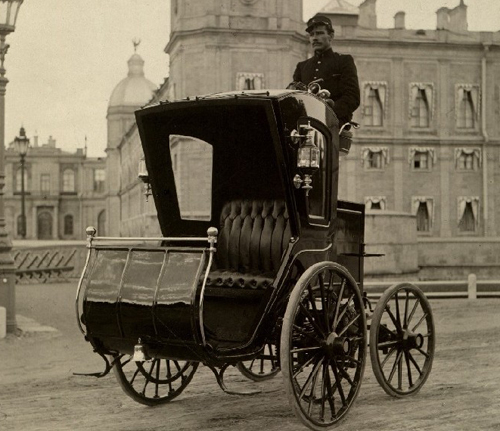
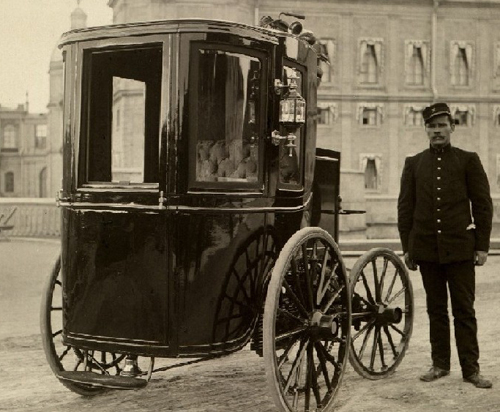
In 1889 the first Russian two-seater electric car appeared. It was created by engineer Ippolit Romanov. In this front-wheel-drive vehicle, passengers were located in front, and the driver was in the back of the seat above them. The batteries located in the compartment behind the cabin were lighter than their analogues, which made it possible to reduce the weight of the car to 720 kg. The French “Zhanto”, popular at that time, weighed 1440 kg The maximum speed was 35 km / h, and the power reserve is just over 1 kilometer. At 1800 rpm, each of the engines gave a power of 4.4 kW, which is equivalent to 5.984 horsepower.


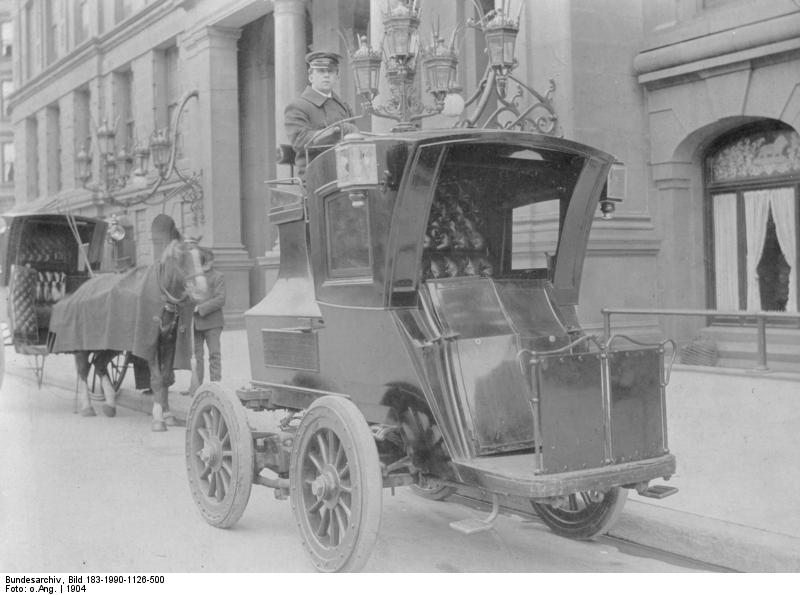
The first electromobile in Germany was built by engineer Andreas Floken in 1888. This photo is one of the German electric-powered cars in 1904.

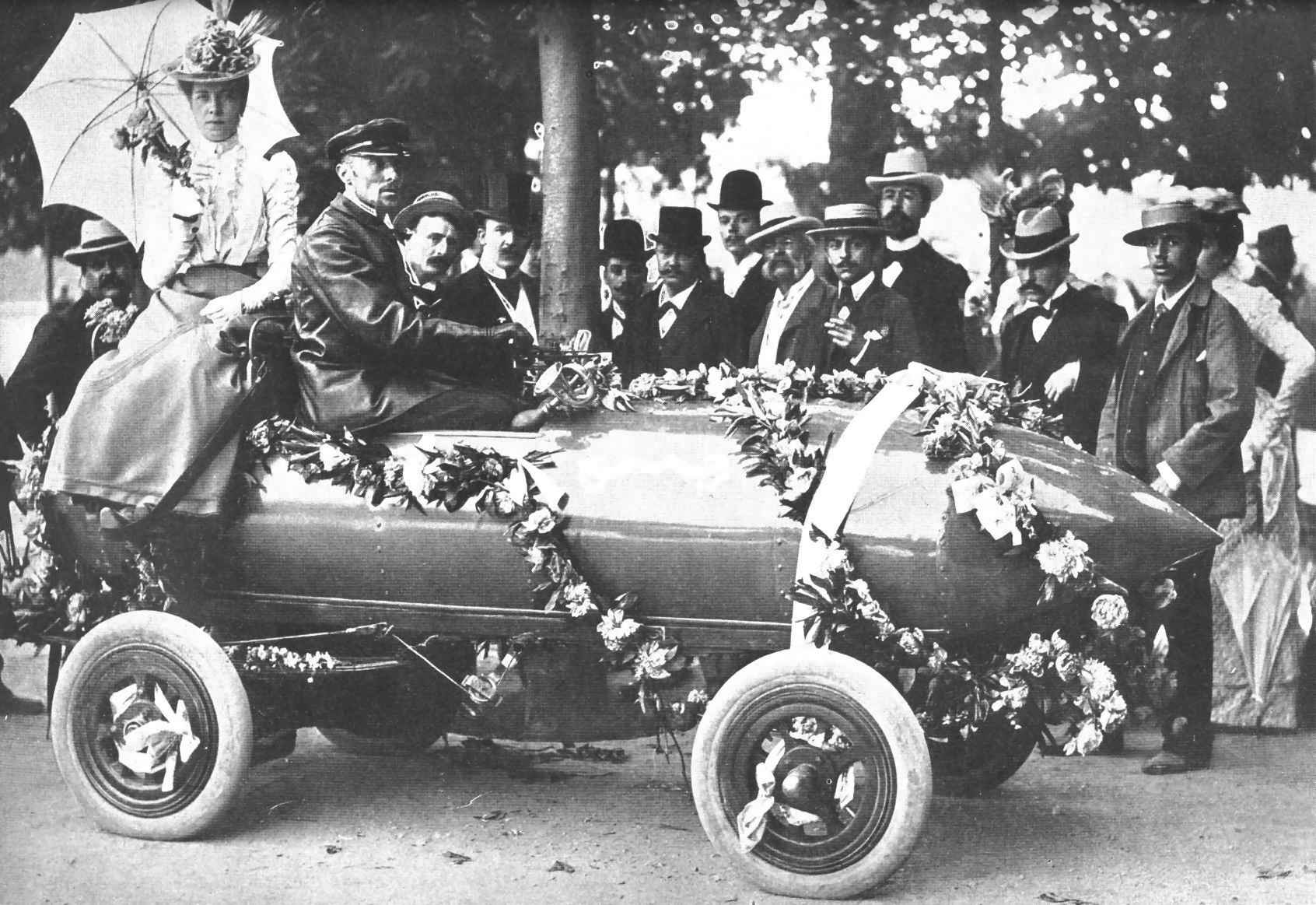
The first speed record of an electric car was made in France on December 18, 1898 in a Jentaud car “charged” with alkaline batteries. The speed was 62.792 km / h. After 4 months the record was broken by the electric car Le Jamais Contende - this time the speed exceeded one hundred and made 105.264 km / h.


Power reserve and speed in the late XIX - early XX century in electric vehicles and cars with an internal combustion engine were about the same, but recharging the batteries was somewhat more difficult - it was impossible to just plug the electric vehicle into an outlet and wait a few hours, an AC-DC converter was needed. For this, an AC-powered electric motor was used - it rotated the generator shaft to which the batteries were connected.
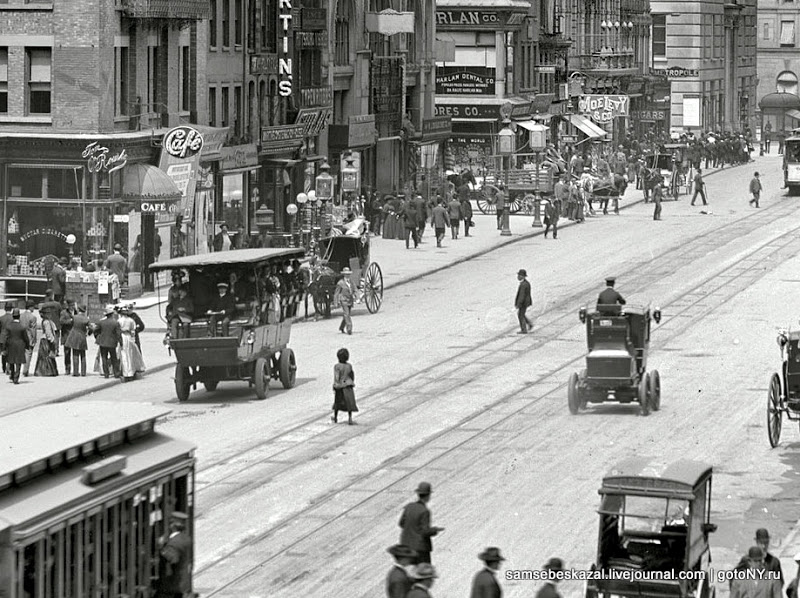
This photograph, taken in 1905, shows two vehicles on electric propulsion: on the left — the bus: on the right — a taxi. Picture taken on Broadway in Times Square.

The history of electric cars, taxis in the United States began with Electrobat from the company Electric Vehicle Co.

Taxi in 1897.

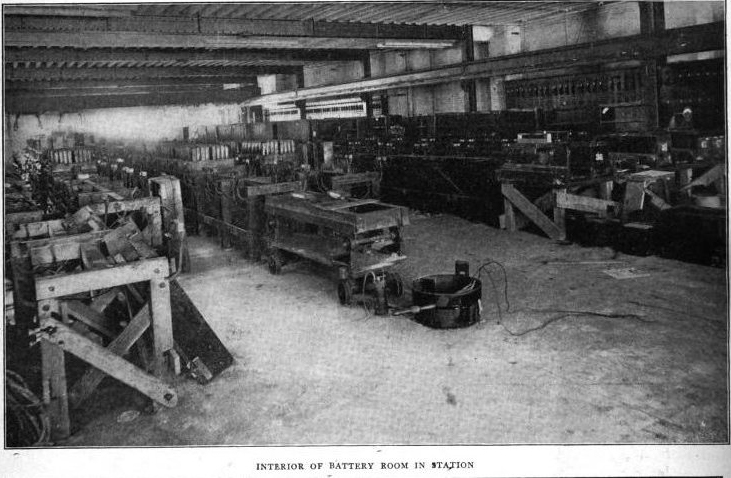
These taxis were charged in a special room.

Continued:
Dawn and sunset of electric vehicles: the first half of the XX century
The whole cycle of articles:
Electric Dawn: 19th Century
Dawn and sunset of electric vehicles: the first half of the XX century
Electric car strikes back: the second half of the XX century
Revenge of the electric car: the beginning of the XXI century
The term electric car means a car that uses electric energy from a chemical power source to drive the driving wheels. O.A. Stavrov
')

The first internal combustion engine, suitable for use, was designed by the French inventor of Belgian origin, Etienne Lenoir, in 1860. The power of this engine was 12 horsepower, it worked on a mixture of air and light gas with electric spark ignition. The electric motor appeared earlier: in 1841 it was equipped with a trolley. Even earlier, in 1828, Hungarian Agnos Dzhedlik used an electric motor for a tiny, skateboard-like car.

In 1888, a three-wheeled vehicle was introduced in the USA. The ten lead-acid batteries manufactured by the Electrical Accumulator Company weighed about forty kilograms. The maximum construction speed was eight miles per hour. Engine power - 0.5 horsepower. It was rather a three-wheeled electric bike.
The lead battery was invented by Gaston Plante in 1859-1860, and in 1878 Camille Faure improved its design. Today, these batteries are used in automotive or moto transport as starter batteries.

Thomas Perker was responsible for the electrification of the London Underground. And he designed and built this electric car in 1884. In addition, he himself developed a battery for his vehicle.

In 1889 the first Russian two-seater electric car appeared. It was created by engineer Ippolit Romanov. In this front-wheel-drive vehicle, passengers were located in front, and the driver was in the back of the seat above them. The batteries located in the compartment behind the cabin were lighter than their analogues, which made it possible to reduce the weight of the car to 720 kg. The French “Zhanto”, popular at that time, weighed 1440 kg The maximum speed was 35 km / h, and the power reserve is just over 1 kilometer. At 1800 rpm, each of the engines gave a power of 4.4 kW, which is equivalent to 5.984 horsepower.


The first electromobile in Germany was built by engineer Andreas Floken in 1888. This photo is one of the German electric-powered cars in 1904.

The first speed record of an electric car was made in France on December 18, 1898 in a Jentaud car “charged” with alkaline batteries. The speed was 62.792 km / h. After 4 months the record was broken by the electric car Le Jamais Contende - this time the speed exceeded one hundred and made 105.264 km / h.


Power reserve and speed in the late XIX - early XX century in electric vehicles and cars with an internal combustion engine were about the same, but recharging the batteries was somewhat more difficult - it was impossible to just plug the electric vehicle into an outlet and wait a few hours, an AC-DC converter was needed. For this, an AC-powered electric motor was used - it rotated the generator shaft to which the batteries were connected.
This photograph, taken in 1905, shows two vehicles on electric propulsion: on the left — the bus: on the right — a taxi. Picture taken on Broadway in Times Square.

The history of electric cars, taxis in the United States began with Electrobat from the company Electric Vehicle Co.

Taxi in 1897.

These taxis were charged in a special room.


Continued:
Dawn and sunset of electric vehicles: the first half of the XX century
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/363129/
All Articles