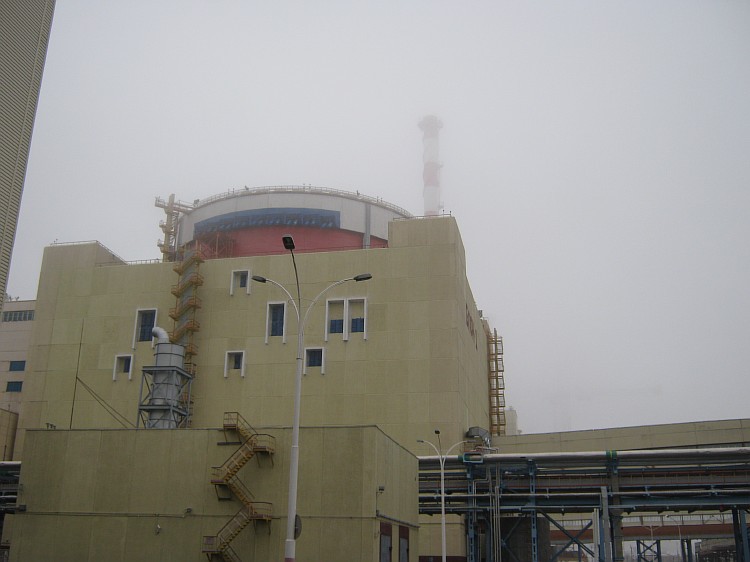
Little about nuclear power plants
Despite the fact that for many years the disputes around nuclear power plants have not abated, most people have little idea what kind of animal they are, although they probably know some legend about nuclear power plants. In the article I will try to tell you in general terms how it all works. Some secrets and revelations should not be expected, but I hope someone will learn something new for themselves.

')
Fuel assemblies consisting of a bundle of zirconium fuel elements (fuel rods) filled with uranium dioxide tablets are loaded into the reactor core.
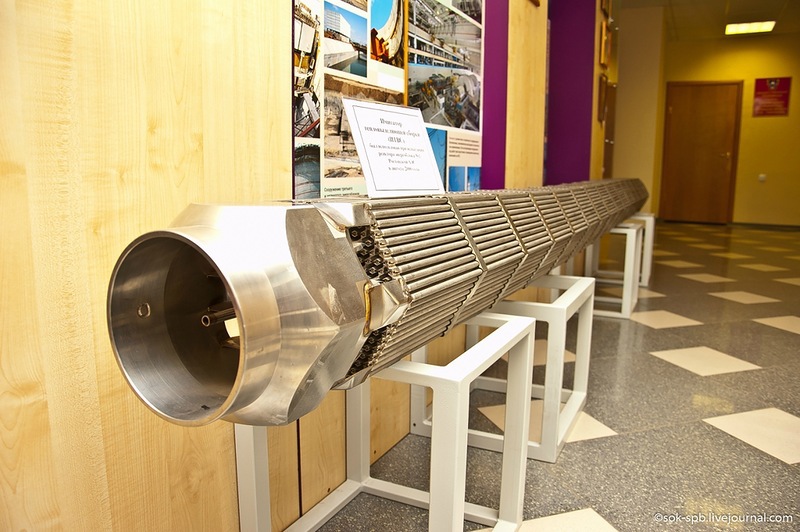

Life size fuel assembly
The uranium nuclei are divided to form neutrons (2 or 3 neutrons), which, falling into other nuclei, can also cause their division. So there is a nuclear chain reaction. The ratio of the number of neutrons formed to the number of neutrons in the previous fission step is called the neutron multiplication factor k. If k <1, the reaction decays. When k = 1, a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction takes place. When k> 1, the reaction is accelerated, up to a nuclear explosion. A controlled nuclear chain reaction is maintained in nuclear reactors, keeping k close to unity.
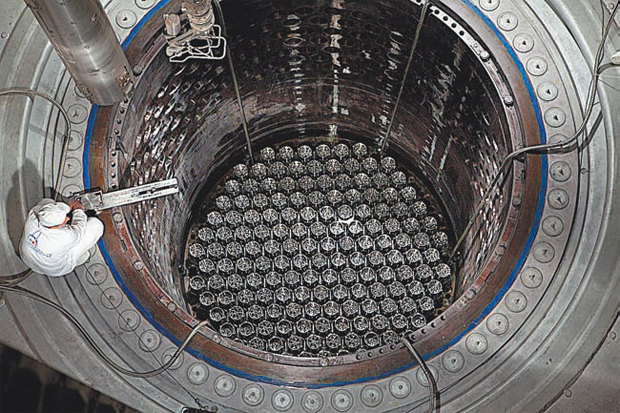
A reactor with loaded fuel assemblies
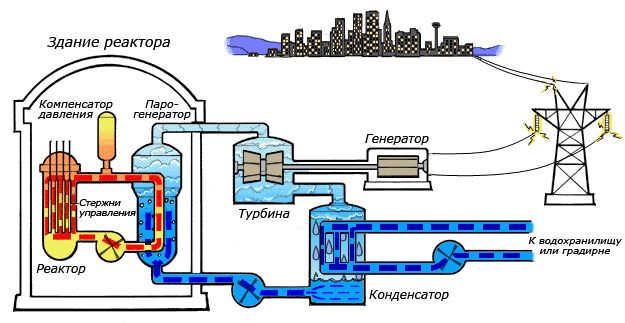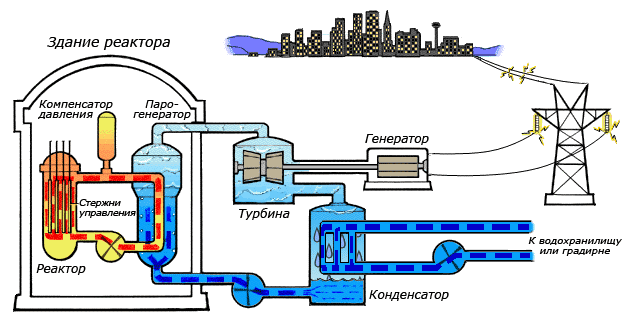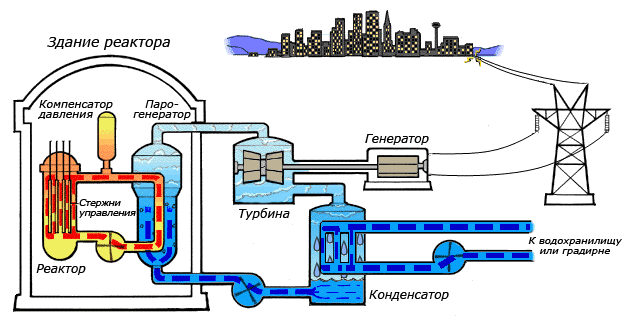
During the course of a chain reaction, a large amount of energy is released in the form of heat, which heats the primary coolant - water, which is fed from below to the reactor core by means of main circulation pumps (MCP). When heated to a temperature of 322 ° C, water enters the steam generator (heat exchanger), where, after passing through thousands of heat exchange tubes and giving up some heat to the water of the second circuit, it enters the core again. Since the pressure of the second circuit is lower, the water in the steam generator boils, forming steam with a temperature of 274 ° C, which is fed to the turbine. As it enters the high-pressure cylinder and then into three low-pressure cylinders, steam spins the turbine, which in turn rotates the generator, generating electricity. Exhaust steam enters the condenser, in which it, as you might guess, is condensed with cold water from a cooling pond or cooling tower and returns to the steam generator again with the help of feed pumps.
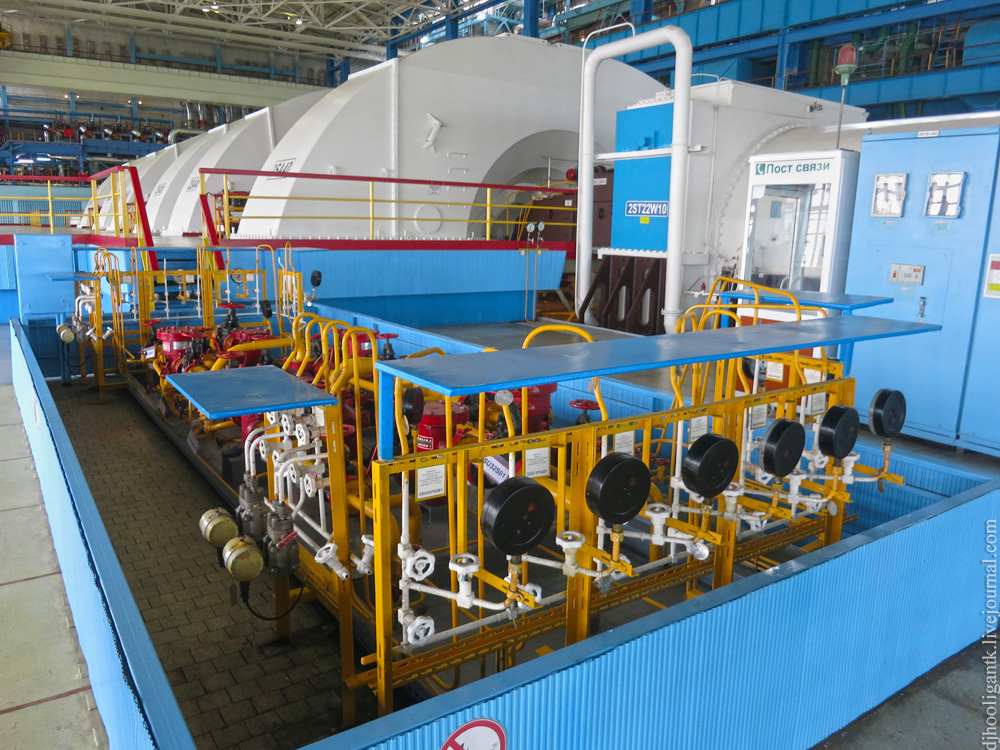

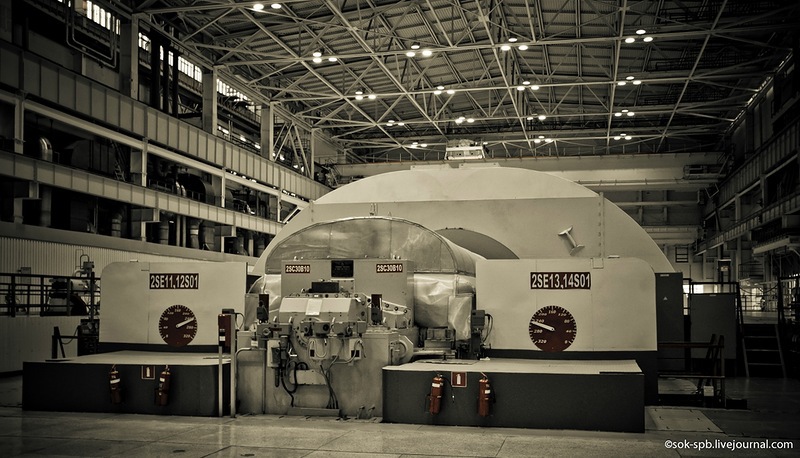
Turbine room and the turbine itself
Such a complex two-circuit system is designed to protect equipment (turbine, condenser), and the environment from radioactive particles from the primary circuit, the appearance of which is possible due to equipment corrosion, induced radioactivity, and depressurization of TVEL shells.
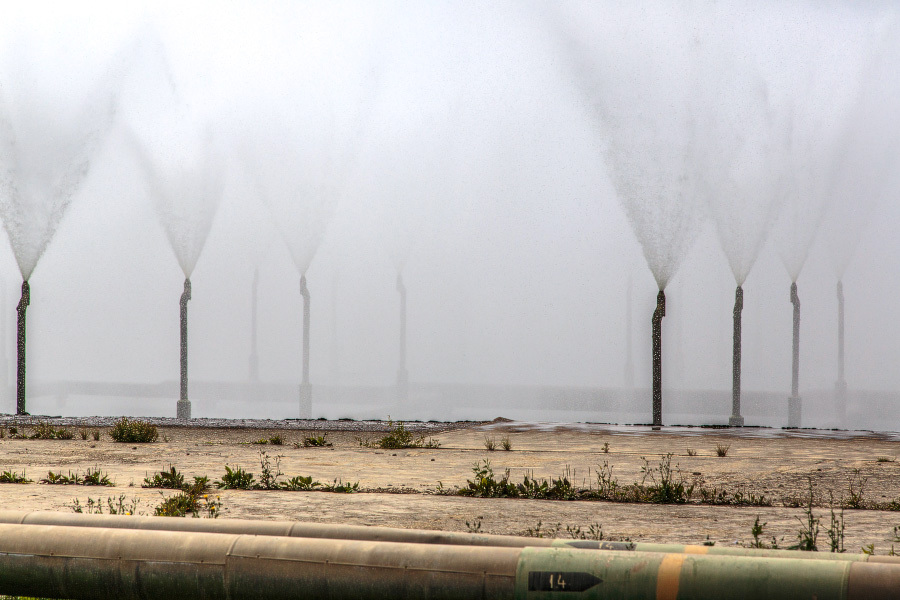

Spray pool cooling backup diesel generators and security systems
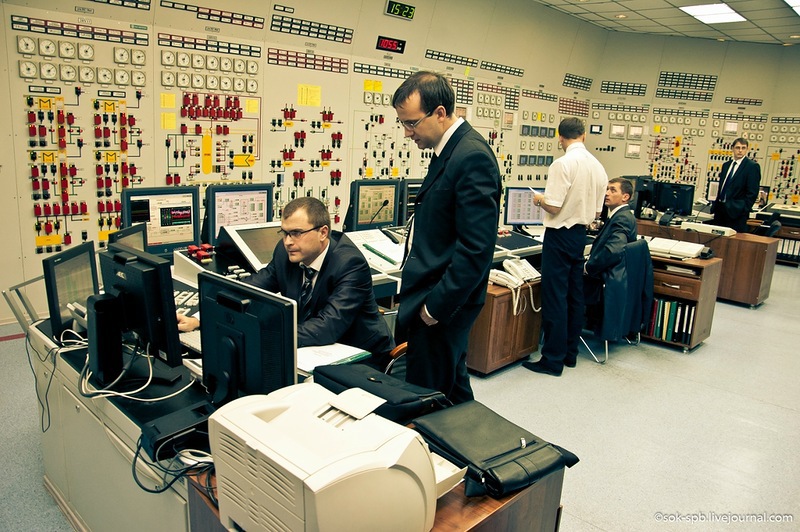
The control of blocks is carried out from a block control panel, which usually fascinates a simple man in the street with an abundance of "lights, twists and buttons".

It is located in the reactor compartment, but in the “clean zone” and on it are constantly located: the lead engineer for managing the reactor, the lead engineer for managing turbines, the lead engineer for managing the unit and the head of the shift unit.

A surveillance zone (the same thirty-kilometer zone) is organized around the nuclear power plant, in which the radiation situation is constantly monitored. There is also a sanitary protection zone with a radius of 3 km (depending on the design capacity of the NPP), in which human habitation is prohibited, and agricultural activities are restricted.
The inner territory of the NPP is divided into two zones: a free access zone (clean zone), where the effects of radiation factors on personnel are practically excluded, and a controlled access zone (ACD), where radiation exposure on personnel is possible.
Access to the access control system is not allowed to everyone and is possible only through the sanitary inspection room, after the procedure of changing clothes in the special. clothing and receiving personal dosimeter. Access to the containment, in which the reactor itself and the primary circuit equipment are located, during the operation of the reactor at power is generally prohibited and is possible only in exceptional cases. Received doses of NPP workers are strictly fixed and normalized, although the actual exposure during normal reactor operation is hundreds of times lower than the dose limits.
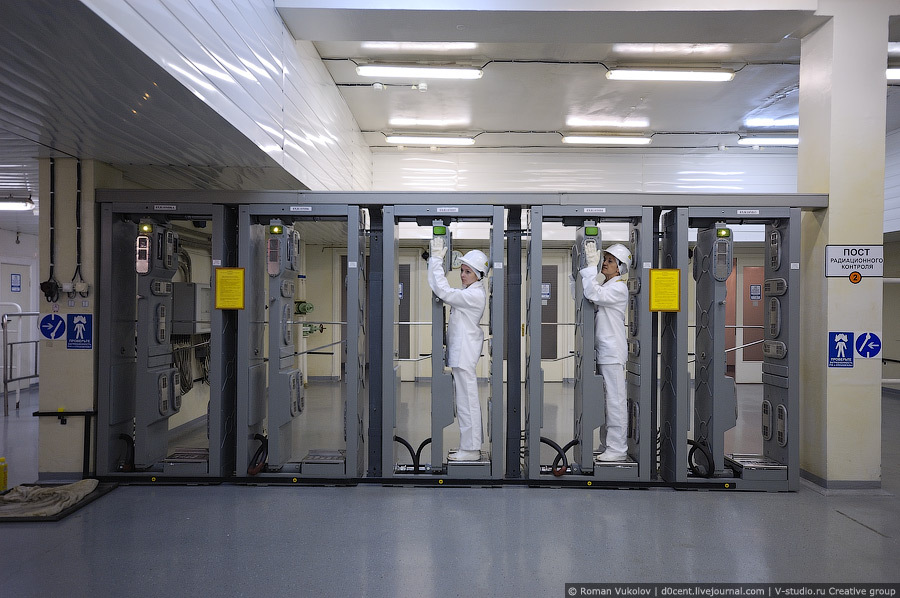

Dosimetric control at the outlet of the ZKD
 Probably the largest number of rumors and speculation go around nuclear power plant emissions. Emissions do exist and they occur, mainly through ventilation pipes - these are the very pipes that stand near each unit and never smoke. For the most part, inert radioactive gases - xenon, krypton and argon - get into the atmosphere.
Probably the largest number of rumors and speculation go around nuclear power plant emissions. Emissions do exist and they occur, mainly through ventilation pipes - these are the very pipes that stand near each unit and never smoke. For the most part, inert radioactive gases - xenon, krypton and argon - get into the atmosphere.
But before being discharged into the atmosphere, the air from the NPP premises passes through a system of complex filters, where most of the radionuclides are removed. Short-lived isotopes decay even before the gases reach the top of the pipe, further reducing radioactivity. As a result, the contribution to the natural radiation background of the gas and aerosol emissions of nuclear power plants to the atmosphere is insignificant and they can generally be neglected. Therefore, atomic energy is one of the cleanest, in comparison with other power plants. In any case, all radioactive emissions from nuclear power plants are strictly controlled by environmentalists and ways are being developed to reduce them further.
All systems of the nuclear power plant are designed and operate according to numerous safety principles. For example, the concept of defense in depth implies the existence of several barriers to the spread of ionizing radiation and radioactive substances into the environment. It is very similar to the principle of Kashchei Immortal: the fuel is grouped into tablets, which are located in zirconium fuel elements, which are placed in a steel reactor vessel, which is placed in a reinforced concrete containment. Thus, the destruction of one of the barriers is compensated by the following. Everything is done to ensure that during any accident radioactive substances do not go beyond the controlled access zone.

Also, all systems have two- and threefold redundancy, in accordance with the principle of single failure, according to which the system should perform its functions without fail even if any of its elements fail. At the same time, the principle of diversity is applied, that is, the use of systems having different operating principles. For example, when an emergency protection is triggered, absorber rods fall into the reactor core and boric acid is injected into the primary coolant.
Power units are regularly displayed in scheduled preventive maintenance (CPD), during periods of which there is an overload of fuel, as well as diagnostics, repair and replacement of equipment, modernization of equipment. Once every four years, the operating power unit is displayed in a major SPR with full unloading of nuclear fuel from the reactor core, examination and testing of the internals, as well as strength testing of the reactor vessel.

Some security systems can be viewed at an interactive presentation from the Rosenergoatom website .
And you can virtually wander around the Balakovo NPP.

All photos are taken from open sources. The article will describe the reactors of the type VVER (water-cooled power reactors), as the most common.
Principle of operation

')
Fuel assemblies consisting of a bundle of zirconium fuel elements (fuel rods) filled with uranium dioxide tablets are loaded into the reactor core.

Life size fuel assembly
The uranium nuclei are divided to form neutrons (2 or 3 neutrons), which, falling into other nuclei, can also cause their division. So there is a nuclear chain reaction. The ratio of the number of neutrons formed to the number of neutrons in the previous fission step is called the neutron multiplication factor k. If k <1, the reaction decays. When k = 1, a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction takes place. When k> 1, the reaction is accelerated, up to a nuclear explosion. A controlled nuclear chain reaction is maintained in nuclear reactors, keeping k close to unity.

A reactor with loaded fuel assemblies
During the course of a chain reaction, a large amount of energy is released in the form of heat, which heats the primary coolant - water, which is fed from below to the reactor core by means of main circulation pumps (MCP). When heated to a temperature of 322 ° C, water enters the steam generator (heat exchanger), where, after passing through thousands of heat exchange tubes and giving up some heat to the water of the second circuit, it enters the core again. Since the pressure of the second circuit is lower, the water in the steam generator boils, forming steam with a temperature of 274 ° C, which is fed to the turbine. As it enters the high-pressure cylinder and then into three low-pressure cylinders, steam spins the turbine, which in turn rotates the generator, generating electricity. Exhaust steam enters the condenser, in which it, as you might guess, is condensed with cold water from a cooling pond or cooling tower and returns to the steam generator again with the help of feed pumps.

Turbine room and the turbine itself
Such a complex two-circuit system is designed to protect equipment (turbine, condenser), and the environment from radioactive particles from the primary circuit, the appearance of which is possible due to equipment corrosion, induced radioactivity, and depressurization of TVEL shells.

Spray pool cooling backup diesel generators and security systems
The control of blocks is carried out from a block control panel, which usually fascinates a simple man in the street with an abundance of "lights, twists and buttons".

It is located in the reactor compartment, but in the “clean zone” and on it are constantly located: the lead engineer for managing the reactor, the lead engineer for managing turbines, the lead engineer for managing the unit and the head of the shift unit.

A surveillance zone (the same thirty-kilometer zone) is organized around the nuclear power plant, in which the radiation situation is constantly monitored. There is also a sanitary protection zone with a radius of 3 km (depending on the design capacity of the NPP), in which human habitation is prohibited, and agricultural activities are restricted.
The inner territory of the NPP is divided into two zones: a free access zone (clean zone), where the effects of radiation factors on personnel are practically excluded, and a controlled access zone (ACD), where radiation exposure on personnel is possible.
Access to the access control system is not allowed to everyone and is possible only through the sanitary inspection room, after the procedure of changing clothes in the special. clothing and receiving personal dosimeter. Access to the containment, in which the reactor itself and the primary circuit equipment are located, during the operation of the reactor at power is generally prohibited and is possible only in exceptional cases. Received doses of NPP workers are strictly fixed and normalized, although the actual exposure during normal reactor operation is hundreds of times lower than the dose limits.

Dosimetric control at the outlet of the ZKD
Emissions
 Probably the largest number of rumors and speculation go around nuclear power plant emissions. Emissions do exist and they occur, mainly through ventilation pipes - these are the very pipes that stand near each unit and never smoke. For the most part, inert radioactive gases - xenon, krypton and argon - get into the atmosphere.
Probably the largest number of rumors and speculation go around nuclear power plant emissions. Emissions do exist and they occur, mainly through ventilation pipes - these are the very pipes that stand near each unit and never smoke. For the most part, inert radioactive gases - xenon, krypton and argon - get into the atmosphere.But before being discharged into the atmosphere, the air from the NPP premises passes through a system of complex filters, where most of the radionuclides are removed. Short-lived isotopes decay even before the gases reach the top of the pipe, further reducing radioactivity. As a result, the contribution to the natural radiation background of the gas and aerosol emissions of nuclear power plants to the atmosphere is insignificant and they can generally be neglected. Therefore, atomic energy is one of the cleanest, in comparison with other power plants. In any case, all radioactive emissions from nuclear power plants are strictly controlled by environmentalists and ways are being developed to reduce them further.
Security
All systems of the nuclear power plant are designed and operate according to numerous safety principles. For example, the concept of defense in depth implies the existence of several barriers to the spread of ionizing radiation and radioactive substances into the environment. It is very similar to the principle of Kashchei Immortal: the fuel is grouped into tablets, which are located in zirconium fuel elements, which are placed in a steel reactor vessel, which is placed in a reinforced concrete containment. Thus, the destruction of one of the barriers is compensated by the following. Everything is done to ensure that during any accident radioactive substances do not go beyond the controlled access zone.

Also, all systems have two- and threefold redundancy, in accordance with the principle of single failure, according to which the system should perform its functions without fail even if any of its elements fail. At the same time, the principle of diversity is applied, that is, the use of systems having different operating principles. For example, when an emergency protection is triggered, absorber rods fall into the reactor core and boric acid is injected into the primary coolant.
Power units are regularly displayed in scheduled preventive maintenance (CPD), during periods of which there is an overload of fuel, as well as diagnostics, repair and replacement of equipment, modernization of equipment. Once every four years, the operating power unit is displayed in a major SPR with full unloading of nuclear fuel from the reactor core, examination and testing of the internals, as well as strength testing of the reactor vessel.

Some security systems can be viewed at an interactive presentation from the Rosenergoatom website .
And you can virtually wander around the Balakovo NPP.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/362667/
All Articles