VPNFilter infected more than 500,000 devices worldwide

More than 500,000 routers and network drives from Linksys, MikroTik, Netgear, Qnap and TP-Link are infected with VPNFilter malware. The scale of the attack is comparable to the acclaimed Mirai, the consequences of which are still felt.
The information about the virus pandemic was published by the Talos division (Cisco), which analyzes cybersecurity threats.
After examining the behavior of this malware on network equipment, Talos experts noted several main features of this software:
')
- theft of web application credentials;
- monitoring of Modbus SCADA protocols;
- disabling the device.
The complexity of the protection and detection of this software is due to the nature of the attacked devices - routers and network drives are located on the network perimeter, are poorly protected and, as a rule, do not contain IDS / IPS systems due to technological simplicity and limited resources typical for embedded / IoT devices.
The malicious program VPNFilter is a modular platform consisting of at least two main components: a dropper and a control module.
After the device has been infected, a so-called device is installed on it A dropper capable of “reliving” a device reboot, and a main module downloading it.
The main module, which does not persist at reboot, can collect files, execute commands, filter data, and manage devices. Also, some versions of this module contain the functions of self-destruction and disabling the device by overwriting critical areas of the network device's memory.
In addition, there are several auxiliary modules that have the functionality of network sniffers for collecting network traffic, monitoring the SCADA Modbus protocol, and a communication module for interacting with hacked devices via the Tor network.
The malware scans TCP ports 23, 80, 2000 and 8080 to detect and attack new Linux / Busybox devices.
It is known about successful attacks on the following devices:
- Linksys E1200;
- Linksys E2500;
- Linksys WRVS4400N;
- Mikrotik RouterOS (1016, 1036 and 1072);
- Netgear DGN2200;
- Netgear R6400;
- Netgear R7000;
- Netgear R8000;
- Netgear WNR1000;
- Netgear WNR2000;
- QNAP TS251;
- QNAP TS439 Pro;
- QNAP NAS with QTS software;
- TP-Link R600VPN.
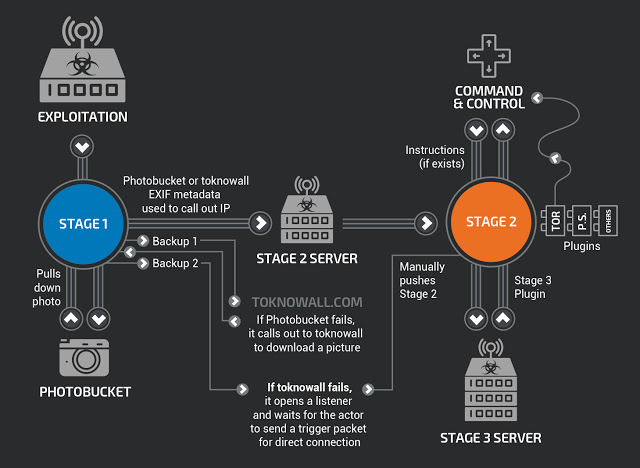
At the moment, the vector of infection and loading of the first VPNFilter module is unclear, but details of loading and managing the infected device are known. After the malware has completed its initialization, it starts loading the pages of Photobucket.com (an image storage site). The malware downloads the first image from the gallery referenced by the URL, and then proceeds to retrieve the IP address of the download server. The IP address is extracted from six integer values for the latitude and longitude of the GPS in the EXIF information.
Currently using the following C & C URLs:
- photobucket.com/user/nikkireed11/library
- photobucket.com/user/kmila302/library
- photobucket.com/user/lisabraun87/library
- photobucket.com/user/eva_green1/library
- photobucket.com/user/monicabelci4/library
- photobucket.com/user/katyperry45/library
- photobucket.com/user/saragray1/library
- photobucket.com/user/millerfred/library
- photobucket.com/user/jeniferaniston1/library
- photobucket.com/user/amandaseyfried1/library
- photobucket.com/user/suwe8/library
- photobucket.com/user/bob7301/library
If it failed to access and retrieve the image from photobucket.com, the malware tries to obtain an image from the domain toknowall.com.
There is also a “fallback” in the form of a listener, which expects connection to an infected device using specialized triggers.
VPNFilter is a rather serious and dangerous threat aimed at devices that are difficult to protect. If the above devices are used in your infrastructure, it is recommended to immediately disconnect it from the network, perform a hard reset of the device and wait for the patch from the manufacturer.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/359210/
All Articles