How to quickly and efficiently work with priorities according to the Lean Prioritization method?
Constant work with priorities is a necessity in product management, an integral part of the development process. If you have enough time, you can study and try to use complex and interesting methods for determining priorities. The Lean Prioritization Technique is one of the simplest and most accessible approaches that helps product managers manage task backlog, especially when they need to be done quickly and efficiently.

In the ideal world of product management, every manager strives to learn as much as possible about how to become a guru in prioritization and be able to apply the maximum number of popular methodologies and professional techniques for this.
It is also important for any member of the team involved in the development and positioning of a product to be able to make the right decisions and correctly prioritize. However, very often in practice we encounter negative examples of decision making. Popular methodologies and techniques come to the rescue.
')
Prioritizing functions in product development helps to identify key points, learn how to effectively plan a roadmap (product roadmap), define boundaries of work, and distinguish between desired and necessary.
Effective priority management is the process of balancing between value delivery and available resources. What can cause bad prioritization?
Many factors can interfere with product managers and owners working with priorities. For example, unscrupulous team members or decision makers. They can have a negative impact on prioritization processes. This could be someone who influences decision-making, based on his seniority in business, who imposes wrong ideas, who actively opposes the opinions of others, or is trying to independently implement a deliberately ineffective solution.
Also, the cause of poor prioritization can be the use of an unusable tool or methodology (which is not suitable for the global goal of the product).
With the first item you can cope on your own and quickly enough, and the selection of relevant tools and methods will require special attention and study of the acquired skills in product management.
The prioritization of functions in product management is a serious process that requires a thorough approach and attention from PM. Experienced product managers apply various simple and complex approaches and methods to prioritize and work with them.
This is a worldwide popular methodology for determining customer satisfaction with product functions. The theory makes it possible to clearly describe the satisfaction of what needs leave consumers indifferent, unmet, or completely happy.
Modeling of the method will require a sample of users who will talk about their emotional state at the sight of a certain function of the product, as well as in its absence.
This way, it will be possible to define functions that users can manage without and which are most important for them. Once, this method was used to test the Wi-Fi function in airplanes.
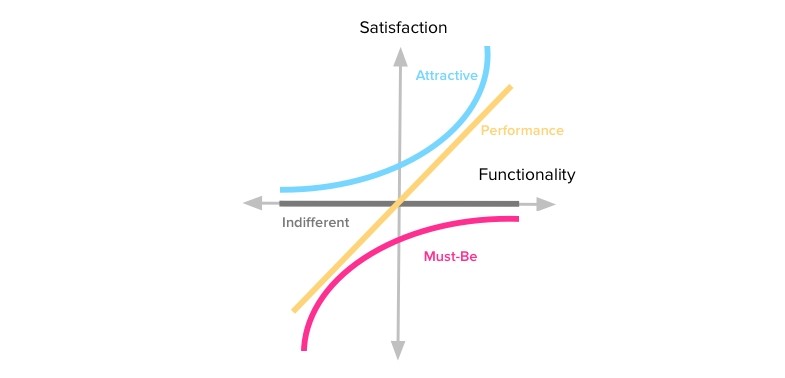
This technique is widely used in project management, business analysis and software development. The methodology is based on four categories of priorities:
The first letters of these categories defined the name of the method (MSCW).
QFD (Quality Function Deployment) is a technique for structuring a quality function, a decision-making technique that is often used by product developers.
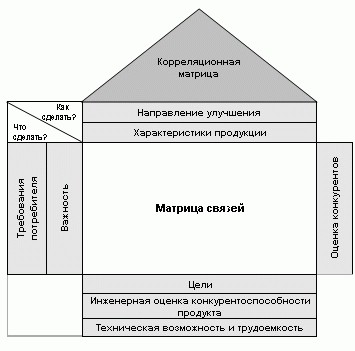
At the heart of the methodology, originated in Japan in 1966, is the construction of a matrix that includes user requirements distributed by priority and a rating of the characteristics of certain functions. The matrix also displays information about the characteristics of competing products.
The QFD matrix helps product managers and developers understand the real feasibility of implementing certain requirements: if a function is present in a competitor and is considered its advantage, then it makes sense to think about its implementation.
The most important thing about QFD is to help focus on the characteristics of the product, viewed from the perspective of the client and the company. The matrix is compared with the figure of the house, calling it "the house of quality."
This "house" is a table, the columns of which correspond to the technical characteristics, and the rows are consumer.
Methodology Story Mapping - building a map of user stories. The method was first described in 2005, after which it had a number of improvements and clarifications.
The essence of Story Mapping is that one-page backlog is an inadequate way to prioritize work. A more solid structure is needed.
The story map is organized as follows:
Groups of related stories can be grouped into Activities (related activities).

These and many other methodologies are actively used for planning product strategies, although, often, they require a lot of time and resources. If you need a quick approach to prioritize on a daily basis, Lean Prioritization is an excellent option.
The Lean Prioritization method is the application of a 2 × 2 matrix, which helps in making decisions and determines what is important, what is risky, and in which direction you need to direct your efforts. Startup entrepreneurs are also actively using this matrix to prioritize product development.
Why is this matrix used to determine priorities? She can help product managers sort out all the tasks and put everything in order.
Agree, if you do not update and maintain the backlog in the normal state , it can quickly become a “dump” for tens, hundreds and even thousands of functions and bugs.
Naturally, it will be more difficult to prioritize if we neglect the timely definition of unacceptable functions. They will simply be overlooked.
To work with the matrix, you can use the big board and simply draw a big plus sign “+” on it, set the directions of the Value (value) and Effort (effort) axes and place the tasks that agree with these criteria.

True, all this is much more convenient to do with the help of a ready-made tool that is offered by many platforms for managing products .
Parameters Value and Efforts can be applicable to each idea or task. Comparing these combinations will help you better prioritize your tasks and select the most important ones for development.
In determining the value of the task, pay attention to the following indicators:
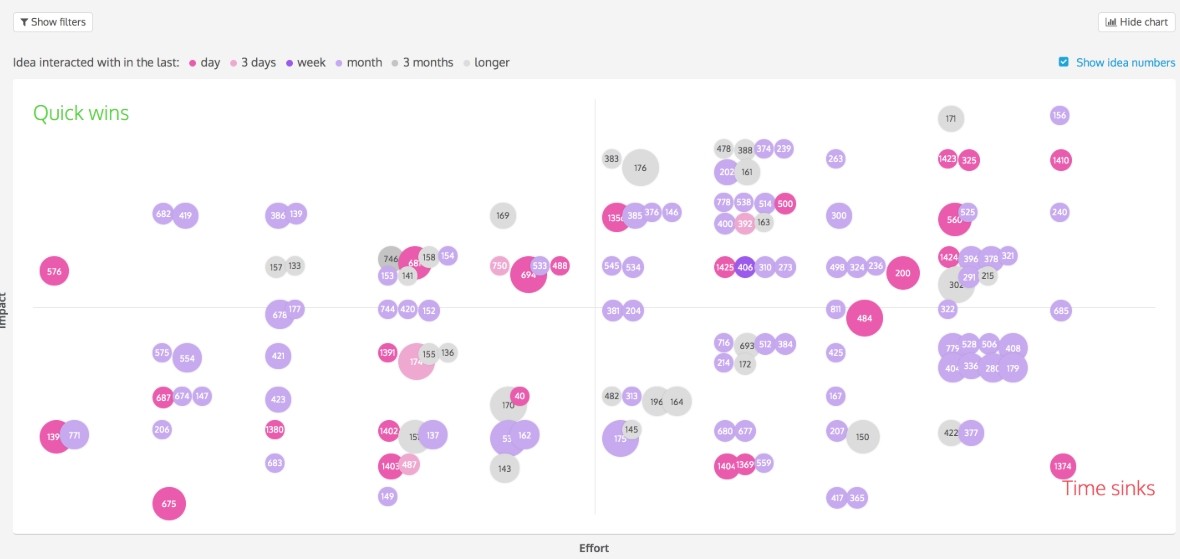
In the universal platform for managing Hygger.io products, it is visualized using the Backlog Priority Chart:

A similar matrix for prioritization can be found in the ProdPad:
Most likely, your product will develop and change over time, so it’s best to review and update the matrix regularly.
Surely, you will learn more about your product and customers using analytics, feedback, A / B tests, additional information about customers, and so on. You may have to make major changes to the matrix, so it may turn out that the questions that were rated low enough last month may now become priorities.
The Lean Prioritization approach today is in demand in many areas, as all companies and products strive to develop and remain competitive.
The matrix presented is a simple and intuitive tool for prioritizing your product. He can come to the rescue when there is not enough time to work with more complex techniques and methodologies. Lean Prioritization helps to focus on the functions that are most valuable to customers, compared with the efforts needed to deliver them.
What do you think about this approach and more complex methodologies?

In the ideal world of product management, every manager strives to learn as much as possible about how to become a guru in prioritization and be able to apply the maximum number of popular methodologies and professional techniques for this.
It is also important for any member of the team involved in the development and positioning of a product to be able to make the right decisions and correctly prioritize. However, very often in practice we encounter negative examples of decision making. Popular methodologies and techniques come to the rescue.
')
What are the priorities for setting priorities?
Prioritizing functions in product development helps to identify key points, learn how to effectively plan a roadmap (product roadmap), define boundaries of work, and distinguish between desired and necessary.
Effective priority management is the process of balancing between value delivery and available resources. What can cause bad prioritization?
Many factors can interfere with product managers and owners working with priorities. For example, unscrupulous team members or decision makers. They can have a negative impact on prioritization processes. This could be someone who influences decision-making, based on his seniority in business, who imposes wrong ideas, who actively opposes the opinions of others, or is trying to independently implement a deliberately ineffective solution.
Also, the cause of poor prioritization can be the use of an unusable tool or methodology (which is not suitable for the global goal of the product).
With the first item you can cope on your own and quickly enough, and the selection of relevant tools and methods will require special attention and study of the acquired skills in product management.
The prioritization of functions in product management is a serious process that requires a thorough approach and attention from PM. Experienced product managers apply various simple and complex approaches and methods to prioritize and work with them.
Common Methodologies for Prioritization
Kano method
This is a worldwide popular methodology for determining customer satisfaction with product functions. The theory makes it possible to clearly describe the satisfaction of what needs leave consumers indifferent, unmet, or completely happy.
Modeling of the method will require a sample of users who will talk about their emotional state at the sight of a certain function of the product, as well as in its absence.
This way, it will be possible to define functions that users can manage without and which are most important for them. Once, this method was used to test the Wi-Fi function in airplanes.

MoSCoW Prioritization Method
This technique is widely used in project management, business analysis and software development. The methodology is based on four categories of priorities:
- Must - the most important and urgent
- Should - important
- Could be delayed for some time.
- Would n’t be a priority
The first letters of these categories defined the name of the method (MSCW).
QFD method: matching customer and company desires
QFD (Quality Function Deployment) is a technique for structuring a quality function, a decision-making technique that is often used by product developers.
At the heart of the methodology, originated in Japan in 1966, is the construction of a matrix that includes user requirements distributed by priority and a rating of the characteristics of certain functions. The matrix also displays information about the characteristics of competing products.
The QFD matrix helps product managers and developers understand the real feasibility of implementing certain requirements: if a function is present in a competitor and is considered its advantage, then it makes sense to think about its implementation.
The most important thing about QFD is to help focus on the characteristics of the product, viewed from the perspective of the client and the company. The matrix is compared with the figure of the house, calling it "the house of quality."
This "house" is a table, the columns of which correspond to the technical characteristics, and the rows are consumer.
- In the roof - data on the correlation between the technical characteristics.
- In the left wing - the priorities of user characteristics.
- In the right wing - ratings of consumer characteristics.
- In the basement - the results of the analysis of the technical characteristics of competitors' products, the results of the strategy for changing the technical characteristics of the product, as well as the importance assessment

User story mapping
Methodology Story Mapping - building a map of user stories. The method was first described in 2005, after which it had a number of improvements and clarifications.
The essence of Story Mapping is that one-page backlog is an inadequate way to prioritize work. A more solid structure is needed.
The story map is organized as follows:
- The horizontal axis represents the sequence of use. Along it are user histories or tasks in the sequence in which they are performed by users.
- The vertical axis means criticality. It contains user stories about how important they are (top to bottom).
Groups of related stories can be grouped into Activities (related activities).

These and many other methodologies are actively used for planning product strategies, although, often, they require a lot of time and resources. If you need a quick approach to prioritize on a daily basis, Lean Prioritization is an excellent option.
Lean Prioritization and the universal matrix of Value and Effort
The Lean Prioritization method is the application of a 2 × 2 matrix, which helps in making decisions and determines what is important, what is risky, and in which direction you need to direct your efforts. Startup entrepreneurs are also actively using this matrix to prioritize product development.
Why is this matrix used to determine priorities? She can help product managers sort out all the tasks and put everything in order.
Agree, if you do not update and maintain the backlog in the normal state , it can quickly become a “dump” for tens, hundreds and even thousands of functions and bugs.
Naturally, it will be more difficult to prioritize if we neglect the timely definition of unacceptable functions. They will simply be overlooked.
To work with the matrix, you can use the big board and simply draw a big plus sign “+” on it, set the directions of the Value (value) and Effort (effort) axes and place the tasks that agree with these criteria.

True, all this is much more convenient to do with the help of a ready-made tool that is offered by many platforms for managing products .
Parameters Value and Efforts can be applicable to each idea or task. Comparing these combinations will help you better prioritize your tasks and select the most important ones for development.
- Valuing a Value will show the business value your product or business can bring.
- Effort score will measure the resources needed to complete the task.
In determining the value of the task, pay attention to the following indicators:
- Acquisition. Will a particular feature help attract new customers?
- Activation (activation). When will customers understand the value of this feature?
- Reach (coverage). How many customers will cover this feature?
- Revenue. How does the function help make money?
- Retention (retention). How does the function help keep or return customers so that they remain active?
- Virality (virality). How does the function affect the virality of the product?
In the universal platform for managing Hygger.io products, it is visualized using the Backlog Priority Chart:

A similar matrix for prioritization can be found in the ProdPad:

Revise the matrix
Most likely, your product will develop and change over time, so it’s best to review and update the matrix regularly.
Surely, you will learn more about your product and customers using analytics, feedback, A / B tests, additional information about customers, and so on. You may have to make major changes to the matrix, so it may turn out that the questions that were rated low enough last month may now become priorities.
Conclusion
The Lean Prioritization approach today is in demand in many areas, as all companies and products strive to develop and remain competitive.
The matrix presented is a simple and intuitive tool for prioritizing your product. He can come to the rescue when there is not enough time to work with more complex techniques and methodologies. Lean Prioritization helps to focus on the functions that are most valuable to customers, compared with the efforts needed to deliver them.
What do you think about this approach and more complex methodologies?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/359208/
All Articles