Phishing with characters from other layouts in the URL does not go away
Phishing has been around for a long time. It is impossible to calculate how many people gave the scammers on a saucer passwords from social networks and mail services, their credit card and bank account data, without making sure that the address bar at the time of entering the login and password was Vkontakte, not Vkontaktle. One of the ways you can disguise an address is to use characters from other alphabets.

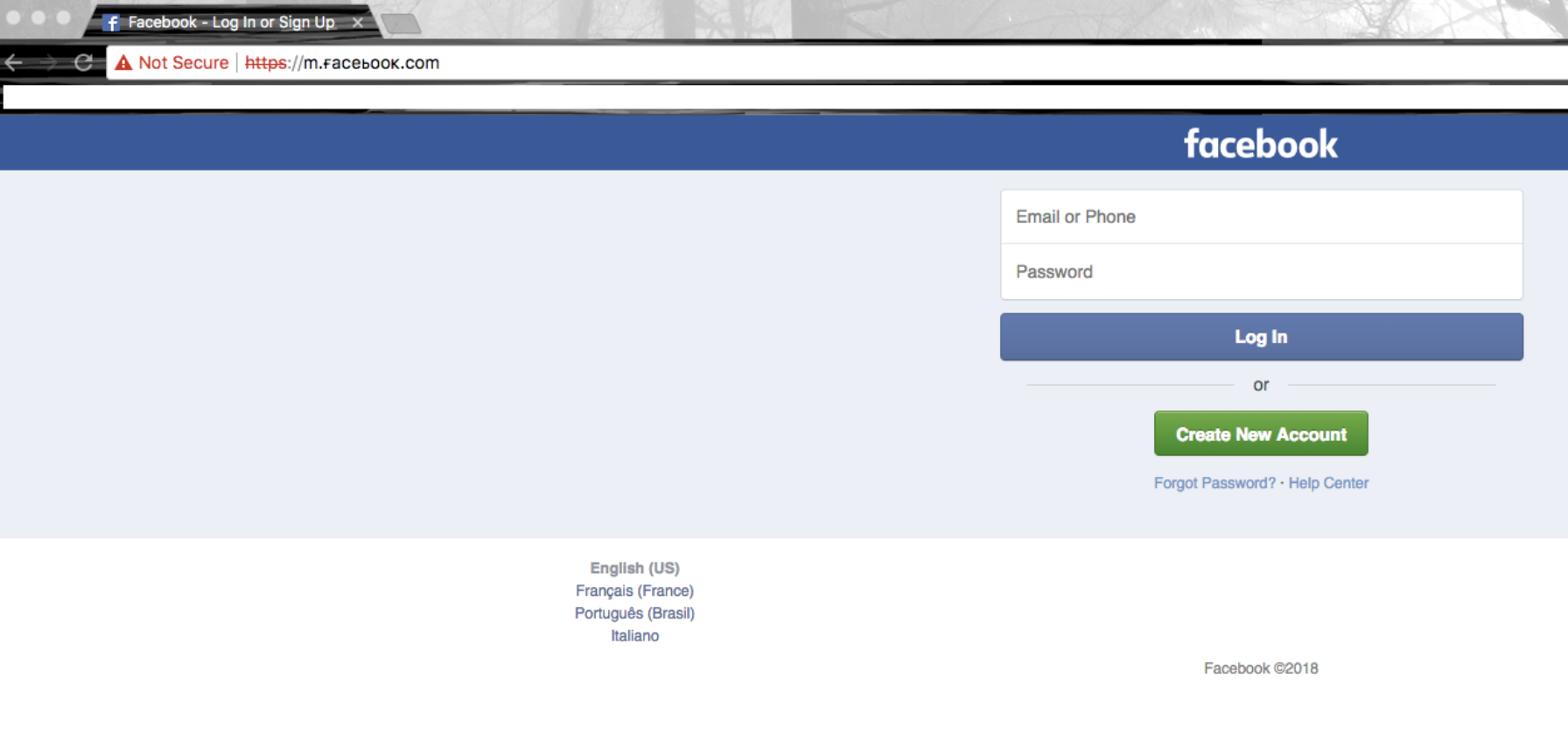
Examples of phishing sites are the polonìex.com page, which copies the cryptocurrency exchange at poloniex.com
Internationalized domain names (IDN) contain characters of national alphabets that are different from Latin characters. To ensure that the structure of the DNS domain name system does not need to be changed, to support other languages, the transformation of addresses containing characters of national alphabets into words from ASCII characters is used . This method was intended to be a "bridge" between English-speaking and non-English-speaking users.
Unicode is used to encode characters from other alphabets into ASCII characters . The Unicode standard includes the signs of almost all the written languages of the world - more than 136 thousand characters from 139 modern and no longer relevant languages. Unicode technically is an array of data in which each of the characters is assigned an ASCII code, which then decodes the UTF format - Unicode Transformation Format .
')
F: U + 0046
A: U + 0041
R: U + 0052
S: U + 0053
I: U + 0049
G: U + 0047
H: U + 0048
T: U + 0054
✪: U + 272A
But in the address bar, we can not use some characters. Then Punycode comes to the rescue (Panicode) - a Unicode conversion system into a sequence of letters and symbols allowed in domain names. In the address bar, we see a character set, starting with the prefix "xn--", which reports the use of Punycode. For example, “Russia. Rf” in Punycode looks like xn - h1alffa9f.xn - p1ai . In the address bar of the browser we see the Cyrillic alphabet, but it is transmitted in Punycode, after which the browser translates the character set into Russian.
Letters from different languages may look similar or absolutely identical. Only in English the “l” and “I” are practically indistinguishable - a small “L” and a large “i”. Russian and English small "a" are completely identical. Such symbols are called “homoglyphs,” and “homoglyphs” are the words in which they are used. This method of cheating users has been used for many years. A few examples of similar address writing:
xn--frsightsecurity-ulm.com -> fightsightsecurity.com
- Cyrillic "a" is used (U + 0430)
xn--farsghtsecurity-xng.com -> farsɩghtsecurity.com
- used the Greek lowercase "Yota" - "ι" (U + 0269)
xn--80ak6aa92e.com -> arrӏe.com
- All characters are Cyrillic.
Farsight Security looked for phishing sites using this vulnerability for three months from October 17, 2017 to January 10, 2018, and during this time it discovered more than 116 thousand pages that copy financial sites, fashion brand pages and cryptocurrency exchanges and, of course, social network.
A few examples:
Farsight Security offers several ways to protect against intruders using this tool, the main of which is the user's vigilance.
Farsight Security advises owners of popular sites on which users enter a username and password, buy goods or download content, try to buy all similar domains, as well as track the registration of homographers.

Examples of phishing sites are the polonìex.com page, which copies the cryptocurrency exchange at poloniex.com
How fraudsters use encoding
Internationalized domain names (IDN) contain characters of national alphabets that are different from Latin characters. To ensure that the structure of the DNS domain name system does not need to be changed, to support other languages, the transformation of addresses containing characters of national alphabets into words from ASCII characters is used . This method was intended to be a "bridge" between English-speaking and non-English-speaking users.
Unicode is used to encode characters from other alphabets into ASCII characters . The Unicode standard includes the signs of almost all the written languages of the world - more than 136 thousand characters from 139 modern and no longer relevant languages. Unicode technically is an array of data in which each of the characters is assigned an ASCII code, which then decodes the UTF format - Unicode Transformation Format .
')
F: U + 0046
A: U + 0041
R: U + 0052
S: U + 0053
I: U + 0049
G: U + 0047
H: U + 0048
T: U + 0054
✪: U + 272A
But in the address bar, we can not use some characters. Then Punycode comes to the rescue (Panicode) - a Unicode conversion system into a sequence of letters and symbols allowed in domain names. In the address bar, we see a character set, starting with the prefix "xn--", which reports the use of Punycode. For example, “Russia. Rf” in Punycode looks like xn - h1alffa9f.xn - p1ai . In the address bar of the browser we see the Cyrillic alphabet, but it is transmitted in Punycode, after which the browser translates the character set into Russian.
Letters from different languages may look similar or absolutely identical. Only in English the “l” and “I” are practically indistinguishable - a small “L” and a large “i”. Russian and English small "a" are completely identical. Such symbols are called “homoglyphs,” and “homoglyphs” are the words in which they are used. This method of cheating users has been used for many years. A few examples of similar address writing:
xn--frsightsecurity-ulm.com -> fightsightsecurity.com
- Cyrillic "a" is used (U + 0430)
xn--farsghtsecurity-xng.com -> farsɩghtsecurity.com
- used the Greek lowercase "Yota" - "ι" (U + 0269)
xn--80ak6aa92e.com -> arrӏe.com
- All characters are Cyrillic.
Farsight Security looked for phishing sites using this vulnerability for three months from October 17, 2017 to January 10, 2018, and during this time it discovered more than 116 thousand pages that copy financial sites, fashion brand pages and cryptocurrency exchanges and, of course, social network.
A few examples:
xn--gucc-tpa.com. --> guccì.com.
ns1.xn--aobe-l6b.com. --> ns1.aɗobe.com.
xn--aple-csa.com. --> apþle.com.
www.xn--amzon-ucc.com. --> www.amȧzon.com.
xn--cinbase-10a.com. --> cõinbase.com.
xn--80aj7b8a.com. --> .com.
www.xn--acebook-js3c.com. --> www.ḟacebook.com.
www.xn--oole-9pb06e.com. --> www.ǥooɡle.com.
www.xn--mcrosoft-c2a.es. --> www.mícrosoft.es.
xn--wiipedia-nmb.com. --> wiĸipedia.com.
www.xn--yndex-0jc.com. --> www.yɑndex.com.
Personal account protection
Farsight Security offers several ways to protect against intruders using this tool, the main of which is the user's vigilance.
- Mostly fraudsters use spam mailings, so you need to be especially careful with letters, text or images that provoke you to immediately click on the link, as well as letters that offer to update or confirm information on the sites you use.
- Instead of clicking on the link in the letter, copy and paste it into the address bar. This will avoid embedding suspicious URLs in the text.
- Enter the password only on sites with a secure connection (https: //). If you do not see in the address bar a green plate indicating a secure connection, the “s” symbol in “https: //”, do not enter the password.
- Pay attention to changing the URL in the address bar.
- Enable two-factor authentication on all sites that support this feature. Less than 10% of all Google users use it . On the one hand, it serves as an additional security tool, and on the other hand, it will let you know about an attempt to hack your account. A smartphone can become a “weak link” in this system, so take care of a strong pin code.
Organization protection
Farsight Security advises owners of popular sites on which users enter a username and password, buy goods or download content, try to buy all similar domains, as well as track the registration of homographers.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/357454/
All Articles