Viruses, statistics and a bit of everything
Everyone “knows” who actually writes viruses, but do you know what the average lifetime of a virus is, what users do by installing an antivirus, and why anti-virus companies rarely tell in the news about penetration methods?
Interesting? We ask under the cut!
Let's start with the time of life. We will not repeat the news that in some organization or company found a virus that went unnoticed ... years. This happens, but usually such cases are associated with targeted attacks, when the introduction occurs in a small number of organizations. The usual malware attack is aimed at a large number of individuals or companies and it is logical that someone will sooner or later pay attention to the new Trojan. The response time of antiviruses (without a cloud) is approximately two hours, respectively, a rather high probability that a malicious file will be destroyed on infected computers in two to three hours.
Unfortunately for users, the development of malware can be automated and malicious users can release malicious programs “for cause” faster than the antivirus update:
')
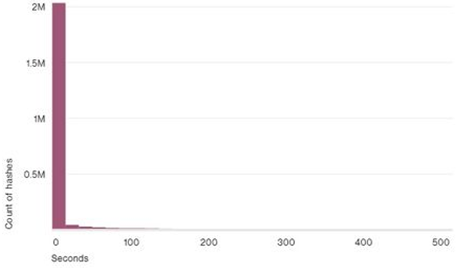
A source
Over 99% of malware samples (hashes) "live" (found in the wild) 58 seconds or less!
How many malicious programs do attackers release per day? The exact figure is not known to anyone, in particular, because it is impossible to guarantee that all malicious programs created during the day on this day will be caught. Up to a million samples per day come to analysis. Signatures are obtained of course smaller, but also a lot :

This is without android, advanced, tool and other signatures.
And now about the sad. It is logical that such a rate of release of malicious programs, plus the use of undetectable tools by attackers (repacking, obfuscation, exclusion of known signatures, etc.) leads to whichever antivirus is, but to catch 100% of malicious programs, including unknown he can not. If anyone thinks that this is the saddest thing, then he is wrong. Two sadness. The first is that the regulators indicate in their documents that the antivirus tool is exclusively an antivirus (and even does not use even heuristics ), and the second is that information security specialists, following the regulators, believe (the result of polls at conferences) that a good antivirus can Detect all malware at the time of penetration into the network.
Findings:
Since we mentioned updates, let's talk about them.
But this is after the epidemics of Wanna Cry and NePetya, about which probably only the most lazy media did not write about!
Well, okay, these are companies, but how do users behave? Microsoft is responsible for this. Thanks to her system of collecting information about users, she now knows how antivirus users behave. Let's open Microsoft Security Intelligence Report Volume 22:

Yellow - antivirus installed and disabled. Impressive, yes? And green - installed, but not updated.
And by the way, the number of computers without antivirus in the latest versions of Windows does not mean that the situation is better there, it’s just that Windows defender is turned on by default - which users may not be aware of.
About the same statistics gives and utility CureIt! - not less than 60 percent of computers are protected. Add to this the lack of updates and default passwords, and we should not be surprised if the encrypter, the atom, how few victims.
But back to updates.drweb.com. Which do you think is the most popular type of trojan? Ciphers (Trojan.Encoder)? Miners (Trojan.BtcMine)?
Loaders:

What do they do? Example
Modern malware is a complex of many parts. The loaders are the first to arrive at the machines, analyze the situation, download the "useful" load, clean the logs and self-delete. As a result, the researchers get the whole malicious complex except the bootloader, as a result of which the infection method (vulnerability in the system) remains unknown and infection may occur again.
Conclusion. Take care of the logs, they are the key to successful analysis of an IT incident.
What time does the attack take place? Legends say that real attackers work at night. Is it so?


A source
It's funny, but the intensity of the attacks completely coincides with the maxima of the activity of the company's employees - arrival at work, time before lunch and time at the end of the working day. The fourth peak - attacks at night can be caused by the fact that at this time the probability of detecting an attack and responding to it from the company's security service is much lower.
By the way, one more figure from the link already given. About three days pass between the publication of vulnerability and the onset of attacks.
Conclusion - postponing security updates for a longer period is dangerous.
I hope it was interesting, if you have any questions, I will be grateful.
Interesting? We ask under the cut!
Let's start with the time of life. We will not repeat the news that in some organization or company found a virus that went unnoticed ... years. This happens, but usually such cases are associated with targeted attacks, when the introduction occurs in a small number of organizations. The usual malware attack is aimed at a large number of individuals or companies and it is logical that someone will sooner or later pay attention to the new Trojan. The response time of antiviruses (without a cloud) is approximately two hours, respectively, a rather high probability that a malicious file will be destroyed on infected computers in two to three hours.
Unfortunately for users, the development of malware can be automated and malicious users can release malicious programs “for cause” faster than the antivirus update:
')

A source
Over 99% of malware samples (hashes) "live" (found in the wild) 58 seconds or less!
How many malicious programs do attackers release per day? The exact figure is not known to anyone, in particular, because it is impossible to guarantee that all malicious programs created during the day on this day will be caught. Up to a million samples per day come to analysis. Signatures are obtained of course smaller, but also a lot :

This is without android, advanced, tool and other signatures.
And now about the sad. It is logical that such a rate of release of malicious programs, plus the use of undetectable tools by attackers (repacking, obfuscation, exclusion of known signatures, etc.) leads to whichever antivirus is, but to catch 100% of malicious programs, including unknown he can not. If anyone thinks that this is the saddest thing, then he is wrong. Two sadness. The first is that the regulators indicate in their documents that the antivirus tool is exclusively an antivirus (and even does not use even heuristics ), and the second is that information security specialists, following the regulators, believe (the result of polls at conferences) that a good antivirus can Detect all malware at the time of penetration into the network.
Findings:
- Despite the widespread use of virus writers, services like VirusTotal - the traditional heuristics of positions does not pass. So one of the two Russian antiviruses discovered Wanna Cry immediately with heuristics
- A behavioral or preventive mechanism for detecting malware in an antivirus is a must. Unfortunately, users in the mass consider that antivirus prevention is superfluous and acquire products without it. A typical example is the results of voting for components that should be in an antivirus.
- Cloud mechanisms have the advantage that updates to the rules on them are laid out immediately and the antivirus can instantly apply them. According to rumors, the second Russian antivirus also detected Wanna Cry, but the cloud and as a result affected companies in which the cloud was disconnected or prohibited at all
- Antivirus is not a wizard and cannot detect 100% of malicious files. Therefore, to protect against the penetration of malicious programs, you need to install updates and restrict rights.
Since we mentioned updates, let's talk about them.
a report from Fortinet showed that in the second quarter of 2017, 90% of organizations registered exploits for vulnerabilities that were more than three years old. The researchers also noted that 10 years after the correction of defects, 60% of companies were still subject to appropriate attacks.
But this is after the epidemics of Wanna Cry and NePetya, about which probably only the most lazy media did not write about!
Well, okay, these are companies, but how do users behave? Microsoft is responsible for this. Thanks to her system of collecting information about users, she now knows how antivirus users behave. Let's open Microsoft Security Intelligence Report Volume 22:

Yellow - antivirus installed and disabled. Impressive, yes? And green - installed, but not updated.
And by the way, the number of computers without antivirus in the latest versions of Windows does not mean that the situation is better there, it’s just that Windows defender is turned on by default - which users may not be aware of.
About the same statistics gives and utility CureIt! - not less than 60 percent of computers are protected. Add to this the lack of updates and default passwords, and we should not be surprised if the encrypter, the atom, how few victims.
But back to updates.drweb.com. Which do you think is the most popular type of trojan? Ciphers (Trojan.Encoder)? Miners (Trojan.BtcMine)?
Loaders:

What do they do? Example
The Trojan.DownLoader23.60762 Trojan contacts the control server to receive commands, including the following:
- Run the file from the temporary folder on the disk of the infected computer;
- integrate into a working process;
- download the specified file;
- run the specified executable file;
- save and transfer to the attackers the SQLite database used by Google Chrome;
- delete cookies;
- reboot the operating system;
- turn off computer.
Modern malware is a complex of many parts. The loaders are the first to arrive at the machines, analyze the situation, download the "useful" load, clean the logs and self-delete. As a result, the researchers get the whole malicious complex except the bootloader, as a result of which the infection method (vulnerability in the system) remains unknown and infection may occur again.
Conclusion. Take care of the logs, they are the key to successful analysis of an IT incident.
What time does the attack take place? Legends say that real attackers work at night. Is it so?


A source
It's funny, but the intensity of the attacks completely coincides with the maxima of the activity of the company's employees - arrival at work, time before lunch and time at the end of the working day. The fourth peak - attacks at night can be caused by the fact that at this time the probability of detecting an attack and responding to it from the company's security service is much lower.
By the way, one more figure from the link already given. About three days pass between the publication of vulnerability and the onset of attacks.
Conclusion - postponing security updates for a longer period is dangerous.
I hope it was interesting, if you have any questions, I will be grateful.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/357426/
All Articles