EFF: we are halfway to safe internet

Governments of different countries are making efforts to control citizens and monitor the entire Internet. The only way to keep freedom is to securely encrypt all connections. The global movement to encrypt the entire Internet has announced an important milestone. Around the beginning of February 2017, the share of HTTPS-protected Internet traffic for the first time exceeded 50% . Russia leads the world in terms of growth in HTTPS traffic.
Thus, as the Electronic Frontier Foundation says, we are halfway to a safe Internet, protected from wiretapping, content spoofing, cookie theft and censorship. HTTPS protects against all these malicious phenomena.
At the end of January 2017, overcoming a milestone of 50% of encrypted traffic was reported by Mozilla . A little later, it was confirmed by Firefox telemetry , which is calculated as a moving average for the last 14 days. According to telemetry, the two-week moving average surpassed the 50% mark on February 6, 2017. If on February 5 the value was 49.98875%, then on February 6 it was 50.37423%.
')
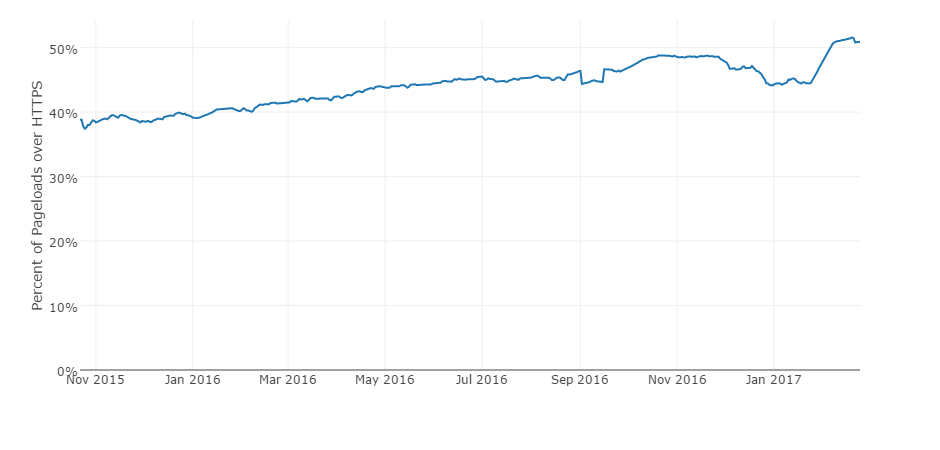
In February 2017, the share of encrypted traffic on the Internet for the first time exceeded 50%, Firefox telemetry data
For the last day, when Firefox statistics are available, February 24, 2016, the moving average is 50.88921%.
One would assume that Firefox users are slightly more advanced than regular users, they often visit good sites with HTTPS support, but the statistics of the world's most popular Chrome browser confirm these conclusions : now more than half of web traffic is protected by HTTPS under all operating systems except Android.
Latest Statistics February 18, 2017:
- Chrome OS: 71%
- Mac OS: 66%
- Linux: 57%
- Windows: 56%
- Android: 49%
Characteristically, the share of protected traffic in some countries is growing faster than in others. For example, in Russia it grows much faster than in Japan. Over the past two years, this share of HTTPS under Windows in Japan has increased from 23% to 37%, in Russia - from 28% to 55%, in the USA - from 44% to 65%.
In recent years, under pressure from the public, many large sites have switched to using HTTPS by default. This was done by Facebook, Twitter and Wikipedia. Then, Google pressed everyone else, starting to consider HTTPS as a ranking factor in search results in August 2014. In the Chrome browser for sites that are not HTTPS-protected, a special security message has appeared since January 2017. Perhaps this, among other things, explains some rise in popularity of HTTPS in January-February 2017, which is noticeable in the graphs. Users are beginning to realize that the lack of cryptographic protection of traffic is a threat to their security on the part of the government and other agents who seek to eavesdrop and intercept traffic. In order not to lose the audience, websites are forced to install free certificates and slightly increase the load on their servers by encrypting traffic.
Some social organizations and the media have joined the safe web movement. For example, the Free Frontier Foundation periodically publishes an Encrypt the Web report on the state of encryption on the Web. The same encryption reports appeared on the Secure the News media sites and on the Pulse government sites. For example, 74% of US government sites have already switched to HTTPS.
An important role in the practical implementation of HTTPS was played by the free certificate authority Let's Encrypt, as well as the Certbot tool, which allows us to obtain a free Let's Encrypt certificate and automatically configure it for your server. The popularity of Let's Encrypt is growing rapidly to the present. In October 2016, it became the largest certification center in the world with 12 million certificates, and now the number of certificates has exceeded 28 million.
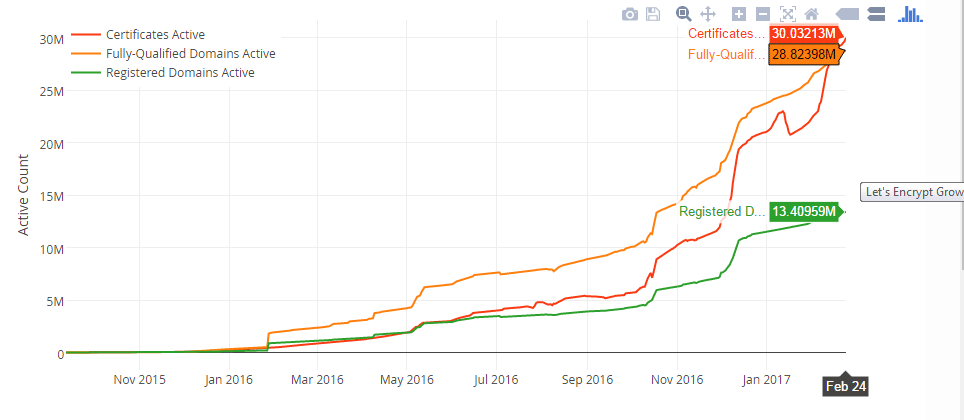
Much of this growth has been achieved thanks to the transition to Let's Encrypt of many major hosting sites and platforms for hosting sites such as WordPress.com, Squarespace, Digital Ocean, Dreamhost.com, OVH.com, SiteGround.com and dozens of others .
Recall that according to the package of laws of Yarovaya-Ozerova, the Russian state wants to record and store all user traffic for a long time. Well, now more than half of this traffic will be encrypted.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/357276/
All Articles