Cryptographers: Past, Present, Future
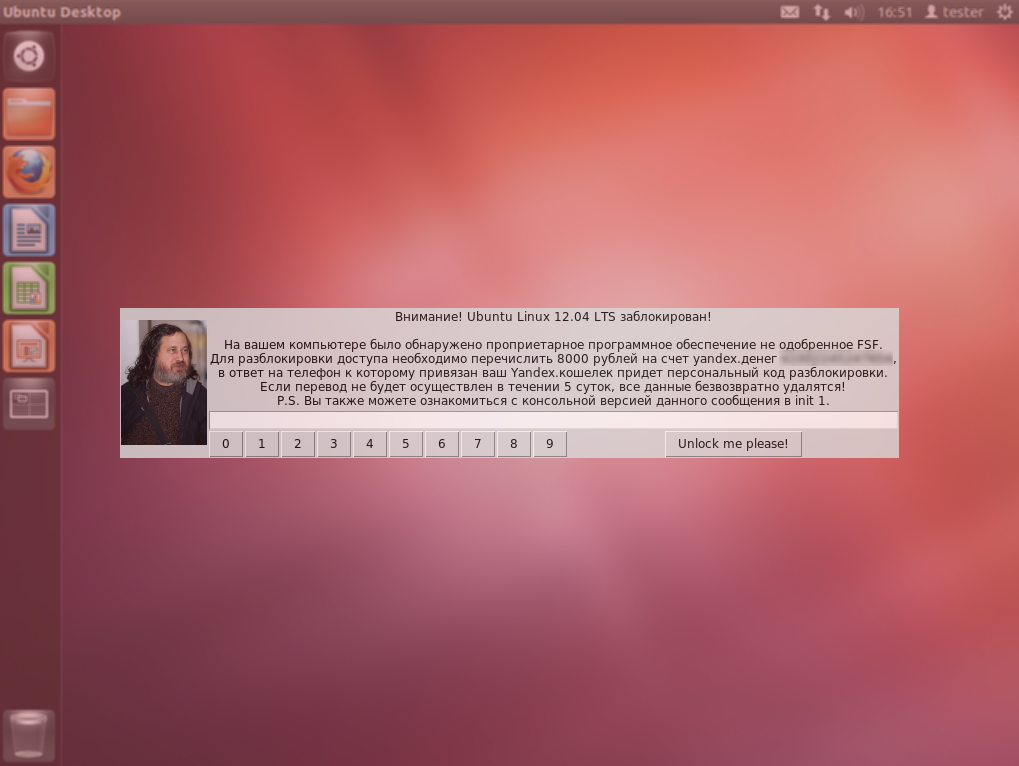
At the end of zero on computers in Russia and the CIS countries, a new and unusual infection began to spread at that time. A version of malicious software that was unfamiliar to users blocked the normal operation of the computer and required to send an SMS message to a paid number to receive an unlock code. The demands were supported by false threats: unlicensed software or some kind of pornography was found on the computer. It is easy to frighten a novice user if you introduce yourself as a law enforcement agency, a teenager behind the monitor of a parent computer - displaying pornography and a window requiring payment.
For a couple of years, utilities for quick cleaning became widespread - such extortion programs only interfered with normal operation, but did not harm the car. However, soon the Web began to walk much more destructive and effective malware. They encrypted the contents of the computer's drives and demanded money to restore the files. A live CD of quick help is powerless against the correct execution of a cryptographer - the encryption key remains only among intruders.
Start
In 1996, Mordechai (Moti) Jung and Adam Yang published Cryptovirology: Extortion-Based Security Threats and Countermeasures ( Crypto-urology: Extortionary Security Threats and Countermeasures ) described the use of traditional defensive encryption methods to attack computer systems. By the way, this work created the term “ crypto-virology ”, which refers to those areas that explore how encryption methods are used in malicious software. Even then, it was described remotely similar to the current scheme of work.
')
- Using the public key embedded in the malware, the cryptovirus encrypts data on the disk using asymmetric cryptography .
- "CryptoVirus" requires contact with the author of the malware.
- After receiving the ransom, the author of the "crypto virus" provides a private key for decryption.
The obvious disadvantage is one pair of private and public key for each version of the "cryptovirus". If one victim gets the freedom, then the rest will be potentially free. In this paper, the researchers suggested a solution to the problem: either to embed a set of keys into the cryptovirus, or the virus will symmetrically encrypt the data with the session key and encrypt the latter, and then the malware author will need to request the ciphertext.
The first encrypted virus appeared even before this, in 1989. The AIDS Trojan horse modified the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, waited for up to 90 system downloads and encrypted the names of all the files on drive C. Then the user received the request to send money to the subscriber box in Panama.

Diskette with AIDS. Jan Hruska, Computer viruses and anti-virus warfare , 1992
On December 11, 1989, about twenty thousand envelopes containing a five-inch floppy disk, the AIDS Information Version 2.00, got into the London postal service. The booklet enclosed in the envelope urged the recipients to insert a floppy disk into the computer and install the software package. In smaller letters on the back it was stated that under the license agreement the user must pay $ 189 or 389 dollars. This requirement pops up after 90 reloads.
AIDS resembles modern cryptographers only remotely: it encrypts not data, but folder names. The first noticeable viruses with file encryption on the disk began to appear in the middle of the zero: PGPCoder , Archiveus , Cryzip and others. They tried to earn money in different ways: someone asked to transfer funds to an E-gold or Liberty Reserve account (now deceased payment systems, which are known for popularity among cybercriminals), someone went into the exotic. For example, Archiveus encrypted the contents of the My Documents folder and asked to buy goods in a certain online pharmacy to get a password.
All these instances lacked several factors. A few technologies that were thought of as useful and convenient, but were used for criminal purposes. These are distributed cryptographic systems for anonymous payments with a high degree of anonymity - Bitcoin and its clones. These are completely anonymous networks - Tor and I2P, which allow you to hide the real location of the command servers on the darknet. Finally, the development of file encryption algorithms, the growth of computer processing power and the presence of a permanent connection to the Internet have played into the hands of crypto viruses.
In 2013, CryptoLocker began to march around the world. Using Tor, the Trojan connected to one of the command servers, received a 2048-bit RSA public key from it to encrypt a 256-bit AES file encryption key, and demanded payment in the amount of 300-400 dollars or euros in several ways, including bitcoins. Bitcoin's network specifications allow you to track how many coins are in any wallet. So the ZDNet researchers tracked four wallets and found that the attackers received tens of millions of dollars in three months. A survey of the University of Kent among Britons revealed a surprisingly high percentage of paid: about 41% among those infected with CryptoLocker, about 30% among other types of cryptographers.
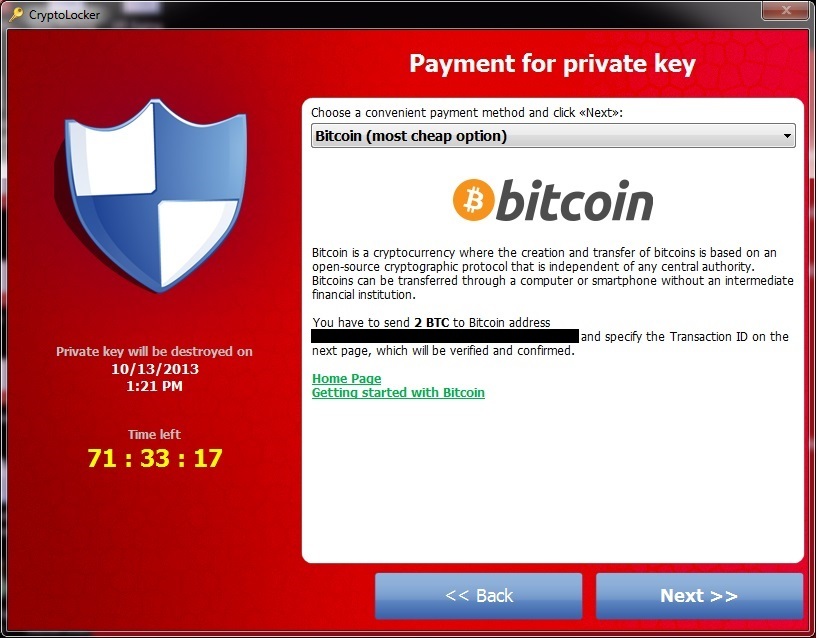
CryptoLocker caused a wave of followers and imitators: Locker, CryptoLocker.F, TorrentLocker , CryptoWall and so on. Today, extortion Trojans are selling and leasing . Their creators began to include a creative streak in the design of a payment requirement: Jigsaw deletes files once an hour , threatening the character from the Saw thrillers. The Ranscam virus simply exploits the reputation of the “product” and only deletes files , but still requires money.
Gradually crypto wickers have become habit. There are regular reports in the news about the paralyzed work of rather big organizations: the functioning of the hospital or transport company of the entire city is disrupted. Of course, companies are willing to pay for their critical files much more than regular users for data on home computers. The size of the ransom for companies is much higher.
What does the struggle with coders in a typical organization look like? This was told to us by the deputy head of the information security department of SKB Kontur, Alexander Delva. According to him, mailing with cryptographers is one of the most popular varieties of spam, letters come to the company with them daily.
According to Delva, incidents of infection and loss of documents happened a couple of years ago, but since then the company has taken action. At the same time, SKB Kontur did not pay attackers, considering that this contributes to the further development of the viral industry and does not bear any guarantees of recovery. Instead, the encrypted versions of the files were saved in the hope of the subsequent appearance of private keys in the public domain. Alexander Delva believes that protection against such cyber threats is not possible in antivirus programs, but in backing up any more or less valuable data.
Violent extortionists for Linux and macOS are already emerging. As Michael Kondrashin, technical director of Trend Micro Russia, a company developing cybersecurity solutions, explained in a comment for Hiktaim, such malware can begin to spread to other classes of computing devices:
Over the past year, we have seen an explosive growth in the number of encryption programs. Trend Micro research labs found 12–15 new encryption software families per month. In the near future, the trend will change. We predict that the rate of appearance of new families will soon decrease. This is primarily due to the advent of such an underground service as an “extortionist-as-a-service” program. Malefactors are ready to make on a stream new unique copies of new programs of extortionists for all who are ready to pay for such a service. As a result of this change, extortionists will be more targeted at choosing a victim in order to maximize financial gain for intruders. It should be noted that the slowdown in the emergence of new types of encryption software will not reduce the overall threat level. Quite the contrary. Surely, next year we will witness attacks on smartphones and other computers that are not user workstations.
Encryption programs have significantly changed the “rules of the game” in the anti-virus market, since it is not the executable files or system areas on the user's computer that are at risk, but the most common files. Not all developers were able to adequately respond to the new challenge, because now a modern antivirus product should be equipped with a completely new layer of technologies, such as creating shadow backup files, behavioral analysis to detect activity similar to encryption, as well as an artificial intelligence mechanism to detect unknown samples. encryption programs. Therefore, it is recommended to use the backup system and not to allow the availability of backups over the network for writing, otherwise the advanced encryption program will be able to encrypt and backup.
The appearance of ransomware viruses for everything that can be infected is hardly a concern. Researchers have demonstrated an instance that blocks the operation of the thermostat. Relatively rare security updates for IoT devices, smartphones and tablets offer a new field of attack.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/357232/
All Articles