Feature perception filters from your Product Backlog
If all the features in the process of product development seem to be equally important, then choosing the most priority of them is sometimes very difficult. Then the product manager can come to the aid of useful filters for determining priorities.

I have a good idea of how hard it is to choose features for development, when your product backlog is simply bursting with “tasty” features. But we, product managers, have to make this choice daily. Because our main task is to give the user value, as soon as possible and as much as possible. And we can not sit back. Our task is to make decisions quickly in the face of some uncertainty.
The question is simple: what is the most important feature for us now? But if they are almost all important? This question weakly helps us in making a decision.
')
Consider a set of filters that will help to better understand the degree of importance or the degree of influence of a feature on your product. And this understanding will help make the right decision at the moment and in this place.
So, let's go:
The feature corresponds to our long-term strategy or not. For example, for us, a strategic feature is integration with Jira. This feature will allow us to get away from direct competition with Jira and occupy a new niche - software for product managers . An example of a tactical function is the support of the new GDRP standard, which must be implemented before May 25, 2018, otherwise we risk falling for a large fine.
A feature can improve some specific indicators, for example, to increase the conversion from registrations to the purchase of a subscription. Or maybe not at all in the case of fix bugs or switching to a new photo processing library.
A feature can improve UX and make the user's life in your product better, and, on the contrary, can complicate his life, but at the same time increase revenue.
Compare: the feature that concerns onboarding and which absolutely new users will see and experience, and the feature that users only need on day 7 after registration. For example, export to PDF time tracking report.
The shortcuts or hot keys feature is often needed by users who actively use Hygger, as opposed to the Kanban to Sprint switchboard feature, which is needed only once when a client imports his data into Hygger from Jira or Trello.
Everything is simple: you need to evaluate the labor costs for the development of features. If there are functions with low costs, but with a large value, then they should be done first. We call them Quick Wins. But we must not forget about the large functions with a large value. It is desirable to break them into smaller pieces and do them gradually. For they can give a good value to your product.
The cost of the feature is not only the development time. For a feature, you need to write documentation, make and edit a video, make a newsletter, set up events in analytics, do a Dashboard in BI Tule, hold a webinar, and so on.
If a feature is requested by a VIP client whose logo you proudly show to all visitors on the landing page, then do not rush to say "no."
If your product does not have the expected function of the Kano model , the user will simply leave. For example, if Hygger had no comments on the tasks, it is unlikely that we would have users.
An example of Kano's desired function is the amount of available memory on Dropbox. The more memory available to the user, the higher his satisfaction. As a rule, these are linear properties of the product, that is, the more of this, the better. Other examples:
If your feature is admirable by Kano, then it will become the easter egg for the user. That is, it is always something unexpected, something that the user does not expect from your product at all. For example, in the case of Hygger, this can be a 2-level commenting of tasks or the ability to use the touchpad to move around the board in different directions.
If this feature is not in your product, well, well - users will not even notice it. But, on the other hand, users can be so impressed with the function that they share their discovery with others.
If competitors have a feature, it only means that competitors have it. But what if no one uses it, and a competitor is going to cut it out soon? But sometimes the feature of competitors becomes expected by Kano, and we have to repeat it at our place. And it is better to make new and cool features first!
Are you ready to give feature into development? Do not rush, make sure that it is studied in detail and described so that it will be clearly and clearly understood by your programmers and testers. The degree of detail you choose - as a product manager, you know your people better. If you understand each other from a half-word - excellent, you can not write "War and Peace." You work with a banking product, you have your own business analytics in your team - fine, let them model the UML feature in at least all 7 diagrams.
Estimate in percent the probability that the feature will really justify the expectations placed on it.
Ideally, if all features are measurable. This enables us to quantify their contribution to the success of the product.
If a problem is identified by usability testing (UX testing), then this gives us confidence that we solve real problems of users, rather than “hallucinate”, as is the case with the hypotheses that we formulate ourselves.
Of course, observing a problem in 5 people is one thing, and a hypothesis based on analyzing the behavior of 1,000,000 users is another. Then you should not compare it, but you need to formulate hypotheses and test them asap.
The team over time accumulates technical debts that must be repaid. This may be a temporary, not very beautiful code that solves the problem, but it is clumsy. This can be a stub for a function that can be called in a very exceptional situation.
If such debts are not repaid, then over time very large percentages can “drip” and the refactoring of the code can take much longer than these debts allowed to win at the start.
Far from the fact that your product will need all these filters. As a rule, the product manager chooses 3-7 criteria and uses them for scoring features. As a result, each feature gets a numeric value, and they can already be compared in one plane.
We at Hygger.io use the Lean Prioritization method. It is lightweight and effective, so we use it almost every day.
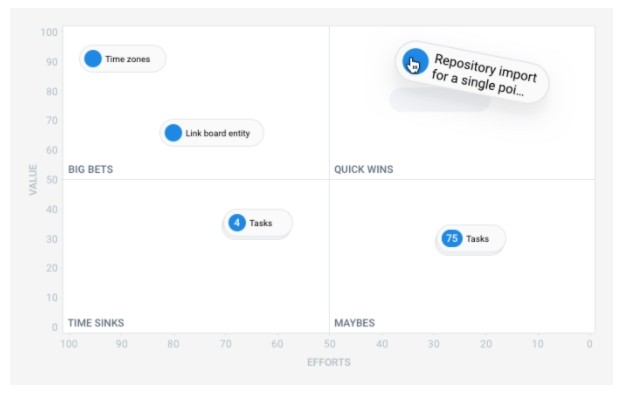
This method is a 2 × 2 matrix that helps in making decisions and determines what is important, what is risky, and where to direct your efforts. The matrix is actively used to prioritize product development.
If you do not maintain backlog constantly, it can quickly become a dump for dozens, hundreds and even thousands of features and bugs.
Using Lean Prioritization for working with a matrix, you can simply draw a large plus sign “+” on the board and set the values of “Value” and “Efforts” along the vertical and horizontal axes. However, many will agree - it will be more efficient and more convenient to use a special online tool, especially if you have a distributed team.
At Hygger, this is the Backlog Priority Chart , where, in addition to the Value and Efforts, four segments are offered: Big Bets, Quick Wins, Time Sinks and Maybes, each of which represents a degree of priority:
Surely, the list of ways to prioritize product features can be expanded. And by what criteria do you rate the features? Perhaps you have a solution that can help others?

I have a good idea of how hard it is to choose features for development, when your product backlog is simply bursting with “tasty” features. But we, product managers, have to make this choice daily. Because our main task is to give the user value, as soon as possible and as much as possible. And we can not sit back. Our task is to make decisions quickly in the face of some uncertainty.
The question is simple: what is the most important feature for us now? But if they are almost all important? This question weakly helps us in making a decision.
')
Consider a set of filters that will help to better understand the degree of importance or the degree of influence of a feature on your product. And this understanding will help make the right decision at the moment and in this place.
So, let's go:
1. Strategic / Tactical
The feature corresponds to our long-term strategy or not. For example, for us, a strategic feature is integration with Jira. This feature will allow us to get away from direct competition with Jira and occupy a new niche - software for product managers . An example of a tactical function is the support of the new GDRP standard, which must be implemented before May 25, 2018, otherwise we risk falling for a large fine.
2. Affects the metric / does not affect (debts, bugs)
A feature can improve some specific indicators, for example, to increase the conversion from registrations to the purchase of a subscription. Or maybe not at all in the case of fix bugs or switching to a new photo processing library.
3. Improves UX / spoils UX
A feature can improve UX and make the user's life in your product better, and, on the contrary, can complicate his life, but at the same time increase revenue.
4. Need many customers / units needed
Compare: the feature that concerns onboarding and which absolutely new users will see and experience, and the feature that users only need on day 7 after registration. For example, export to PDF time tracking report.
5. Frequently needed / rarely needed.
The shortcuts or hot keys feature is often needed by users who actively use Hygger, as opposed to the Kanban to Sprint switchboard feature, which is needed only once when a client imports his data into Hygger from Jira or Trello.
6. Development time and cost: high / low
Everything is simple: you need to evaluate the labor costs for the development of features. If there are functions with low costs, but with a large value, then they should be done first. We call them Quick Wins. But we must not forget about the large functions with a large value. It is desirable to break them into smaller pieces and do them gradually. For they can give a good value to your product.
7. Time and cost of implementation: high / low
The cost of the feature is not only the development time. For a feature, you need to write documentation, make and edit a video, make a newsletter, set up events in analytics, do a Dashboard in BI Tule, hold a webinar, and so on.
8. Requires vip client / require non-paying client
If a feature is requested by a VIP client whose logo you proudly show to all visitors on the landing page, then do not rush to say "no."
9. Expected / No
If your product does not have the expected function of the Kano model , the user will simply leave. For example, if Hygger had no comments on the tasks, it is unlikely that we would have users.
10. Desired / No
An example of Kano's desired function is the amount of available memory on Dropbox. The more memory available to the user, the higher his satisfaction. As a rule, these are linear properties of the product, that is, the more of this, the better. Other examples:
- more distance between the seats in the plane
- more different codecs support video player, etc.
11. Delighting / No
If your feature is admirable by Kano, then it will become the easter egg for the user. That is, it is always something unexpected, something that the user does not expect from your product at all. For example, in the case of Hygger, this can be a 2-level commenting of tasks or the ability to use the touchpad to move around the board in different directions.
If this feature is not in your product, well, well - users will not even notice it. But, on the other hand, users can be so impressed with the function that they share their discovery with others.
12. Have competitors / innovation
If competitors have a feature, it only means that competitors have it. But what if no one uses it, and a competitor is going to cut it out soon? But sometimes the feature of competitors becomes expected by Kano, and we have to repeat it at our place. And it is better to make new and cool features first!
13. Idea worked / not worked
Are you ready to give feature into development? Do not rush, make sure that it is studied in detail and described so that it will be clearly and clearly understood by your programmers and testers. The degree of detail you choose - as a product manager, you know your people better. If you understand each other from a half-word - excellent, you can not write "War and Peace." You work with a banking product, you have your own business analytics in your team - fine, let them model the UML feature in at least all 7 diagrams.
14. Confidence in shooting: high / low
Estimate in percent the probability that the feature will really justify the expectations placed on it.
15. Measurable / None
Ideally, if all features are measurable. This enables us to quantify their contribution to the success of the product.
16. Problem identified on UX
If a problem is identified by usability testing (UX testing), then this gives us confidence that we solve real problems of users, rather than “hallucinate”, as is the case with the hypotheses that we formulate ourselves.
Of course, observing a problem in 5 people is one thing, and a hypothesis based on analyzing the behavior of 1,000,000 users is another. Then you should not compare it, but you need to formulate hypotheses and test them asap.
17. Technical debt
The team over time accumulates technical debts that must be repaid. This may be a temporary, not very beautiful code that solves the problem, but it is clumsy. This can be a stub for a function that can be called in a very exceptional situation.
If such debts are not repaid, then over time very large percentages can “drip” and the refactoring of the code can take much longer than these debts allowed to win at the start.
Lean Prioritization or how we prioritize in Hygger
Far from the fact that your product will need all these filters. As a rule, the product manager chooses 3-7 criteria and uses them for scoring features. As a result, each feature gets a numeric value, and they can already be compared in one plane.
We at Hygger.io use the Lean Prioritization method. It is lightweight and effective, so we use it almost every day.
This method is a 2 × 2 matrix that helps in making decisions and determines what is important, what is risky, and where to direct your efforts. The matrix is actively used to prioritize product development.
If you do not maintain backlog constantly, it can quickly become a dump for dozens, hundreds and even thousands of features and bugs.
Using Lean Prioritization for working with a matrix, you can simply draw a large plus sign “+” on the board and set the values of “Value” and “Efforts” along the vertical and horizontal axes. However, many will agree - it will be more efficient and more convenient to use a special online tool, especially if you have a distributed team.
At Hygger, this is the Backlog Priority Chart , where, in addition to the Value and Efforts, four segments are offered: Big Bets, Quick Wins, Time Sinks and Maybes, each of which represents a degree of priority:
- Quick wins are ideas with really high value instructor and low efforts. It's like ripe fruits that hang low and it's time to pick them. The sooner you deal with them, the more results you get.
- Big Bets are ideas with high value and efforts. You can do them after Quick Wins. They will take more working time than Quick Wins, but they will bring the same profit. Try to break such features into smaller ones.
- Maybes - these features with lower value for customers, but easy to implement. They often fill out work time when there is a small “simple” in work or between larger features.
- Time Sinks are ideas with a low value, but a significant indicator of efforts. Despite the fact that they have some benefit for customers, such features should not be prioritized at this time.

Surely, the list of ways to prioritize product features can be expanded. And by what criteria do you rate the features? Perhaps you have a solution that can help others?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/354800/
All Articles