Quest to eliminate heart arrhythmia

Hi, Habr! Today we offer to go on an exciting journey to the very heart of the human body (in the literal sense of the word) to find out how to find and neutralize the sources of arrhythmia.
Physiology
Before you talk about the operation itself and the methods of its implementation, you need to understand the physiology. The heart has an automatism function, i.e. able to produce electrical impulses independently. Only cells of the sinus node and the atrial and ventricular conduction systems have the function of automatism. Also, the heart has the function of conduction - it is the ability to conduct excitation. Due to the generation of electrical impulses and their conduction, the heart shrinks. Normally, the only pacemaker is the sinus node, which suppresses the automatic activity of other causative agents of rhythm. This node is located in the wall of the right atrium. Below, in drawing, normal distribution of excitement is shown.
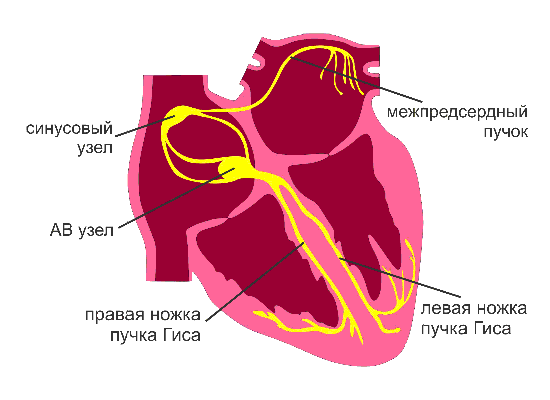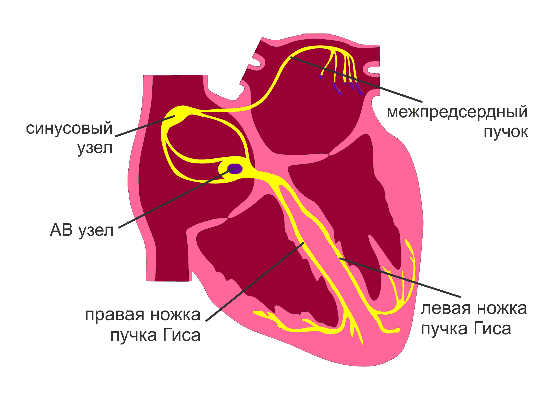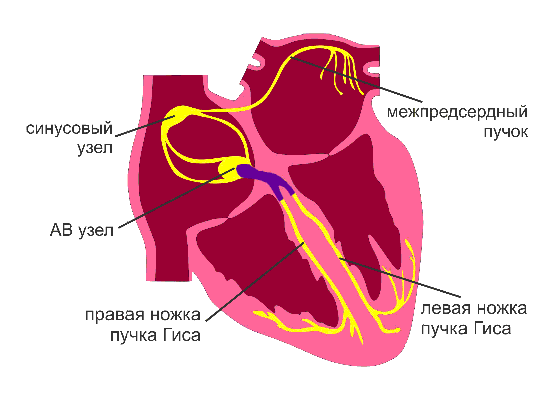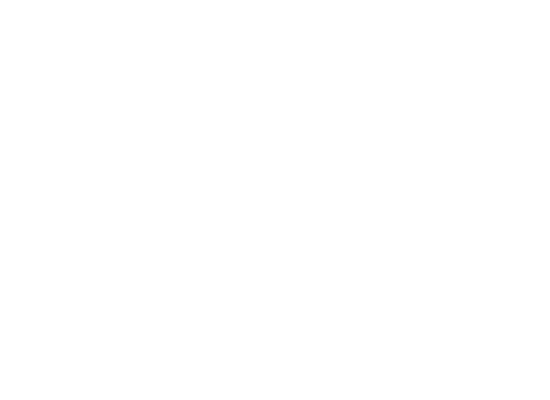
We start operation
For various reasons, some cells of the heart can impose their rhythm. When this occurs, there is a violation of the frequency, sequence of excitation and contraction of the heart. This is a type of arrhythmia. The result can be a number of serious complications. However, the cells of the offenders can be neutralized using so-called catheter ablation. This is a minimally invasive intervention, during which special catheters are inserted into the heart cavity.
')
Used catheters are thin flexible tubes with several electrodes (poles) at the end. The poles are able to carry out impulses in the heart, and from him. Catheters vary in shape and number of poles.
The insertion of catheters can be done in the groin, arm, shoulder, or neck. The location depends on which department of the heart is planned to operate. Local anesthesia is sufficient for the operation. A small incision is made on the skin and a needle is punctured a blood vessel. Then one or more catheters are inserted into the incision made. Catheters are carried through the blood vessels to the desired heart chamber.
There are types of arrhythmias when the cardiologist can determine the location of problem areas before the operation. But this is not always possible. In such cases, operations are technically difficult and time consuming. Without special support, most of the time the doctor has to act blindly. Usually, doctors use x-ray equipment to navigate. But this approach allows you to see only a flat picture and does not provide an understanding of the spatial position of the catheter. In addition, the patient and staff are exposed to radiation.
Consider how with the help of modern technology you can simplify the task and find an undesirable source. As an example, take one of the types of arrhythmias - ventricular premature beats.
Position determination
Let's start with navigation. There are options that allow you to programmatically calculate the position of the catheters. Let us dwell on the method based on the measurement of the potential difference between the electrodes. The main advantage of this approach is that standard catheters can be used.
At least two catheters are necessary to ensure the greatest accuracy. For the first catheter, a reference pole is selected, against which all calculations will be performed. It was found that such a pole is more convenient to have in the coronary sinus (a blood vessel flowing into the right atrium). First of all, this point is the least mobile during the work of the heart, which allows minimizing navigation errors. Secondly, from this point one can catch the impulse from any part of the heart, which will be important when building a map. Throughout the operation, the position of the reference pole should not change. The second catheter is called mapping. It is this catheter that will move in the cavity of the heart and be used to find the rhythm disturbers. To determine its position relative to the reference on the surface of the patient's body set three pairs of electrodes. The electrodes from one pair are placed on different sides of the body, and the pairs are mutually orthogonal (chest - back, left - right side, neck - thigh). An alternating current is allowed between the electrodes of one pair. To avoid the imposition of frequencies for each pair is set its own frequency.

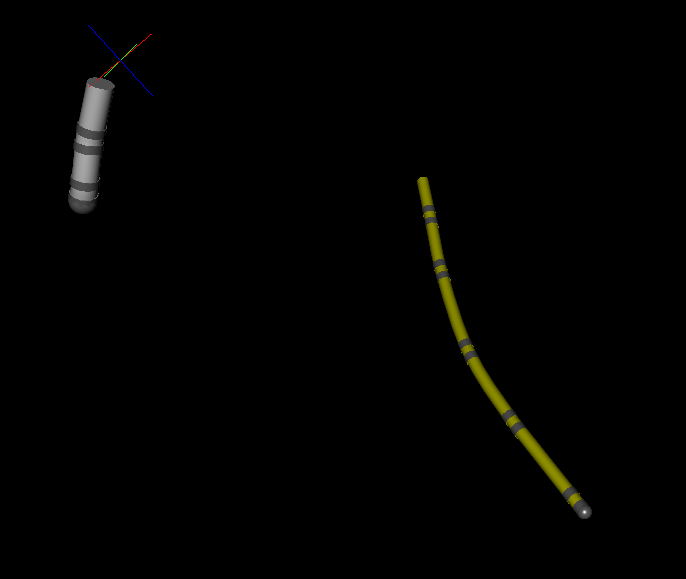
Throughout the operation, the potential difference between the poles of the mapping catheter and the reference is calculated. Moreover, we obtain the potential difference in three orthogonal axes. In the heart, the change in potential is linearly dependent on the distance of the catheter from the current sources. This allows, multiplying volts by a certain factor, to proceed to the determination of coordinates in millimeters. Thus, without any magic, it is possible to determine the relative position of ordinary electrodes. In the image, gray is a mapping catheter, yellow is a reference.
Building a heart model
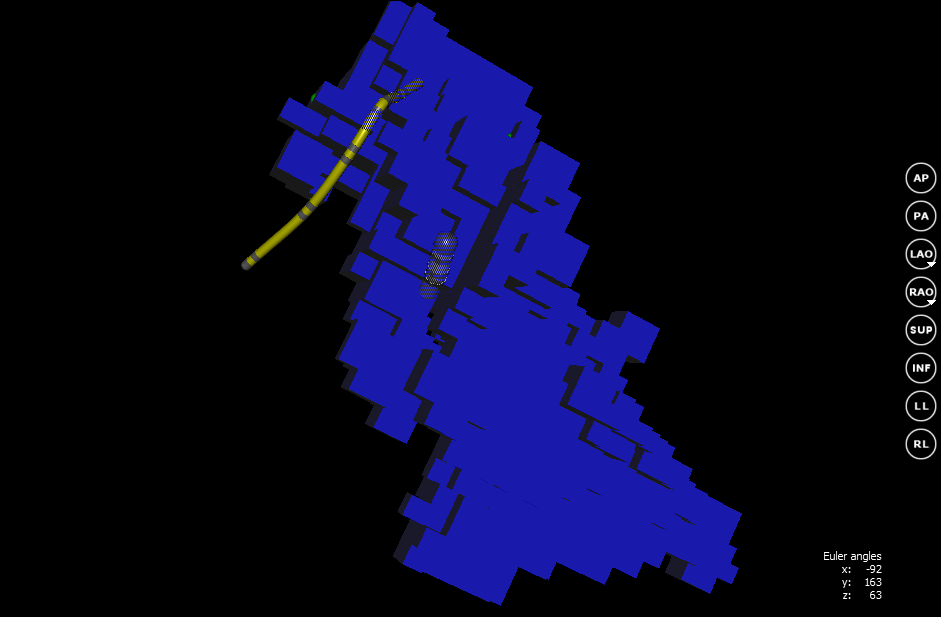
While the movement of the catheter is relatively opornoy point for the surgeon does not carry important information. But thanks to this, it became possible to build a 3D model of the heart. Before the construction of the surface mesh, the program sets the reconstruction area. This is the area within which the operated department of the heart is located. To do this, place the mapping catheter in the center of the heart section. You must also specify the size of the reconstruction area. Usually a radius of 10 cm is enough for mapping. Next, the resulting cube is divided into voxels with the specified size. A voxel is an element of a three-dimensional image, a kind of three-dimensional analogue of a pixel. Each voxel may contain a specific value. In our case, 0 and 1 will be used as the value. A value of 0 indicates that the voxel is outside the heart section. 1 - value is set, voxel inside the model. Initially, all voxels are not installed.
After the initial data are specified, you can begin building a model of the heart. When the catheter is moved, its coordinates are compared with the coordinates of the voxel. If the coordinates of the voxel coincide with the coordinates of the catheter, then this voxel is set to 1. During the construction of the model, the doctor gradually brings the catheter to the walls of the heart. Thus, a voxel model of the entire cavity of the operated department is gradually built.
We are primarily interested in the inner surface. For this, based on the voxel model, a grid is constructed using the Marching cubes algorithm . The essence of this algorithm is that for each voxel, on the basis of its neighbors, a certain part of the surface is specified. The result will be a closed surface “covering” the voxel model.
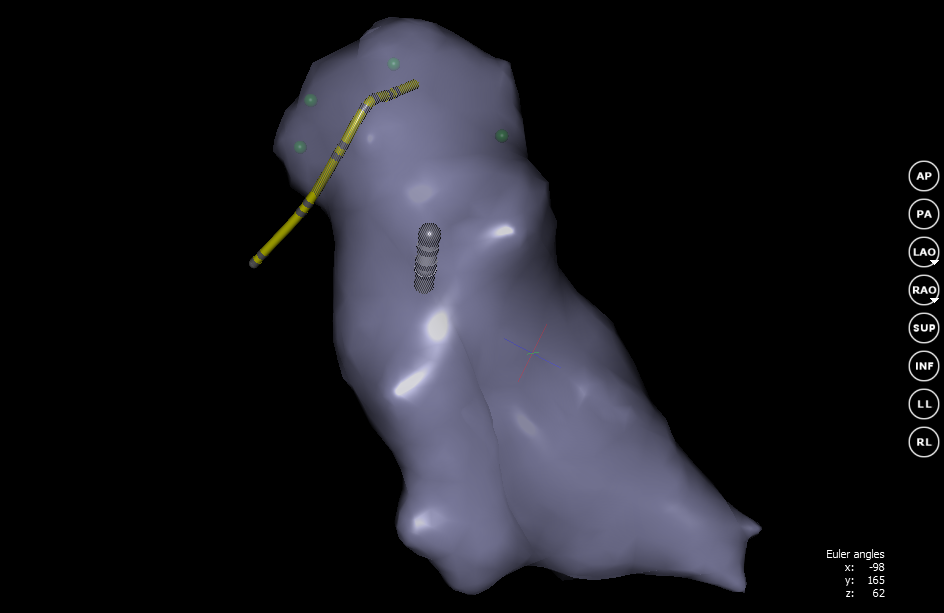
Rebuilding the grid occurs constantly in the process of changing the voxel model. The screen immediately displays the surface without a voxel model. When the grid is fully ready, the 3D model creation mode is turned off. Further changes in the position of the catheters do not affect the geometry of the mesh.
In our case, to better match the real picture, you can cut out a part of the grid, thereby marking the valve of the right atrium.
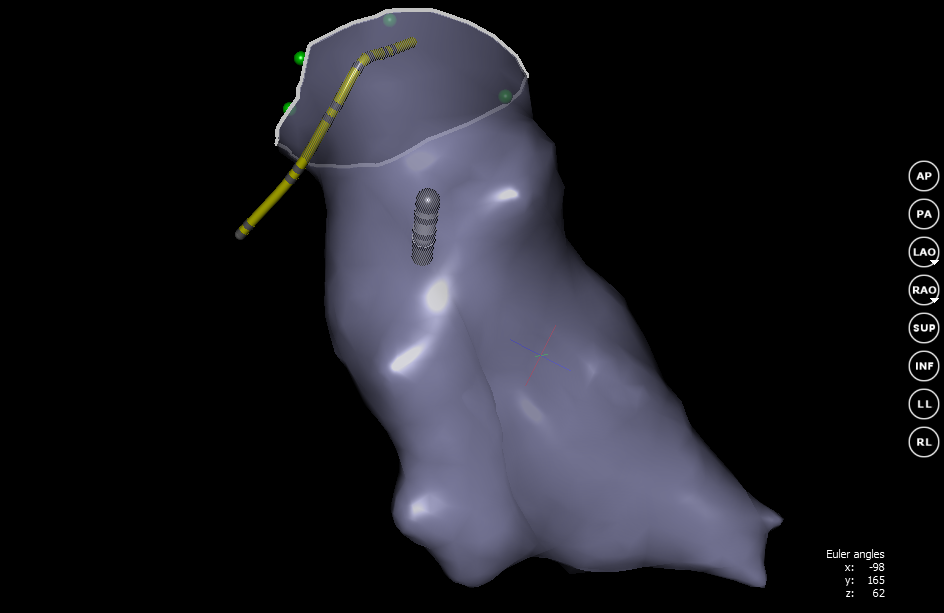
The result is the inner surface of the desired department. Now the doctor sees the movement of the catheter relative to the walls of the heart. Thanks to this, it becomes much easier to control the catheter and you can start searching for rhythm disturbers.
Mapping
The next step is the study of the spread of excitation through the myocardium. It is worth noting that during the entire operation, the connected catheters and standard leads are recorded in the same time scale.
The study is as follows. The doctor brings the mapping catheter to the wall of the heart and removes the data. One of the main indicators is the time of activation (excitation) at this point. It is possible to determine the moment of excitation by the electrocardiogram from the pole of the mapping catheter. During activation on the ECG there will be a prong. The moment of activation on the chart can be set either by the doctor manually or determined automatically.
Next, the lag time is calculated. This is the difference in time between the activation at the point under study with the activation fixed at one of the leads. As such assignments can act either the poles of the reference catheter or chest leads. In our case, we will use the standard lead III. Thus, we compare the moment of excitation at a specific point with the average value of excitation throughout the heart. In the example below, the red point marks the moment of activation from lead III, green from the mapping catheter.

The cardiologist can decide, at his discretion, which data should be taken into account and which should not be taken into account. We will understand why this is important. For the type of arrhythmia in question, sources of unwanted arousal manifest themselves with a certain interval (often non-permanent). In the intervals between the extraordinary contraction of the heart, the excitation pulse is distributed in the usual way, and the ECG from standard leads has a normal appearance. The distribution of normal arousal is well studied and is of no interest during surgery. The doctor is interested in the spread of excitement from the violator of the rhythm. To determine the occurrence of unwanted pulse (extrasystoles) can be on an ECG from standard leads. The ECG at this moment has a deviation from the normal view. This is the time when it is worth taking readings from the surface of the heart.
Sometimes extrasystoles appear too rarely during surgery. In such cases, the surgeon can artificially provoke an arrhythmia using electrical impulses transmitted from the catheter. Under the supervision of specialists in the operating room, such stimulation is fairly safe.
If the data of interest is obtained, the doctor records the results and they are saved. On a 3D model of the heart, a point is set at the place where the catheter was located. Now you can begin to explore a new point. So, alternately moving the catheter from one point to another, readings are taken from the inner surface of the mapped department. In general, it takes from several tens to hundreds of points in difficult cases. Based on the delay time, an isochronous myocardium activation map is constructed using interpolation.
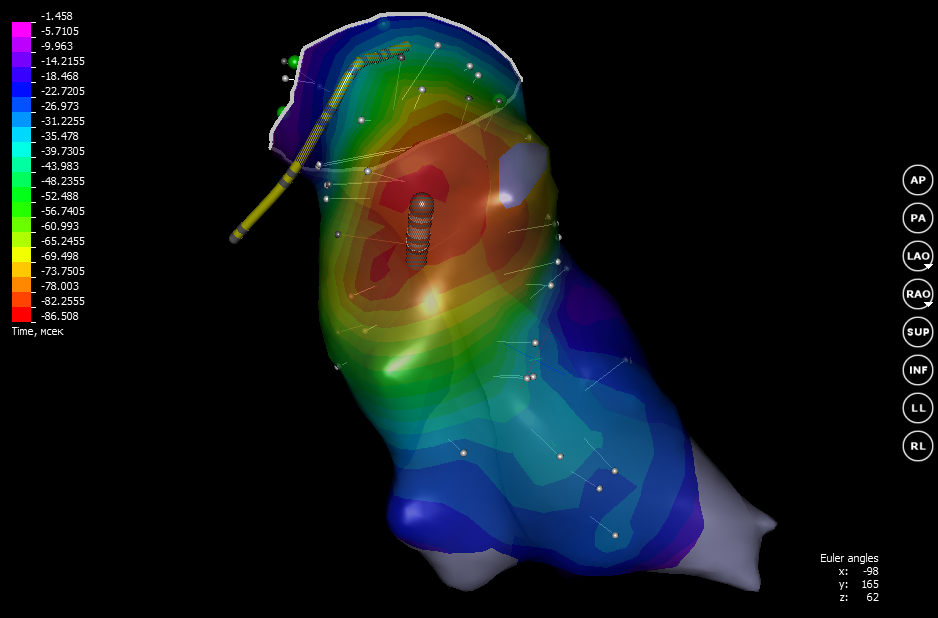
On such a map, the activation time is indicated by color. Excitement extends from red to purple. An isochronous map can be displayed in a somewhat different form: to show the picture not as a whole, but to display the distribution of arousal only at a certain point in time. Such a card is called an activation card.
Eliminate unwanted source
On maps constructed in this way, one can clearly see the spread of excitation along the myocardium and, most importantly, the sources of arousal themselves. As a result, the doctor knows exactly where to act to eliminate the arrhythmia. The process of neutralization of arrhythmogenic zones is as follows:
- Relying on the constructed map, the doctor presses the pole of the catheter to a point on the heart that generates unwanted impulses.
- Through the catheter is fed high frequency current. Electrical energy is converted to heat. Due to the high conductivity of the pole, it is not the pole itself that is heated, but the fabric surrounding this electrode. Heating is adjusted to 45 degrees Celsius. As a result, a small portion of the heart tissue, in which the pathological path passes, is destroyed. Important: the catheter with which the operation is performed must have thermal sensors. This is due to the fact that you need to constantly monitor the heat, because at higher temperatures it is possible to cause serious damage to the heart cells.
- After all unwanted foci are eliminated, pulse propagation measurements are taken again to evaluate the effectiveness of the operation.
Instead of conclusion
There are other ways to program navigation with its pros and cons. For example, positioning on the basis of magnetic fields has a higher accuracy, but such systems require special, expensive catheters.
This article showed a basic example of operation in a simplified form. Within one article it is impossible to describe all the details and types of operations.
Thank you for your attention and be healthy!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/354344/
All Articles