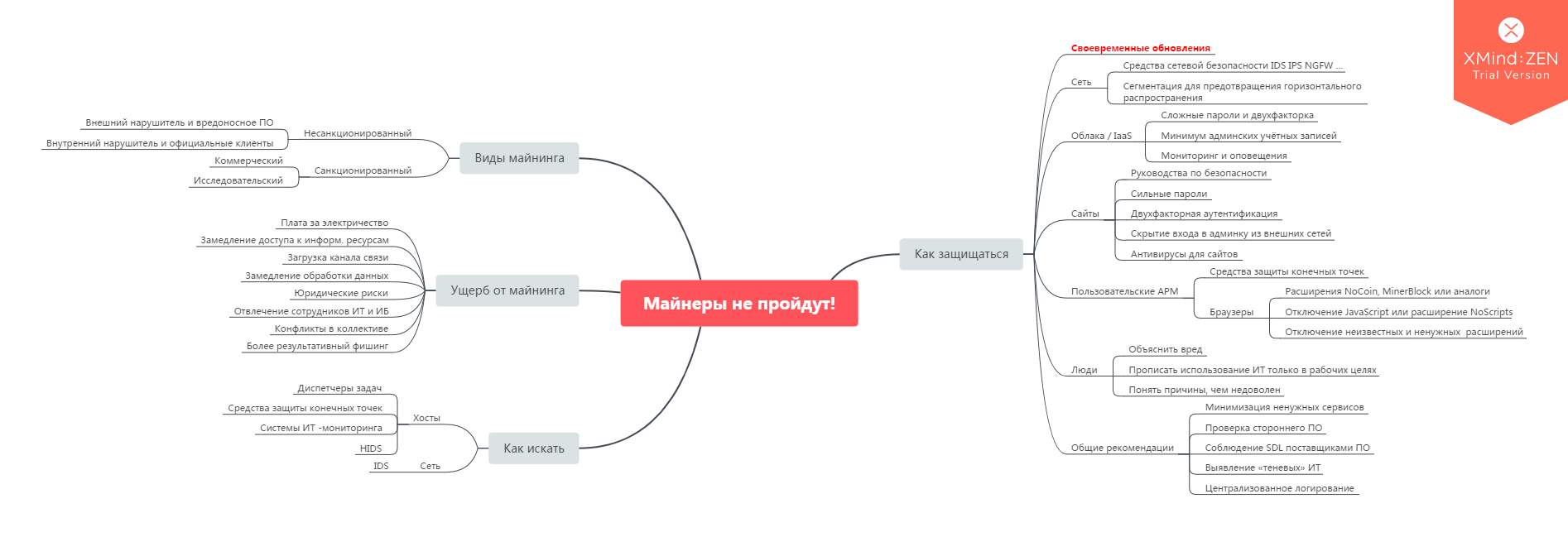
Miners will not pass
Well, or at least stumble.
Since the beginning of 2017, our Information Security Monitoring Center sees attempts to mine cryptocurrency on corporate IT resources connected to monitoring. Well, he sees and sees, why do you want a cue ball, or what?
Indeed, and what harm do miners in the corporate network? What are the threats to the business? Let's try to figure out and understand how to look for miners and deal with them (if, of course, we decide to do it).
')

Marco Krohn, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International
Mining is a strange threat to IB. At first glance, it is not even clear why he is a threat. Miner clients do not touch your data, and malicious miners, as a rule, are also not really needed.
To analyze the damage done by the miners, I suggest using the McCumber Cube model . Since autumn 2017, John McCamber is responsible for the promotion of information security in North America in (ISC) ² (they are certified on CISSP, SSCP, CCSP, CSSLP and other incomprehensible abbreviations). Before that, John worked in the USAF and Gartner.
McCamber proposed a model that reflects the three main areas of information security.
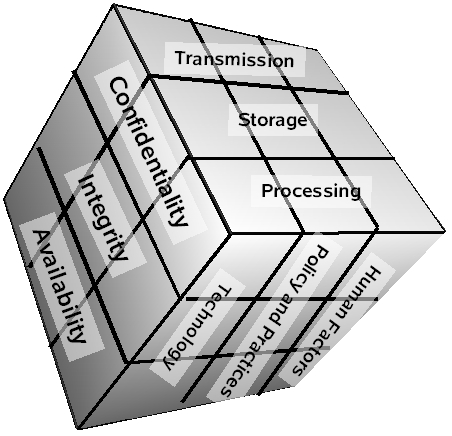
Safety goals (Desired goals)
Information states
Safeguards or protective measures (Safeguards)
Let's go over the edges of the cube and see how mining affects each.
Somehow too many potential problems so that you can simply ignore the mining on your infrastructure. So, we still catch.
Usually, user suspicions appear when the computer suddenly starts to slow down. First of all, let's check what we have with the processes.
For Windows, this can be done using Task Manager (Ctrl + Alt + Del or Ctrl + Shift + Esc), for Mac - Activity monitor , for "UNIX, Unix-like and other POSIX-compatible operating systems" - ps .
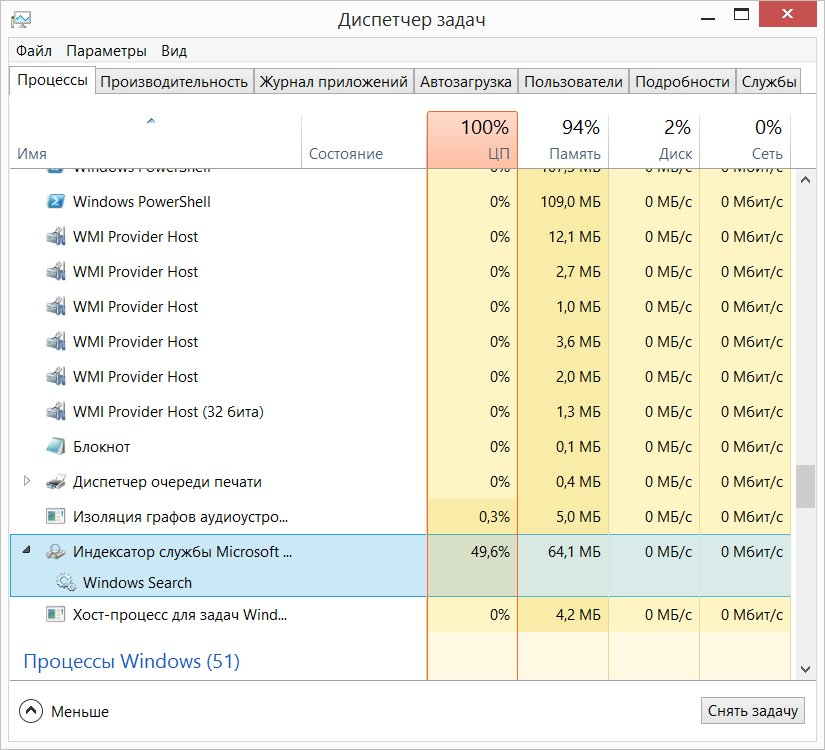
Real DZ, after which the idea to write an article appeared. But then it turned out, it turned out that several resource-intensive legitimate processes were launched simultaneously.
The problem is that some miners have learned how to track the launch of Task Manager. They stop working while the DZ is open, and then restart themselves. Alternatively, try alternatives :
If we see an unfamiliar or suspicious process, google the name. If this is something bad, there will almost certainly be instructions on how to remove it, and what to do so that it does not happen again.
In this difficult task, oddly enough, the creators of miners themselves can help. Since for them the main goal is computer computing resources, they do not want to compete for them with other miners. At the very end of March, security consultant Xavier Mertens ( xme ) discovered code that “dampens” competing mining processes and non-critical OS processes to free up resources for themselves. The code contains the names of the miner processes:
If any of these processes are running on the machine, congratulations! Most likely, you mine for someone. This is how the creator of the Malvari did part of the research work for us.

Do not forget about endpoint security systems. Good antiviruses have learned to catch miners. The main thing is not to forget in the Settings to tell the antivirus that they should be blocked. This is not always enabled by default, because the user can consciously download, install and run this software.
We go to the site of the anti-virus vendor, download the recovery disk image, write to the media, load from it and check the system. Long, but not particularly difficult.
Everything that was written above refers to the case when the user does not want to have a miner program on his PC. He is conscious, noticed and informed. But what if the user wants to mine himself and is not going to tell anyone about this?
Of course, there is something to catch and on the net! I came across such an amusing picture:
Network monitoring is a way to find "irresponsible" users and malicious mining software.
What should alert us:
Unfortunately, the latter method works only for well-known miners, domains and IP addresses, provided that the firewalls and network IDS / IPS are correctly configured and timely updated. Port blocking is a so-called method, because there can be legal activity on these ports.
The question arises: where to get the data for detection? A couple of years ago, I did a large internal research on Threat Intelligence and one of the types of sources called the Community Open Source Threat Exchange (COSTE). The table below shows their list, the links at the time of this writing were working. I also removed anti-spam, phishing, and publicly available vulnerability databases from this list.
If you have something to add, write in the comments or in a personal.
OK, we:
But most often the presence of a miner in the infrastructure says that the problem is not in the miner. The problem is wider - in people, in managing vulnerabilities, in setting up equipment and GIS. Removing software, we solve only a specific problem with this instance of software. And what to do so that the situation does not repeat?
Backup and upgrade!
All the data below recommendations will work only if the nodes are updated regularly. Otherwise, all efforts will be similar to the picture from one of our previous articles .

Thanks to network security tools, we will find traces of mining software in our infrastructure. Even if these tools work in the detection mode, we will get enough information for further investigation.
Many IT and IB administrators do not like to include network protection in blocking mode, for which they have good and understandable reasons related to the availability of services. Therefore, it would not be possible to recommend blocking by reputation lists at once. Miner, as a rule, does not threaten your data right at the moment of detection, there is time to figure it out.
As another preventive measure, you can segment the network to prevent the “horizontal” distribution of malware.
Who has a lot of computing power? Do cloud providers! Who will pay for virtualochka? Provider's customer! Here is the exciting story of almost $ 12,000 on a friendly site.
To avoid problems:
Most likely, you yourself will not suffer from the fact that your site will be placed malicious code, forcing the visitors' machines to extract cryptocurrency for attackers. Anyway, some time. Then there is the risk of getting it.

and pessimization in search results and reduced attendance.
For every popular CMS and platform there are security guides . It would be good to follow them, if possible.
Also it is worth checking whether your sites are already infected. It would be inappropriate to recommend any particular antivirus, read reviews and tips. I found topics on both the Toaster and Stackoverflow.
There is a good article about mining on machines visitors sites .
As usual, humans are the biggest problem. To be honest, I don’t know how to reliably catch a sysadmin or a security guard if he wants (well, he really wants to, decisively!) To mine at work. All methods resemble crutches.
But a few recommendations can still be given.
First, it’s worth explaining the damage to mining for the company. As a cheat sheet, you can use the section about the McCumber Cube.
Secondly, in the employment contract it is necessary to prescribe a ban on the use of corporate IT resources for personal purposes. There will be at least some argument in a dispute with a careless employee.
Thirdly, if the fact of mining was confirmed, one should understand the motives of the person. Money is tight? Did not know what can punish? Was it just interesting to try? This may not solve the peacefully specific situation, but it will show what you should pay attention to in the future.
And you can just decide that mining is quite a business and start mining crypt on an industrial scale. You can not fight - lead!
And finally, keep mayndkart about everything written.
Original size .
Colleagues told another absolutely non-technical way to identify miners-employees - "The server room suddenly became clean." Admins for quite a long time "cool" belonged to the order in the server, and suddenly she began to shine clean. There was no apparent reason for such a sharp change of mood. And the monitoring of several servers showed a flat, almost one hundred percent load.
Since the beginning of 2017, our Information Security Monitoring Center sees attempts to mine cryptocurrency on corporate IT resources connected to monitoring. Well, he sees and sees, why do you want a cue ball, or what?
Indeed, and what harm do miners in the corporate network? What are the threats to the business? Let's try to figure out and understand how to look for miners and deal with them (if, of course, we decide to do it).
')

Marco Krohn, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International
Is it necessary to even catch them
Mining is a strange threat to IB. At first glance, it is not even clear why he is a threat. Miner clients do not touch your data, and malicious miners, as a rule, are also not really needed.
To analyze the damage done by the miners, I suggest using the McCumber Cube model . Since autumn 2017, John McCamber is responsible for the promotion of information security in North America in (ISC) ² (they are certified on CISSP, SSCP, CCSP, CSSLP and other incomprehensible abbreviations). Before that, John worked in the USAF and Gartner.
McCamber proposed a model that reflects the three main areas of information security.

Safety goals (Desired goals)
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
Information states
- Broadcast
- Storage
- Treatment
Safeguards or protective measures (Safeguards)
- Human factor
- Policies and practices
- Technology
Let's go over the edges of the cube and see how mining affects each.
| Direction | Mining effect |
|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Does not break. |
| Integrity | Does not break. |
| Availability | Violates, can slow down, but not stop access to information (in this paragraph, the opinions of the reviewers are divided). |
| Storage | Does not break. |
| Broadcast | Network interaction of software with mining pools (or C & C servers in the case of malware operation) loads the channel, and traffic can be expensive (for legal entities sometimes several times more expensive than for individuals) or limited. |
| Treatment | If the miner completely utilizes the resources of the hardware (and this is an alarm and suspicious), users will observe delays when working with data. A typical situation is “Why are you so stupid, huh ?!” |
| Policies and practices | First, someone enriched at the expense of the company or institution. For the extraction of the crypt need electricity, which has to pay the company. Secondly, IT and IS staff are distracted from other tasks, they have to investigate these incidents and respond to them. Thirdly, there are legal risks for the company, since the legal status of cryptocurrency and its production in Russia has not yet been determined (on March 20, 2018, the Federal Law Project On Digital Financial Assets was submitted to the State Duma). |
| Human factor | If not all employees of a department or team in collusion, then questions arise who put the miner? Who "laid" a colleague? They will be followed by claims in the style of “Vasya Pupkin constantly monitors exchange rates in order to extract the most profitable, and is not engaged in basic work. Do I have to rake this pile of applications alone? ”Besides, the game of curiosity and greed works well during periods of the peak of the cryptocurrency rate and information noise, so people are more susceptible to attacks by social engineers and phishing. |
| Technology | At McCumber, this item is devoted to the assessment of the work of remedies. Therefore, if we found a miner, then we need to understand how he got into our infrastructure? Which of the SZI allowed? What else could get to us in the same way? This clearly indicates that there are problems or vulnerabilities that you have to deal with. But I would not call it “damage.” Rather, the argument for control. |
Somehow too many potential problems so that you can simply ignore the mining on your infrastructure. So, we still catch.
How to search
On hosts
Usually, user suspicions appear when the computer suddenly starts to slow down. First of all, let's check what we have with the processes.
For Windows, this can be done using Task Manager (Ctrl + Alt + Del or Ctrl + Shift + Esc), for Mac - Activity monitor , for "UNIX, Unix-like and other POSIX-compatible operating systems" - ps .

Real DZ, after which the idea to write an article appeared. But then it turned out, it turned out that several resource-intensive legitimate processes were launched simultaneously.
The problem is that some miners have learned how to track the launch of Task Manager. They stop working while the DZ is open, and then restart themselves. Alternatively, try alternatives :
- System explorer
- Process hacker
- Process lasso
- Process Explorer ( hello, Mark !)
- Process Monitor
If we see an unfamiliar or suspicious process, google the name. If this is something bad, there will almost certainly be instructions on how to remove it, and what to do so that it does not happen again.
In this difficult task, oddly enough, the creators of miners themselves can help. Since for them the main goal is computer computing resources, they do not want to compete for them with other miners. At the very end of March, security consultant Xavier Mertens ( xme ) discovered code that “dampens” competing mining processes and non-critical OS processes to free up resources for themselves. The code contains the names of the miner processes:
| Silence | vshell | taskhots |
| Carbon | winlogan | svchostx |
| xmrig32 | winlogo | xmr86 |
| nscpucnminer64 | logon | xmrig |
| mrservicehost | win1nit | xmr |
| servisce | wininits | win1ogin |
| svchosts3 | winlnlts | win1ogins |
| svhosts | taskngr | ccsvchst |
| system64 | tasksvr | nscpucnminer64 |
| systemiissec | mscl | update_windows |
| taskhost | cpuminer | |
| vrmserver | sql31 |
If any of these processes are running on the machine, congratulations! Most likely, you mine for someone. This is how the creator of the Malvari did part of the research work for us.

Do not forget about endpoint security systems. Good antiviruses have learned to catch miners. The main thing is not to forget in the Settings to tell the antivirus that they should be blocked. This is not always enabled by default, because the user can consciously download, install and run this software.
We go to the site of the anti-virus vendor, download the recovery disk image, write to the media, load from it and check the system. Long, but not particularly difficult.
Everything that was written above refers to the case when the user does not want to have a miner program on his PC. He is conscious, noticed and informed. But what if the user wants to mine himself and is not going to tell anyone about this?
Online
Of course, there is something to catch and on the net! I came across such an amusing picture:

Network monitoring is a way to find "irresponsible" users and malicious mining software.
What should alert us:
- Visiting sites, forums, board pro mining. The analysts of our Monitoring Center and colleagues sitting next to me are already looking askance at me).
- Downloading software for mining, and with the latest news about multiple forks of popular products on a githaba followed by embedding droppers there - in general, any software. Either forcefully check everything that has flown in (there are commercial solutions that do not send scanned files to the cloud), or ask users to send software distributions, attachments or executable files to Virustotal.
- Networking nodes with pools to exchange information about the received blocks and hashes.
Unfortunately, the latter method works only for well-known miners, domains and IP addresses, provided that the firewalls and network IDS / IPS are correctly configured and timely updated. Port blocking is a so-called method, because there can be legal activity on these ports.
The question arises: where to get the data for detection? A couple of years ago, I did a large internal research on Threat Intelligence and one of the types of sources called the Community Open Source Threat Exchange (COSTE). The table below shows their list, the links at the time of this writing were working. I also removed anti-spam, phishing, and publicly available vulnerability databases from this list.
If you have something to add, write in the comments or in a personal.
OK, we:
- found suspicious in traffic;
- came to a specific site and made sure that the miner works;
- removed it, using recommendations for a particular VPO;
- dismissed the employee who mine on our servers;
- and even sent a sample of malware and a traffic dump for analysis to Virustotal or to your favorite vendor.
But most often the presence of a miner in the infrastructure says that the problem is not in the miner. The problem is wider - in people, in managing vulnerabilities, in setting up equipment and GIS. Removing software, we solve only a specific problem with this instance of software. And what to do so that the situation does not repeat?
How to defend?
Backup and upgrade!
All the data below recommendations will work only if the nodes are updated regularly. Otherwise, all efforts will be similar to the picture from one of our previous articles .

Network
Thanks to network security tools, we will find traces of mining software in our infrastructure. Even if these tools work in the detection mode, we will get enough information for further investigation.
Many IT and IB administrators do not like to include network protection in blocking mode, for which they have good and understandable reasons related to the availability of services. Therefore, it would not be possible to recommend blocking by reputation lists at once. Miner, as a rule, does not threaten your data right at the moment of detection, there is time to figure it out.
As another preventive measure, you can segment the network to prevent the “horizontal” distribution of malware.
IaaS
Who has a lot of computing power? Do cloud providers! Who will pay for virtualochka? Provider's customer! Here is the exciting story of almost $ 12,000 on a friendly site.
To avoid problems:
- Use complex and unique passwords.
- Configure 2-FA.
- Reduce to the required minimum the number of admins uchetok.
- If you pay for the actual consumption of resources, constantly monitor the activity and set up alerts for everyone.
Sites
Most likely, you yourself will not suffer from the fact that your site will be placed malicious code, forcing the visitors' machines to extract cryptocurrency for attackers. Anyway, some time. Then there is the risk of getting it.

and pessimization in search results and reduced attendance.
For every popular CMS and platform there are security guides . It would be good to follow them, if possible.
Also it is worth checking whether your sites are already infected. It would be inappropriate to recommend any particular antivirus, read reviews and tips. I found topics on both the Toaster and Stackoverflow.
There is a good article about mining on machines visitors sites .
Custom AWP
As usual, humans are the biggest problem. To be honest, I don’t know how to reliably catch a sysadmin or a security guard if he wants (well, he really wants to, decisively!) To mine at work. All methods resemble crutches.
- Why do we have more electricity bills? - Well, spring, air conditioners included.
- And what is this new box in the rack? - Special equipment for compliance. Don't ask such silly questions anymore.
- Let's keep logs of all admin actions! - Will the same administrators view them?
But a few recommendations can still be given.
First, it’s worth explaining the damage to mining for the company. As a cheat sheet, you can use the section about the McCumber Cube.
Secondly, in the employment contract it is necessary to prescribe a ban on the use of corporate IT resources for personal purposes. There will be at least some argument in a dispute with a careless employee.
Thirdly, if the fact of mining was confirmed, one should understand the motives of the person. Money is tight? Did not know what can punish? Was it just interesting to try? This may not solve the peacefully specific situation, but it will show what you should pay attention to in the future.
And you can just decide that mining is quite a business and start mining crypt on an industrial scale. You can not fight - lead!
And finally, keep mayndkart about everything written.

Original size .
Bonus
Colleagues told another absolutely non-technical way to identify miners-employees - "The server room suddenly became clean." Admins for quite a long time "cool" belonged to the order in the server, and suddenly she began to shine clean. There was no apparent reason for such a sharp change of mood. And the monitoring of several servers showed a flat, almost one hundred percent load.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/354338/
All Articles