Veeam Backup & Replication: 10 Tips for Beginners
Something quite a while ago we did not write about our flagship product. We are correcting, especially as another portion of useful tips from the guys from the Veeam Support Team arrived. Today my colleague Yevgeny Ivanov is with you again, now from Bucharest, where he was called up as a mentor for the Romanian technical support team.
In the course of his work, Eugene and his comrades gathered a decent collection of “rakes”, which novice users most often attack when deploying and configuring Veeam Backup & Replication. And so that you do not repeat their mistakes, Zhenya explains how to do everything correctly.
So, welcome under cat.

“Direct incremental” or “infinitely incremental” are usually recommended, as they are the fastest. An infinitely-incremental chain (without periodic full backups) takes up less space and is fairly quickly processed. A custom incremental chain takes up more space, but it is also more “resilient”, so to speak, as it contains not only incremental backups, but also periodically created full ones.
')
The reverse (reverse) incremental method is the oldest and, of course, the slowest. Depending on the storage system, it can be 3 or even more times slower than others. However, there are some advantages to using it: the last in the chain is always a full backup, and therefore you can recover faster than from chains of other types. Note, however, that the difference with the usual incremental chain is not very significant (unless you keep such a chain unnecessarily long, that is, more than 30 days).
Learn more about the methods here .
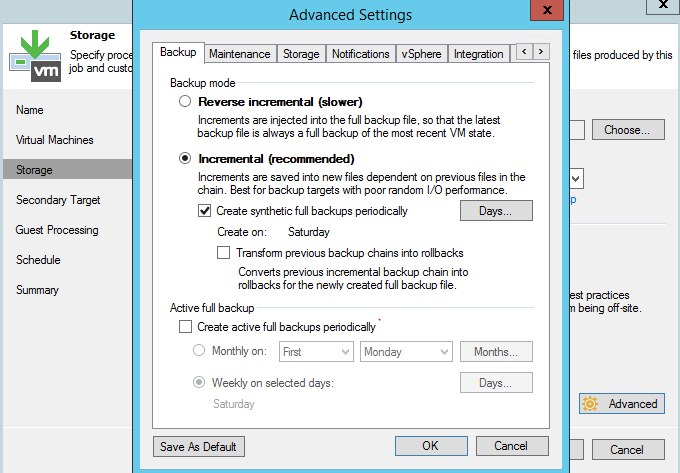
The operation of creating a synthetic full backup uses restore points that are stored in the repository. But it must be borne in mind that not every storage system is able to provide sufficient performance for this operation. Therefore, we recommend as an alternative the creation of active full backups.
When you specify the settings for creating a synthetic full backup, pay attention to the option “Transform previous backup chains into rollbacks” (convert previous chains to rollback points). Its use will cause the task of converting an incremental backup (.VIB) to rollback points (.VRB) (which will, however, consume a significant portion of the storage resources of the repository). For example, using this option, you can convert the current chain into inverse-incremental, in particular, for archival storage.
But if you use this option as a backup method, then you will end up with a very peculiar chain from a full backup file and incremental and reverse-incremental backup files.
Processing the guest OS allows you to create consistent backups of virtual machines. And if such applications as Microsoft Exchange, Active Directory, SharePoint, SQL Server or Oracle are working on the VM, then you can use the capabilities of Veeam Explorers tools to restore them granularly. Work from the guest OS is based on the VSS functionality (supported by Windows), which must be configured correctly, otherwise the backup tasks will not be able to complete successfully.
To activate the guest OS processing settings:
If you enable the VM Guest File System Indexing option in the backup settings, Veeam Backup & Replication will create VM file directories. This will allow you to search for files and restore in 1 click through the web interface Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager.
If you are not working with Enterprise Manager, then we advise you not to enable this option - this will reduce the backup window (sometimes quite significantly) and save space on the C: drive of the Veeam backup server. Recovery of VM files through the Veeam Backup & Replication console will not affect it in any way.
No storage vendor guarantees absolute data integrity. Of course, Veeam checks the backup file when writing to disk, but despite the fact that millions of operations are performed on the storage system, a random permutation of the bits is still possible, and the result is “invisible” damage. To detect such damage in the early stages, Veeam Backup & Replication suggests using the SureBackup and health checks features. But this is not a panacea, so we advise to adopt the rule 3-2-1 , which requires the use of different types of media for backup and store them in at least 2 sites.
To do this, it is recommended that after creating the main backup task, set up a backup transfer task. Such a task can use backup storage or cloud storage as a target storage location. You can also archive backups to tape.
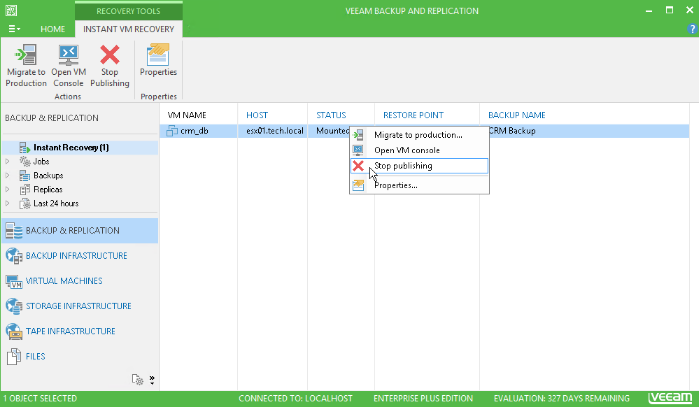
Instant VM Recovery VM Instant VM Recovery allows you to start the machine in the shortest possible time directly from the backup. However, you need to remember that this machine is placed in your repository and consumes its resources until you transfer it to production. Do not forget about this important final step - believe me, over the years of work in technical support for Veeam, we have seen many cases with VMs that have been functioning in the “from backup” mode for weeks without being transferred to production. The result was usually quite pitiable: data overflow and data loss.
Details on how to perform instant recovery correctly, read here .
Veeam supports a variety of repositories as repositories. Many of our users from year to year prefer to use a Windows or Linux physical server for this purpose, since in most cases this gives maximum performance. You can read about it on our forum .
Repositories on CIFS share are also quite popular, despite the fact that their performance is lower than others.
Many modern NAS devices support iSCSI, so it’s best to still configure the iSCSI drive and make it available for the Veeam backup server (or proxy). It should be borne in mind that in such a scenario (using the repository on the NAS) it is not recommended to use the method of reverse-incremental backup, since It gives a large load on the storage system due to the intensity of reading / writing.
If you are going to perform replication over WAN, then we recommend that you configure a backup proxy server on a remote site and specify it in the replication task settings. This way you get a reliable channel between the two sites. We advise you to enable this proxy in the Network mode (NBD), since working in the Virtual Appliance mode (hot-add) during replication can lead to the appearance of "lost" snapshots.
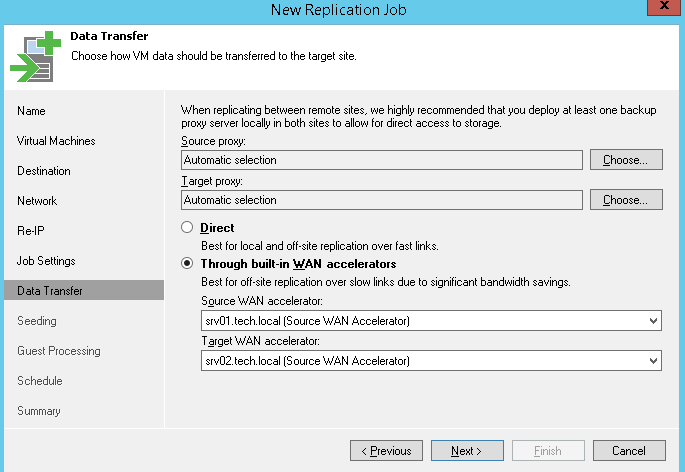
We recommend using a proxy on a remote site in the case of operation via a WAN accelerator. You can deploy a WAN accelerator and proxy on different machines or even on one (of course, if it has enough resources).

The Veeam uses a tape server to transfer data to the tape device. It is placed on the physical server to which this tape device is connected.
Important! Connecting to VM with “forwarding” through an ESXi host is not supported!
Veeam Backup & Replication obtains information about the tape library from the operating system, so make sure that you have the latest drivers installed, and the tape device is correctly displayed in the device manager console.
More helpful tips on working with magnetic tape can be found in this article .
There is nothing you can do, you have to make a request on the technical support portal. We urge you to do a couple of simple things:
I hope our recommendations will help someone avoid common mistakes when deploying and configuring Veeam Backup & Replication. Today I have everything. Wishing you success, Veeam Support Team.
In the course of his work, Eugene and his comrades gathered a decent collection of “rakes”, which novice users most often attack when deploying and configuring Veeam Backup & Replication. And so that you do not repeat their mistakes, Zhenya explains how to do everything correctly.
So, welcome under cat.

# 1: Choose the best backup method
“Direct incremental” or “infinitely incremental” are usually recommended, as they are the fastest. An infinitely-incremental chain (without periodic full backups) takes up less space and is fairly quickly processed. A custom incremental chain takes up more space, but it is also more “resilient”, so to speak, as it contains not only incremental backups, but also periodically created full ones.
')
The reverse (reverse) incremental method is the oldest and, of course, the slowest. Depending on the storage system, it can be 3 or even more times slower than others. However, there are some advantages to using it: the last in the chain is always a full backup, and therefore you can recover faster than from chains of other types. Note, however, that the difference with the usual incremental chain is not very significant (unless you keep such a chain unnecessarily long, that is, more than 30 days).
Learn more about the methods here .
# 2: Think about the settings for synthetic full backups
The operation of creating a synthetic full backup uses restore points that are stored in the repository. But it must be borne in mind that not every storage system is able to provide sufficient performance for this operation. Therefore, we recommend as an alternative the creation of active full backups.
When you specify the settings for creating a synthetic full backup, pay attention to the option “Transform previous backup chains into rollbacks” (convert previous chains to rollback points). Its use will cause the task of converting an incremental backup (.VIB) to rollback points (.VRB) (which will, however, consume a significant portion of the storage resources of the repository). For example, using this option, you can convert the current chain into inverse-incremental, in particular, for archival storage.
But if you use this option as a backup method, then you will end up with a very peculiar chain from a full backup file and incremental and reverse-incremental backup files.

# 3: Customize guest OS handling
Processing the guest OS allows you to create consistent backups of virtual machines. And if such applications as Microsoft Exchange, Active Directory, SharePoint, SQL Server or Oracle are working on the VM, then you can use the capabilities of Veeam Explorers tools to restore them granularly. Work from the guest OS is based on the VSS functionality (supported by Windows), which must be configured correctly, otherwise the backup tasks will not be able to complete successfully.
To activate the guest OS processing settings:
- In the properties of the backup job, go to the step Guest Processing .
- Enable the option Application-aware processing (processing based on the state of the application).
- In the Guest OS credentials section, specify an account with administrator privileges to access the guest OS.
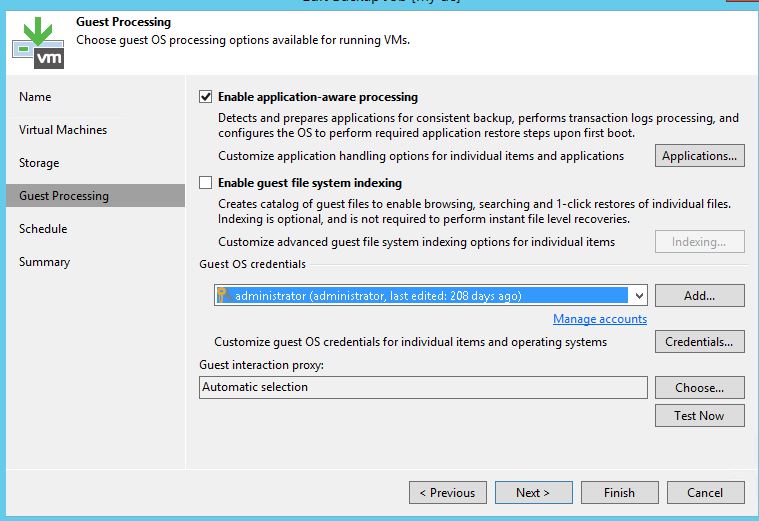
- If you need a separate account for any VM in the backup job, then click the Credentials button. Next you need to click on Set User ... and specify the necessary data.
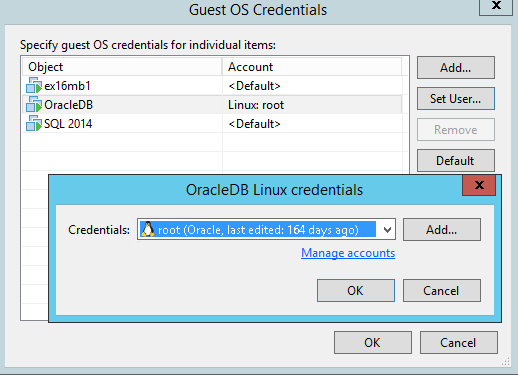
- Settings for processing specific applications are set in a separate dialog that opens after clicking Applications .... If necessary, you can also disable the processing of guest OS for individual machines.
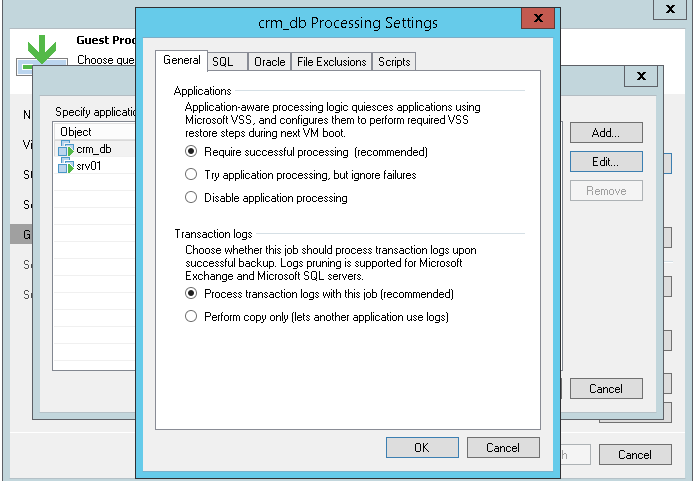
# 4: Do not index files unnecessarily
If you enable the VM Guest File System Indexing option in the backup settings, Veeam Backup & Replication will create VM file directories. This will allow you to search for files and restore in 1 click through the web interface Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager.
If you are not working with Enterprise Manager, then we advise you not to enable this option - this will reduce the backup window (sometimes quite significantly) and save space on the C: drive of the Veeam backup server. Recovery of VM files through the Veeam Backup & Replication console will not affect it in any way.
# 5: Make extra backups
No storage vendor guarantees absolute data integrity. Of course, Veeam checks the backup file when writing to disk, but despite the fact that millions of operations are performed on the storage system, a random permutation of the bits is still possible, and the result is “invisible” damage. To detect such damage in the early stages, Veeam Backup & Replication suggests using the SureBackup and health checks features. But this is not a panacea, so we advise to adopt the rule 3-2-1 , which requires the use of different types of media for backup and store them in at least 2 sites.
To do this, it is recommended that after creating the main backup task, set up a backup transfer task. Such a task can use backup storage or cloud storage as a target storage location. You can also archive backups to tape.
# 6: Finalize Instant Recovery
Instant VM Recovery VM Instant VM Recovery allows you to start the machine in the shortest possible time directly from the backup. However, you need to remember that this machine is placed in your repository and consumes its resources until you transfer it to production. Do not forget about this important final step - believe me, over the years of work in technical support for Veeam, we have seen many cases with VMs that have been functioning in the “from backup” mode for weeks without being transferred to production. The result was usually quite pitiable: data overflow and data loss.
Details on how to perform instant recovery correctly, read here .

# 7: Think about where to put the repository
Veeam supports a variety of repositories as repositories. Many of our users from year to year prefer to use a Windows or Linux physical server for this purpose, since in most cases this gives maximum performance. You can read about it on our forum .
Repositories on CIFS share are also quite popular, despite the fact that their performance is lower than others.
Many modern NAS devices support iSCSI, so it’s best to still configure the iSCSI drive and make it available for the Veeam backup server (or proxy). It should be borne in mind that in such a scenario (using the repository on the NAS) it is not recommended to use the method of reverse-incremental backup, since It gives a large load on the storage system due to the intensity of reading / writing.
# 8: Use proxy for replication
If you are going to perform replication over WAN, then we recommend that you configure a backup proxy server on a remote site and specify it in the replication task settings. This way you get a reliable channel between the two sites. We advise you to enable this proxy in the Network mode (NBD), since working in the Virtual Appliance mode (hot-add) during replication can lead to the appearance of "lost" snapshots.

We recommend using a proxy on a remote site in the case of operation via a WAN accelerator. You can deploy a WAN accelerator and proxy on different machines or even on one (of course, if it has enough resources).

# 9: Consider important details when archiving to tape
The Veeam uses a tape server to transfer data to the tape device. It is placed on the physical server to which this tape device is connected.
Important! Connecting to VM with “forwarding” through an ESXi host is not supported!
Veeam Backup & Replication obtains information about the tape library from the operating system, so make sure that you have the latest drivers installed, and the tape device is correctly displayed in the device manager console.
More helpful tips on working with magnetic tape can be found in this article .
# 10: If something went wrong anyway
There is nothing you can do, you have to make a request on the technical support portal. We urge you to do a couple of simple things:
- Check what level of severity you set for your application - for this, match it with the relevant criteria. We understand that all problems are serious for our users (otherwise they would not have contacted us), and our responsibility is to consider applications as soon as possible. But if you set the level of Severity 1, and the application does not meet the criteria of this level, you risk losing valuable time that it takes to re-qualify your application and redirect to the appropriate queue.
- To make it easier and faster to find the cause of the problem, be sure to prepare logs for sending to us. How to do it correctly, is written here. In some cases, our engineers may ask for logs of other components of your infrastructure, so you should be prepared.

I hope our recommendations will help someone avoid common mistakes when deploying and configuring Veeam Backup & Replication. Today I have everything. Wishing you success, Veeam Support Team.
Additional links
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/354302/
All Articles