Configure BGP to bypass locks, or “How I stopped being afraid and fell in love with the RKN”
Well, okay, about “loved” is an exaggeration. Rather, "could coexist with."
As you all know, from April 16, 2018, Roskomnadzor with extremely broad strokes blocks access to resources on the network, adding to the “Unified Register of Domain Names, website page indexes on the Internet and network addresses to identify sites on the Internet, containing information whose distribution in the Russian Federation is prohibited "(in the text - just a register) by / 10 sometimes. As a result, citizens of the Russian Federation and business suffer, losing access to the absolutely legal resources they need.
After I said in the comments to one of the articles on Habré that I was ready to help the victims with setting up the bypass scheme, several people asked me for such help. When everything worked for them, one of them recommended to describe the methodology in the article. Upon reflection, I decided to break my silence on the site and try for once to write something intermediate between the project and the post on Facebook, i.e. habrapost The result is in front of you.
Disclaimer
Since it is not very legal to publish ways to bypass access to information that is prohibited on the territory of the Russian Federation, the purpose of this article will be to talk about a method that allows you to automate access to resources allowed on the territory of the Russian Federation, but because of someone else’s actions through your provider. And access to other resources, obtained as a result of actions from the article, is an annoying side effect and the purpose of the article is by no means the case.
Also, since I am primarily a network architect by profession, vocation and life, programming and Linux are not my strengths. Therefore, of course, you can write better scripts, security issues in the VPS can be worked out deeper, etc. Your suggestions will be gratefully accepted if they are detailed enough - I will gladly add them to the text of the article.
TL; DR
We automate access to resources through your existing tunnel, using a copy of the registry and BGP protocol. The goal is to remove all traffic addressed to blocked resources to the tunnel. Minimum explanation, mostly step by step instructions.
What do you need for this?
Unfortunately, this post is not for everyone. In order to use this technique, you will need to bring together several elements:
- You must have a linux server somewhere outside the lock box. Or at least the desire to have such a server - the benefit is it now costs from $ 9 / year, and perhaps less. The method is also suitable if you have a separate VPN tunnel, then the server can be located inside the blocking field.
- Your router must be smart enough to be able to
- Any VPN client you like (I prefer OpenVPN, but this could be PPTP, L2TP, GRE + IPSec, and any other option that creates a tunnel interface);
- BGPv4 protocol. Which means that for SOHO it can be Mikrotik or any router with OpenWRT / LEDE / similar custom firmware, allowing you to install Quagga or Bird. Using a PC router is also not forbidden. In the case of an enterprise, see the BGP support in the documentation for your border router.
- You should have an understanding of the use of Linux and network technologies, including the BGP protocol. Or at least want to get such an idea. Since I am not ready to embrace the immense this time, you will have to study some incomprehensible moments for you on your own. However, of course, I will answer specific questions in the comments and are unlikely to be the only one to answer, so do not hesitate to ask.
What is used in the example
- A copy of the registry - from https://github.com/zapret-info/zi
- VPS - Ubuntu 16.04
- Routing Service - bird 1.6.3
- Router - Mikrotik hAP ac
- Working folders - since we work from the root, most of all will be placed in the home folder of the root. Respectively:
- / root / blacklist - working folder with compilation script
- / root / zi - registry copy with github
- / etc / bird - standard bird service settings folder
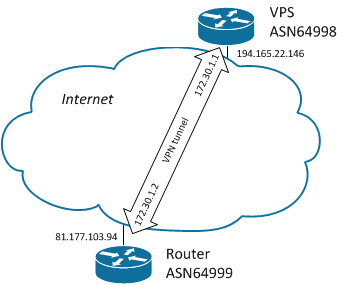
- The external IP address of the VPS with the routing server and the tunnel termination point is 194.165.22.146, ASN 64998; external IP-address of the router - 81.177.103.94, ASN 64999
- The IP addresses inside the tunnel are 172.30.1.1 and 172.30.1.2, respectively.
Of course, you can use any other routers, operating systems and software products, adjusting the decision according to their logic.
Briefly - decision logic
- Preparatory actions
- We get VPS
- Raise the tunnel from the router to the VPS
- We receive and regularly update the copy of the registry
- Install and configure the routing service
- Create a list of static routes for the routing service based on the registry
- We connect the router to the service and configure sending all the traffic through the tunnel.
Actually the decision
Preparatory actions
In the vastness of the network there are many services that provide VPS for extremely reasonable money. So far I have found and use the option for $ 9 / year, but even if I don’t really bother, there are a lot of options for 1E / month on every corner. The question of choosing a VPS is far beyond the scope of this article, so if someone doesn’t understand something about this, ask in the comments.
If you use VPS not only for the routing service, but also for the tunnel termination on it - you need to raise this tunnel and, almost unambiguously, configure NAT for it. There are a large number of instructions on these actions in the network, here I will not repeat them. The main requirement for such a tunnel is that it must create a separate interface on your router supporting the tunnel in the direction of the VPS. Most of the VPN technologies used meet this requirement — for example, OpenVPN in tun mode is perfect.
Getting a copy of the registry
As Jabrail said, "He who bothers us will help us." Since the VKN creates a registry of prohibited resources, it would be a sin to not use this registry to solve our problem. We will receive a copy of the registry with github.
We go to your Linux server, fall into the root context ( sudo su - ) and install git if it is not already installed.
apt install git.
cd ~ && git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/zapret-info/z-i ( 20 , ). crontab -e :
*/20 * * * * cd ~/z-i && git pull && git gc, . /root/z-i/.git/hooks/post-merge :
#!/usr/bin/env bash
changed_files="$(git diff-tree -r --name-only --no-commit-id ORIG_HEAD HEAD)"
check_run() {
echo "$changed_files" | grep --quiet "$1" && eval "$2"
}
check_run dump.csv "/root/blacklist/makebgp"chmod +x /root/z-i/.git/hooks/post-mergemakebgp, , .
bird. , Ubuntu bird , PPA .
add-apt-repository ppa:cz.nic-labs/bird
apt update
apt install birdbird IPv6 — .
systemctl stop bird6
systemctl disable bird6bird (/etc/bird/bird.conf), ( , )
log syslog all;
router id 172.30.1.1;
protocol kernel {
scan time 60;
import none;
# export all; # Actually insert routes into the kernel routing table
}
protocol device {
scan time 60;
}
protocol direct {
interface "venet*", "tun*"; # Restrict network interfaces it works with
}
protocol static static_bgp {
import all;
include "pfxlist.txt";
#include "iplist.txt";
}
protocol bgp OurRouter {
description "Our Router";
neighbor 81.177.103.94 as 64999;
import none;
export where proto = "static_bgp";
local as 64998;
passive off;
multihop;
}
router id — , IPv4-, . 32- IPv4-, IPv4- ( VPS).
protocol direct , . , . , IPv4-.
protocol static — , ip- ( , , /32) . — . , ip- , — . , 78 , ip- — 85898. , ip — . 85 .
protocol bgp, , bgp- . ip- — ( ), 64998 64999 — . 16- , AS , RFC6996 — 64512-65534 ( 32- ASN, ). eBGP , .
, IP- , private (RFC1918) shared (RFC6598) , , .
, — protocol bgp IP- . , . , IP- .
, , ip-, protocol static. , /root/blacklist/makebgp
#!/bin/bash
cut -d";" -f1 /root/z-i/dump.csv| tr '|' '\n' | tr -d ' ' > /root/blacklist/tmpaddr.txt
cat /root/blacklist/tmpaddr.txt | grep / | sed 's_.*_route & reject;_' > /etc/bird/pfxlist.txt
cat /root/blacklist/tmpaddr.txt | sort | uniq | grep -Eo "([0-9]{1,3}[\.]){3}[0-9]{1,3}" | sed 's_.*_route &/32 reject;_' > /etc/bird/iplist.txt
/etc/init.d/bird reload
logger 'bgp list compiled'chmod +x /root/blacklist/makebgp/etc/bird.
, bird , , . , :
systemctl start bird
birdc show route80 ( , , ) :
54.160.0.0/12 unreachable [static_bgp 2018-04-19] * (200)birdc show protocol. (. ), OurRouter start ( Connect Active), up ( Established). , :
BIRD 1.6.3 ready.
name proto table state since info
kernel1 Kernel master up 2018-04-19
device1 Device master up 2018-04-19
static_bgp Static master up 2018-04-19
direct1 Direct master up 2018-04-19
RXXXXXx1 BGP master up 13:10:22 Established
RXXXXXx2 BGP master up 2018-04-24 Established
RXXXXXx3 BGP master start 2018-04-22 Connect Socket: Connection timed out
RXXXXXx4 BGP master up 2018-04-24 Established
RXXXXXx5 BGP master start 2018-04-24 Passive
, , , — . , — .
. — BGP- nexthop, ( p2p ) ip- , ethernet).
, Mikrotik RouterOS
/routing bgp instance set default as=64999 ignore-as-path-len=yes router-id=172.30.1.2
/routing bgp peer add in-filter=dynamic-in multihop=yes name=VPS remote-address=194.165.22.146 remote-as=64998 ttl=default
/routing filter add action=accept chain=dynamic-in protocol=bgp comment="Set nexthop" set-in-nexthop=172.30.1.1Cisco IOS —
router bgp 64999
neighbor 194.165.22.146 remote-as 64998
neighbor 194.165.22.146 route-map BGP_NEXT_HOP in
neighbor 194.165.22.146 ebgp-multihop 250
!
route-map BGP_NEXT_HOP permit 10
set ip next-hop 172.30.1.1, BGP-, , nexthop , . — .
, — , .
, BGP-, , , bird , ip-,
systemctl reload bird, 85 . , :)
, IP- .
, , . , ip- perl python. perl, Net::CIDR::Lite, 85 60 ( ), , , , .
ISO/OSI, /, , . github nxdomain.txt, , , SwitchyOmega Chrome.
, , , - (, - ). , , .
— , .
UPD2. , , , VPS . .
— , VPN- (, ). , . , " OpenVPN" , VPS, " OpenVPN" — , , .
UPD3. Unsacrificed , dump.csv bird ip-. " " . https://habr.com/post/354282/#comment_10782712
UPD4. ( ):
1) systemctl reload bird birdc configure.
2) Mikrotik IP /routing filter add action=accept chain=dynamic-in protocol=bgp comment="Set nexthop" set-in-nexthop=172.30.1.1 , /routing filter add action=accept chain=dynamic-in protocol=bgp comment="Set nexthop" set-in-nexthop-direct=< >
UPD5. https://antifilter.download, ip-. . "route… reject".
, , .
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/354282/
All Articles