Building a network for data storage systems of the small and medium business sector Part 2. Practical issues of organizing small infrastructures
Preface to the 2nd part
The first part dealt with the basic aspects of building storage systems. Now we will talk about the practical component, in particular, the use of selected equipment, exchange protocols and topology of the internal network.
Network Protocols and Required Functions
Before you begin to build a storage system, you need to decide, it has to be used.
At present, there are quite a lot of different protocols that one way or another can be used in the exchange between the server and the storage system. However, it is best to choose the most versatile, and, at the same time, the most undemanding ones.
')
All storage systems and protocols for data exchange can be divided according to the type of access into: file and block.
File access storages are network resources with which data is exchanged via popular application layer protocols. The most commonly used: CIFS, NFS, AFP. Other file transfer protocols are used, such as FTP, TFTP, SFTP, and so on. Such devices are called Network Attached Storage, in abbreviated form - NAS. In essence, a NAS is a file server whose hardware and software is optimized for storing and sharing files.
Storage with block access provides for the use of specially organized volumes with unique numbers - Logical Unit Number, LUN. At the same time, connected storage resources from the point of view of logical organization look like local hard drives. In this case, special access protocols are used, such as FCP (for the Fiber Channel), and iSCSI, FCoE, ATAoE, and others - for Ethernet networks. Storage systems of this type are called Storage Area Network, abbreviated as “SAN” and represent disk arrays connected to a high-performance data transfer network. The iSCSI protocol is very popular among budget storage systems due to its ease of implementation and unpretentiousness to resources.
IMPORTANT NOTICE . Within this article it is impossible to talk about all aspects of the creation and operation of storage. Therefore, for additional information it is worth contacting with other sources. Some of them are listed at the end of the article.
Block-access storage (like a local hard disk) under normal use does not allow for more than one connection without risk of data loss, while file storages may be available to connect to multiple clients.
NOTE . Under certain conditions, block storage can be connected to several clients, for example, when using shared disk file systems. In particular, VMware ESX (i) host servers can simultaneously connect and work with block access storage systems with a VMFS file system.
Restriction requires certain access control measures. In the Fiber Channel networks, zoning is used for this, for the Ethernet family - an authentication mechanism for passwords and division into virtual subnets (VLANs).
NOTE . A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is an artificially limited LAN segment as a group of ports with a single set of properties, for example, with the same security requirements. Allows you to exchange information among themselves within a single virtual broadcast domain, regardless of the physical location of the connected devices.
Another important parameter that dictates the block access to us is the reservation of the communication channel. If in the event of a line break when copying to a network share, you just have to overwrite the file, then with block access this is fraught with serious errors in the file system. The combination of several data lines in the Ethernet family of networks into one logical channel will come in handy here. This function is called link aggregation - Link Aggregation, abbreviated - LAGG. In addition to improving fault tolerance, channel aggregation allows for increased bandwidth.
In operating UNIX-like systems: Linux, BSD, Solaris, which are taken as the basis for building various storage systems, the most commonly used protocol is LACP - Link Aggregation Control Protocol. This open standard protocol is described in the IEEE 802.3ad and IEEE 802.1aq documents and is commonly used to aggregate channels in simple systems.
To improve system performance, it is extremely important to reduce the cost of traffic maintenance. One way is to use larger data packets. Accordingly, if fewer packets are required to transmit the same information, this will reduce processing time and save hardware resources. Therefore, the function Jumbo Frame will also be superfluous.
NOTE . Jumbo frame - a mechanism in the Ethernet family of networks, thanks to which, it is possible to transmit data blocks exceeding 1500 bytes (the value specified by the IEEE 802.3 group standards) - or, as they say, increase the MTU by more than 1500 bytes). The most popular practice in IP-based storage systems is to set the frame size to 9000 bytes of data, for example, to speed up the exchange via the iSCSI, NFS, GIFS (SMB) protocols.
All the above features: VLAN, LAGG (LACP) and Jumbo Frames - are in our chosen switch Zyxel XS1920 Series.
Storage System Topology
Building small storage systems for medium and small businesses, on the one hand, imposes certain restrictions in terms of cost, on the other hand, it allows some relief in the area of resiliency and security.
To begin, consider the simple scheme itself in Figure 1.
In this case, there is a virtual system of 4 servers connected to one storage through a dedicated switch. To increase bandwidth, all connections are duplicated via the port aggregation function. Thus, 10 RJ45 ports on 10 Gigabit Ethernet are involved. The remaining 2 universal 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports are reserved and can later be used to connect another storage system or server.
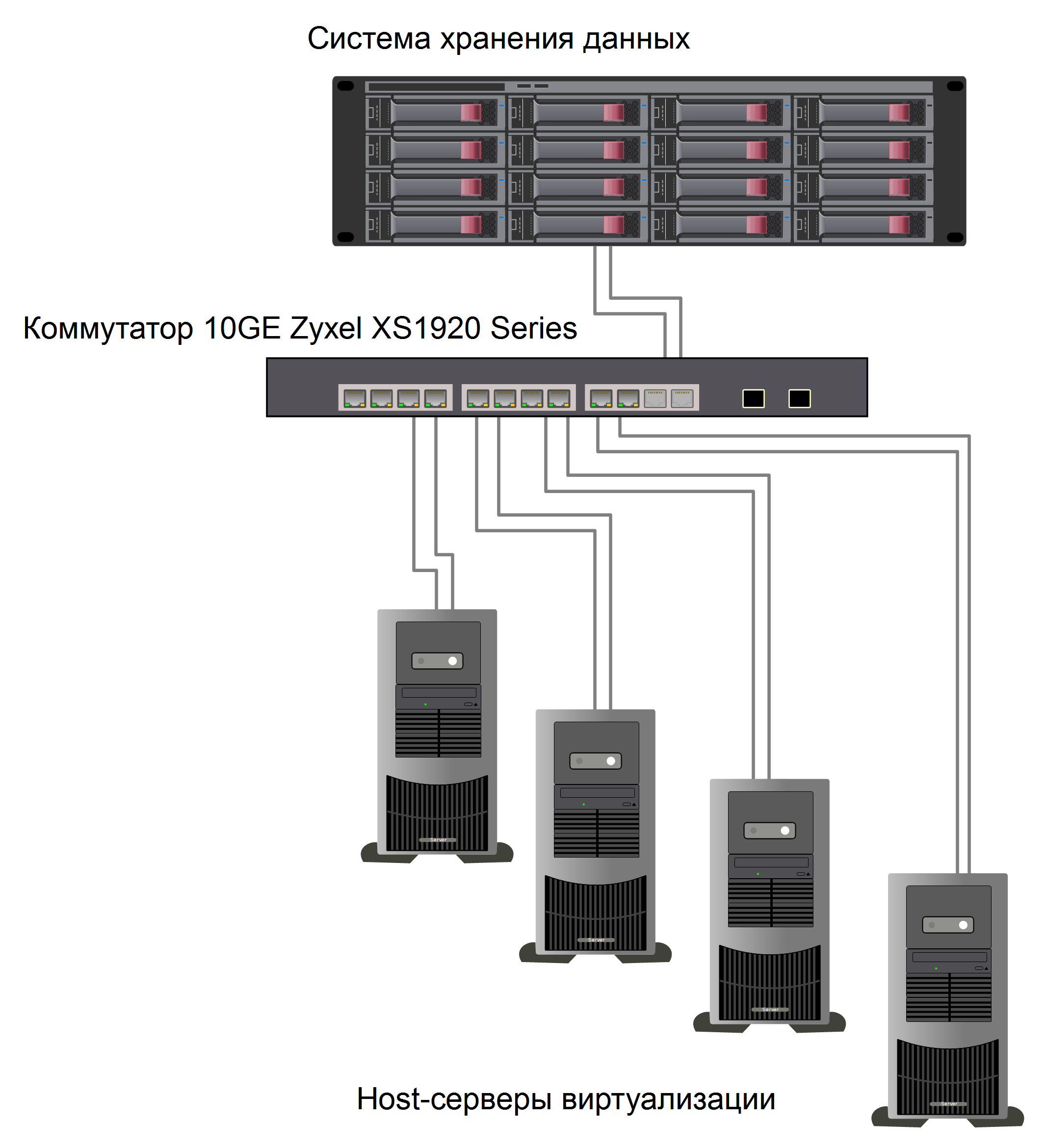
Figure 1. A simple storage network.
Please note that the switch in the above scheme is used completely offline. There is no connection to other network segments (Uplink / Downlink) and nothing is connected to it except for servers and the storage system. This isolation is justified both in terms of fault tolerance, and to optimize and simplify network exchange.
When building this simple network, it should be noted that most storage systems and servers have a special port for management, for example, via IPMI. In addition, to improve the control over home-made storage systems, an additional network card is often used, to which the management interface is sent via HTTP / HTTPS or Telnet / SSH protocols.
NOTE . IPMI - Intelligent Platform Management Interface, - a dedicated interface for monitoring and management. The most famous implementations are: iLO made by HP and IMM2, developed by IBM. IPMI is available even when the main device is in an inactive state. Through IPMI, you can turn off, turn on, reboot the system, capture the console to control, take readings from sensors, such as temperature, power, and so on.
As an inexpensive solution for the organization of such a network, any switch with a Fast Ethernet interface (100Mb / s) or Gigabit Ethernet is suitable. In order to minimize the costs of its acquisition, as well as management, staff training, and so on, it makes sense to choose equipment from one manufacturer as the main storage network. For example, in our case, the Zyxel GS1100-8HP model, a switch with 8 Gigabit ports, will do quite well.

Figure 2. An example of the organization of a dedicated control network.
If the requirements for fault tolerance are high, you must use a circuit with two switches. In order to avoid conflict when accessing the same iSCSI volumes across different connections, the multipathing mechanism is used. An additional bonus in this case will be the possibility of balancing and an increase in the number of ports that can be used both to connect devices and to expand the channel.
NOTE . Multipathing is a technology for connecting storage nodes using several independent lines. For example, one storage device can be connected to a server using multiple iSCSI channels. In case of failure of one of the connections, the operating system will use the remaining healthy communication lines to access the device. This architecture increases the resiliency of the system and allows you to distribute the load, which leads to an increase in speed in general.

Figure 3. Diagram with two switches. (To simplify the perception, the control network is not shown).
The Zyxel XS1920 Series Switch is well-suited for small data storage. For larger infrastructures, we can recommend another model - 24 port switch 10GbE L2 + XS3700 Series.
Conclusion
Building an inexpensive data storage system that meets the requirements of a business is not an easy task, but it can be implemented. Of course, in a brief narrative it is impossible to cover all aspects of this vast area of IT. For example, issues such as duplication of storage systems for fault tolerance, the creation of geographically distributed storage systems, and so on have remained behind the scenes. However, as a first step, the experience of building simple solutions for centralized data storage will certainly be useful and will allow in the future to organize an effective infrastructure for various purposes.
Sources:
- Berezhnoy A. Use of iSCSI when building storage systems // System Administrator, No. 3, 2017
- ESXi 6.5 for iSCSI Shared Storage
- LACP (description) - xgu.ru/wiki/LACP
- Ethernet Alliance. Ethernet Jumbo Frames
- Zyxel XS1920 Series Switch Switch Description
- Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI)
- Description of unmanaged switches on 8/10/16/24 GbE ports - Zyxel GS1100 Series
- Multipath (description)
- Zyxel XS3700 Series Switch Switch Description
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/354194/
All Articles