From the routine to the pleasant process: what is the backlog of the product and how to manage it?
Product managers and their owners can not pay serious attention to the product backlog. Not only to facilitate the planning of releases and iterations, but also to optimize the entire product life cycle that the team intends to work on.

The backlog of a product (product backlog) is an ordered set of elements, a queue of tasks, a list of all the functions that interested people want from the product. This list contains brief descriptions of all desired product features.
The product manager or product owner represents the backbone of the team and manages it, describes its main elements during the sprint planning rally. The backlog description should be made in a simple and accessible language, without technical specifications, so that it is clear to everyone in the team. Any changes and product requirements should be promptly reflected in this task queue.
')
These two components of Scrum carry different meanings, but they are often confused.
A sprint backlog is a list of specific tasks for implementing the selected backlog items of a product. This is a list for optimization, which the team will do in the next sprint, as well as a description of how they will implement this optimization.
Both backlogs can be presented in a regular Excel spreadsheet, but today for this purpose experienced managers and product owners use special tools for managing the product , which allow them to visualize the state of affairs correctly.
The product backlog is the product owner, and the development team is responsible for the backlog of the sprint. Another important difference is the backlog time: the product backlog is created at the very first sprint planning, and the Sprint backlog must be created by the team at each new sprint planning. Thus, the first backlog lives throughout the development of the product, and the Sprint backlog lives for 1-4 weeks, that is, for one sprint.
Work on Agile projects does not imply long documentation of all requirements. Usually, the product owner and other team members begin work on the project, noting everything they need to prioritize backlog. Already this backlog is enough for the first sprint. Then you can grow and change it.
The usual backlog of the product includes the following items:
The backlog of a product cannot be complete, as it is dynamically changing and constantly improving.
Backlog items are “user stories” or user stories. Such elements are ordered depending on their business "weight". The higher the specific element in the backlog, the sooner the developers will work on it. The top positions will be described in more detail and clear compared to the bottom elements. All of them should be understandable for non-technical team members and stakeholders.
Each element in the product backlog has its own rating, which is done by the developers. The rating system is used to determine the number of items that will be selected for a particular sprint.
Usually the team adds the necessary details and estimates to the backlog elements during a special project called backlog grooming or refinement.
Backlog refinement (improvement, optimization, “cleaning”) is an action or event, during which the team adds details, ratings and order to the elements of the product. The process should not cover more than 10% of the working time of the development team.
This ongoing process means the collaboration of the product owner and the developers when they review and revise all the elements of the product.
A product backlog has certain properties:
Focusing on key priorities is one of the key tasks of a product manager or product owner. However, very often they do not have time to study and monitor all new opportunities of competitors. Users constantly offer improvements and give advice, team members offer new ideas, updates are happening. When the backlog of a product increases, it becomes difficult to control it. How to keep track of priorities if ideas in backlog grow like a snowball ?

The solution can be found in modern product management platforms such as Hygger.io . The functionality of the platform helps to cope with the following issues:
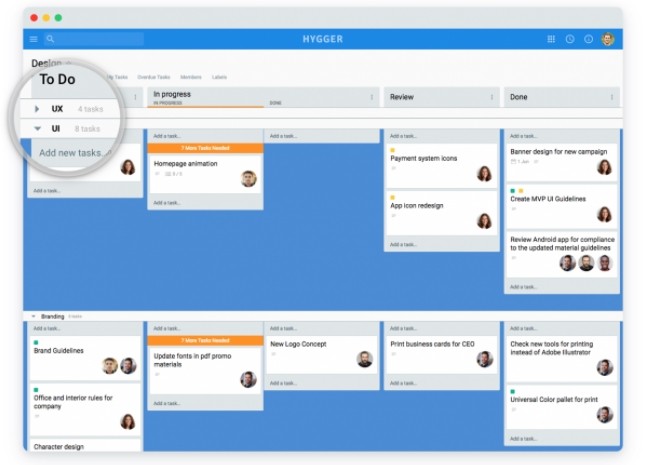
In the Hygger backlog, a simple list of ideas is presented on a two-dimensional whiteboard. Here you will find useful labels (Labels) and horizontal columns (Swimlanes). You can use the columns on the back panel to visualize the work steps for ideas:
Hygger swimlanes can be used to organize ideas. These horizontal columns on the Kanban board are used to separate the different kinds of problems that team members are busy with. They help teams more easily determine which issue to work on next.
The Labels option can be used to represent ideas from specific users or from specific employees.
At Hygger, you can evaluate all your ideas using 2 criteria: Value and Efforts . Comparing these values for each task helps to better prioritize and select the most important tasks for the next development.
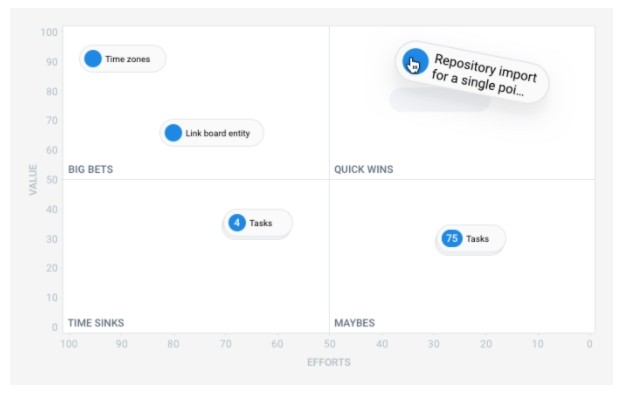
All evaluated ideas can be displayed on the Backlog Priority Chart. This graph is useful for evaluating ideas about each other. In addition to the Value and Effort scales, 4 quadrants are offered here:
Whatever the product, service or service being developed, backlog optimization is an integral part of the management functionality. A professional product owner can easily switch back to “you,” including through professional backlog management tools that turn him from a routine into a pleasant process.

The backlog of a product (product backlog) is an ordered set of elements, a queue of tasks, a list of all the functions that interested people want from the product. This list contains brief descriptions of all desired product features.
The product manager or product owner represents the backbone of the team and manages it, describes its main elements during the sprint planning rally. The backlog description should be made in a simple and accessible language, without technical specifications, so that it is clear to everyone in the team. Any changes and product requirements should be promptly reflected in this task queue.
')
Backlog of product vs backlog of sprint
These two components of Scrum carry different meanings, but they are often confused.
A sprint backlog is a list of specific tasks for implementing the selected backlog items of a product. This is a list for optimization, which the team will do in the next sprint, as well as a description of how they will implement this optimization.
Both backlogs can be presented in a regular Excel spreadsheet, but today for this purpose experienced managers and product owners use special tools for managing the product , which allow them to visualize the state of affairs correctly.
The product backlog is the product owner, and the development team is responsible for the backlog of the sprint. Another important difference is the backlog time: the product backlog is created at the very first sprint planning, and the Sprint backlog must be created by the team at each new sprint planning. Thus, the first backlog lives throughout the development of the product, and the Sprint backlog lives for 1-4 weeks, that is, for one sprint.
What is the meaning of product backlog?
Work on Agile projects does not imply long documentation of all requirements. Usually, the product owner and other team members begin work on the project, noting everything they need to prioritize backlog. Already this backlog is enough for the first sprint. Then you can grow and change it.
The usual backlog of the product includes the following items:
- Product features (for example, user story forms — descriptions of desired functionality)
- Different bugs
- Obtaining new knowledge (for example, updating jobs)
- Technical works (for example, any useful research)
The backlog of a product cannot be complete, as it is dynamically changing and constantly improving.
Backlog items are “user stories” or user stories. Such elements are ordered depending on their business "weight". The higher the specific element in the backlog, the sooner the developers will work on it. The top positions will be described in more detail and clear compared to the bottom elements. All of them should be understandable for non-technical team members and stakeholders.
Each element in the product backlog has its own rating, which is done by the developers. The rating system is used to determine the number of items that will be selected for a particular sprint.
Usually the team adds the necessary details and estimates to the backlog elements during a special project called backlog grooming or refinement.
What is backlog refinement for?
Backlog refinement (improvement, optimization, “cleaning”) is an action or event, during which the team adds details, ratings and order to the elements of the product. The process should not cover more than 10% of the working time of the development team.
This ongoing process means the collaboration of the product owner and the developers when they review and revise all the elements of the product.
How does product backlog in Agile differ from a simple to-do list?
A product backlog has certain properties:
- Any mark in the backlog of the product adds value to customers.
- All entries in the product backlog are graded.
- All marks get their priority and order.
- The level of detail depends on the position of the mark in the scrum backlog.
- A product backlog is a living document with no inaction or low priority tasks.
What if backlog grows tirelessly?
Focusing on key priorities is one of the key tasks of a product manager or product owner. However, very often they do not have time to study and monitor all new opportunities of competitors. Users constantly offer improvements and give advice, team members offer new ideas, updates are happening. When the backlog of a product increases, it becomes difficult to control it. How to keep track of priorities if ideas in backlog grow like a snowball ?

The solution can be found in modern product management platforms such as Hygger.io . The functionality of the platform helps to cope with the following issues:
- Structuring backlog based on Kanban boards, labels and horizontal swimlanes.
- Evaluation of ideas (using the convenient criteria of Value and Effort).
- Visualization and prioritization of important ideas based on the Backlog Priority Chart.
Backlog structuring
In the Hygger backlog, a simple list of ideas is presented on a two-dimensional whiteboard. Here you will find useful labels (Labels) and horizontal columns (Swimlanes). You can use the columns on the back panel to visualize the work steps for ideas:
- Collect Ideas - to collect all the ideas.
- Review Ideas - to explore ideas and clarify obscure points. It is not necessary to describe ideas at the start in detail, since it is not known whether the idea will be selected exactly for development.
- Score Ideas - for evaluating ideas.
- Approval - to test ideas Scrum-master or project manager.
- Developing - to send ideas to the development.
- Done - for realized ideas. This means that the function is "flooded" for production.
Hygger swimlanes can be used to organize ideas. These horizontal columns on the Kanban board are used to separate the different kinds of problems that team members are busy with. They help teams more easily determine which issue to work on next.
The Labels option can be used to represent ideas from specific users or from specific employees.

Evaluation of ideas
At Hygger, you can evaluate all your ideas using 2 criteria: Value and Efforts . Comparing these values for each task helps to better prioritize and select the most important tasks for the next development.
- Value shows what business value your product or business can bring.
- Efforts measure the resources needed to complete a task.
Backlog Priority Chart
All evaluated ideas can be displayed on the Backlog Priority Chart. This graph is useful for evaluating ideas about each other. In addition to the Value and Effort scales, 4 quadrants are offered here:
- Quick wins for ideas with really high value and low effort.
- Big Bets for ideas of great value and effort.
- Maybes for ideas with low value and effort.
- Time Sinks for ideas with low advantage but high resource costs.

Whatever the product, service or service being developed, backlog optimization is an integral part of the management functionality. A professional product owner can easily switch back to “you,” including through professional backlog management tools that turn him from a routine into a pleasant process.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/354168/
All Articles