Comparison of LAN scanning tools

When I worked in several government organizations as a
An old and experienced
In order to smooth out our contradictions, it was decided to conduct a blitz testing of network vulnerability scanners. Holivar among hacks pentesters led us to a new task - to conduct a comparative characteristic of the scan results. Four scanners were chosen to compare the scan performance: Rapid7 Nexpose, Tenable Nessus, OpenVAS 9, and Nmap. They were chosen on the basis of analytics online publications and personal experience. Personally, I bet on Nessus, but alas, I did not guess.
Rapid7 Nexpose is a vulnerability scanner that actively scans the IT infrastructure for erroneous configurations, holes, malicious codes, and provides recommendations for fixing them. All infrastructure components, including networks, operating systems, databases and web applications, are included in the analysis. According to the results of the verification, Rapid7 Nexpose in priority mode classifies detected threats and generates reports on their elimination. [2]
')
Tenable Nessus Scanner is a scanner designed to assess the current state of security of a traditional IT infrastructure, mobile and cloud environments, containers, etc. According to the results of the scan, it reports the found vulnerabilities. It is recommended to use as part of the Nessus Security Center. [3]
OpenVAS is an open source vulnerability scanner. OpenVAS is designed to actively monitor computer network nodes for security issues, assess the severity of these problems, and monitor their elimination. Active monitoring means that OpenVAS performs some actions on the host: scans open ports, sends specially formed packets to simulate an attack, or even logs in on the host, gains access to the management console, and executes commands on it. Then OpenVAS analyzes the collected data and makes conclusions about the presence of any security problems. These problems, in most cases, relate to non-upgraded software installed on a node, in which there are known and described vulnerabilities, or insecurely configured software. [1,6]
Nmap is a free utility designed for a variety of customizable scanning of IP networks with any number of objects, determining the state of objects of the scanned network (ports and their corresponding services). Initially, the program was implemented for UNIX systems, but now versions are available for many operating systems. [4,5]
Test environment
For testing, I assembled a test network on VMware Workstation 12 Pro into the circuit shown in Figure. one.
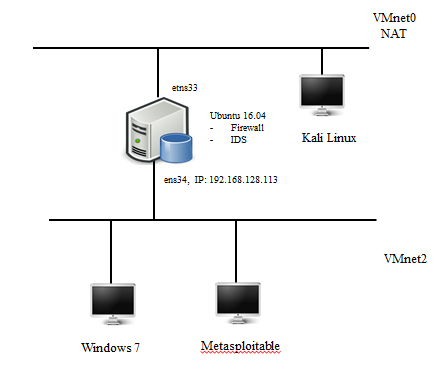
Fig. 1. Network diagram
Raised virtuals:
- Windows 7 with all installed updates, running the XAMPP application, deployed MySQL and Apache services. Also deployed test system DVWA.
- Metasploitable 2 is an operating system with pre-installed vulnerable services and applications that is used for testing.
- Ubuntu 16.04 with installed IDS Suricata [10] and configured iptables [9].
- Kali Linux is a Linux distribution that is used for penetration testing.
- The list of vulnerable services in Metasploitable 2 is shown in Table 1.
Table 1
| Service | Port | Status |
| Vsftpd 2..four | 21 | Open |
| OpenSSH four.7p1 Debian 8ubuntu 1 (protocol 2.zero) | 22 | Open |
| Linux telnetd service | 23 | Open |
| Postfix smtpd | 25 | Open |
| ISC BIND 9.four.2 | 53 | Open |
| Apache httpd 2.2.eight Ubuntu DAV / 2 | 80 | Open |
| A RPCbind service | 111 | Open |
| Samba smbd .x | 139, 445 | Open |
| r companies | 512, 513, 514 | Open |
| GNU Classpath grmiregistry | 1099 | Open |
| Metasploitable root shell | 1524 | Open |
| A NFS service | 2048 | Open |
| ProFTPD 1..1 | 2121 | Open |
| MySQL 5.zero.51a-3ubuntu5 | 3306 | Open |
| PostgreSQL DB eight..zero - eight..7 | 5432 | Open |
| VNC protocol v1. | 5900 | Open |
| X11 service | 6000 | Open |
| Unreal ircd | 6667 | Open |
| Apache Jserv protocol 1. | 8009 | Open |
| Apache Tomcat / Coyote JSP engine 1.1 | 8180 | Open |
In practice, when internal networks are scanned on the firewall and IPS, rules are created that exclude scanning blocking. Therefore, Suricata was used in detection mode, and permission rules were written on the firewall.
Iptables configuration [9]:
#!/bin/sh echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -i ens34 -o ens33 -j ACCEPT iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o ens33 -s 192.168.234.0/24 -j MASQUERADE iptables -A FORWARD -i ens33 -m state --state ESTABLISHED, RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -i ens33 -o ens34 -j REJECT Nessus Scanner was launched in the “Basic Network Scanning” mode. [3]
Rapid 7 Nexpose was launched in the "Full audit without Web Spider" mode. [2]
OpenVAS 9 was launched in “default” mode. [1,6]
Nmap was started by two commands: [4,5]
- nmap -sV -T4 -O -F --version-light 192.168.234.130-131
- nmap -Pn --script vuln 192.168.234.130-131
Test results
Nexpose discovered 527 vulnerabilities (see Diagram 1), of which:
Report
167 - received the status of “critical” - vulnerabilities must be closed first.
349 - received the status of “severe” - vulnerabilities are difficult to operate, but can lead to serious consequences.
46 - received the status of “moderate” - the found vulnerabilities can provide an attacker with information about the system, which he can use during the attack.
Vulnerabilities not only of tested systems were found, but also potential vulnerabilities in the virtualization system.

Tenable Nessus discovered 168 vulnerabilities (see Diagram 2), of which:
Report
3 - received the status of “critical”
9 - received the status of "high"
33 - received the status of “medium”
5 - received the status of "low"
118 received the status of “info”
Vulnerabilities of “critical” and “high” should be closed first.
Vulnerabilities of the “medium” level are difficult to operate, but with proper study they can cause damage.
Vulnerabilities of “low” and “info” levels can provide an attacker with information about the system, which he can use when conducting an attack through other vectors.

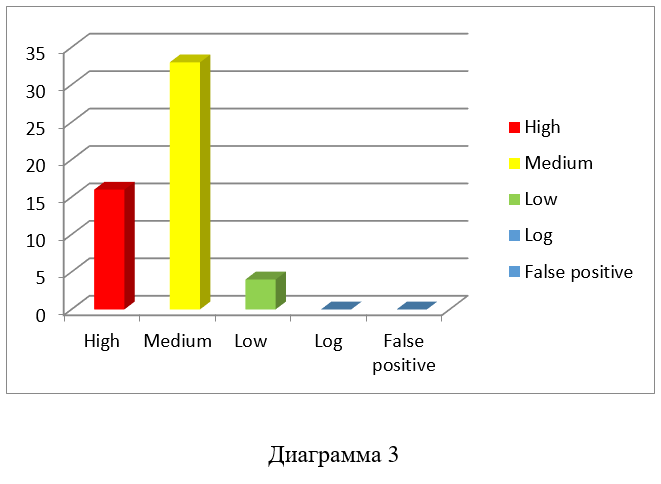
OpenVAS 9 found 53 vulnerabilities (see Diagram 3), of which:
Report
IDS Results
16 - received the status of "high"
33 - received the status of “medium”
4 - received the status of "low"
High level vulnerabilities must be closed first.
Vulnerabilities of the “medium” level are difficult to operate, but with proper study they can cause damage.
Vulnerabilities of the “low” level can provide an attacker with information about the system, which he can use when conducting an attack through other vectors.
Separately, we should note the results obtained using the Nmap scanner. Scanning was carried out by two teams, which were described above. The result of the execution was the output of information about the operating system, open services and possible vulnerabilities and links found.
Using the “vuln” script has identified the following types of vulnerabilities:
- open telnet
- http-csrf
- http-enum
- http-sql-injection
- http-vuln-cve2017-1001000
- rmi-vuln-classloader
- mysql-vuln-cve2012-2122
- ssl-ccs-injection
- ssl-dh-params
- ssl-poodle
- irc-botnet-channels
- http-flags
Nmap and IDS Results
Nmap results using the vuln script and IDS
findings
To draw conclusions, I applied a quantitative assessment method based on the total number of vulnerabilities found. As a result, it turned out that Nexpose was carrying out the greatest depth of scanning. Nessus worked rather poorly, as in the network scanning mode, he produced a lot of service data about systems and services, which only provide information for analytics. From a very weak side, the OpenVAS 9 scanner showed itself with the latest updates. Separate words are required by Nmap - a very good tool for analytic testing with the possibility of extension using NSE-scripts.
During testing, IDS Suricata found NMap and OpenVAS scanners.
This testing is not canonical, such as the Gartner or NSS Labs tests. But despite this, I think the article will be relevant for specialists in the field of system administration and technical audit.
PS And what was all this done for?
It was necessary to
Sources
- habrahabr.ru/post/203766
- www.rapid7.com
- www.tenable.com/products/nessus/nessus-professional
- nmap.org
- habrahabr.ru/post/131433
- www.openvas.org
- metasploit.help.rapid7.com/docs/metasploitable-2-exploitability-guide
- blog.securitymetrics.com/2016/03/vulnerability-scanners-101-what-why-and-how.html eax.me/iptables
- suricata-ids.org
- www.resolver.com/trust/policies/threat-vulnerability-management-standard
- osxdaily.com/2014/05/20/port-scanner-mac-network-utility
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/353856/
All Articles