46 skills and characteristics that make up the portrait of an ideal product manager
Product Manager is often the first representative of a product or service to the outside world. Successful PM requires experience, enthusiasm and, of course, professional management skills, communication and other abilities. The set of these qualities helps the expert to correctly present the product and bring it to the market.

The product manager should take care of the success of the product or service from the conceptual stage to the final release and market positioning. It is in the interests of the manager to always know how to correctly use the product strategy and focus on global management trends.
Young professionals at the very beginning of their career as a product manager may feel pressured by management or personnel managers who, logically, will want to discover the potential and “pull out” all the professional skills and abilities of the new talent. Often they have their own virtual list of expectations, the purpose of which is to determine the professional and personal qualities of future product managers. Applicants are confronted with this list during interviews.
')
The list of expectations can be simple, and sometimes carefully thought out and long enough. In general, product owners, CEOs, and HRs always have a portrait of an ideal product manager who consists of certain expectations. What are the skills, abilities and qualities that a modern product manager should possess?
For many large corporations, the role of product manager is fairly new. In startups, such a position can be found more often. Time very quickly showed the benefits of this role for companies of different sizes and industries.
The duties and responsibilities of PM in companies may differ, since much depends on the specifics of the product, audience, market, team and other factors. Technical PM is different from a business-oriented product manager , the roles of managers in an IT company or in retail will also vary. However, the key skills for the product manager remain similar.

You can find many classifications of the necessary PM skills and qualities or suggest your own version. We propose to consider 6 main categories: key professional skills and abilities of a product manager, personal qualities, interpersonal characteristics, analytical skills, cross-functional skills, as well as the skills that are so necessary today to effectively use professional tools and services for managing products .

The ability to use modern tools and services for product management does not just simplify the lives of managers, but opens up great opportunities. Such tools help to apply all your knowledge and skills with the help of intelligent technologies and, thereby, optimize and structure your work and the work of the whole team.
A modern product manager is not limited to a basic set of services for efficient operation, but uses special management platforms.
Separate PM functionality requires separate services or tools options. For example, managing the backlog of a product is an important part of the work of a product manager.
Product Backlog is a unique repository of ideas, initiatives, requests from customers and important product requirements. Working with backlog helps to prioritize and streamline all ideas for further iteration planning.
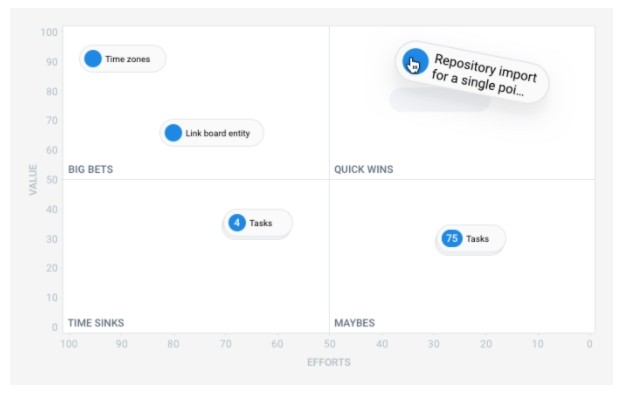
In the Hygger.io platform, backend controls offer convenient Value and Efforts parameters for each idea.
Backlog Priority Chart helps to easily visualize backlog - a chart for optimizing product priorities. With its help it is easy to identify the most important and least significant tasks at the moment.
The schedule consists of four segments, each of which represents a certain block of priorities:
Another example of a mandatory tool in the arsenal of a modern product manager is the Product Roadmap ( roadmap or product development plan ).
Product managers can share this visualized plan with other team members and product stakeholders. This includes global and small-scale initiatives, product requirements, and planned ideas.

These are just two examples of strategic product management tools. The manager’s work also helps track time, delegate tasks, communicate with the team, prepare reports and work schedules, organize tasks, and many other functions that offer platforms for managing products.
What PM tools do you use? And how do they help apply the skills, skills and qualities of a product manager?

The product manager should take care of the success of the product or service from the conceptual stage to the final release and market positioning. It is in the interests of the manager to always know how to correctly use the product strategy and focus on global management trends.
Young professionals at the very beginning of their career as a product manager may feel pressured by management or personnel managers who, logically, will want to discover the potential and “pull out” all the professional skills and abilities of the new talent. Often they have their own virtual list of expectations, the purpose of which is to determine the professional and personal qualities of future product managers. Applicants are confronted with this list during interviews.
')
The list of expectations can be simple, and sometimes carefully thought out and long enough. In general, product owners, CEOs, and HRs always have a portrait of an ideal product manager who consists of certain expectations. What are the skills, abilities and qualities that a modern product manager should possess?
Skills of a successful product manager
For many large corporations, the role of product manager is fairly new. In startups, such a position can be found more often. Time very quickly showed the benefits of this role for companies of different sizes and industries.
The duties and responsibilities of PM in companies may differ, since much depends on the specifics of the product, audience, market, team and other factors. Technical PM is different from a business-oriented product manager , the roles of managers in an IT company or in retail will also vary. However, the key skills for the product manager remain similar.

You can find many classifications of the necessary PM skills and qualities or suggest your own version. We propose to consider 6 main categories: key professional skills and abilities of a product manager, personal qualities, interpersonal characteristics, analytical skills, cross-functional skills, as well as the skills that are so necessary today to effectively use professional tools and services for managing products .
Professional skills product manager
- Creation and implementation of product strategy. Everyone knows that without a quality strategy, the further fate of the product does not seem to be successful.
- Prioritize tasks, projects, and all important issues related to a product or service.
- Drawing up a development roadmap and product roadmap
- Development and definition of new features
- Release management
- Product launch and version optimization
- Work with professional documentation
- Evaluation of promotional offers and product features
- Management of risks
Personal qualities and skills PM
- Deadline reconciliation and punctuality, time management
- Ability to work with details
- Task coordination
- Creativity
- Ability to solve urgent issues
- Critical thinking
- Ability to motivate other team members
- Ability to work in multitasking
- Organization skills
- Customer focus
Interpersonal characteristics of the product manager
- Leadership skills
- Skill teamwork with the team, the ability to be a team player
- The ability to effectively conduct meetings, negotiations and presentations
- Ability to influence others
- Interviewing skills
- Ability to work with multi-functional teams
- Partner Relationship Management
- Verbal communication skills
- Writing skills

Analytical abilities of the product manager
- The ability to analyze the target audience
- Defining goals and requirements
- The financial analysis
- Sales forecasting
- Product Performance Measurement
- Evaluation of product functionality
- Work with various metrics
- Making report
- Understanding market trends and understanding competitors
- Manage customer reviews
Cross-functional and other skills for product manager
- Pricing system development
- Project Management Skills
- Marketing and advertising communications
- Budget management
- Ability to work with applications
- Design Basics
- Work with social networks
Work with professional services and tools for product management
The ability to use modern tools and services for product management does not just simplify the lives of managers, but opens up great opportunities. Such tools help to apply all your knowledge and skills with the help of intelligent technologies and, thereby, optimize and structure your work and the work of the whole team.
A modern product manager is not limited to a basic set of services for efficient operation, but uses special management platforms.
Separate PM functionality requires separate services or tools options. For example, managing the backlog of a product is an important part of the work of a product manager.
Product Backlog is a unique repository of ideas, initiatives, requests from customers and important product requirements. Working with backlog helps to prioritize and streamline all ideas for further iteration planning.
In the Hygger.io platform, backend controls offer convenient Value and Efforts parameters for each idea.
- Value indicates what value a particular function can bring to a business or product.
- Efforts helps assess the resources needed to complete a task.
Backlog Priority Chart helps to easily visualize backlog - a chart for optimizing product priorities. With its help it is easy to identify the most important and least significant tasks at the moment.
The schedule consists of four segments, each of which represents a certain block of priorities:
- Time Sinks - for tasks that are not worth working on now.
- Maybes - for tasks that now do not carry much value, but they are easy to implement. You can return to them later.
- Big Bets - for tasks that can bring more value, but difficult to implement.
- Quick Wins - for tasks that are valuable and fairly simple to implement.

Another example of a mandatory tool in the arsenal of a modern product manager is the Product Roadmap ( roadmap or product development plan ).
Product managers can share this visualized plan with other team members and product stakeholders. This includes global and small-scale initiatives, product requirements, and planned ideas.

These are just two examples of strategic product management tools. The manager’s work also helps track time, delegate tasks, communicate with the team, prepare reports and work schedules, organize tasks, and many other functions that offer platforms for managing products.
What PM tools do you use? And how do they help apply the skills, skills and qualities of a product manager?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/353814/
All Articles