Disruption of a large-scale hacker attack on Windows users in Russia: part 2
More recently, we have prevented a massive attack using the Dofoil Trojan , the goal of which was to install malware for mining cryptocurrency on hundreds of thousands of computers. With the help of behavioral monitoring, machine learning models and a multi-level protection system, Windows Defender antivirus software was able to effectively detect and block an attack within a few milliseconds.
Today, we will tell you more about the attack itself, the ways of infection and share the time scale. Look under the cat!
')
Immediately after detecting the attack, we were able to determine where exactly a huge number of attempts were made to install malware. As a rule, Dofoil Trojan (also known as Smoke Loader) is distributed in a variety of ways, including spam messages and exploit kits. For the attack, which began on March 6, another scheme was used: most of the malicious files were created by the process mediaget.exe.
This process relates to MediaGet, a BitTorrent client, which corresponds to the classification of families of potentially unwanted applications . Users often use the MediaGet application to search and download programs and multimedia files from sites with a dubious reputation. Using such file sharing applications increases the risk of downloading malware.
However, after studying the attack, we came to the conclusion that the infection with Dofoil crypto-miner is not associated with downloading torrent files. Previously, we did not observe such a scheme in other file-sharing applications. The mediaget.exe process has always written Dofoil samples in the% TEMP% folder named my.dat. The most common source of infection was the% LOCALAPPDATA% \ MediaGet2 \ mediaget.exe file (SHA-1: 3e0ccd9fa0a5c40c2abb40ed6730556e3d36af3c).
Recommended materials : statistics on the attack, useful information and data on the response of Windows Defender, see the article Disrupting a massive hacker attack on Windows users in Russia .
A comprehensive study of the Dofoil attack, launched on March 6, revealed that it had been a carefully planned campaign that had been prepared by attackers from mid-February. To accomplish this, the attackers first spread the virus through an update to the MediaGet program, which users installed on their computers. The timeline below shows the main events as part of the Dofoil attack.
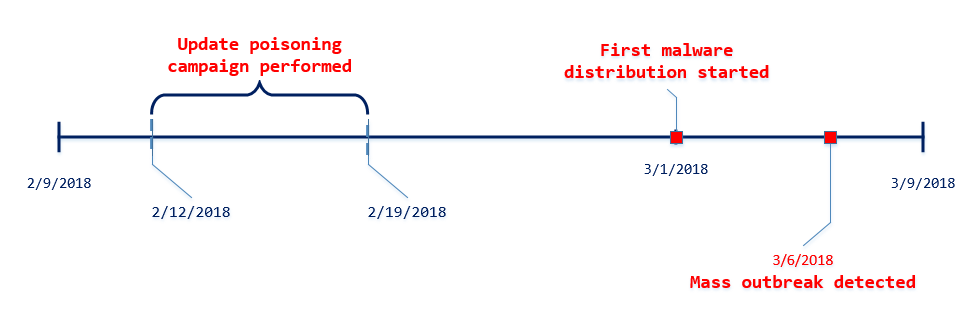
Fig. 1. The timeline of the attack through MediaGet
The infection infection process for MediaGet, which eventually led to a massive attack, is described in the following diagram. The trusted mediaget.exe application downloads the update.exe executable file and runs it on the computer to install the new mediaget.exe instance. A new instance of the mediaget.exe application has all the same functions as the authentic one, but it also provides a loophole.

Fig. 2. Procedure for infecting an update file
The whole process of installing an infected update file is monitored by the Windows Defender ATP service. The following process tree shows how the mediaget.exe process injects an infected signed update.exe file.
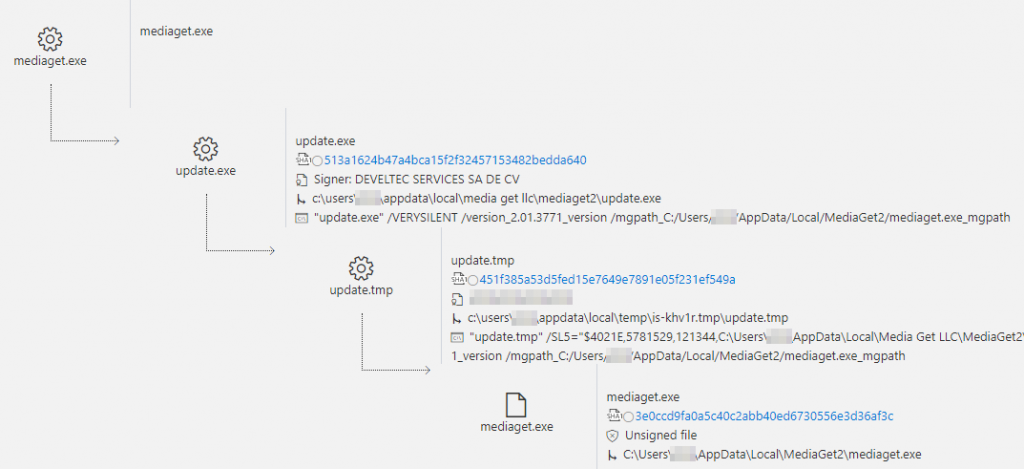
Fig. 3. Detection of the malicious update process in Windows Defender ATP
Downloaded update.exe is an InnoSetup SFX batch file with the trojan-infected mediaget.exe embedded in it. When launched, this executable file injects an unsigned version of the mediaget.exe application infected with a trojan.
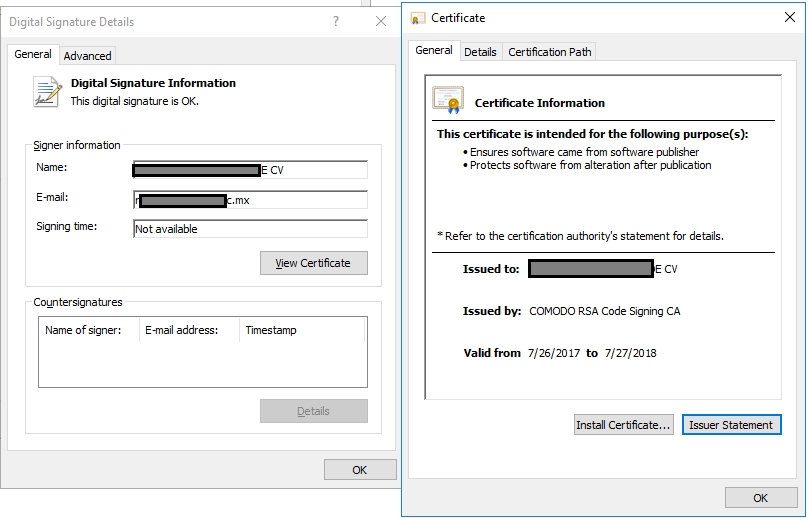
Fig. 4. Certificate data of the infected update.exe file
Update.exe is signed by a third-party software developer not affiliated with MediaGet (it is likely that this company is a victim of intruders). The executable file contains code signed by another certificate whose task is to simply transfer the same signature confirmation requirement as in the original mediaget.exe file. The update code verifies the certificate data, confirming that it is valid and properly signed. If the certificate is signed, it checks whether the hash value matches the value received from the hash server in the mediaget.com infrastructure. The following illustration shows a code snippet that checks for valid signatures for the update.exe file.
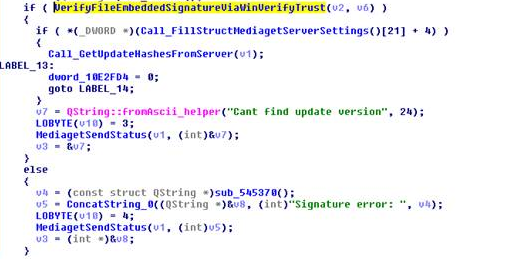
Fig. 5. Update code mediaget.exe
The trojan-infected mediaget.exe file, recognized by Windows Defender AV as Trojan: Win32 / Modimer.A, performs the same functions as the source file, however, it is not signed and has a loophole. This malicious binary code is 98% identical to the original MediaGet binary code. According to the following PE data, other PDB data and a different file path are indicated in the executable file.
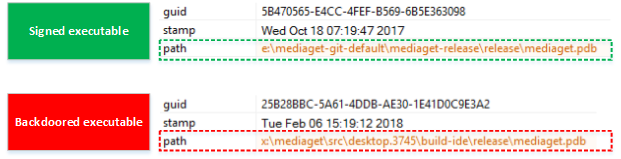
Fig. 6. Comparison of the PDB paths of the executable file signed by the Trojan and infected
When launching a malicious program, a list of management and control servers (C & C) is created.
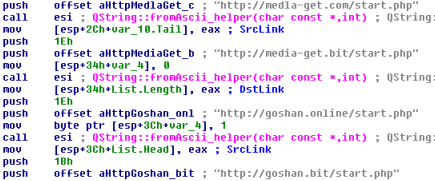
Fig. 7. List of C & C Servers
Regarding the built-in C & C list, it is important to note that the top-level domain .bit is not an ICANN approved domain and is supported by the NameCoin infrastructure. NameCoin is a distributed system of alternative root DNS servers in which the blockchain model principle is implemented. This system provides anonymous domains. Since .bit domain names are not resolved by standard DNS servers, malware builds a list of 71 IPv4 addresses that are used as NameCoin DNS servers.
The malware then uses NameCoin servers for DNS search in .bit domains. From this point on, these names are placed in the computer's DNS cache and all future lookups are resolved without specifying NameCoin DNS servers.
The first call to the C & C server occurs one hour after the launch of the program.
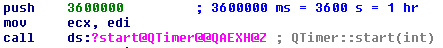
Fig. 8. Timer start connecting to C & C server.
The malware selects one of four C & C servers. The program uses the HTTP protocol to exchange management and control data.

Fig. 9. Connecting to a C & C server
The loophole code collects information about the system and sends it to the C & C server via a POST request.

Fig. 10. System Information
The C & C server returns various commands to the client. The following answer contains the HASH, IDLE, and OK commands. The IDLE command sets the process to wait for a certain period (in seconds, for example, 7200 seconds = 2 hours) before re-accessing the C & C server.
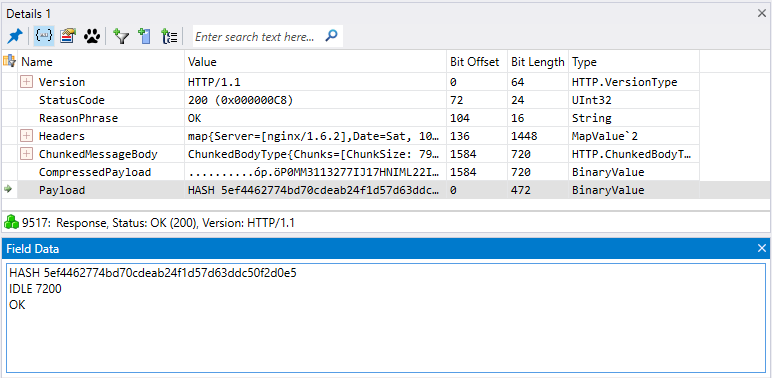
Fig. 11. Management and control teams
One of the loophole commands is RUN, which gets the URL from the command line of the C & C server. Then the malware downloads the file from the URL, saves it to the% TEMP% \ my.dat folder and launches it.

Fig. 12. RUN command processing code
This RUN command has been used to spread the Dofoil Trojan since March 1, and as part of an attack launched on March 6. The Windows Defender ATP alert process tree demonstrates the exchange of data between the malicious process mediaget.exe and goshan.online, one of the confirmed C & C servers. After that, the program injects and runs the file my.dat (Dofoil), which eventually leads to the CoinMiner component.

Fig. 13. Dofoil, the process of loading and running CoinMiner

Fig. 14. Windows Defender ATP alert system process tree
As part of the attack, the Dofoil Trojan was used to deliver CoinMiner, a malicious program whose task is to use the resources of users' computers to mine cryptocurrencies in favor of attackers. The Dofoil trojan used sophisticated techniques for introducing malicious code into the address space of processes, the mechanisms for ensuring sustainability, and detection evasion techniques. Windows Defender ATP successfully detects this behavior at all stages of infection.

Fig. 15. Detection of the implementation of the Dofoil process in Windows Defender ATP
We reported the results of our research to MediaGet developers to help them competently analyze the incident.
We also told the certificate holders about how their code signing certificate is used by attackers in the update.exe file (fingerprint: 5022EFCA9E0A9022AB0CA6031A78F66528848568).
A carefully planned and well-prepared campaign using Dofoil, discovered on March 6, is a prime example of multi-level viral cyber attacks that are becoming more common today. When making typical cybercrimes, now more and more sophisticated techniques are used that were previously associated with more sophisticated cyber attacks. Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (Windows Defender ATP) provides an advanced set of new-generation security tools that protect clients in real time against a wide variety of attacks.
Corporate clients using Windows Defender AV antivirus, which activated protection against potentially unreliable applications , were protected from MediaGet software infected with a trojan that turned out to be the source of a virus attack on March 6.
Windows Defender AV has provided reliable protection for customers against attacks using Dofoil. Behavioral monitoring and analysis technologies revealed an unusual Dofoil endurance mechanism and immediately sent the appropriate signal to the cloud protection service , where numerous machine learning models instantly blocked most of the detected threats as they appeared.
A comprehensive analysis of the attack also revealed that the advanced detection libraries in Windows Defender ATP tagged Dofoil malicious behavior at all stages of infection. Malicious behavior can include code injection, methods of protection against detection and the introduction of components for mining cryptocurrencies. Security professionals can use the Windows Defender ATP platform to detect attacks and effectively respond to them. Windows Defender ATP also provides built-in protection tools for Windows Defender AV, Windows Defender Exploit Guard and Windows Defender Application Guard, ensuring flawless security management at all levels.
Today, we will tell you more about the attack itself, the ways of infection and share the time scale. Look under the cat!

')
Immediately after detecting the attack, we were able to determine where exactly a huge number of attempts were made to install malware. As a rule, Dofoil Trojan (also known as Smoke Loader) is distributed in a variety of ways, including spam messages and exploit kits. For the attack, which began on March 6, another scheme was used: most of the malicious files were created by the process mediaget.exe.
This process relates to MediaGet, a BitTorrent client, which corresponds to the classification of families of potentially unwanted applications . Users often use the MediaGet application to search and download programs and multimedia files from sites with a dubious reputation. Using such file sharing applications increases the risk of downloading malware.
However, after studying the attack, we came to the conclusion that the infection with Dofoil crypto-miner is not associated with downloading torrent files. Previously, we did not observe such a scheme in other file-sharing applications. The mediaget.exe process has always written Dofoil samples in the% TEMP% folder named my.dat. The most common source of infection was the% LOCALAPPDATA% \ MediaGet2 \ mediaget.exe file (SHA-1: 3e0ccd9fa0a5c40c2abb40ed6730556e3d36af3c).
Recommended materials : statistics on the attack, useful information and data on the response of Windows Defender, see the article Disrupting a massive hacker attack on Windows users in Russia .
Attack Timeline
A comprehensive study of the Dofoil attack, launched on March 6, revealed that it had been a carefully planned campaign that had been prepared by attackers from mid-February. To accomplish this, the attackers first spread the virus through an update to the MediaGet program, which users installed on their computers. The timeline below shows the main events as part of the Dofoil attack.

Fig. 1. The timeline of the attack through MediaGet
Infecting MediaGet software update
The infection infection process for MediaGet, which eventually led to a massive attack, is described in the following diagram. The trusted mediaget.exe application downloads the update.exe executable file and runs it on the computer to install the new mediaget.exe instance. A new instance of the mediaget.exe application has all the same functions as the authentic one, but it also provides a loophole.

Fig. 2. Procedure for infecting an update file
The whole process of installing an infected update file is monitored by the Windows Defender ATP service. The following process tree shows how the mediaget.exe process injects an infected signed update.exe file.

Fig. 3. Detection of the malicious update process in Windows Defender ATP
Infected update.exe file
Downloaded update.exe is an InnoSetup SFX batch file with the trojan-infected mediaget.exe embedded in it. When launched, this executable file injects an unsigned version of the mediaget.exe application infected with a trojan.

Fig. 4. Certificate data of the infected update.exe file
Update.exe is signed by a third-party software developer not affiliated with MediaGet (it is likely that this company is a victim of intruders). The executable file contains code signed by another certificate whose task is to simply transfer the same signature confirmation requirement as in the original mediaget.exe file. The update code verifies the certificate data, confirming that it is valid and properly signed. If the certificate is signed, it checks whether the hash value matches the value received from the hash server in the mediaget.com infrastructure. The following illustration shows a code snippet that checks for valid signatures for the update.exe file.

Fig. 5. Update code mediaget.exe
Trojan-infected mediaget.exe
The trojan-infected mediaget.exe file, recognized by Windows Defender AV as Trojan: Win32 / Modimer.A, performs the same functions as the source file, however, it is not signed and has a loophole. This malicious binary code is 98% identical to the original MediaGet binary code. According to the following PE data, other PDB data and a different file path are indicated in the executable file.

Fig. 6. Comparison of the PDB paths of the executable file signed by the Trojan and infected
When launching a malicious program, a list of management and control servers (C & C) is created.

Fig. 7. List of C & C Servers
Regarding the built-in C & C list, it is important to note that the top-level domain .bit is not an ICANN approved domain and is supported by the NameCoin infrastructure. NameCoin is a distributed system of alternative root DNS servers in which the blockchain model principle is implemented. This system provides anonymous domains. Since .bit domain names are not resolved by standard DNS servers, malware builds a list of 71 IPv4 addresses that are used as NameCoin DNS servers.
The malware then uses NameCoin servers for DNS search in .bit domains. From this point on, these names are placed in the computer's DNS cache and all future lookups are resolved without specifying NameCoin DNS servers.
The first call to the C & C server occurs one hour after the launch of the program.
Fig. 8. Timer start connecting to C & C server.
The malware selects one of four C & C servers. The program uses the HTTP protocol to exchange management and control data.

Fig. 9. Connecting to a C & C server
The loophole code collects information about the system and sends it to the C & C server via a POST request.

Fig. 10. System Information
The C & C server returns various commands to the client. The following answer contains the HASH, IDLE, and OK commands. The IDLE command sets the process to wait for a certain period (in seconds, for example, 7200 seconds = 2 hours) before re-accessing the C & C server.

Fig. 11. Management and control teams
One of the loophole commands is RUN, which gets the URL from the command line of the C & C server. Then the malware downloads the file from the URL, saves it to the% TEMP% \ my.dat folder and launches it.

Fig. 12. RUN command processing code
This RUN command has been used to spread the Dofoil Trojan since March 1, and as part of an attack launched on March 6. The Windows Defender ATP alert process tree demonstrates the exchange of data between the malicious process mediaget.exe and goshan.online, one of the confirmed C & C servers. After that, the program injects and runs the file my.dat (Dofoil), which eventually leads to the CoinMiner component.

Fig. 13. Dofoil, the process of loading and running CoinMiner

Fig. 14. Windows Defender ATP alert system process tree
As part of the attack, the Dofoil Trojan was used to deliver CoinMiner, a malicious program whose task is to use the resources of users' computers to mine cryptocurrencies in favor of attackers. The Dofoil trojan used sophisticated techniques for introducing malicious code into the address space of processes, the mechanisms for ensuring sustainability, and detection evasion techniques. Windows Defender ATP successfully detects this behavior at all stages of infection.

Fig. 15. Detection of the implementation of the Dofoil process in Windows Defender ATP
We reported the results of our research to MediaGet developers to help them competently analyze the incident.
We also told the certificate holders about how their code signing certificate is used by attackers in the update.exe file (fingerprint: 5022EFCA9E0A9022AB0CA6031A78F66528848568).
Protection against real-time virus attacks
A carefully planned and well-prepared campaign using Dofoil, discovered on March 6, is a prime example of multi-level viral cyber attacks that are becoming more common today. When making typical cybercrimes, now more and more sophisticated techniques are used that were previously associated with more sophisticated cyber attacks. Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (Windows Defender ATP) provides an advanced set of new-generation security tools that protect clients in real time against a wide variety of attacks.
Corporate clients using Windows Defender AV antivirus, which activated protection against potentially unreliable applications , were protected from MediaGet software infected with a trojan that turned out to be the source of a virus attack on March 6.
Windows Defender AV has provided reliable protection for customers against attacks using Dofoil. Behavioral monitoring and analysis technologies revealed an unusual Dofoil endurance mechanism and immediately sent the appropriate signal to the cloud protection service , where numerous machine learning models instantly blocked most of the detected threats as they appeared.
A comprehensive analysis of the attack also revealed that the advanced detection libraries in Windows Defender ATP tagged Dofoil malicious behavior at all stages of infection. Malicious behavior can include code injection, methods of protection against detection and the introduction of components for mining cryptocurrencies. Security professionals can use the Windows Defender ATP platform to detect attacks and effectively respond to them. Windows Defender ATP also provides built-in protection tools for Windows Defender AV, Windows Defender Exploit Guard and Windows Defender Application Guard, ensuring flawless security management at all levels.
Compromise Indicators (IOCs)
| File name | SHA-1 | Description | Signatory | date of signing | The name of the detected malware |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mediaget.exe | 1038d32974969a1cc7a79c3fc7b7a5ab8d14fd3e | Official executable mediaget.exe | GLOBAL MICROTRADING PTE. LTD. | 2:04 PM 10/27/2017 | PUA: Win32 / MediaGet |
| mediaget.exe | 4f31a397a0f2d8ba25fdfd76e0dfc6a0b30dabd5 | Official executable mediaget.exe | GLOBAL MICROTRADING PTE. LTD. | 4:24 PM 10/18/2017 | PUA: Win32 / MediaGet |
| update.exe | 513a1624b47a4bca15f2f32457153482bedda640 | Trojan infected executable update file | DEVELTEC SERVICES SA DE CV | - | Trojan: Win32 / Modimer.A |
| mediaget.exe | 3e0ccd9fa0a5c40c2abb40ed6730556e3d36af3c, fda5e9b9ce28f62475054516d0a9f5a799629ba8 | Trojan-infected mediaget.exe executable | Not signed | - | Trojan: Win32 / Modimer.A |
| my.dat | d84d6ec10694f76c56f6b7367ab56ea1f743d284 | Embedded Malicious Executable File | - | - | TrojanDownloader: Win32 / Dofoil.AB |
| wuauclt.exe | 88eba5d205d85c39ced484a3aa7241302fd815e3 | CoinMiner implemented | - | - | Trojan: Win32 / CoinMiner.D |
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/351692/
All Articles