How to get PCI DSS certification: IT GRAD experience
In one of the past posts, we noted that we had successfully re-certified our infrastructure using PCI DSS and talked about the types of PCI DSS hosting: co-location, IaaS Basic and IaaS Advanced. Today we will talk more about the certification process and our own audit experience.

/ photo NTNU CC
The requirements of the standard apply to all enterprises that process, transmit or store data of at least one credit card. In one of our previous materials, we provided a simple flowchart to help you understand who needs PCI DSS certification.
')
Its essence lies in the fact that the leadership of the organization is enough to answer these questions:
If the answer to both of these questions is yes, then the company needs to be certified. For non-compliance with the requirements of PCI DSS, the organization is obliged to pay a fine in the amount of 10 to 200 thousand dollars, depending on:
The first time we were certified by PCI DSS in 2015, becoming one of the first cloud providers that were audited for compliance with the requirements of the standard.
Further we will tell how this process took place.
Before being audited, the company must prepare regulatory and regulatory documents on information security (instructions, regulations, policies). At the time of the first certification, most of them were already developed by us, but some still had to be finalized.
For example, we had to edit a policy that contains goals, objectives and methods for ensuring information security in an enterprise. We also adjusted the regulations governing the management of vulnerabilities and incidents. For example, we have created the “Information Access Control Regulations” - it describes the rules for working with access rights and the requirements for user credentials.
Note that all documents need to be reviewed and adjusted annually. Especially if there were changes in the IT structure of the company.
The next stage is infrastructure preparation. If the organization is being audited for the first time, then the management needs to determine the OSP to be certified, that is, to limit the individual infrastructure unit that will support all the processes to be certified. This is necessary in order to avoid having to make any changes to the infrastructure with new tests for meeting the requirements of the standard.
To do this, we had to organize a separate infrastructure with a dedicated network, deploy ESX, vSphere and vCenter servers, install switches and a firewall to prevent malicious attacks. We have duplicated all this equipment, and then have made the schemes of services, networks and business processes.
The certified infrastructure must be separated from other networks of the organization - access to it must be provided through an isolated interface. To fulfill this requirement, we use a VPN with 2FA and isolate each client's segment.
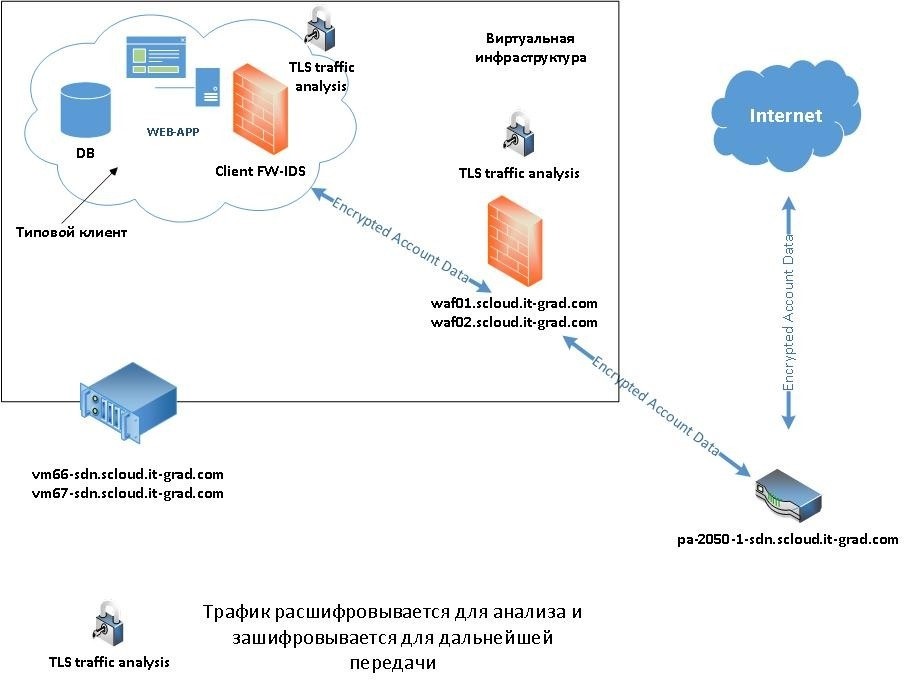
Inside the perimeter is an NTP server, logging services, antivirus, firewall, as well as solutions to prevent cyber attacks and control data integrity. You can see the scheme of our network here .
Pentest conducts a special team on behalf of the auditing company. Auditors verify the work of solutions that are used to protect cardholder data and identify potential security holes.
Before starting to check the infrastructure for penetration resistance, our team prepared two osprey. The first with service services and applications involved in testing. The second one was configured VM with OS, assigned the necessary rights to the appropriate accounts.
/ Osprey example with hosted services and applications
Pentest of our infrastructure was carried out in several stages.
The auditors checked the white IP addresses of our company. They could not find open ports on machines with public IP addresses (only those responsible for the operation of our infrastructure were open).
The Pentest team attempted to gain access from an untrusted network. The test results showed that it is impossible to penetrate into the infrastructure of "IT-GRAD" via VPN without 2FA. Checking the internal network also revealed no violations.
On a third-party resource (this resource was iaas-blog.it-grad.ru), the experts obtained the credentials of one of our colleagues. This colleague also had accounting in the IT-GRAD testing infrastructure. The auditors tried to log in using his account and password, but they did not succeed, because the network was rather segmented.
In total, according to the results of the inspection, we found 7 vulnerabilities of varying degrees of criticality: one high and 3 medium and low levels of “danger”.
Our most critical vulnerability - the improper operation of WAF - was due to the fact that the firewall in use could not cope with complex attacks. In order to eliminate the vulnerability, we deployed an Apache web server with the Modsecurity module, and then updated the WAF signature database.
There were three intermediate vulnerabilities. The first is the included TRACE method, which attackers can use, for example, for cross-site scripting . To eliminate the vulnerability, we deactivate the TRACE method.
The second discrepancy is the lack of secure HTTP headers. Vulnerability can cause attackers to attack the user interface. We solved this task by including secure headers on the corresponding application server.
And the third vulnerability is software insecurity on one of the hosts (due to outdated software version). To eliminate this vulnerability, we configured regular software updates on all nodes.
Among the vulnerabilities of low criticality, auditors found test data with password hashes in the production environment. We also pointed to unreliable passwords and unnecessary software. We replaced vulnerable passwords with secure passwords and removed unused data and software. After fixing all the vulnerabilities, we successfully passed the repeated pentest.
At the final stage of the audit, the auditor assesses the completeness and parameters of software and hardware, the network topology, the OS configuration, the isolation of infrastructure segments and other characteristics. In addition, he can check the documentation and knowledge of employees, ask questions of an organizational or technical nature.
If your company shows minor deviations from the requirements of the standard, they can be eliminated during the audit. For example, we have found an inactive computer account in Active Directory, which we promptly deleted.
If you needed to change something before or during the audit, this is also not a problem. The main thing here is to make changes in the way that PCI DSS requires.
For example, before the audit, in IT-GRAD, we needed to track the loading and unloading of files on an SFTP server. To do this, we had to urgently write a decoder for the avusm server. Without a decoder, the server did not save the necessary messages, since it could not “parse” the logs and generate alerts.
Ultimately, we received a certificate of compliance with the requirements of PCI DSS and became one of the first IaaS providers in Russia that provides the hosting service of PCI DSS.
PS Several materials on the topic from the First Corporate IaaS Blog:

/ photo NTNU CC
Who needs to be certified
The requirements of the standard apply to all enterprises that process, transmit or store data of at least one credit card. In one of our previous materials, we provided a simple flowchart to help you understand who needs PCI DSS certification.
')
Its essence lies in the fact that the leadership of the organization is enough to answer these questions:
- Does the company work with PD cardholders?
- Do the company's business processes affect the integrity and security of these cards?
If the answer to both of these questions is yes, then the company needs to be certified. For non-compliance with the requirements of PCI DSS, the organization is obliged to pay a fine in the amount of 10 to 200 thousand dollars, depending on:
- type of payment system (Visa or MasterCard);
- company status (member, service provider or trade organization);
- recurrence of violations (first, second and subsequent).
The first time we were certified by PCI DSS in 2015, becoming one of the first cloud providers that were audited for compliance with the requirements of the standard.
Further we will tell how this process took place.
Stage 1: documentation preparation
Before being audited, the company must prepare regulatory and regulatory documents on information security (instructions, regulations, policies). At the time of the first certification, most of them were already developed by us, but some still had to be finalized.
For example, we had to edit a policy that contains goals, objectives and methods for ensuring information security in an enterprise. We also adjusted the regulations governing the management of vulnerabilities and incidents. For example, we have created the “Information Access Control Regulations” - it describes the rules for working with access rights and the requirements for user credentials.
Note that all documents need to be reviewed and adjusted annually. Especially if there were changes in the IT structure of the company.
Stage 2: IT infrastructure building
The next stage is infrastructure preparation. If the organization is being audited for the first time, then the management needs to determine the OSP to be certified, that is, to limit the individual infrastructure unit that will support all the processes to be certified. This is necessary in order to avoid having to make any changes to the infrastructure with new tests for meeting the requirements of the standard.
To do this, we had to organize a separate infrastructure with a dedicated network, deploy ESX, vSphere and vCenter servers, install switches and a firewall to prevent malicious attacks. We have duplicated all this equipment, and then have made the schemes of services, networks and business processes.
The certified infrastructure must be separated from other networks of the organization - access to it must be provided through an isolated interface. To fulfill this requirement, we use a VPN with 2FA and isolate each client's segment.
Inside the perimeter is an NTP server, logging services, antivirus, firewall, as well as solutions to prevent cyber attacks and control data integrity. You can see the scheme of our network here .
Stage 3: Pentest
Pentest conducts a special team on behalf of the auditing company. Auditors verify the work of solutions that are used to protect cardholder data and identify potential security holes.
Before starting to check the infrastructure for penetration resistance, our team prepared two osprey. The first with service services and applications involved in testing. The second one was configured VM with OS, assigned the necessary rights to the appropriate accounts.

/ Osprey example with hosted services and applications
Pentest of our infrastructure was carried out in several stages.
Nmap scanning
The auditors checked the white IP addresses of our company. They could not find open ports on machines with public IP addresses (only those responsible for the operation of our infrastructure were open).
VPN connection and internal network checking
The Pentest team attempted to gain access from an untrusted network. The test results showed that it is impossible to penetrate into the infrastructure of "IT-GRAD" via VPN without 2FA. Checking the internal network also revealed no violations.
Attempt to access the infrastructure connection account
On a third-party resource (this resource was iaas-blog.it-grad.ru), the experts obtained the credentials of one of our colleagues. This colleague also had accounting in the IT-GRAD testing infrastructure. The auditors tried to log in using his account and password, but they did not succeed, because the network was rather segmented.
In total, according to the results of the inspection, we found 7 vulnerabilities of varying degrees of criticality: one high and 3 medium and low levels of “danger”.
Our most critical vulnerability - the improper operation of WAF - was due to the fact that the firewall in use could not cope with complex attacks. In order to eliminate the vulnerability, we deployed an Apache web server with the Modsecurity module, and then updated the WAF signature database.
There were three intermediate vulnerabilities. The first is the included TRACE method, which attackers can use, for example, for cross-site scripting . To eliminate the vulnerability, we deactivate the TRACE method.
The second discrepancy is the lack of secure HTTP headers. Vulnerability can cause attackers to attack the user interface. We solved this task by including secure headers on the corresponding application server.
And the third vulnerability is software insecurity on one of the hosts (due to outdated software version). To eliminate this vulnerability, we configured regular software updates on all nodes.
Among the vulnerabilities of low criticality, auditors found test data with password hashes in the production environment. We also pointed to unreliable passwords and unnecessary software. We replaced vulnerable passwords with secure passwords and removed unused data and software. After fixing all the vulnerabilities, we successfully passed the repeated pentest.
Stage 4: Final Audit
At the final stage of the audit, the auditor assesses the completeness and parameters of software and hardware, the network topology, the OS configuration, the isolation of infrastructure segments and other characteristics. In addition, he can check the documentation and knowledge of employees, ask questions of an organizational or technical nature.
If your company shows minor deviations from the requirements of the standard, they can be eliminated during the audit. For example, we have found an inactive computer account in Active Directory, which we promptly deleted.
If you needed to change something before or during the audit, this is also not a problem. The main thing here is to make changes in the way that PCI DSS requires.
For example, before the audit, in IT-GRAD, we needed to track the loading and unloading of files on an SFTP server. To do this, we had to urgently write a decoder for the avusm server. Without a decoder, the server did not save the necessary messages, since it could not “parse” the logs and generate alerts.
Ultimately, we received a certificate of compliance with the requirements of PCI DSS and became one of the first IaaS providers in Russia that provides the hosting service of PCI DSS.
PS Several materials on the topic from the First Corporate IaaS Blog:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/351548/
All Articles