Annual Report on Cyber and Info Security for 2017
Hello, Habr. We would like to present you a brief version of the annual report on cyber- and information security for 2017, which we wrote together with the main partner, Wallarm , who provided information on the most notable vulnerabilities and hacks.
In 2017, Qrator Labs and Wallarm noted the growing diversification of threats due to the increasing number of possible attack vectors. The range of critical vulnerabilities of the modern global network is so wide that attackers can choose various ways to create problems for almost any organization. And an increasing number of tools can work automatically, making centralized management redundant.
If 2016 can be called the year of botnets and terabit attacks, then 2017 was the year of networks and routing. Incidents such as Google’s leaked Japanese network routes , interception of someone else’s Level3 traffic in the United States and Rostelecom in Russia, like many others, demonstrate sustained and high risks associated with human factors based on mismanagement and insufficient automation of processes. A brave engineer who confidently stops an important automated script can create serious problems in the availability of network resources.
')
Dynamics of the number of attacks in 2016–2017
We have already seen how quickly the world moved from one state to another last year. Emails that attackers extort a cryptocurrency with threats of organizing DDoS attacks can sow panic among employees. Panic condition does not contribute to any long-term planning or active protection of the resource in real time. Threats should be viewed from afar, looking for time for review and preliminary preparation.
Looking at BlueBorne, you can easily predict the appearance of much larger in number and scale of the devices involved and, of course, much more dangerous botnets in terms of capabilities.
We expect the active emergence of even larger botnets than Mirai, capable of flood attacks even without the use of amplification protocols.
Application-level attacks are extremely dangerous, as before. If your company is connected to a communication provider by a dedicated L2 channel, then it is only a matter of time when a vulnerability is used against you in a single unprotected equipment or third-party service used to maintain performance. Commercial DDoS attacks became more complicated in 2017: bypassing, hacking, and eventually finding a way to cause damage. 2017 also demonstrated that botnets based on infected Windows machines have not gone away. The effects and consequences of outbreaks of cryptographers, such as WannaCry, Petya and NotPetya, can be recreated in the form of a DDoS attack, when invisible software users will command the generation of traffic from each individual infected machine within any large-scale network. According to our observations, botnets are growing in size - the point is not far in which the malware of the new generation will gain enough scale to attack large connected pieces of the Internet and individual networks of large providers.
High-speed attacks based on Windows-botnets turned last year's joke about the attacks into 1 Tbit / s. on the application level into a sad reality visible more and more often. Not far off that day, when hundreds of Gbit / s, beating on the same L7 (application level), will enter our daily life. Most likely, this will happen in 2018, because already now everything that can be broken with the help of such an attack turns off much faster than the attack reaches the limits of the channel capacity.

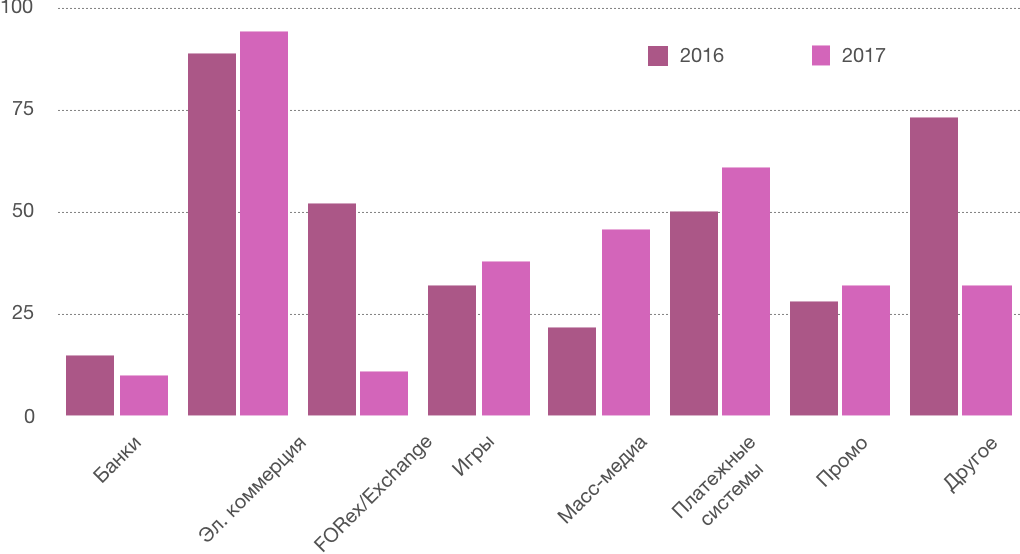
Average number of attacks in certain consumer segments
In 2017, routing incidents became as infamous as botnets in 2016. A successful DDoS attack could always make one single resource or application inaccessible. In the case of popular social networks or libraries that developers use to create and maintain the normal operation of Internet services, an attack can threaten entire ecosystems that use interconnected parts of the infrastructure (including hosting and a common Internet service provider). As we have seen, routing incidents can be no less large-scale and dangerous than attacks by a record botnet, leaving almost the entire country without access to popular resources. What happens if one day you cannot open a single web page at all? This makes electronic communication impossible in the form in which we know it and which we take for granted.
The network incident caused by Google in Japan was perhaps the most striking example of what could happen if a large BGP configuration was incorrect, however, the only content provider.
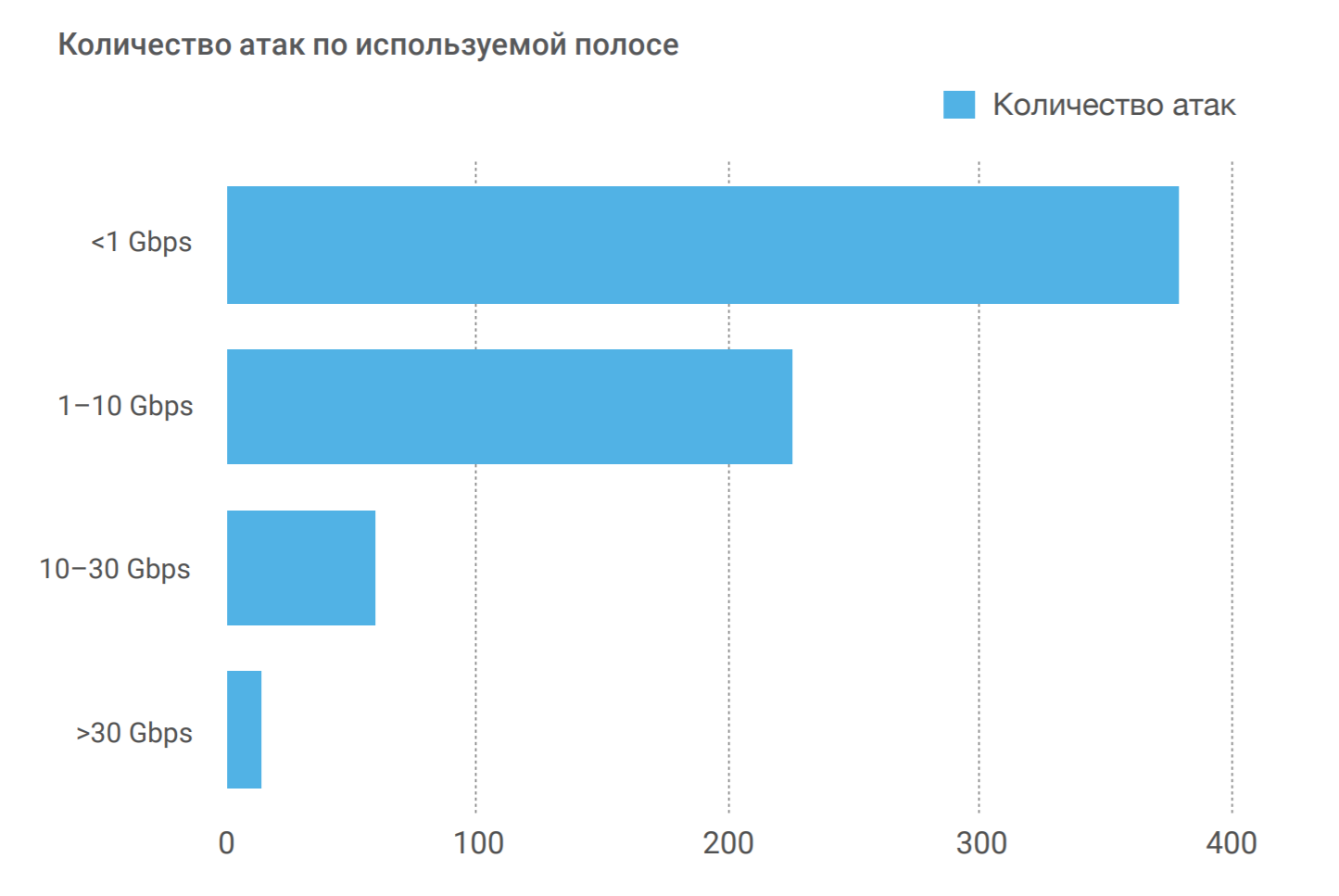
The number of attacks on the band used
2017 has become a real year of hacking. From epidemics cryptographers to the discoveries of the archives of Vault7 and Shadow Brokers, in addition to noticeable leaks due to human errors, where Uber and Equifax are the two loudest examples.
Everything is vulnerable. So it’s worth talking not about “what is most vulnerable,” but “where vulnerability can be found earlier.” Where there are vulnerabilities, there are also attacks. Moreover, there are a number of widely used technologies that reproduce vulnerabilities — when one is fixed and the other breaks. The attackers are closely watching such activities - they know that the larger the supplier in front of them, the more time it will take to develop and deliver the update to its customers.
The cloud also goes into legacy status with all the problems that are inherited by new generations of devices and technologies. The leaks of Uber and OneLogin began with the fact that the keys to the Amazon repository were published on GitHub or elsewhere - it is possible that the sticker stuck to the monitor.
Another major problem is the situation with MongoDB, Cassandra, Memcached and other popular databases. When their administrators forget to establish an appropriate level of security, it’s easy for an attacker to find loopholes. This is exactly what happened in the case of the software keyboard for Ai.Type smartphones, which lost all data of 31 million of its own users.
The main goal of creating a solution to neutralize DDoS is ultimately the establishment of protection, whose support is cheaper than the organization of attacks. Only by taking away the economic advantage of the attackers, you can begin to fight on some conditions. And this is a difficult task, primarily due to two factors:
A. Reckless approach to the basics of information security and threat analysis;
B. Fear of news and publicity, trying to hide information in case of problems.
The new and large ICO market has become a real revelation for hackers in 2017. The tendency to attack at the most stressful moment for the organization (fundraising, advertising campaigns) persists, and with a growing number of cryptocurrency projects, hacking attacks are combined with DDoS. If the market for issuing cryptocurrency tokens continues to grow, this trend will only intensify.
ICOs are of particular interest to all market parties. Because of cryptocurrency and ICO, a new industry of hacks has grown before our eyes. Huge amounts of funds are already involved in this market, and the technical side of the implementation of many projects is frankly weak, as we said in 2017. They are constantly hacked.
Mining pools are attacked in the last seconds of the signature of each block in order to get a reward for the block signature by a competing pool. Cloud cryptocurrency wallets are constantly under attack - during 2017 we saw major hacking of such services with the loss of all cryptocurrencies by their creators. Even mining with the help of scripts in the browser can be profitable, not to mention the infection of a large number of old computers, servers, or game consoles with malware that performs calculations at the expense of victims.
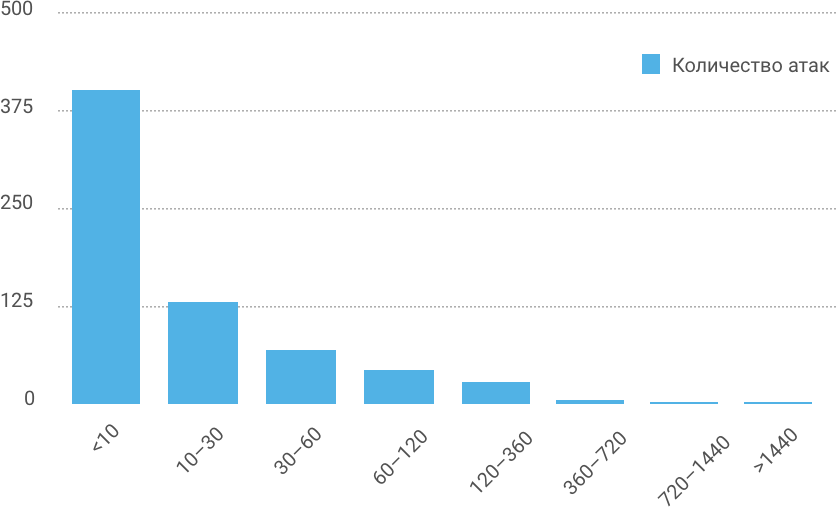
Duration of attacks, minutes
APIs are becoming increasingly important for large clients - they are professional and want to have maximum control over the processes of cleaning and filtering traffic. This process should not be underestimated.
The most notable fact in this area is not even the attacks themselves, but the progress that all security solution providers have made in the process of training, communication and cooperation, and not just competition, in order to find answers to the most serious questions of our time, such as countering botnets When such large-scale threats appear, calling into question the existence of no longer separate web services, but the entire industry as such, companies are merged at several levels at once: formal, informal, B2G and B2C. We have already seen successes associated with such cooperation in countering major botnets in 2017 among the largest companies working in the field of information security - we hope that this will happen more often in the future.
Thanks for reading.
Direct link to Russian PDF.
In 2017, Qrator Labs and Wallarm noted the growing diversification of threats due to the increasing number of possible attack vectors. The range of critical vulnerabilities of the modern global network is so wide that attackers can choose various ways to create problems for almost any organization. And an increasing number of tools can work automatically, making centralized management redundant.
If 2016 can be called the year of botnets and terabit attacks, then 2017 was the year of networks and routing. Incidents such as Google’s leaked Japanese network routes , interception of someone else’s Level3 traffic in the United States and Rostelecom in Russia, like many others, demonstrate sustained and high risks associated with human factors based on mismanagement and insufficient automation of processes. A brave engineer who confidently stops an important automated script can create serious problems in the availability of network resources.
')

Dynamics of the number of attacks in 2016–2017
How deep is the rabbit hole
We have already seen how quickly the world moved from one state to another last year. Emails that attackers extort a cryptocurrency with threats of organizing DDoS attacks can sow panic among employees. Panic condition does not contribute to any long-term planning or active protection of the resource in real time. Threats should be viewed from afar, looking for time for review and preliminary preparation.
Many IoT devices are still cracked using trivial methods, such as vulnerabilities in the web interface. Almost all such vulnerabilities are critical, but the manufacturer has extremely limited ability to quickly create a patch and deliver it as an update.Hacking IoT devices has become more frequent since the Mirai toolkit has become the basic framework for creating a botnet in 2017. However, earlier incarnations of botnet frameworks were also known, from which Mirai drew inspiration for its own code, for example Hajime.
Looking at BlueBorne, you can easily predict the appearance of much larger in number and scale of the devices involved and, of course, much more dangerous botnets in terms of capabilities.
We expect the active emergence of even larger botnets than Mirai, capable of flood attacks even without the use of amplification protocols.
Application-level attacks are extremely dangerous, as before. If your company is connected to a communication provider by a dedicated L2 channel, then it is only a matter of time when a vulnerability is used against you in a single unprotected equipment or third-party service used to maintain performance. Commercial DDoS attacks became more complicated in 2017: bypassing, hacking, and eventually finding a way to cause damage. 2017 also demonstrated that botnets based on infected Windows machines have not gone away. The effects and consequences of outbreaks of cryptographers, such as WannaCry, Petya and NotPetya, can be recreated in the form of a DDoS attack, when invisible software users will command the generation of traffic from each individual infected machine within any large-scale network. According to our observations, botnets are growing in size - the point is not far in which the malware of the new generation will gain enough scale to attack large connected pieces of the Internet and individual networks of large providers.
High-speed attacks based on Windows-botnets turned last year's joke about the attacks into 1 Tbit / s. on the application level into a sad reality visible more and more often. Not far off that day, when hundreds of Gbit / s, beating on the same L7 (application level), will enter our daily life. Most likely, this will happen in 2018, because already now everything that can be broken with the help of such an attack turns off much faster than the attack reaches the limits of the channel capacity.

Average number of attacks in certain consumer segments
Infrastructure legacy
In 2017, routing incidents became as infamous as botnets in 2016. A successful DDoS attack could always make one single resource or application inaccessible. In the case of popular social networks or libraries that developers use to create and maintain the normal operation of Internet services, an attack can threaten entire ecosystems that use interconnected parts of the infrastructure (including hosting and a common Internet service provider). As we have seen, routing incidents can be no less large-scale and dangerous than attacks by a record botnet, leaving almost the entire country without access to popular resources. What happens if one day you cannot open a single web page at all? This makes electronic communication impossible in the form in which we know it and which we take for granted.
The network incident caused by Google in Japan was perhaps the most striking example of what could happen if a large BGP configuration was incorrect, however, the only content provider.
In the case of BGP, you need to be extremely careful, as the potential damage may be enormous. Since BGP controls the transmission of all traffic from one AS to another, we are talking not only about increased delays in access to resources for users, but, more importantly, about the likelihood of MiTM attacks on encrypted traffic. Such incidents can affect millions of users in different countries.We still live in the world of an open network, but the further, the more it is perceived as a luxury, and not for granted. In 2017, the fact that any organization can still receive LIR status and acquire an autonomous system, thus becoming a telecom operator, deserves some words of gratitude.
On the one hand, human factors have always been, are and will remain the most vulnerable points for any company or Internet service. On the other hand, the human element is also the strongest defense, as people do their work in full control of the circumstances in which they find themselves. Technological problems are strongly interconnected, since all the code was written by man.

The number of attacks on the band used
Vulnerabilities and Intranets
2017 has become a real year of hacking. From epidemics cryptographers to the discoveries of the archives of Vault7 and Shadow Brokers, in addition to noticeable leaks due to human errors, where Uber and Equifax are the two loudest examples.
Everything is vulnerable. So it’s worth talking not about “what is most vulnerable,” but “where vulnerability can be found earlier.” Where there are vulnerabilities, there are also attacks. Moreover, there are a number of widely used technologies that reproduce vulnerabilities — when one is fixed and the other breaks. The attackers are closely watching such activities - they know that the larger the supplier in front of them, the more time it will take to develop and deliver the update to its customers.
The cloud also goes into legacy status with all the problems that are inherited by new generations of devices and technologies. The leaks of Uber and OneLogin began with the fact that the keys to the Amazon repository were published on GitHub or elsewhere - it is possible that the sticker stuck to the monitor.
Another major problem is the situation with MongoDB, Cassandra, Memcached and other popular databases. When their administrators forget to establish an appropriate level of security, it’s easy for an attacker to find loopholes. This is exactly what happened in the case of the software keyboard for Ai.Type smartphones, which lost all data of 31 million of its own users.
2017 has demonstrated how diverse types of equipment can be vulnerable to different types of cyber attacks. In the future, we will see even more incidents involving outdated software and hardware.Attacks with the use of smartphones can be made either on the basis of infection by malicious applications, even if they are installed from official stores, or with the help of similar BlueBorne vulnerabilities. Browser extensions and plug-ins, network devices (which have already suffered enough over the past three years), any equipment at the interfaces of providers - everything can be tested for resistance to attacks again and again and probably will not stand.
The main goal of creating a solution to neutralize DDoS is ultimately the establishment of protection, whose support is cheaper than the organization of attacks. Only by taking away the economic advantage of the attackers, you can begin to fight on some conditions. And this is a difficult task, primarily due to two factors:
A. Reckless approach to the basics of information security and threat analysis;
B. Fear of news and publicity, trying to hide information in case of problems.
Cryptomania
The new and large ICO market has become a real revelation for hackers in 2017. The tendency to attack at the most stressful moment for the organization (fundraising, advertising campaigns) persists, and with a growing number of cryptocurrency projects, hacking attacks are combined with DDoS. If the market for issuing cryptocurrency tokens continues to grow, this trend will only intensify.
ICOs are of particular interest to all market parties. Because of cryptocurrency and ICO, a new industry of hacks has grown before our eyes. Huge amounts of funds are already involved in this market, and the technical side of the implementation of many projects is frankly weak, as we said in 2017. They are constantly hacked.
Mining pools are attacked in the last seconds of the signature of each block in order to get a reward for the block signature by a competing pool. Cloud cryptocurrency wallets are constantly under attack - during 2017 we saw major hacking of such services with the loss of all cryptocurrencies by their creators. Even mining with the help of scripts in the browser can be profitable, not to mention the infection of a large number of old computers, servers, or game consoles with malware that performs calculations at the expense of victims.
Network attacks on the hyperledger infrastructure (such as DDoS attacks on the mining pools at the end of the calculation of each block) will grow in proportion to the growth of cryptocurrency projects. Every complex technology has a foundation. Finding cracks in it, you can destroy a house of any size.

Duration of attacks, minutes
Epilogue
APIs are becoming increasingly important for large clients - they are professional and want to have maximum control over the processes of cleaning and filtering traffic. This process should not be underestimated.
The most notable fact in this area is not even the attacks themselves, but the progress that all security solution providers have made in the process of training, communication and cooperation, and not just competition, in order to find answers to the most serious questions of our time, such as countering botnets When such large-scale threats appear, calling into question the existence of no longer separate web services, but the entire industry as such, companies are merged at several levels at once: formal, informal, B2G and B2C. We have already seen successes associated with such cooperation in countering major botnets in 2017 among the largest companies working in the field of information security - we hope that this will happen more often in the future.
Thanks for reading.
Direct link to Russian PDF.
Link to Slideshare
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/351466/
All Articles