FastTrack Training. "Network Basics". "Equipment for data centers." Eddie Martin December 2012
About a year ago, I noticed an interesting and fascinating series of lectures by Eddie Martin, which, thanks to its history and real-life examples, as well as its tremendous learning experience, is amazingly comprehensible and allows you to gain an understanding of quite complex technologies.

We continue the cycle of 27 articles based on his lectures:
')
01/02: “Understanding the OSI Model” Part 1 / Part 2
03: "Understanding the Cisco Architecture"
04/05: “The Basics of Switching or Switches” Part 1 / Part 2
06: "Switches from Cisco"
07: "Area of use of network switches, the value of Cisco switches"
08/09: "Basics of a Wireless LAN" Part 1 / Part 2
10: "Products in the field of wireless LAN"
11: The Value of Cisco Wireless LANs
12: Routing Basics
13: "The structure of routers, routing platforms from Cisco"
14: The Value of Cisco Routers
15/16: “The Basics of Data Centers” Part 1 / Part 2
17: "Equipment for data centers"
18: "The Value of Cisco in Data Centers"
19/20/21: "The Basics of Telephony" Part 1 / Part 2 / Part 3
22: "Cisco Collaboration Software"
23: The Value of Collaboration Products from Cisco
24: "The Basics of Security"
25: "Cisco Security Software"
26: "The Value of Cisco Security Products"
27: "Understanding Cisco Architectural Games (Review)"
And here is the seventeenth of them.
Consider the equipment Cisco, which is used for data centers. Let's start with the standardized chassis for fiber optic networks (UCS, Unified Computing System, Unified Fabric) - the Nexus 7000 series. This is our newest development, it has 9 slots and is designed specifically to replace the Catalyst 6500. This is exactly the same chassis size. Model 7009 has 9 slots and this is indicated in the model number. If we open the door, we will see the numbering of slots from 1 to 9 from top to bottom. Each of them contains up to 5 modules of the fabric (Fabric Module).
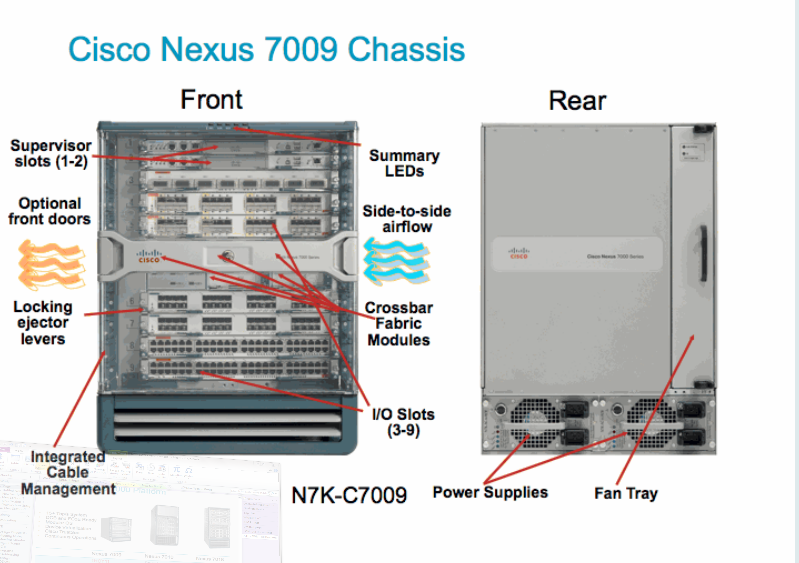
And each of the modules can provide 110 gigabits between each of the “blades”, that is, you have 110 gigabits of bandwidth. If I insert another module, I will get 220 gigabit of bandwidth and so on, up to 550 gigabits in total. If one of the modules fails, I still have hundreds of gigabits. There is an interconnect between them.
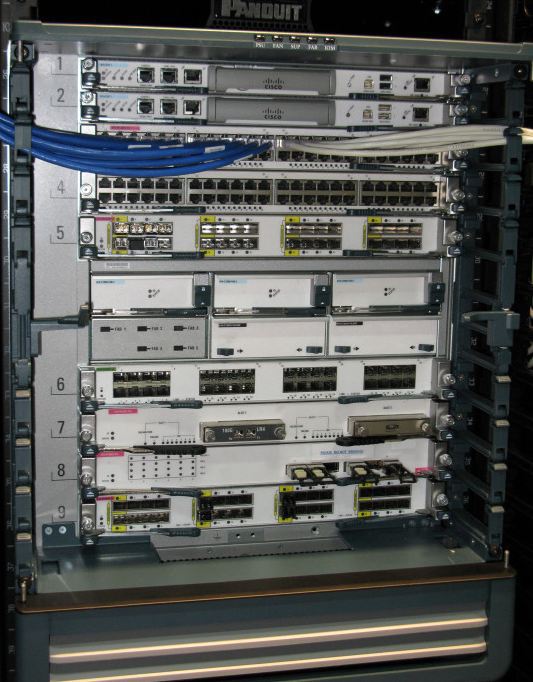

We can use a different set of line cards (line card) and different modules of supervisors - on the screen we see the characteristics of the selected configuration.

Here is a 24 port 10 Gigabit line card that supports IPv6 and can support up to a million routes. Again, we repeat that the M-boards look outward, and the F-boards look inside, which must be taken into account when placed in the data center. I will route traffic to the outside using M-boards, which are designed for routing with the provision of BGP or OSPF, depending on the protocol you choose. While the F-boards (optical cards) have a large bandwidth, but do not contain any number of additional functions, except for the routing tables, therefore, in fact, these cards are the same everywhere. In more detail the Cisco Nexus 7000 architecture is reviewed here .

A 10-slot chassis has a slightly different form factor — here, the Fabric Module modules are pulled back.
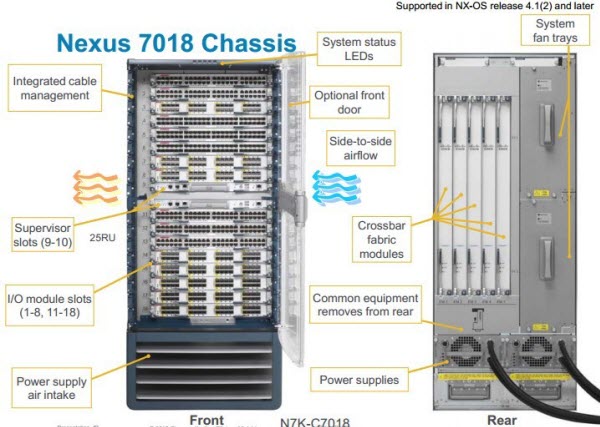
The chassis, designed to accommodate 18 modules, is indicated by the Nexus 7018. It has the same functionality, but large size. These are the biggest switches of this series. The difference between them can be well seen in the pictures and here .
But if you do not need such a large chassis, then it is better to look at the Nexus 5000 series. They also received the Nexus OS. You can put different expansion modules into the 5020 chassis, depending on what you want to do. We have three modifications of modules for 4, 6 and 8 ports with a capacity of 10 gigabits. It can be used as a traditional fiber, and Ethernet. This chassis can serve as a supervisor for the 2200 series switches.

Factory extenders. There are several factory extenders. This is what the FEX 2248 TP switch module looks like. It has 4 10 Gbps Ethernet Uplink ports and 48 ports for gigabit connections and provides data rates of 40 gigabits per second in each direction, that is only 80 gigabits.

If you need a 10-gigabit factory expander, then you should take the FEX 2232PP model and there will be 32 10-gigabit ports.
Again, you can have several similar expanders that will be controlled by the 5000 series chassis.
The Nexus 1010V looks like a plastic box, because it is virtualization software, not hardware. This is a virtual supervisor module.
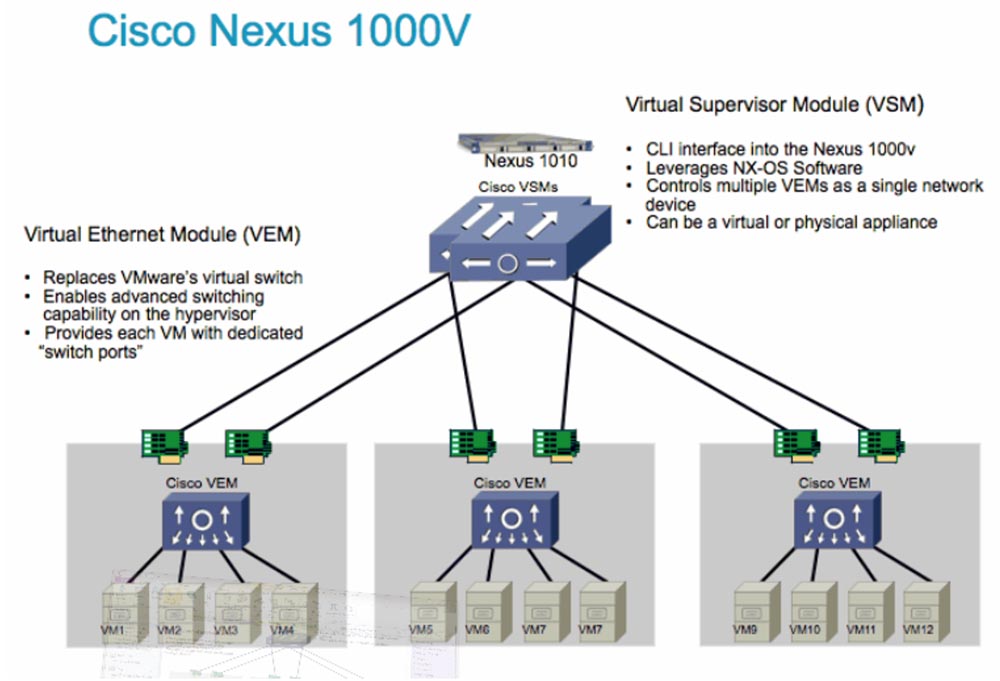
It works as a 4-port switch that you put inside your virtual server, and as a result you get up to 128 virtual ports – interfaces. All this can be used for security purposes and for many other things that we do for you in data centers. We discussed this issue in detail in previous lectures.
Now I will show you what the 5108 chassis looks like, which is installed on top of the Nexus 6200 chassis. This is the chassis for hosting the UCSB 200 server blades. The letter “B” means “blade”. The two after shows the number of sockets, in this case 2. The numbers after it show the model, 00 is the basic model, 20 or 30 have more RAM and storage space. Here, the picture shows VIC network cards, virtualized NIC cards. So, how many sockets are in the UCSB 400 model? 4 sockets, each with 8 cores. In this way, you can get up to 32 cores and 48 DIMMs. This is the B-series, the blade server series.

Now we will look at the servers intended for mounting in racks - the C-series. The UCS C460M1 model is a standalone server with four sockets. Up to 4 eight-core Intel Xeon 7500 processors can be placed under its cover.

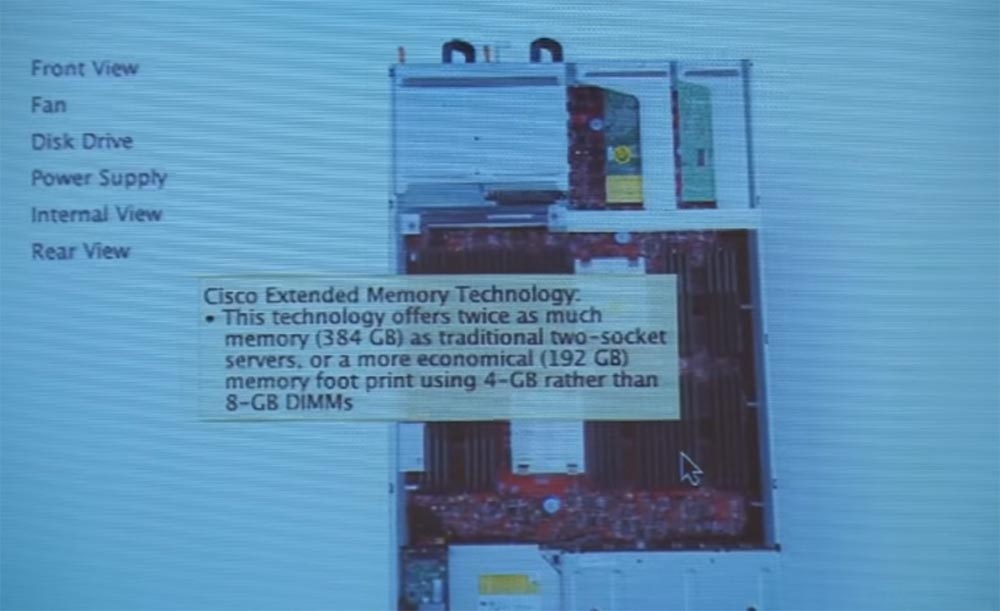
Let me show you a sample of the memory expansion technology using the example of the USC C250 series module, in which our ASICs are installed to expand the memory capacity. They have 2 times more memory than traditional modules for 2 sockets - 384 GB against 198 GB. Modules with less memory cost less.
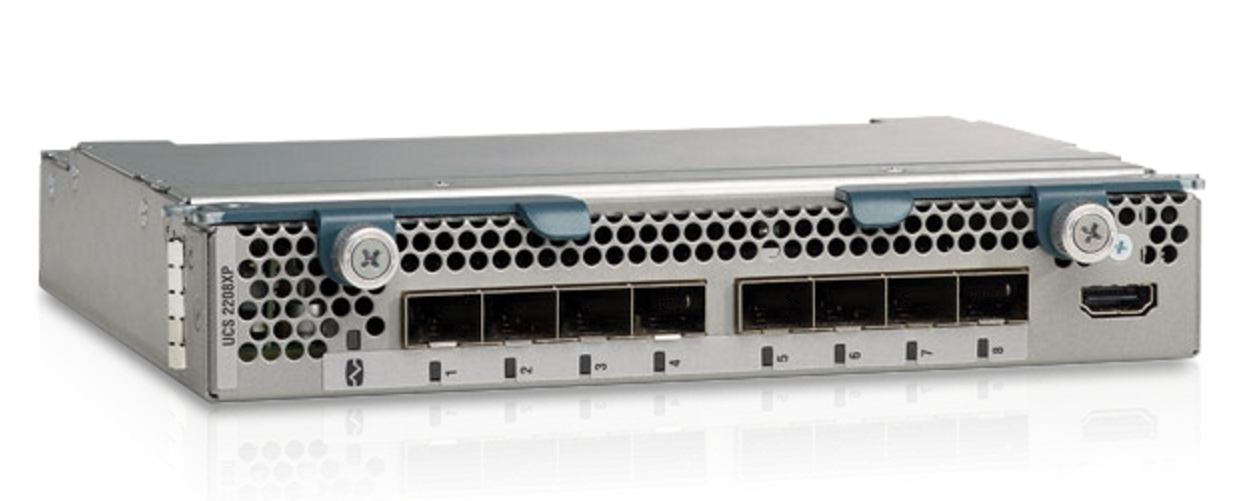
Consider the network module USC 2208 XP Fabric Extender. Their function is Fabric Interconnect. Each consists of 8 ports of 10 gigabits. Up to 2 extenders can be installed on each 6200 chassis and get a throughput of 160 gigabits per second.


We already spoke with you about VBlock earlier . VBlock chassis are similar to the system blocks of personal computers. This is a virtual data center, a solution for creating a large virtual architecture in which you can place blades, switches, storages, etc., that is, almost the entire line of modern physical Cisco devices.
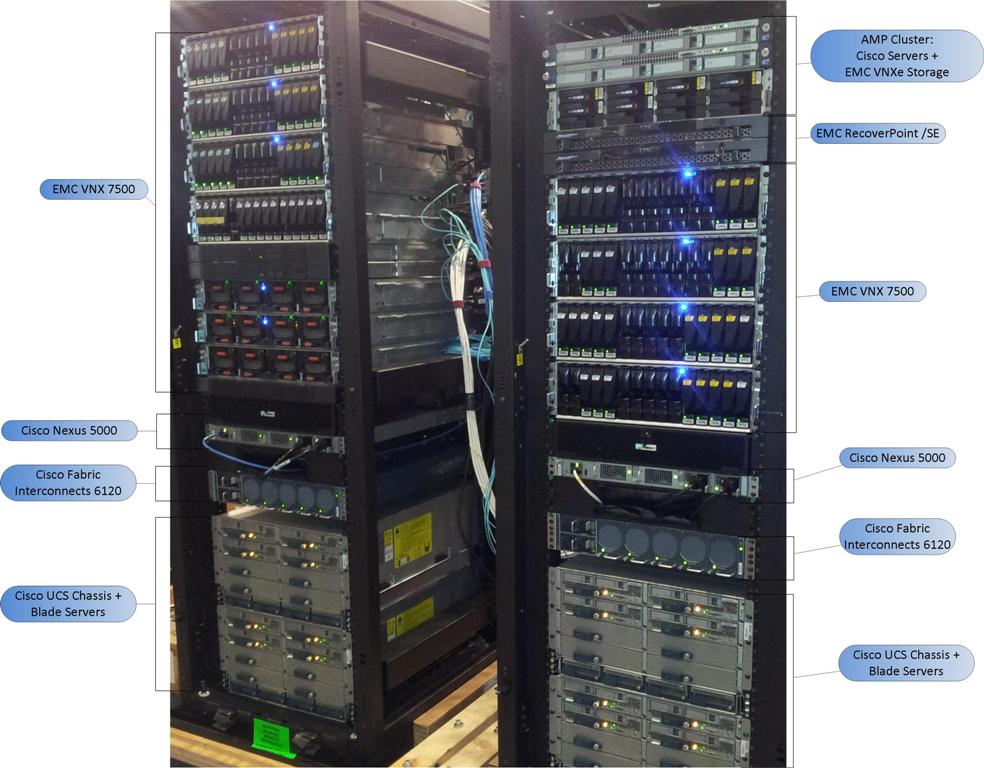

You can place exactly the equipment you need for your data storage in this chassis. This is a turnkey solution for the construction of full-featured data centers.
Continued:
FastTrack Training. "Network Basics". "The value of Cisco in data centers." Eddie Martin December 2012
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The Truth About VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?

We continue the cycle of 27 articles based on his lectures:
')
01/02: “Understanding the OSI Model” Part 1 / Part 2
03: "Understanding the Cisco Architecture"
04/05: “The Basics of Switching or Switches” Part 1 / Part 2
06: "Switches from Cisco"
07: "Area of use of network switches, the value of Cisco switches"
08/09: "Basics of a Wireless LAN" Part 1 / Part 2
10: "Products in the field of wireless LAN"
11: The Value of Cisco Wireless LANs
12: Routing Basics
13: "The structure of routers, routing platforms from Cisco"
14: The Value of Cisco Routers
15/16: “The Basics of Data Centers” Part 1 / Part 2
17: "Equipment for data centers"
18: "The Value of Cisco in Data Centers"
19/20/21: "The Basics of Telephony" Part 1 / Part 2 / Part 3
22: "Cisco Collaboration Software"
23: The Value of Collaboration Products from Cisco
24: "The Basics of Security"
25: "Cisco Security Software"
26: "The Value of Cisco Security Products"
27: "Understanding Cisco Architectural Games (Review)"
And here is the seventeenth of them.
FastTrack Training. "Network Basics". "Equipment for data centers." Eddie Martin December 2012
Consider the equipment Cisco, which is used for data centers. Let's start with the standardized chassis for fiber optic networks (UCS, Unified Computing System, Unified Fabric) - the Nexus 7000 series. This is our newest development, it has 9 slots and is designed specifically to replace the Catalyst 6500. This is exactly the same chassis size. Model 7009 has 9 slots and this is indicated in the model number. If we open the door, we will see the numbering of slots from 1 to 9 from top to bottom. Each of them contains up to 5 modules of the fabric (Fabric Module).

And each of the modules can provide 110 gigabits between each of the “blades”, that is, you have 110 gigabits of bandwidth. If I insert another module, I will get 220 gigabit of bandwidth and so on, up to 550 gigabits in total. If one of the modules fails, I still have hundreds of gigabits. There is an interconnect between them.

We can use a different set of line cards (line card) and different modules of supervisors - on the screen we see the characteristics of the selected configuration.

Here is a 24 port 10 Gigabit line card that supports IPv6 and can support up to a million routes. Again, we repeat that the M-boards look outward, and the F-boards look inside, which must be taken into account when placed in the data center. I will route traffic to the outside using M-boards, which are designed for routing with the provision of BGP or OSPF, depending on the protocol you choose. While the F-boards (optical cards) have a large bandwidth, but do not contain any number of additional functions, except for the routing tables, therefore, in fact, these cards are the same everywhere. In more detail the Cisco Nexus 7000 architecture is reviewed here .

A 10-slot chassis has a slightly different form factor — here, the Fabric Module modules are pulled back.

The chassis, designed to accommodate 18 modules, is indicated by the Nexus 7018. It has the same functionality, but large size. These are the biggest switches of this series. The difference between them can be well seen in the pictures and here .

But if you do not need such a large chassis, then it is better to look at the Nexus 5000 series. They also received the Nexus OS. You can put different expansion modules into the 5020 chassis, depending on what you want to do. We have three modifications of modules for 4, 6 and 8 ports with a capacity of 10 gigabits. It can be used as a traditional fiber, and Ethernet. This chassis can serve as a supervisor for the 2200 series switches.

Factory extenders. There are several factory extenders. This is what the FEX 2248 TP switch module looks like. It has 4 10 Gbps Ethernet Uplink ports and 48 ports for gigabit connections and provides data rates of 40 gigabits per second in each direction, that is only 80 gigabits.

If you need a 10-gigabit factory expander, then you should take the FEX 2232PP model and there will be 32 10-gigabit ports.
Again, you can have several similar expanders that will be controlled by the 5000 series chassis.
The Nexus 1010V looks like a plastic box, because it is virtualization software, not hardware. This is a virtual supervisor module.

It works as a 4-port switch that you put inside your virtual server, and as a result you get up to 128 virtual ports – interfaces. All this can be used for security purposes and for many other things that we do for you in data centers. We discussed this issue in detail in previous lectures.
Now I will show you what the 5108 chassis looks like, which is installed on top of the Nexus 6200 chassis. This is the chassis for hosting the UCSB 200 server blades. The letter “B” means “blade”. The two after shows the number of sockets, in this case 2. The numbers after it show the model, 00 is the basic model, 20 or 30 have more RAM and storage space. Here, the picture shows VIC network cards, virtualized NIC cards. So, how many sockets are in the UCSB 400 model? 4 sockets, each with 8 cores. In this way, you can get up to 32 cores and 48 DIMMs. This is the B-series, the blade server series.

Now we will look at the servers intended for mounting in racks - the C-series. The UCS C460M1 model is a standalone server with four sockets. Up to 4 eight-core Intel Xeon 7500 processors can be placed under its cover.

Let me show you a sample of the memory expansion technology using the example of the USC C250 series module, in which our ASICs are installed to expand the memory capacity. They have 2 times more memory than traditional modules for 2 sockets - 384 GB against 198 GB. Modules with less memory cost less.

Consider the network module USC 2208 XP Fabric Extender. Their function is Fabric Interconnect. Each consists of 8 ports of 10 gigabits. Up to 2 extenders can be installed on each 6200 chassis and get a throughput of 160 gigabits per second.


We already spoke with you about VBlock earlier . VBlock chassis are similar to the system blocks of personal computers. This is a virtual data center, a solution for creating a large virtual architecture in which you can place blades, switches, storages, etc., that is, almost the entire line of modern physical Cisco devices.

You can place exactly the equipment you need for your data storage in this chassis. This is a turnkey solution for the construction of full-featured data centers.
Continued:
FastTrack Training. "Network Basics". "The value of Cisco in data centers." Eddie Martin December 2012
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The Truth About VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/351024/
All Articles