Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 3 - Formation of requirements for the protection system
What research
Links to other parts of the study
- Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 1 - Economic fundamentals.
- Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 2 - Typical IT infrastructure of the bank.
- Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 3 - Formation of requirements for the protection system. ( You are here )
- Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 4 - Overview of threat modeling standards.
- Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 5 - 100+ thematic links about hacking banks.
- Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 6 - Analysis of banking crimes.
- Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 7 - The basic threat model.
- Information security of bank non-cash payments. Part 8 - Typical threat models.
In the previous parts of the study, we discussed the economic fundamentals and IT infrastructure of bank cashless payments. In this part, we will focus on the formation of requirements for the created information security system (IB).
Next we look at:
')
- the role of security in the life of a commercial organization;
- the place of information security service in the organization’s management structure;
- practical aspects of security;
- application of the theory of risk management in information security;
- main threats and potential damage from their implementation;
- The list of mandatory requirements for the IB system of bank non-cash payments.
The role of security in the life of a commercial organization

In the modern Russian economic environment there are many different types of organizations. These can be state-owned enterprises (FSUE, MUP), public funds and, finally, ordinary commercial organizations. The main difference between the latter and all the others is that their main goal is to maximize profits, and everything they do is directed towards this.
A commercial organization can earn in various ways, but profit is always determined in the same way - it is income minus expenses. At the same time, if security is not the main activity of the company, then it does not generate income, and if so, then in order for this activity to make sense, it must reduce costs.
The economic effect of ensuring the security of a business is to minimize or completely eliminate losses from threats. But it should also be borne in mind that the implementation of protective measures also costs money, and therefore the true profit from security will be equal to the amount saved from the realization of security threats, reduced by the cost of protective measures.
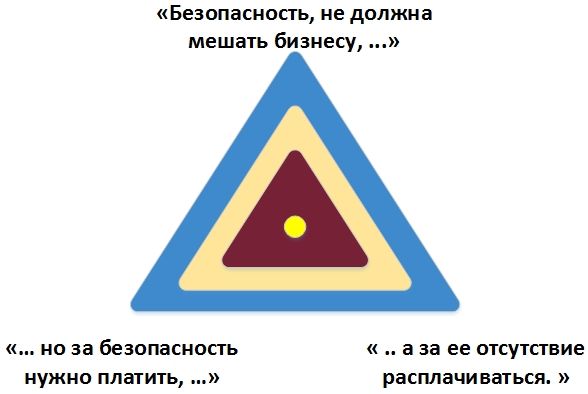
Once, a conversation was held between the owner of a commercial bank and the head of the security department of his organization on the economic effect of security. The essence of this conversation most accurately reflects the role and place of ensuring security in the life of the organization:
- Security should not interfere with business.
“But you have to pay for security, and pay for its absence.”
The ideal security system is the golden mean between neutralized threats, resources expended on this, and business profitability.
The place of information security service in the organization’s management structure
The structural unit responsible for ensuring information security may be called differently. This may be a department, office or even an information security department. Further, for unification, this structural unit will be called simply the information security service (ISS).
The reasons for creating an NIB may be different. We distinguish two main ones:
- Fear
The company's management is aware that computer attacks or information leaks can lead to catastrophic consequences, and makes efforts to neutralize them. - Ensuring compliance with legal requirements .
The current legislative requirements impose obligations on the company to form an NIB, and top management undertakes efforts to fulfill them.
In relation to credit organizations, the need for an NIB is recorded in the following documents:
- Government Decree of 01.11.2012 N 1119 “On the approval of requirements for the protection of personal data when they are processed in personal data information systems”.
- “Regulations on information security requirements for money transfers and the procedure for the Bank of Russia to monitor compliance with the information security requirements for money transfers” (approved by the Bank of Russia 09.06.2012 N 382-P) (as amended by August 14, 2014) (Registered in the Ministry of Justice of Russia June 14, 2012 N 24575).
- “Regulations on information security requirements in the payment system of the Bank of Russia” (approved by the Bank of Russia 08/24/2016 N 552-P) (Registered in the Ministry of Justice of Russia December 6, 2016 N 44582).
- Requirements of the license of the Federal Security Service of Russia for cryptography: Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2012 No. 313 , Order of FAPSI of June 13, 2001 No. 152 (NIB, as a cryptographic authority).
- For banks possessing significant objects of key information infrastructure - Order of FSTEC of Russia of December 21, 2017 N 235 “On approval of requirements for creating security systems of important objects of critical information infrastructure of the Russian Federation and ensuring their functioning” (Registered in the Ministry of Justice of Russia February 22, 2008 N 50118) .
The required functionality from the NIB is specified in the above documents. The staff number is not strictly regulated, with the exception, perhaps, of the licensing requirements of the FSB of Russia for cryptography (at least 2 employees, but they can be in different departments) and can be chosen by the organization independently. To justify the size of the state, it is recommended to use the document - Recommendations in the field of standardization of the Bank of Russia “Ensuring the information security of organizations of the banking system of the Russian Federation. Resource support information security "RS BR IBBS-2.7-2015"
From the point of view of SIB subordination, there is only one limitation specified in the above provisions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation - “The information security service and the informatization (automation) service should not have a common curator,” otherwise the organization is left to choose. Consider the typical options.
Table 1.
| Subordination | Special features |
|---|---|
| NIB in IT | 1. The organization of protection is possible only against an external attacker. The main likely internal attacker is an IT employee. To fight him in the IT impossible. 2. Violation of the requirements of the Bank of Russia. 3. Direct dialogue with IT, simple implementation of information security systems. |
| NIB in the security service | 1. Protection against the actions of both internal intruders and external. 2. SB - a single point of interaction between top management on any security issues. 3. The complexity of interaction with IT, since communication takes place at the level of heads of IT and Security Council, and the latter, as a rule, has minimal knowledge in IT. |
| NIB reports to the Chairman of the Board | 1. The SIB has the maximum authority and its own budget. 2. For the Chairman of the Board, an additional point of control and interaction is created, requiring particular attention. 3. Possible conflicts of the Security Council and the ISS in areas of responsibility for investigating incidents. 4. A separate NIB can “politically” balance the powers of the Security Council. |
When interacting with other structural subdivisions and top management of the bank, the ISS of any organization has one common problem - evidence of the need for its existence (financing).
The problem is that the amount of savings from neutralized information security threats cannot be accurately determined. If the threat has not been realized, then there is no damage from it, and if there are no problems, then there is no need to solve them.
To solve this problem, an NIB can act in two ways:
- Show economic importance
To do this, it needs to keep records of incidents and assess the potential damage from their implementation. The cumulative amount of potential damage can be considered money saved. To resolve disagreements on the size of the estimated damage, it is recommended to develop and approve a methodology for its assessment. - Engage in internal PR
Ordinary employees of the organization usually do not know what the NIB does and consider its employees to be idlers and charlatans who interfere with work, which leads to unnecessary conflicts. Therefore, the NIB should periodically communicate to colleagues the results of its activities, talk about current threats to information security, conduct training and raise their awareness. Any employee of the company should feel that if he has a problem related to information security, he can contact the NIB and they will be helped there.
Practical safety aspects

Let us highlight the practical aspects of security, which must necessarily be brought to the top management and other structural divisions, and also taken into account when building an information security system:
- Security is a continuous, endless process. The degree of security achieved with its help will fluctuate over time depending on the harmful factors acting and the efforts aimed at neutralizing them.
- Security cannot be ensured after the fact, that is, at the moment when the threat has already been realized. To neutralize the threat, the security process must begin before attempting to implement it.
- Most of the threats are of an anthropogenic character, that is, organizations are threatened in some way or another by people. As computer criminologists say: “It’s not programs that are stolen, people are stealing.”
- People whose safety is ensured,
whether they are business owners or customers. - Security is a derivative of corporate culture. The discipline required for the implementation of protective measures can not be higher than the general discipline in the work of the organization.
Summing up the interim result under the above, we note that the created IB system of cashless payments must have a practical orientation and be cost-effective. The best help in achieving these properties is the use of a risk-based approach.
Risk management

Information security is just one of the areas of security (economic security, physical security, fire safety, ...). In addition to threats to information security, any organization is exposed to other, equally important threats, for example, threats of theft, fire, fraud by unscrupulous customers, threats of violation of mandatory requirements (compliance), etc.
Ultimately, the organization doesn’t care what particular threat it will incur losses, be it theft, fire, or computer hacking. The size of the loss (damage) is important.
In addition to the amount of damage, an important factor in assessing the threat is the likelihood of implementation, which depends on the characteristics of the organization’s business processes, its infrastructure, external harmful factors and countermeasures taken.
A characteristic that takes into account the damage and the likelihood of a threat occurring is called risk.
Note. Scientific definition of risk can be obtained in GOST R 51897-2011
Risk can be measured both quantitatively, for example, by multiplying damage by probability, and qualitatively. A qualitative assessment is carried out when neither damage nor probability are quantified. The risk in this case can be expressed as a set of values, for example, the damage is “medium”, the probability is “high”.
Evaluation of all threats as risks allows an organization to efficiently use its resources to neutralize precisely those threats that are most significant and dangerous for it.
Risk management is the main approach to building an integrated, cost-effective organization's security system. Moreover, almost all banking regulations are based on the risk management recommendations of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision .
The main threats and assessment of potential damage from their implementation

Let us highlight the main threats inherent in the implementation of banking non-cash payments, and determine the maximum possible damage from their implementation.
Table 2.
| No | Threat | Maximum possible damage |
| one | Termination (long stop) of activity | Banking license withdrawal |
| 2 | Cash theft | In the amount of cash balance on accounts |
| 3 | Violation of mandatory requirements for activities established by applicable law and agreements with the Bank of Russia | Banking license withdrawal |
Here, the composition of the analyzed activity includes a set of business processes:
- the implementation of correspondent relations with partner banks and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- carrying out settlements with customers.
In the future, we will consider only the issues of ensuring the security of correspondent relations with the Bank of Russia. However, the results obtained can be used to ensure security and other types of calculations.
Mandatory requirements for the IB system of non-cash payments

When considering the main threats, we estimated their damage, but did not assess the likelihood of their realization. The fact is that if the maximum possible damage will be the same for any banks, then the likelihood of threats will vary from bank to bank and depend on the protective measures applied.
One of the main measures to reduce the likelihood of threats to information security will be:
- implementation of best practices in IT and infrastructure management;
- creation of an integrated information security system.
We will not talk about IT practices here, we will only touch on information security issues.
The main nuance that must be taken into account in matters of ensuring information security is that this type of activity is rather tightly regulated by the state and the Central Bank. No matter how the risks are assessed, no matter how small the resources available to the bank are, its protection must meet the established requirements. Otherwise, it will not work.
Consider the requirements for the organization of information security imposed on the business process of correspondent relations with the Bank of Russia.
Table 3.
We also denote additional requirements for the organization of information security. These requirements will apply only to some banks and only in some cases:
- STO BR IBBS . The standard and complex of related documents is valid only if it is voluntarily accepted by a credit institution.
- PCI DSS . The standard will be valid only if full non-masked payment card numbers (PAN) are transmitted in payment documents.
- Corporate information security policy. The requirements are relevant for large banking groups, where a unified information security policy is established for all banks of the group and where each bank must develop internal documents on its basis.
The end results of the application of all these requirements should be the information security system that satisfies any of the listed documents. In order to create such a system, the requirements are reduced to a single table and in cases where there are several similar requirements, the most stringent of them are chosen.
There is an important nuance here: the requirements specified in the regulatory documents, as a rule, do not contain rigid specifics. They indicate how the security system should look, from what means it should consist and what tactical characteristics it should have. An exception will be the requirements arising from the operational documentation for the applicable information security tools, for example, on SCAD SKZI Signature.
Consider, for example, a fragment of the requirements of the Order FSTEC № 21
Table 4.
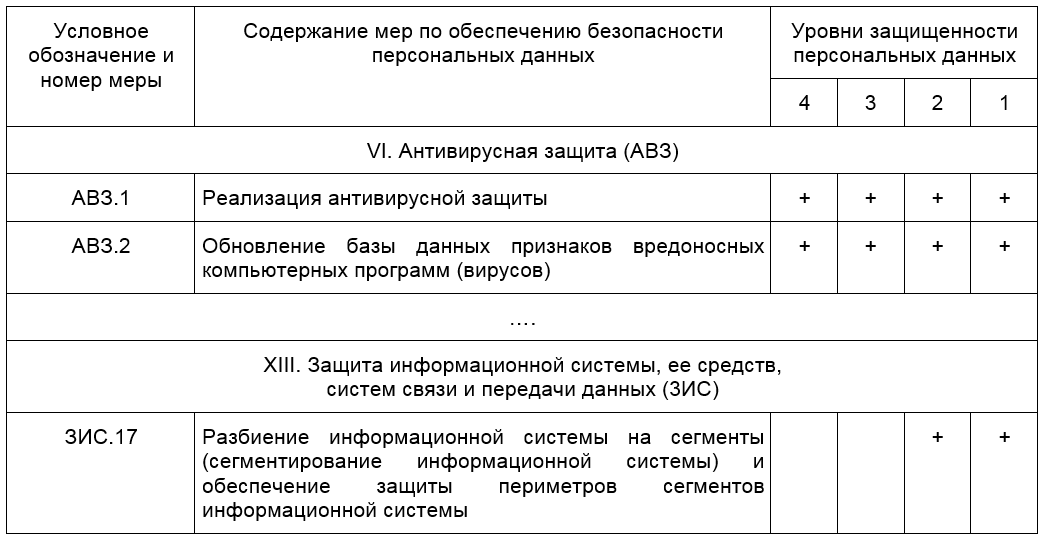
As we see, the requirements of AVZ.1 and AVZ.2 suggest that there should be anti-virus protection. How exactly to configure it, on what network nodes to install, these requirements are not regulated ( Letter of the Bank of Russia dated 03/24/2014 N 49-T recommends that banks have anti-viruses from different manufacturers on ARMs, servers and gateways).
Similarly, the situation with the segmentation of the computer network - the requirement of VMS.17 . The document only prescribes the need to use this practice for protection, but does not say how the organization should do this.
The way the information security tools are specifically configured and the protection mechanisms are implemented is learned from a private technical assignment for an information protection system generated from the simulation of information security threats.
Thus, a comprehensive information security system should be a set of protective business processes (controls in the English language literature), built with regard to the fulfillment of mandatory requirements, current threats and the practice of ensuring information security.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/350852/
All Articles