SSO and Kibana: Kibana integration with integrated Windows authentication (Single Sign-On)
In this article, I would like to share a way to configure single sign-on (SSO) in the Elastic Stack, which uses X-Pack to authenticate users and restrict access to data.
I must say that active attempts to configure SSO in Kibana with Active Directory began after reading the article Integrating third party Auth with Kibana . As always, a simple and working example was given in such blogs, which is suitable for "home use", but not very applicable in enterprises with complex infrastructure. And only after the release of Elastic Stack v.5.6.2, and more specifically, the patch in X-Pack 5.6.2, which finally made it possible to use “user impersonation” with Active Directory, single sign-on (SSO) earned in full least
“User impersonation” (user impersonation) is a key component in this system, through which one account (for example, technical user) is allowed to send requests on behalf of other, already authenticated users. In Elastic Stack X-Pack, this function is called run_as .
To be fair, it should be noted that SSO could have been configured even before this patch - if using LDAP. But since the LDAP realm in Elasticsearch does not support nested groups, it was not serious to consider this solution.
Architecture
The architecture of the proposed solution will be as follows:
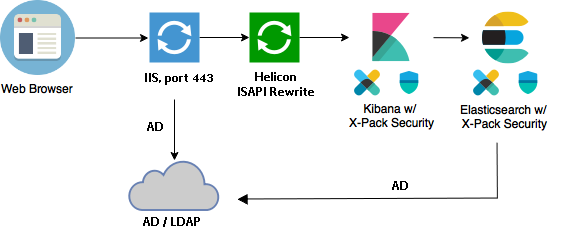
The picture is borrowed in the already mentioned blog, only the names of several components are changed. I hope that Elastic will not object (if it finds out), and if it does, then you will have to draw your own squares in PPT.
Description of work
- Users send a request to a web server (IIS), which authenticates them through the Windows Authenticated mechanism (all other authentication methods are disabled in the configuration of this website).
- If the authentication is successful, then IIS sets the environment variable
REMOTE_USER=DOMAIN\user. - This variable will be used in the Helicon rewrite extension module to set up an impersonation HTTP header (impersonation header)
es-security-runas-user. - The Helicon rewrite module also sets the HTTP authentication header (Basic) for the special technical internal user Elasticsearch.
- A special role in Elasticsearch is used to allow search queries to run on behalf of other users . Since impersonation should be allowed only for domain users, this role will look something like this:
*@domain.name. - Configuring AD realm for X-Pack
- Since user access to indexes will be regulated only through AD groups, AD-realm should use the
unmapped_groups_as_roles: true. This means that the name of the AD group will be the name of the role in Elasticsearch (see security and performance 1 below). - All users of our system (Kibana), regardless of which indices in Elasticsearch have access to them, should have read and write
.kibanaindex. So, in AD you need to create a special group, which will include all those users who need to use Kibana. In addition, in Elasticsearch you need to create a role with the same name and with the rights to modify the.kibanaindex. For example, this is what the user configuration of the network equipment administration department will look like:- Kibana user: AD-group = ES role =
ELK.Usersrights to the.kibana*index.kibana*:manage,read,index,delete
- Access to network logs: AD-group = ES role =
ELK.Network.Adminsrights tonet-*indices:read,view_index_metadata
- Kibana user: AD-group = ES role =
Installation
- Configure TLS on Kibana and Elasticsearch server: instruction . This item is optional, but desirable - it is undignified to offer an authentication system without traffic encryption.
- Install IIS (Microsoft Internet Information Services) to authenticate users through NTLM. Since this web server will be used as a proxy and will not perform any other work, you can install IIS on the same server as Kibana.
- Improving IIS:
- Application Request Routing (ARR) is an extension that allows IIS to work as a load balancer. In our case, it will be used as a reverse proxy server (reverse proxy).
- Helicon ISAPI_Rewrite 3 engine is a third-party module that emulates the operation of the Apache rewrite engine. It is needed because IIS (at the moment) cannot set the
REMOTE_USERvariable when using NTLM, since the embedded IIS Rewrite module is called before the user is authenticated.
Configuration
We start to configure all components (the dream is to write an installer ...).
IIS
- SSL setup
The network is full of instructions for configuring SSL / TLS in IIS, for example, IIS SSL how-to . But I still list some steps. Suppose that we already have a PEM certificate, we convert it into PKCS # 12 format for IIS:
openssl pkcs12 -export -out domain.name.pfx -inkey domain.name.key -in domain.name.crt - Import this certificate into IIS:
- IIS Manager ⇒ Top level navigation tree ⇒ Server certificates ⇒ Import ...
- We select this certificate in Binding for HTTPS (port 443) in our website:
- IIS Manager ⇒ Top level navigation tree ⇒ Sites ⇒ Default Web Site ⇒ Bindings ...
- Configuring reverse proxy for IIS ⇔ Kibana communication (it is assumed that Kibana works locally on the same server and uses its standard port - 5601)
- IIS Manager ⇒ Top level navigation tree ⇒ Application Request Routing Cache ⇒ Server Proxy Settings ... ⇒
- IIS Manager ⇒ Top level navigation tree ⇒ Sites ⇒ Default Web Site ⇒ Bindings ...
Enable proxy [x] Reverse proxy: localhost:5601 - Certificate Authority Certificate Kibana
If it happens that the Kibana certificate is signed by an "unfamiliar" CA (not from the organization's PKI), then this CA must be added to the "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" on the server with IIS:- Call
mmc(with administrator rights) ⇒ Add or Remove Snap-ins ⇒ Certificates ⇒ Add ⇒ Computer account ⇒ Local computer ⇒ Certificates (Local computer) ⇒ Trusted Root Certification Authorities ⇒ Certificate ⇒ import CA.crt
- Call
Helicon Rewrite engine
By default, the module is installed in C:\Program Files .
Add the following to the configuration file C:\Program Files\Helicon\ISAPI_Rewrite3\httpd.conf :
RewriteEngine on RewriteCond %{REMOTE_USER} (.*)\\(.*) RewriteHeader es-security-runas-user: .* (%2)(@company.com) RewriteHeader Authorization: .* (Basic\ aWlzOnNlY3JldHBhc3N3b3Jk) RewriteRule ^/logout / [R,L] How it works:
- after the user is authenticated, his login
DOMAIN\userconverted by the module into theuserPrincipalNameformat (user@company.com) and sent to Kibana by the new HTTP headeres-security-runas-user - Add another HTTP header for Basic authentication, where the
aWlzOnNlY3JldHBhc3N3b3Jkvalue is the base64-encoded technical user login:iis:secretpassword(we will create it in Elasticsearch a bit later). - Well, if the user clicks on
/logout, we will simply redirect him to the Kibana start page, where he again automatically/logout
Kibana
For SSO, add the following parameters to kibana.yml :
elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ es-security-runas-user, authorization ] xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ es-security-runas-user, authorization ] Elasticsearch
X-Pack is already installed, configuring AD in elasticsearch.yml :
xpack: security: authc: realms: native_realm: type: native order: 0 company_ad_realm: enabled: true type: active_directory order: 1 domain_name: company.com user_search: base_dn: "DC=company,DC=com" group_search: base_dn: "DC=company,DC=com" url: ldaps://server.company.com:636 ssl.verification_mode: none bind_dn: "CN=user,OU=People,DC=company,DC=com" bind_password: "XXXXXXXXXX" unmapped_groups_as_roles: true cache.ttl: 300s The user specified in bind_dn must have rights to connect and search in AD.
AD certificate verification is disabled ( ssl.verification_mode: none ) because the CA (CA) AD is not specified (parameter: ssl.certificate_authorities ).
Create a technical user ( iis ) in Elasticsearch and a role (also iis ) for impersonization ("user impersonation" sounds even worse):
POST _xpack/security/role/iis
{ "run_as": [ "*@company.com" ] } POST _xpack/security/user/iis
{ "password": "secretpassword", "roles": [ "iis" ], "full_name": "Service Account for IIS reverse proxy" } Now we create a role for all Kibana users. Let me remind you - the name of the role should be the name of a group in AD, whose members will have access to Kibane (let this group be called "ELK.Users"):
POST _xpack/security/role/ELK.Users
{ "indices": [ { "names": [ ".kibana*" ], "privileges": ["read", "manage", "index", "delete"] } ] } Kibana stores all settings in a single index ( .kibana or .kibana-6 ), so all Kibana users must have read and write access to this index.
Now, for example, let's create a role whose members will have access to net-* indices that store data from network devices:
POST _xpack/security/role/ELK.Network.Admins
{ "indices": [ { "names": [ "net-*" ], "privileges": ["read", "view_index_metadata"] } ] } Another example is the "custom" super-user role for the administrators of Elasticsearch 2 :
POST _xpack/security/role/ELK.Admins
{ "cluster": [ "all" ], "indices": [ { "names": [ "*" ], "privileges": [ "all" ] } ] } Thus, members of the AD-group "ELK.Admins" get full access to the Elasticsearch cluster.
Result
Turn on and wonder! You can forget about entering a login.

When opening the root page of our IIS-proxy site, the user was successfully authenticated.
Note: if this user has access only to the net-* index net-* , then he will still see all the configured indexes in Kibana - pay attention to the drop-down list. But when selecting the indexes to which it does not have access, the user will see No results found . But this problem has nothing to do with SSO.
"Something went wrong"
Testing and troubleshooting.
Case 1 : The user (or his group) was forgotten to add "Kibana users" ( ELK.Users ) to the AD group, or he should not have access to the Kibana at all:
Config: Error 403 Forbidden: action [indices:data/write/update] is unauthorized for user [iis] run as [user@company.com]: [security_exception] action [indices:data/write/update] is unauthorized for user [iis] run as ... 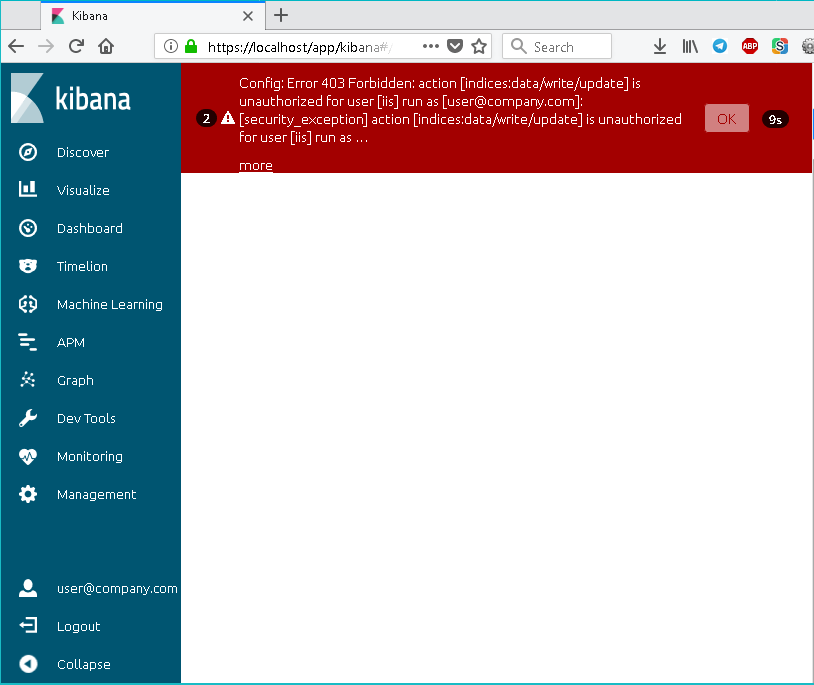
The user was successfully authenticated by IIS (NTLM, Kerberos, etc.) and authenticated by the technical user iis in Kibane. But since Since the real user@company.com account is not in the Kibana lovers AD group, it does not have a write / read role in the .kibana index in .kibana .
I do not know how to make the message or the page "access denied" more "friendly."
Case 2 : IIS uses SSL in the proxy module configuration (the "Enable SSL offloading" option is disabled, as intended), and in Kiban they forgot to configure HTTPS. Then we can observe the following in kibana.log :
{"type":"log","@timestamp":"2017-10-03T15:11:32Z","tags":["connection","client","error"],"pid":10416,"level":"error","message":"Parse Error","error":{"message":"Parse Error","name":"Error","stack":"Error: Parse Error\n at Error (native)","code":"HPE_INVALID_METHOD"}} Case 3 : The Kibana Certificate Authority Certificate Authority unknown to IIS
Open the IIS-Kibana start page:
HTTP Error 502.3 - Bad Gateway A security error occurred and the corresponding error in the Kibana log:
"code":"ECONNRESET" "message":"socket hang up" Case 4 : Windows authentication is not enabled for our website.
Then users will be authenticated in Kibana as iis user: "Service Account for IIS reverse proxy"
Test 1 : Is everything OK with AD / LDAP? And how are things going with the membership?
We use ldapsearch or adfind - in every possible way I recommend downloading here.
ldapsearch -h server.company.com -b "DC=company,DC=com" -D "CN=user,OU=People,DC=company,DC=com" -w "XXXXXXX" samaccountname=user adfind -f "userprincipalname=user@company.com" Test 2 : We are testing impersonation
curl -k -v -u iis:secretpassword -H "es-security-runas-user: user@company.com" https://elastic-server:9200/.kibana/_search If this test is passed ( HTTP/1.1 200 OK ), then Elasticsearch is configured correctly, and can check the user's rights in AD.
Well, if we get something like:
{"error":{"root_cause":[{"type":"security_exception","reason":"action [indices:data/read/search] is unauthorized for user [iis] run as [user@company.com]"}],"type":"security_exception","reason":"action [indices:data/read/search] is unauthorized for user [iis] run as [user@company.com]"},"status":403} This is the time to enable debugging and read Elasticsearch logs:PUT /_cluster/settings
{ "transient": { "logger.org.elasticsearch.xpack.security.authc": "trace" } } Test 3 : Change user membership in AD and, so that Elasticsearch does not expect cache invalidation, manually clear the latter
curl -k -u 'elastic:changeme' -X POST https://elastic-server:9200/_xpack/security/realm/company_ad_realm/_clear_cache Note: elastic is a built-in user with a default password (in version 5.x) or changed to the same (version 6.x).
To-dos
- Create a “Friendly” Page When “Internal Server Error” Occurs
If Elasticsearch cannot verify the user, for any reason (for example, there is no connection to AD), then Kibana will display the following JSON page:
{ statusCode: 500, error: Internal Server Error, message: An internal server error occurred } In principle, it is possible in the same Helicon Rewrite to write a redirect when this error appears on the custom page, which can be placed in:
<kibana-home>\optimize\bundles The page will be available at:
https://localhost/bundles/custom/error.htm Thanks for attention!
I hope that now in your organization the level of "user experience" and other "satisfaction" will be even greater!
[1] The following safety and performance considerations should be taken into account when using unmapped_groups_as_roles: true
- The AD administrator theoretically gets full access to the ES cluster: when you create a group in AD called
superuserand add your account to it, the administrator becomes a super-user of the cluster, because Thesuperuserrole is built-in and cannot be disabled or removed. The same will be true for other built-in roles:logstash_admin,machine_learning_admin, etc. I can’t offer any kind of work rounds, just an AD audit. - You must carefully plan and comply with the group naming convention in AD (naming convention) to avoid unauthorized access to data. Use prefixes (suffixes) in group names to access the ES cluster, for example,
ELK.*. - Elasticsearch will check each user group, according to its role in the cluster. With a large number of groups in which the user is included, this check will affect performance. In large organizations, where users have hundreds, or even thousands of groups, this can be a problem. But forewarned is forearmed. In addition, Elasticsearch caches groups and does not access AD on every search request; see the
cache.ttlparameter.
If you nevertheless decided not to use this automatic mapping through AD-groups for the reasons described above, then you will have to display the groups in the role either through files or through the API . ↩
[2] It is not recommended to create such a super-user role in products. It is better to administer in the old manner - with the super-user elastic and through curl . ↩
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/350744/
All Articles