Using the KOMPAS-3D API → Lesson 8 → More complex methods of writing to the title block
We continue the cycle of articles on working with the CAD API KOMPAS-3D Sergey Norseev, an engineer-programmer of the All-Russian Scientific-Research Institute “Signal”, the author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”. C ++ Builder is used as the medium. We have already considered working with the title block in the fourth part of our series of articles. In this article, I would like to consider more complex techniques for writing in the main title. But first we need to get acquainted with a number of new interfaces.
The dynamic array in the KOMPAS system is described by the ksDynamicArray interface. You can get it using the KompasObject interface's GetDynamicArray method. As a single parameter, it takes an integer array type, which determines what type of elements are stored in the array. As a rule, it stores other interfaces. I will not give all possible types of arrays, as there are a lot of them.
The ksDynamicArray interface has only one property. reference - interface pointer. Consider interface methods.
')
ksAddArrayItem - add an item to the array. Below is a prototype of this method.
The index parameter specifies the ordinal number of the element in front of which you want to insert a new element. Elements are numbered from scratch . If the value of this parameter is -1 , then the new element is inserted at the end of the array.
If successful, this method returns the value 1 , and in case of error, it returns zero .
ksClearArray () - removes all elements of the array, but not the array itself. It has no input parameters. If successful, returns 1 , and in case of error, it returns zero .
ksDeleteArray () - deletes an array. If the array is non-empty, all its elements are automatically deleted. It has no input parameters. If successful, returns 1 , and in case of error, it returns zero .
ksExcludeArrayItem - deletes an element of an array. As the only parameter takes the index of the element to be deleted. If successful, returns one , and in case of error, it returns zero .
ksGetArrayCount () - returns the number of elements in the array.
ksGetArrayItem - returns the specified element of the array. Below is a prototype of this method.
The index parameter specifies the sequence number of the requested element of the array (numbering is carried out from scratch ).
The item parameter contains the interface in which the readable element of the array is written. The type of this interface depends on the type of array.
If successful, the ksGetArrayItem method returns the value 1 , and in case of error, zero . Note: the requested item is returned in the item parameter.
ksGetArrayType () - returns the type of the array.
ksSetArrayItem - changes the specified element of the array. Below is a prototype of this method.
The item parameter contains the interface that is written in place of the element with the index number (numbering is from zero ). The type of this interface depends on the type of array.
If successful, the ksSetArrayItem method returns the value 1 , and in the case of an error, it returns zero .
The ksTextLineParam interface describes a string of text. You can get it using the KompasObject interface's GetParamStruct method . To do this, as a single parameter, this method needs to pass the constant ko_TextLineParam ( 29 ). The ksTextLineParam interface has only one property.
style - text style (will be discussed in the next articles of the cycle).
Consider the methods of the ksTextLineParam interface. There are only three of them.
GetTextItemArr () - returns a dynamic array ( ksDynamicArray ) of ksTextItemParam interfaces. This array is of type TEXT_ITEM_ARR ( 4 ).
Init () - reset all interface properties. Returns true if successful.
SetTextItemArr - sets a dynamic array of ksTextItemParam interfaces. It takes an array to be set as the only parameter ( ksDynamicArray interface). Returns true on success, false on error.
From this description it is easy to see that the ksTextLineParam interface is essentially a wrapper over a dynamic array of ksTextItemParam interfaces.
The following is an example of a program that demonstrates how to fill a title block using the ksTextLineParam interface.
For simplicity, this example omits the code responsible for connecting to KOMPAS, creating and executing a document, and freeing up resources (these issues were discussed in previous articles of the cycle). The figure below shows the title block formed by this program.

1. In the example, we get the ksDynamicArray interface from the KompasObject interface. But nothing prevents us from getting it from the ksTextLineParam interface. Moreover, if the ksDynamicArray interface were obtained by the GetTextItemArray () method, we could not call the SetTextItemArray method, since the array would already be associated with the ksTextLineParam interface.
2. To denote cell numbers, we use the constants ksStPartNumber and ksStMaterial . These constants are entered by KOMPAS for the most frequently used cells. You can get acquainted with them in the section “Parameters Structures and Constants / Constants / Constants of Design Objects / ksStampEnum - Stamp Cell Identifiers” of the COMPASS documentation.
3. To write lines to the main label, we use the ksTextLine method of the ksStamp interface. The same method was used in the fourth part of the loop, where we looked at the ksTextItemParam interface. This method as a parameter can take both the ksTextLineParam interface and the simpler ksTextItemParam .
4. Two lines are entered in the title block. The first line is simple and consists of only one component. The second line consists of three components. In the figure below, they are separated by vertical red lines. In principle, the last two components could be combined into one. But I specifically used three components to more clearly show the principle of operation of the interface ksTextLineParam .
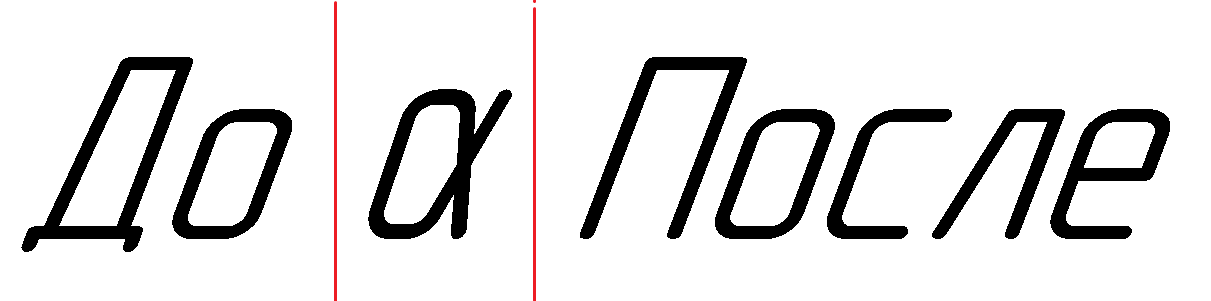
The ksSetStampColumnText method of the ksStamp interface sets the text in the specified cell of the title block . Below is a prototype of this method.
The text to be set is specified as a dynamic ksDynamicArray array. If successful, the ksSetStampColumnText method returns the value 1 , and in the case of an error, it returns zero .
Note, the ksSetStampColumnText method is used only in the main text editing mode. That is, after calling the ksOpenStamp () method, but before calling the ksCloseStamp () method of the ksStamp interface.
The textArr array is of type TEXT_LINE_ARR ( 3 ). This means that the elements of the array are the ksTextLineParam interfaces, each of which also contains a dynamic array, but already of the ksTextItemParam interfaces. The figure below shows the structure of the textArr parameter.
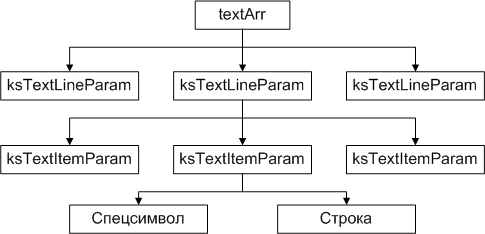
Although in the figure above the number of array elements is three, in reality it can be anything. If the textArr array consists of several elements, then all ksTextLineParam strings are glued together and displayed in the numb cell.
The following is an example of a program that demonstrates how to fill a title block using the ksSetStampColumnText method.
The result of this program is similar to the result of the previous example.
Note: since the number of the cell to which the string is written is already transferred to the ksSetStampColumnText method, it is not necessary to call the ksColumnNumber method.
Conclusion
We looked at three ways to write rows to cells in the title block : based on the ksTextItemParam interface ( covered in part 4 of the article series ), based on the ksTextLineParam interface , and using the ksSetStampColumnText method.
The first way is the easiest. It does not require working with dynamic arrays. It is ideal for writing strings. With it, you can also form complex strings. Control characters are used for this, which will be discussed in the next articles of the cycle.
The second method (the ksTextLineParam interface) is not much more complicated than the first. The ksTextLineParam interface is also used in the third method. Therefore, it must be understood in order to understand the third method.
The third method (the ksSetStampColumnText method) is the most difficult to implement. Its only real advantage over the first two methods is that there is no need to call the ksColumnNumber method. However, the approach used in this method is used when reading the contents of the cells of the inscription (about this in the next article of the cycle).
You can use any of these methods. Personally, I usually use the first one.
To be continued, stay tuned to the blog.
 Sergey Norseev, author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”.
Sergey Norseev, author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”.

Content of the cycle of lessons “Working with the API KOMPAS-3D”
1. Basics
2. Design drawing
3. Correct connection to COMPAS
4. Title Block
5. Graphic primitives
6. Saving a document in various formats
7. Getting to know the settings
8. More complex methods of writing to the main title
Dynamic array ( ksDynamicArray )
The dynamic array in the KOMPAS system is described by the ksDynamicArray interface. You can get it using the KompasObject interface's GetDynamicArray method. As a single parameter, it takes an integer array type, which determines what type of elements are stored in the array. As a rule, it stores other interfaces. I will not give all possible types of arrays, as there are a lot of them.
The ksDynamicArray interface has only one property. reference - interface pointer. Consider interface methods.
')
ksAddArrayItem - add an item to the array. Below is a prototype of this method.
long ksAddArrayItem ( long index, // LPDISPATCH item // ); The index parameter specifies the ordinal number of the element in front of which you want to insert a new element. Elements are numbered from scratch . If the value of this parameter is -1 , then the new element is inserted at the end of the array.
If successful, this method returns the value 1 , and in case of error, it returns zero .
ksClearArray () - removes all elements of the array, but not the array itself. It has no input parameters. If successful, returns 1 , and in case of error, it returns zero .
ksDeleteArray () - deletes an array. If the array is non-empty, all its elements are automatically deleted. It has no input parameters. If successful, returns 1 , and in case of error, it returns zero .
ksExcludeArrayItem - deletes an element of an array. As the only parameter takes the index of the element to be deleted. If successful, returns one , and in case of error, it returns zero .
ksGetArrayCount () - returns the number of elements in the array.
ksGetArrayItem - returns the specified element of the array. Below is a prototype of this method.
long ksGetArrayItem ( long index, // LPDISPATCH item // ); The index parameter specifies the sequence number of the requested element of the array (numbering is carried out from scratch ).
The item parameter contains the interface in which the readable element of the array is written. The type of this interface depends on the type of array.
If successful, the ksGetArrayItem method returns the value 1 , and in case of error, zero . Note: the requested item is returned in the item parameter.
ksGetArrayType () - returns the type of the array.
ksSetArrayItem - changes the specified element of the array. Below is a prototype of this method.
long ksSetArrayItem( long index, // LPDISPATCH item // ); The item parameter contains the interface that is written in place of the element with the index number (numbering is from zero ). The type of this interface depends on the type of array.
If successful, the ksSetArrayItem method returns the value 1 , and in the case of an error, it returns zero .
Line Parameters ( ksTextLineParam )
The ksTextLineParam interface describes a string of text. You can get it using the KompasObject interface's GetParamStruct method . To do this, as a single parameter, this method needs to pass the constant ko_TextLineParam ( 29 ). The ksTextLineParam interface has only one property.
style - text style (will be discussed in the next articles of the cycle).
Consider the methods of the ksTextLineParam interface. There are only three of them.
GetTextItemArr () - returns a dynamic array ( ksDynamicArray ) of ksTextItemParam interfaces. This array is of type TEXT_ITEM_ARR ( 4 ).
Init () - reset all interface properties. Returns true if successful.
SetTextItemArr - sets a dynamic array of ksTextItemParam interfaces. It takes an array to be set as the only parameter ( ksDynamicArray interface). Returns true on success, false on error.
From this description it is easy to see that the ksTextLineParam interface is essentially a wrapper over a dynamic array of ksTextItemParam interfaces.
Example 1
The following is an example of a program that demonstrates how to fill a title block using the ksTextLineParam interface.
// TextItemParamPtr TextItemParam; TextItemParam = (TextItemParamPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_TextItemParam); TextLineParamPtr TextLineParam; TextLineParam = (TextLineParamPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_TextLineParam); // DynamicArrayPtr DynamicArray; DynamicArray = (DynamicArrayPtr)kompas->GetDynamicArray(TEXT_ITEM_ARR); // StampPtr Stamp; Stamp = (StampPtr)Document2D->GetStamp(); // Stamp->ksOpenStamp(); // TextItemParam->set_s(SysAllocString(L"")); DynamicArray->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextItemParam); TextLineParam->SetTextItemArr(DynamicArray); // Stamp->ksColumnNumber(ksStPartNumber); Stamp->ksTextLine(TextLineParam); // DynamicArray->ksClearArray(); // TextItemParam->set_s(SysAllocString(L" ")); DynamicArray->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextItemParam); // TextItemParam->Init(); TextItemParam->set_type(SPECIAL_SYMBOL); TextItemParam->set_iSNumb(51); DynamicArray->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextItemParam); // TextItemParam->set_type(0);; TextItemParam->set_s(SysAllocString(L" ")); DynamicArray->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextItemParam); // TextLineParam->SetTextItemArr(DynamicArray); Stamp->ksColumnNumber(ksStMaterial); Stamp->ksTextLine(TextLineParam); // Stamp->ksCloseStamp(); For simplicity, this example omits the code responsible for connecting to KOMPAS, creating and executing a document, and freeing up resources (these issues were discussed in previous articles of the cycle). The figure below shows the title block formed by this program.

Pay attention to a few points.
1. In the example, we get the ksDynamicArray interface from the KompasObject interface. But nothing prevents us from getting it from the ksTextLineParam interface. Moreover, if the ksDynamicArray interface were obtained by the GetTextItemArray () method, we could not call the SetTextItemArray method, since the array would already be associated with the ksTextLineParam interface.
2. To denote cell numbers, we use the constants ksStPartNumber and ksStMaterial . These constants are entered by KOMPAS for the most frequently used cells. You can get acquainted with them in the section “Parameters Structures and Constants / Constants / Constants of Design Objects / ksStampEnum - Stamp Cell Identifiers” of the COMPASS documentation.
3. To write lines to the main label, we use the ksTextLine method of the ksStamp interface. The same method was used in the fourth part of the loop, where we looked at the ksTextItemParam interface. This method as a parameter can take both the ksTextLineParam interface and the simpler ksTextItemParam .
4. Two lines are entered in the title block. The first line is simple and consists of only one component. The second line consists of three components. In the figure below, they are separated by vertical red lines. In principle, the last two components could be combined into one. But I specifically used three components to more clearly show the principle of operation of the interface ksTextLineParam .
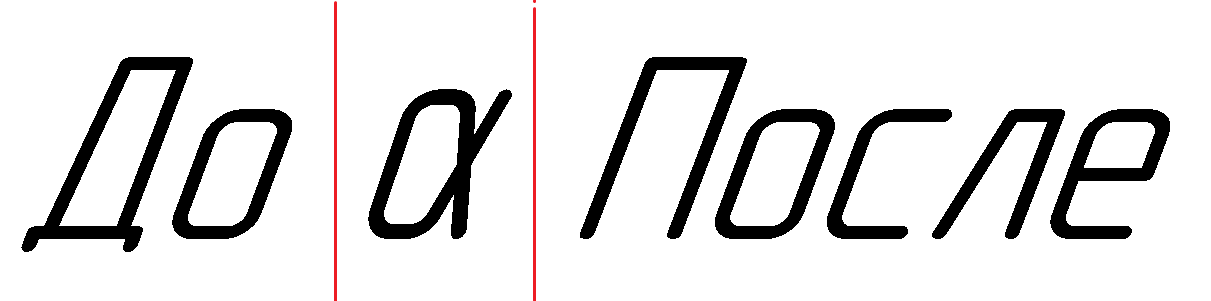
KsSetStampColumnText Method
The ksSetStampColumnText method of the ksStamp interface sets the text in the specified cell of the title block . Below is a prototype of this method.
long ksSetStampColumnText ( long numb, // LPDISPATCH textArr // ); The text to be set is specified as a dynamic ksDynamicArray array. If successful, the ksSetStampColumnText method returns the value 1 , and in the case of an error, it returns zero .
Note, the ksSetStampColumnText method is used only in the main text editing mode. That is, after calling the ksOpenStamp () method, but before calling the ksCloseStamp () method of the ksStamp interface.
The textArr array is of type TEXT_LINE_ARR ( 3 ). This means that the elements of the array are the ksTextLineParam interfaces, each of which also contains a dynamic array, but already of the ksTextItemParam interfaces. The figure below shows the structure of the textArr parameter.

Although in the figure above the number of array elements is three, in reality it can be anything. If the textArr array consists of several elements, then all ksTextLineParam strings are glued together and displayed in the numb cell.
Example 2
The following is an example of a program that demonstrates how to fill a title block using the ksSetStampColumnText method.
// TextItemParamPtr TextItemParam; TextItemParam = (TextItemParamPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_TextItemParam); TextLineParamPtr TextLineParam; TextLineParam = (TextLineParamPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_TextLineParam); // ksTextItemParam DynamicArrayPtr DynamicArrayItems; DynamicArrayItems = (DynamicArrayPtr)kompas->GetDynamicArray(TEXT_ITEM_ARR); DynamicArrayItems->ksClearArray(); // ksTextLineParam DynamicArrayPtr DynamicArrayLines; DynamicArrayLines = (DynamicArrayPtr)kompas->GetDynamicArray(TEXT_LINE_ARR); DynamicArrayLines->ksClearArray(); // StampPtr Stamp; Stamp = (StampPtr)Document2D->GetStamp(); // Stamp->ksOpenStamp(); // TextItemParam->set_s(SysAllocString(L"")); DynamicArrayItems->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextItemParam); TextLineParam->SetTextItemArr(DynamicArrayItems); // DynamicArrayLines->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextLineParam); // Stamp->ksSetStampColumnText(ksStPartNumber, DynamicArrayLines); // DynamicArrayLines->ksClearArray(); DynamicArrayItems->ksClearArray(); // TextItemParam->set_s(SysAllocString(L" ")); DynamicArrayItems->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextItemParam); // TextItemParam->Init(); TextItemParam->set_type(SPECIAL_SYMBOL); TextItemParam->set_iSNumb(51); DynamicArrayItems->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextItemParam); // TextItemParam->set_type(0); TextItemParam->set_s(SysAllocString(L" ")); DynamicArrayItems->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextItemParam); // TextLineParam->SetTextItemArr(DynamicArrayItems); DynamicArrayLines->ksAddArrayItem(-1, TextLineParam); // Stamp->ksSetStampColumnText(ksStMaterial, DynamicArrayLines); // Stamp->ksCloseStamp(); The result of this program is similar to the result of the previous example.
Note: since the number of the cell to which the string is written is already transferred to the ksSetStampColumnText method, it is not necessary to call the ksColumnNumber method.
Conclusion
We looked at three ways to write rows to cells in the title block : based on the ksTextItemParam interface ( covered in part 4 of the article series ), based on the ksTextLineParam interface , and using the ksSetStampColumnText method.
The first way is the easiest. It does not require working with dynamic arrays. It is ideal for writing strings. With it, you can also form complex strings. Control characters are used for this, which will be discussed in the next articles of the cycle.
The second method (the ksTextLineParam interface) is not much more complicated than the first. The ksTextLineParam interface is also used in the third method. Therefore, it must be understood in order to understand the third method.
The third method (the ksSetStampColumnText method) is the most difficult to implement. Its only real advantage over the first two methods is that there is no need to call the ksColumnNumber method. However, the approach used in this method is used when reading the contents of the cells of the inscription (about this in the next article of the cycle).
You can use any of these methods. Personally, I usually use the first one.
To be continued, stay tuned to the blog.
 Sergey Norseev, author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”.
Sergey Norseev, author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”.Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/350516/
All Articles