Using the KOMPAS-3D API → Lesson 7 → Getting to know the settings
We continue the cycle of articles on working with the CAD API KOMPAS-3D Sergey Norseev, an engineer-programmer of the All-Russian Scientific-Research Institute “Signal”, the author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”. C ++ Builder is used as the medium. In this lesson we will talk about the KOMPAS system settings.

To read the settings, use the KompasObject interface's ksGetSysOptions method . Below is its prototype.
The optionsType parameter contains an integer specifying which setting we want to receive. The param parameter is a pointer to the interface in which the requested setting will be written. The type of this interface depends on the setting we requested. The correspondence between the optionsType and param parameters is given in the table below.
')
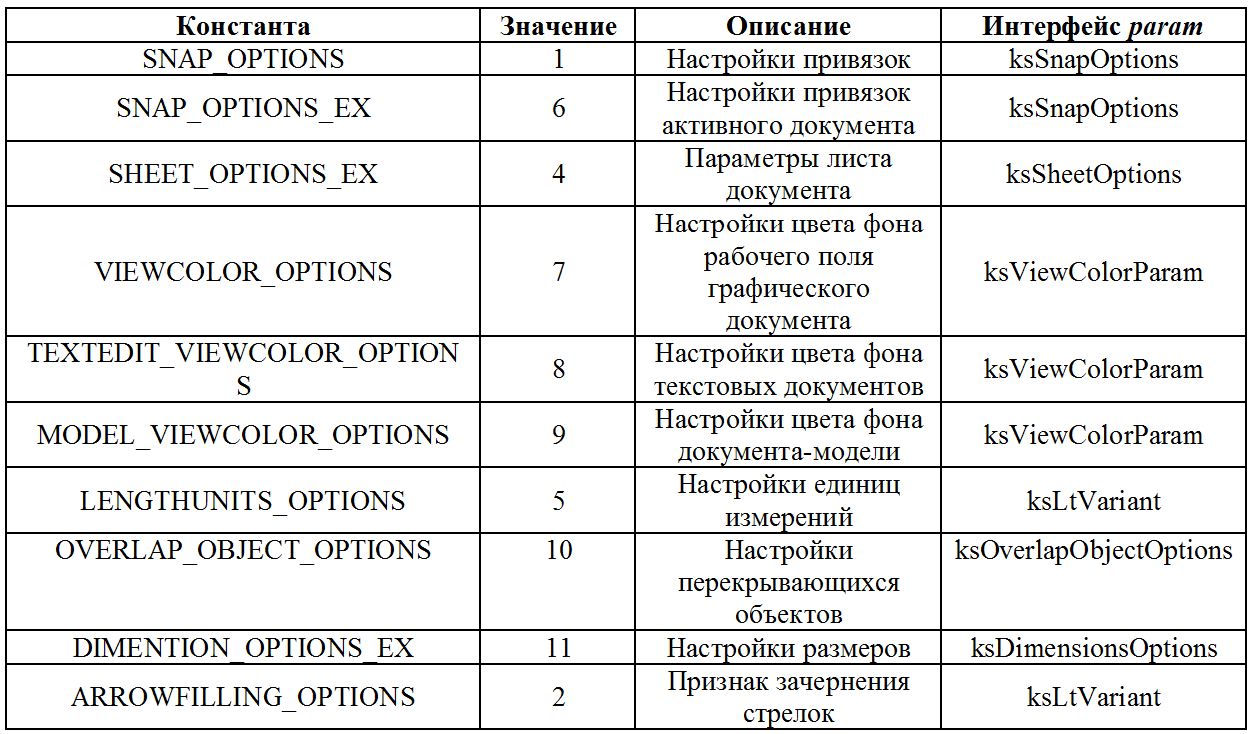
Table 1. Correspondence between optionsType and param parameters
These constants are declared in the ldefin2d.h file.
If successful, the ksGetSysOptions method returns the value 1 , and in case of error, the value zero .
In a number of places in the KOMPAS documentation, it is indicated that the ksGetSysOptions method allows you to get this or that interface. However, it is not. This method allows you to fill the interface, but not get it. You must get the interface yourself using the KompasObject interface's GetParamStruct method . If a failed interface is passed to the ksGetSysOptions method, the method will return zero (error).
Looking at Table 1, one can unwittingly assume that to get the SNAP_OPTIONS_EX setting , you must have an active document, and to get the SNAP_OPTIONS setting , the document is not necessary. In fact, it is not. As shown by my experiments, if you do not have an active document, the ksGetSysOptions method returns a value of zero (error) for SNAP_OPTIONS , and not for SNAP_OPTIONS_EX . An error message is displayed.
Error message
Please also note that if you encounter the error described above, then you may need to restart KOMPAS to correct it. The fact is that all subsequent calls to the ksGetSysOptions method, even if there is an active document, will fail.
Briefly consider the interface ksSnapOptions . His properties:
angSnap - whether the “snap” snap is on ( true - on, false - off);
angleStep - angle pitch ( in degrees );
commonOpt - set of flags of common bindings (we will not consider);
grid — whether gridding is enabled ( true — enabled, false — disabled);
intersect - if the “intersection” binding is enabled ( true - enabled, false - disabled);
localSnap - type of local binding;
nearestMiddle - whether the midpoint binding is on ( true - on, false - off);
nearestPoint — whether the “nearest point” snap is on ( true — on, false — off);
pointOnCurve - whether the “point on curve” snap is on ( true - on, false - off);
tangentToCurve - whether the “touch” binding is enabled ( true - enabled, false - disabled);
xyAlign - whether the alignment binding is on ( true - on, false - off).
There are only three methods for the ksSnapOptions interface:
Init () - resets all properties, if successful returns true ;
GetCommonOptValue and SetCommonOptValue are designed to work with the commonOpt property.
Below is an example of a program that demonstrates how to work with the ksSnapOptions interface.
In this example, we define the angle pitch. For example, on my home computer it was 45 ° (you may have another). Note that this is an extremely simplified example. It does not implement a correct connection to KOMPAS and error handling is omitted.
Sheet parameters in the context of settings are described by the ksSheetOptions interface. This interface is similar to the ksSheetPar interface, which we discussed in the second part of this series of articles. Consider the properties of the interface ksSheetOptions .
layoutName is the path to the layout library.
sheetType - sheet type ( true - custom format, false - standard sheet);
shtType - the type of the title block from the layoutName library.
The layoutName and shtType properties are similar to those of the ksSheetPar interface with the same name.
There are only two methods for the ksSheetOptions interface:
GetSheetParam - returns the sheet parameters interface ( ksStandartSheet for standard sheets and ksSheetSize for non-standard sheets). As a single parameter, it accepts a sheet format attribute ( true — non-standard sheet, false — standard sheet). Note that the parameter value must match the value of the sheetType property. This duplication of information remained because of the need for compatibility with some old libraries.
Init () - resets the values of all interface properties.
The following is an example of using this interface to define a sheet format.
This example defines the parameters of a document sheet. If it has a non-standard size, then the line “Non-standard sheet” is displayed. If it has a standard format, then a number indicating the format is displayed on the screen. For example, on my home computer the number 4 is displayed, which sets an A4 sheet (it may differ from you).
You probably noticed that the example does not create any document. A reasonable question arises: the format of the sheet of which document we define in the program, if there is no document? The example defines the format of the new document by default.
The KOMPAS documentation also mentions the SHEET_OPTIONS ( 3 ) constant as an analogue of the SHEET_OPTIONS_EX constant. However, the SHEET_OPTIONS constant is deprecated and left for compatibility with some older libraries.
Background colors are described by the ksViewColorParam interface. Consider the properties of this interface.
BottomColor - lower transition color, available only for document models.
Color - background color. If the value of this property is -1 , the window color set in the Windows system is used.
TopColor - top color transition, available only for model documents.
UseGradient - sign of using gradient transition ( true - used, false - not used).
Although the KOMPAS API documentation does not explicitly state which color format is used, like in KOMPAS itself, the RGB format is used in the API.
There is only one method for the ksViewColorParam interface.
Init () - reset values of all interface properties. Returns true if successful.
The following is an example of using this interface.
This example determines the background color of the working area of the document and displays it as components of red, green, and blue.
A variant is a variable storing a value of some type. KOMPAS implements options using the ksLtVariant interface. It has a lot of properties and it is most convenient to consider them relative to the main property - valType . This property specifies the type of value stored in the variant. Valid values for this property, as well as other properties for the ksLtVariant interface, are shown in the table below.
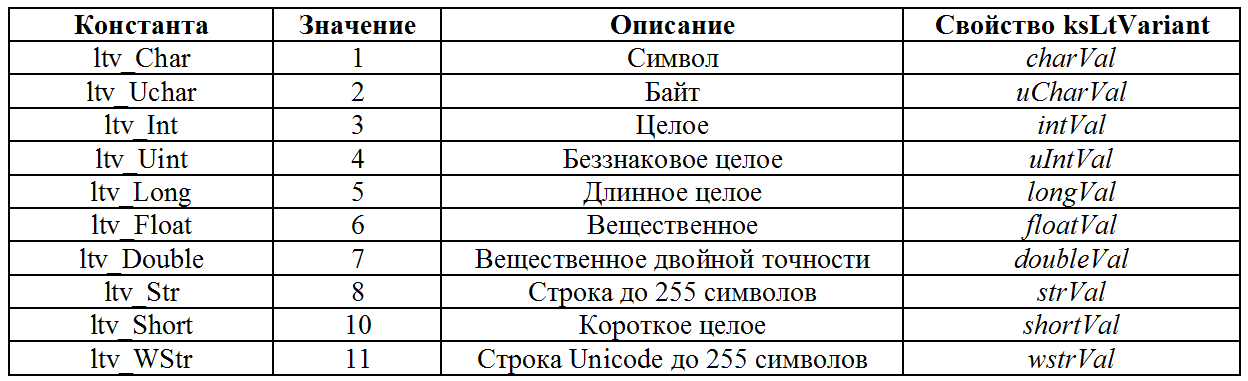
Table 2. ksLtVariant interface properties
These constants are declared in the ldefin2d.h file.
For example, if the value of the valType property is ltv_Uint , then the value stored in the variant is in the uIntVal property. If the value of the valType property is ltv_Double , then the value stored in the variant is in the doubleVal property.
There is only one method for the ksLtVariant interface.
Init () - resets the values of all interface properties. Returns true if successful.
According to Table 1, the unit settings are requested using the LENGTHUNITS_OPTIONS constant. In this case, the ksGetSysOptions method fills in the ksLtVariant variant of the ltv_Short type. One of the valid values shown in the table below is recorded in the variant.
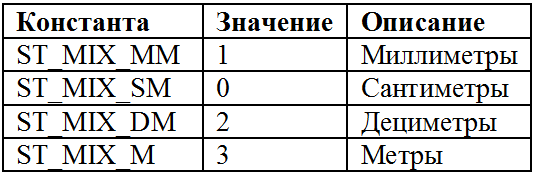
Table 3. Valid ksLtVariant values of type ltv_Short
These constants are declared in the ldefin2d.h file.
Note that the decimeter unit is not supported.
The following is an example of a program that demonstrates unit definitions.
This program determines the current unit of measurement and displays it on the screen.
In this example, we do not check the type of the variant, relying on the fact that it is of type ltv_Short . I did this to simplify the example. In real-world applications, you should always check the type of the variant.
To change the settings, use the KompasObject interface's ksSetSysOptions method . Below is a prototype of this method.
It is easy to see that the prototype of this method is similar to the prototype of the ksGetSysOptions method. The relationship between the type of setting and the interface describing it is also determined by table 1. If successful, the ksSetSysOptions method returns the value 1 , and in the case of an error, it returns zero .
Note that the modified settings "exist" only during the current KOMPAS session. After it is restarted, all settings will return to their original value.
Below is an example of a program that demonstrates changing the background color of a document using the ksSetSysOptions method.
In this example, we set the background color to green.
Note: KOMPAS is made visible almost immediately, before changing the settings. If KOMPAS is made visible after changing a setting, it will not be changed, although the ksSetSysOptions method returns 1 .
Unfortunately, the ksSetSysOptions method does not allow changing the format of a document sheet.
The ksDocument2D interface contains the ksGetDocOptions and ksSetDocOptions methods that are analogous to the ksGetSysOptions and ksSetSysOptions methods of the KompasObject interface. All these methods have the same prototype and allow you to read (change) any setting. The difference is that the methods of the ksDocument2D interface return (change) the settings of not the entire system, but only one document.
The KompasObject interface also contains the ksGetDocOptions and ksSetDocOptions methods . They are similar to the ksDocument2D interface methods of the same name and return (change) the settings of the current document.
The ksGetDocOptions method (of both interfaces) has one (undocumented) difference from the ksGetSysOptions method. It handles the SHEET_OPTIONS_EX setting somewhat differently. If the ksGetSysOptions method always returns a one if successful, then this is not the case for the ksGetDocOptions method. The value returned by it depends on the type of document (standard or not). If successful, it returns the value lt_DocSheetStandart ( 1 ) for a standard document and lt_DocSheetUser ( 2 ) for a non-standard document.
Note that in the case of multi-sheet documents, the ksGetDocOptions methods return the SHEET_OPTIONS_EX settings for the first sheet of the document only. It is impossible to determine the format of subsequent sheets using APIs version 5. For this you need to use API interfaces 7 versions.
The ksSetDocOptions method (of both interfaces) as well as the ksSetDocOptions method does not allow changing the document format.
Conclusion
In this article, we met with the properties. Unfortunately, it’s impossible to describe them all in detail in one article. We did not consider in particular the settings of overlapping objects and the size settings, but they are not very complex.
To be continued, stay tuned to the blog.
 Sergey Norseev, author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”.
Sergey Norseev, author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”.

Content of the cycle of lessons “Working with the API KOMPAS-3D”
1. Basics
2. Design drawing
3. Correct connection to COMPAS
4. Title Block
5. Graphic primitives
6. Saving a document in various formats
7. Getting to know the settings
8. More complex methods of writing to the main title
Read settings
To read the settings, use the KompasObject interface's ksGetSysOptions method . Below is its prototype.
long ksGetSysOptions ( long optionsType, // LPDISPATCH param // ); The optionsType parameter contains an integer specifying which setting we want to receive. The param parameter is a pointer to the interface in which the requested setting will be written. The type of this interface depends on the setting we requested. The correspondence between the optionsType and param parameters is given in the table below.
')

Table 1. Correspondence between optionsType and param parameters
These constants are declared in the ldefin2d.h file.
If successful, the ksGetSysOptions method returns the value 1 , and in case of error, the value zero .
In a number of places in the KOMPAS documentation, it is indicated that the ksGetSysOptions method allows you to get this or that interface. However, it is not. This method allows you to fill the interface, but not get it. You must get the interface yourself using the KompasObject interface's GetParamStruct method . If a failed interface is passed to the ksGetSysOptions method, the method will return zero (error).
Bindings Settings
Looking at Table 1, one can unwittingly assume that to get the SNAP_OPTIONS_EX setting , you must have an active document, and to get the SNAP_OPTIONS setting , the document is not necessary. In fact, it is not. As shown by my experiments, if you do not have an active document, the ksGetSysOptions method returns a value of zero (error) for SNAP_OPTIONS , and not for SNAP_OPTIONS_EX . An error message is displayed.

Error message
Please also note that if you encounter the error described above, then you may need to restart KOMPAS to correct it. The fact is that all subsequent calls to the ksGetSysOptions method, even if there is an active document, will fail.
Briefly consider the interface ksSnapOptions . His properties:
angSnap - whether the “snap” snap is on ( true - on, false - off);
angleStep - angle pitch ( in degrees );
commonOpt - set of flags of common bindings (we will not consider);
grid — whether gridding is enabled ( true — enabled, false — disabled);
intersect - if the “intersection” binding is enabled ( true - enabled, false - disabled);
localSnap - type of local binding;
nearestMiddle - whether the midpoint binding is on ( true - on, false - off);
nearestPoint — whether the “nearest point” snap is on ( true — on, false — off);
pointOnCurve - whether the “point on curve” snap is on ( true - on, false - off);
tangentToCurve - whether the “touch” binding is enabled ( true - enabled, false - disabled);
xyAlign - whether the alignment binding is on ( true - on, false - off).
There are only three methods for the ksSnapOptions interface:
Init () - resets all properties, if successful returns true ;
GetCommonOptValue and SetCommonOptValue are designed to work with the commonOpt property.
Below is an example of a program that demonstrates how to work with the ksSnapOptions interface.
// KompasObjectPtr kompas; kompas.CreateInstance(L"KOMPAS.Application.5"); // DocumentParamPtr DocumentParam; DocumentParam=(DocumentParamPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_DocumentParam); DocumentParam->Init(); DocumentParam->type= lt_DocSheetStandart;// // Document2DPtr Document2D; Document2D = (Document2DPtr)kompas->Document2D(); Document2D->ksCreateDocument(DocumentParam); // ksSnapOptionsPtr SnapOptions; SnapOptions = (ksSnapOptionsPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_SnapOptions); kompas->ksGetSysOptions(SNAP_OPTIONS, SnapOptions); ShowMessage(FloatToStr(SnapOptions->get_angleStep())); // DocumentParam.Unbind(); Document2D.Unbind(); SnapOptions.Unbind(); kompas->set_Visible(true); kompas.Unbind(); In this example, we define the angle pitch. For example, on my home computer it was 45 ° (you may have another). Note that this is an extremely simplified example. It does not implement a correct connection to KOMPAS and error handling is omitted.
Sheet options
Sheet parameters in the context of settings are described by the ksSheetOptions interface. This interface is similar to the ksSheetPar interface, which we discussed in the second part of this series of articles. Consider the properties of the interface ksSheetOptions .
layoutName is the path to the layout library.
sheetType - sheet type ( true - custom format, false - standard sheet);
shtType - the type of the title block from the layoutName library.
The layoutName and shtType properties are similar to those of the ksSheetPar interface with the same name.
There are only two methods for the ksSheetOptions interface:
GetSheetParam - returns the sheet parameters interface ( ksStandartSheet for standard sheets and ksSheetSize for non-standard sheets). As a single parameter, it accepts a sheet format attribute ( true — non-standard sheet, false — standard sheet). Note that the parameter value must match the value of the sheetType property. This duplication of information remained because of the need for compatibility with some old libraries.
Init () - resets the values of all interface properties.
The following is an example of using this interface to define a sheet format.
// KompasObjectPtr kompas; kompas.CreateInstance(L"KOMPAS.Application.5"); // SheetOptionsPtr SheetOptions; SheetOptions = (ksSheetOptionsPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_SheetOptions); // kompas->ksGetSysOptions(SHEET_OPTIONS_EX, SheetOptions); if(SheetOptions->get_sheetType()) ShowMessage(" "); else { // ksStandartSheetPtr StandartSheet; StandartSheet = (ksStandartSheetPtr)SheetOptions->GetSheetParam(false); ShowMessage(IntToStr(StandartSheet->get_format())); StandartSheet.Unbind(); } // SheetOptions.Unbind(); kompas->set_Visible(true); kompas.Unbind(); This example defines the parameters of a document sheet. If it has a non-standard size, then the line “Non-standard sheet” is displayed. If it has a standard format, then a number indicating the format is displayed on the screen. For example, on my home computer the number 4 is displayed, which sets an A4 sheet (it may differ from you).
You probably noticed that the example does not create any document. A reasonable question arises: the format of the sheet of which document we define in the program, if there is no document? The example defines the format of the new document by default.
The KOMPAS documentation also mentions the SHEET_OPTIONS ( 3 ) constant as an analogue of the SHEET_OPTIONS_EX constant. However, the SHEET_OPTIONS constant is deprecated and left for compatibility with some older libraries.
Background colors
Background colors are described by the ksViewColorParam interface. Consider the properties of this interface.
BottomColor - lower transition color, available only for document models.
Color - background color. If the value of this property is -1 , the window color set in the Windows system is used.
TopColor - top color transition, available only for model documents.
UseGradient - sign of using gradient transition ( true - used, false - not used).
Although the KOMPAS API documentation does not explicitly state which color format is used, like in KOMPAS itself, the RGB format is used in the API.
There is only one method for the ksViewColorParam interface.
Init () - reset values of all interface properties. Returns true if successful.
The following is an example of using this interface.
// KompasObjectPtr kompas; kompas.CreateInstance(L"KOMPAS.Application.5"); // ksViewColorParamPtr ViewColor; ViewColor = (ksViewColorParamPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_ViewColorParam); kompas->ksGetSysOptions(VIEWCOLOR_OPTIONS, ViewColor); DWORD color; color = ViewColor->get_color(); AnsiString str; str = "(0x"+IntToHex(GetRValue(color),2) + ";0x"+IntToHex(GetGValue(color),2) + ";0x"+IntToHex(GetBValue(color),2) + ")"; ShowMessage(str); // ViewColor.Unbind(); kompas->set_Visible(true); kompas.Unbind(); This example determines the background color of the working area of the document and displays it as components of red, green, and blue.
Data Type Option
A variant is a variable storing a value of some type. KOMPAS implements options using the ksLtVariant interface. It has a lot of properties and it is most convenient to consider them relative to the main property - valType . This property specifies the type of value stored in the variant. Valid values for this property, as well as other properties for the ksLtVariant interface, are shown in the table below.

Table 2. ksLtVariant interface properties
These constants are declared in the ldefin2d.h file.
For example, if the value of the valType property is ltv_Uint , then the value stored in the variant is in the uIntVal property. If the value of the valType property is ltv_Double , then the value stored in the variant is in the doubleVal property.
There is only one method for the ksLtVariant interface.
Init () - resets the values of all interface properties. Returns true if successful.
Unit Settings
According to Table 1, the unit settings are requested using the LENGTHUNITS_OPTIONS constant. In this case, the ksGetSysOptions method fills in the ksLtVariant variant of the ltv_Short type. One of the valid values shown in the table below is recorded in the variant.

Table 3. Valid ksLtVariant values of type ltv_Short
These constants are declared in the ldefin2d.h file.
Note that the decimeter unit is not supported.
The following is an example of a program that demonstrates unit definitions.
// KompasObjectPtr kompas; kompas.CreateInstance(L"KOMPAS.Application.5"); // ksLtVariantPtr Variant; Variant = (ksLtVariantPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_LtVariant); kompas->ksGetSysOptions(LENGTHUNITS_OPTIONS, Variant); AnsiString str; switch(Variant->get_shortVal()) { case ST_MIX_MM: str = ""; break; case ST_MIX_SM: str = ""; break; case ST_MIX_DM: str = "" ; break; case ST_MIX_M : str = "" ; break; default: str = ""; } ShowMessage(str); // Variant.Unbind(); kompas->set_Visible(true); kompas.Unbind(); This program determines the current unit of measurement and displays it on the screen.
In this example, we do not check the type of the variant, relying on the fact that it is of type ltv_Short . I did this to simplify the example. In real-world applications, you should always check the type of the variant.
Change settings
To change the settings, use the KompasObject interface's ksSetSysOptions method . Below is a prototype of this method.
long ksSetSysOptions ( long optionsType, // LPDISPATCH param // ); It is easy to see that the prototype of this method is similar to the prototype of the ksGetSysOptions method. The relationship between the type of setting and the interface describing it is also determined by table 1. If successful, the ksSetSysOptions method returns the value 1 , and in the case of an error, it returns zero .
Note that the modified settings "exist" only during the current KOMPAS session. After it is restarted, all settings will return to their original value.
Below is an example of a program that demonstrates changing the background color of a document using the ksSetSysOptions method.
// KompasObjectPtr kompas; kompas.CreateInstance(L"KOMPAS.Application.5"); // kompas->set_Visible(true); // DocumentParamPtr DocumentParam; DocumentParam=(DocumentParamPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_DocumentParam); DocumentParam->Init(); DocumentParam->type= lt_DocSheetStandart;// // Document2DPtr Document2D; Document2D = (Document2DPtr)kompas->Document2D(); Document2D->ksCreateDocument(DocumentParam); // ViewColorParamPtr ViewColorParam; ViewColorParam = (ViewColorParamPtr)kompas->GetParamStruct(ko_ViewColorParam); ViewColorParam->set_color(RGB(0,0xFF,0)); // kompas->ksSetSysOptions(VIEWCOLOR_OPTIONS, ViewColorParam); // ViewColorParam.Unbind(); DocumentParam.Unbind(); Document2D.Unbind(); kompas.Unbind(); In this example, we set the background color to green.
Note: KOMPAS is made visible almost immediately, before changing the settings. If KOMPAS is made visible after changing a setting, it will not be changed, although the ksSetSysOptions method returns 1 .
Unfortunately, the ksSetSysOptions method does not allow changing the format of a document sheet.
The ksGetDocOptions and ksSetDocOptions methods
The ksDocument2D interface contains the ksGetDocOptions and ksSetDocOptions methods that are analogous to the ksGetSysOptions and ksSetSysOptions methods of the KompasObject interface. All these methods have the same prototype and allow you to read (change) any setting. The difference is that the methods of the ksDocument2D interface return (change) the settings of not the entire system, but only one document.
The KompasObject interface also contains the ksGetDocOptions and ksSetDocOptions methods . They are similar to the ksDocument2D interface methods of the same name and return (change) the settings of the current document.
The ksGetDocOptions method (of both interfaces) has one (undocumented) difference from the ksGetSysOptions method. It handles the SHEET_OPTIONS_EX setting somewhat differently. If the ksGetSysOptions method always returns a one if successful, then this is not the case for the ksGetDocOptions method. The value returned by it depends on the type of document (standard or not). If successful, it returns the value lt_DocSheetStandart ( 1 ) for a standard document and lt_DocSheetUser ( 2 ) for a non-standard document.
Note that in the case of multi-sheet documents, the ksGetDocOptions methods return the SHEET_OPTIONS_EX settings for the first sheet of the document only. It is impossible to determine the format of subsequent sheets using APIs version 5. For this you need to use API interfaces 7 versions.
The ksSetDocOptions method (of both interfaces) as well as the ksSetDocOptions method does not allow changing the document format.
Conclusion
In this article, we met with the properties. Unfortunately, it’s impossible to describe them all in detail in one article. We did not consider in particular the settings of overlapping objects and the size settings, but they are not very complex.
To be continued, stay tuned to the blog.
 Sergey Norseev, author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”.
Sergey Norseev, author of the book “Development of applications for KOMPAS in Delphi”.Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/350512/
All Articles