Proper bookmarking: how to work more efficiently and memorize more
When someone of my acquaintances opens a browser with me, I see a wall of hundreds of old and new bookmarks. Some of them are so old that during the time that has elapsed since the addition, favicons and page descriptions have changed several times. As a rule, the list goes on far down and hides somewhere below the HD screen, forcing you to forget about the hope of finding something.
At some point I was surprised why many users do not pay attention to the obvious advantages that the “bookmark system” gives, because it allows not only to work faster, but also to remember more (remember, the main function of bookmarks is to remember )!
This article is devoted to the basics of creating your own system of browser bookmarks and will be useful to anyone who works a lot with information and is interested in improving personal efficiency and reducing the information load.
')
The material was collected based on an analysis of the Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Opera, Yandex.Browser, Opera Mobile and Chrome Mobile browsers, which cost me more to check the layout of sites, but also allowed me to compare browser-based browsing capabilities on their own (I know that Yandex.Browser and Chrome are somewhere nearby, but I wanted to specifically clarify).
First we introduce a small glossary (in alphabetical order).
Association (eng. "Association") - a conceivable connection of one object with another for one reason or another.
Associative psychology - the direction of psychology, exploring the role of associations in the mental life of the individual.
Browser (English "browser") - a computer program for viewing web pages.
Bookmark (English “bookmark”) - a link to a web page saved in the browser by the user, as well as meta information about this link (nesting level, favicon, description, label).
Meta-information - information describing other, basic information.
Bookmarking system (English “bookmarks system”) - a set of bookmarks of an arbitrary number, stored in the browser according to user-defined principles.
Favicon (or "favicon"; the English. "Favicon") - a small image displayed in the browser next to the name of the site and its pages.
Let us examine each of the principles in turn.
This principle means that all bookmarks should be in folders. If part of the bookmarks is outside the category, it should be in a special folder of the “Without category” type.
Folders must have multiple levels. They may not be all equally important, there are always folders of the 1st level, 2nd level, 3rd level and so on.
It has already been said about the meta-information. This topic is raised due to the need to work on the visual presentation of your bookmarks system.
It would seem that there is a visual? There is a long list of inscriptions, and in the near future they are unlikely to think of anything new.
Many (if not most) browsers now contain visual bookmarks and are able to present information in the form of large icons, but this does not solve all the problems.
The design principle contains the following rules:
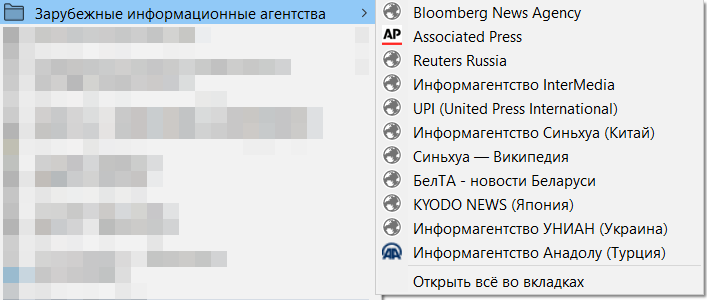
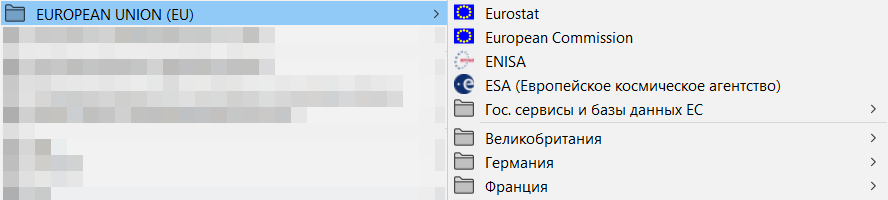
Many sites contain their own functions for storing favorites (this is true for Vkontakte, Yandex.Kartinok and Yandex.Music, YouTube, Habra, Picaba and many others), so if you frequently use these portals you must have separate accounts.
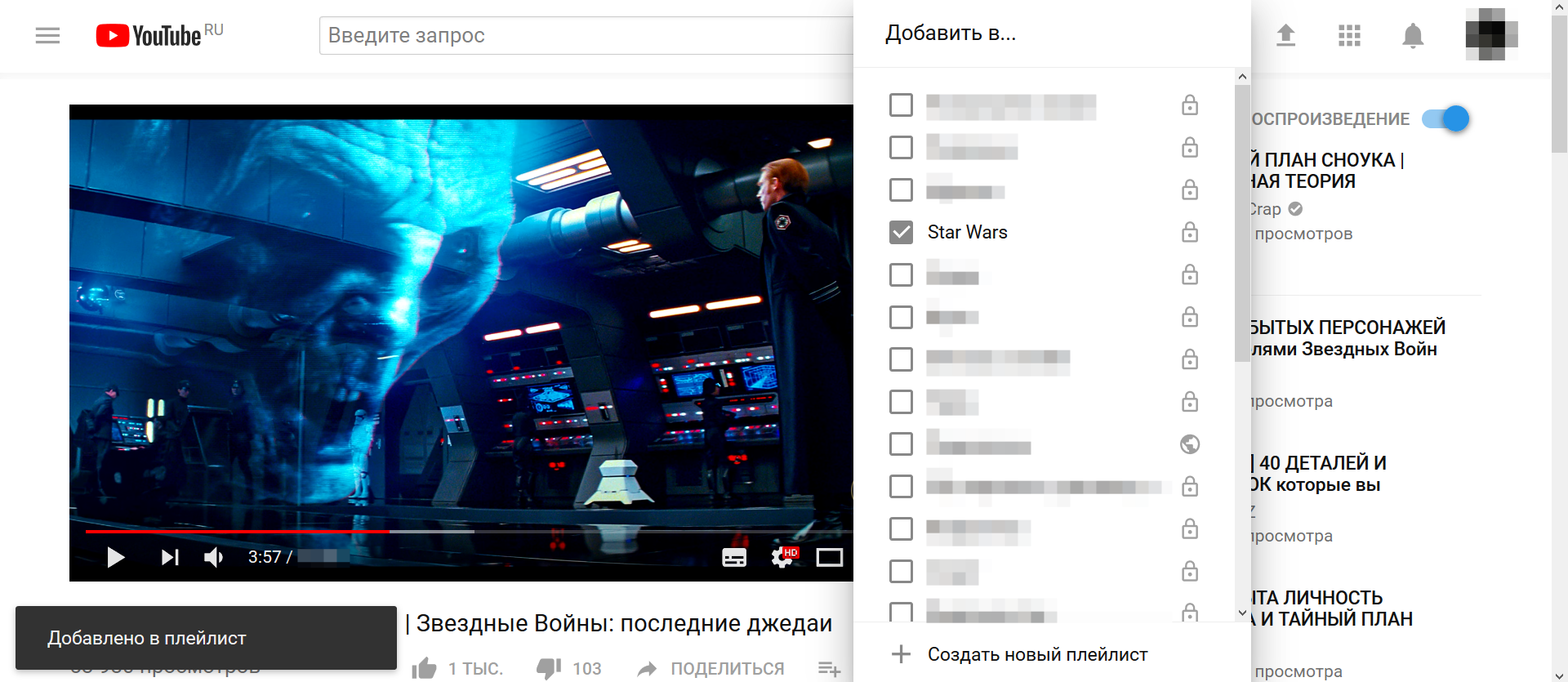
As a rule, the function of bookmarks (no matter how it is called: “watch later”, “I like”, “saved posts”) allows you to create folders or playlists. Accordingly, the browser bookmark system in this case is freed from storing tons of posts and videos (it only remains to add the tab to the sites themselves).
All browsers have one or more of the following bookmarking capabilities:
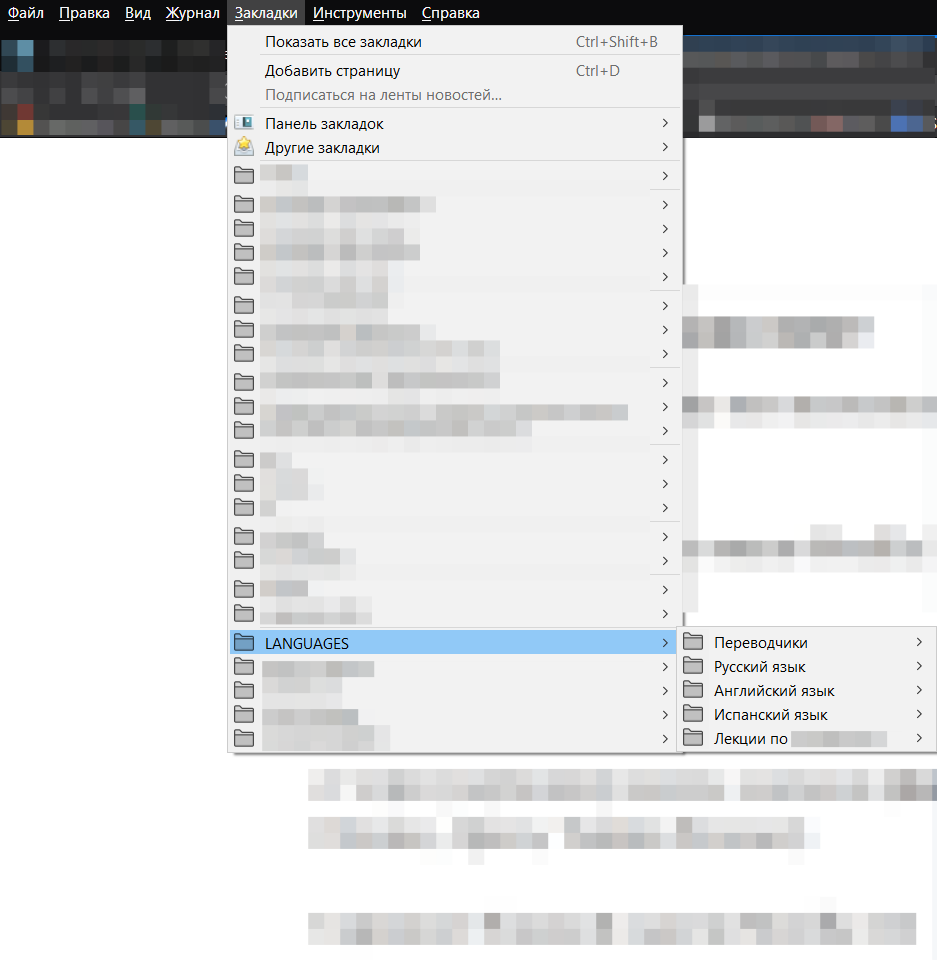

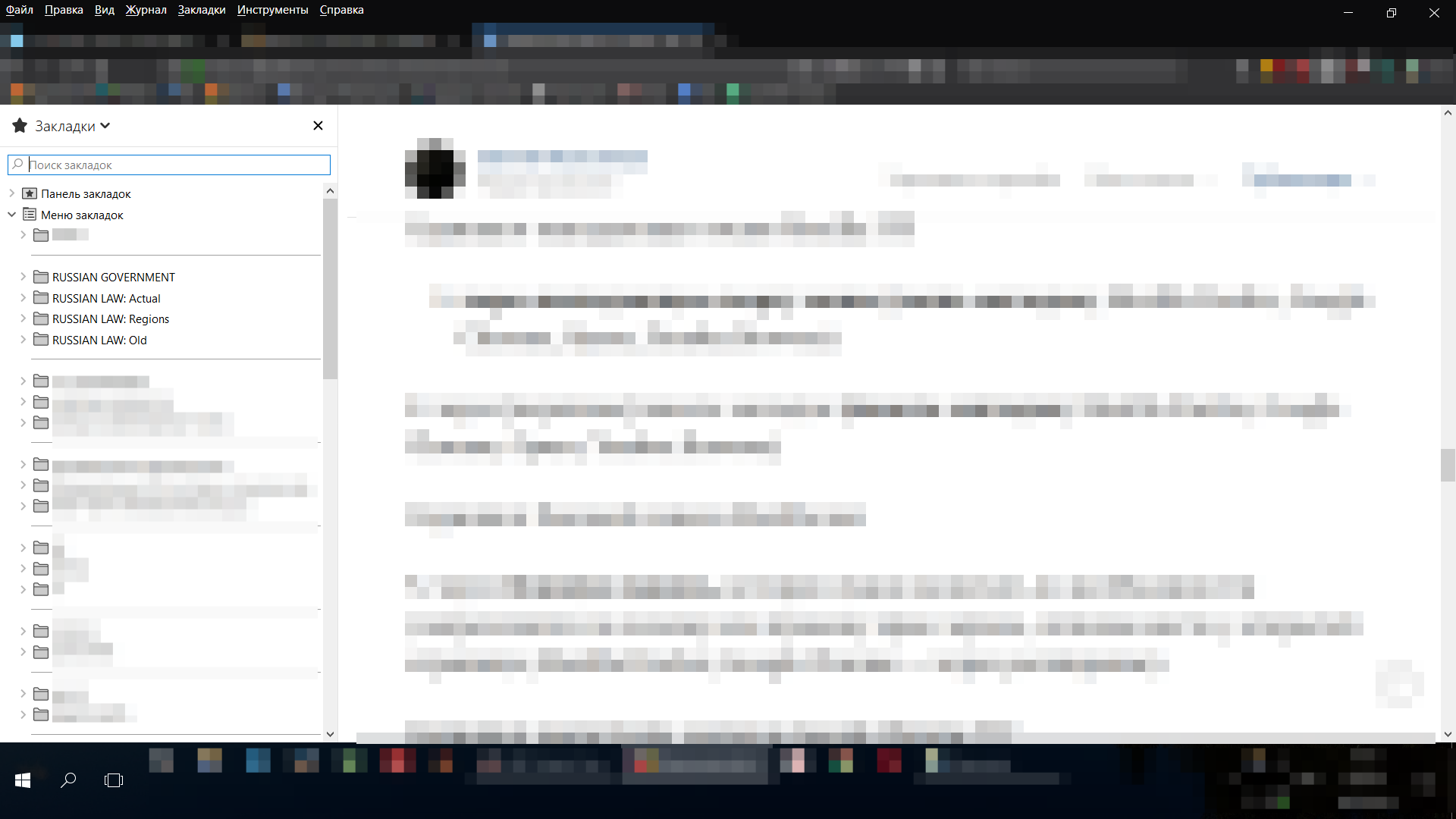


As you can see, the functionality practically does not differ from different manufacturers, with the exception of the side panel.
Working with the log / dispatcher and in the sidebar is convenient when you need to climb on large levels of nesting (beyond the 2nd), and also if the drop-down menu is not provided or made uncomfortable, for the remaining cases you can use the menu and [top] panel.

All browsers have the ability to search in the saved. This is another way to reduce work time and an additional reason to rename the keyword-saturated links.
You can back up 2 ways (well, as always) - either as a local file or in the cloud.
I’m not a fan of bookmark synchronization services (both built-in browsers and third-party browsers), because experience shows that at times synchronization does not go according to plan and something can be lost or duplicated. In any case, separate files scattered in different secluded places, make saving more reliable.
There is another reason: synchronization services to render in the form of large icons, which takes more pixels than necessary (although I do not agitate for 10pt fonts at all, but more than 5-10 bookmarks should be placed on the screen, otherwise we are all sliding to clip thinking).
Backups can and should be saved at least once a month, and then it would be nice to copy them somewhere else (definitely not on the desktop). At worst, they can be sent by email to your own email.
Bookmarks can usually be saved in .html format (depending on the browser; Firefox also allows you to save to .json).
Modern mobile browsers also allow you to organize a bookmark system. Although they are arranged differently, everywhere there is the possibility of categorization (it usually represents work not with folders, but with special forms that allow you to drag bookmarks to each other and thereby distinguish one category from another, as in the screenshot).

A big plus of mobile devices is that bookmarks can be dragged directly to the desktop.
Effective bookmarks work on the principles of associative psychology - you scatter links into folders that the brain considers categories. People think in categories (even if they don’t think about it), and categories (or, if you prefer, sets) include elements.
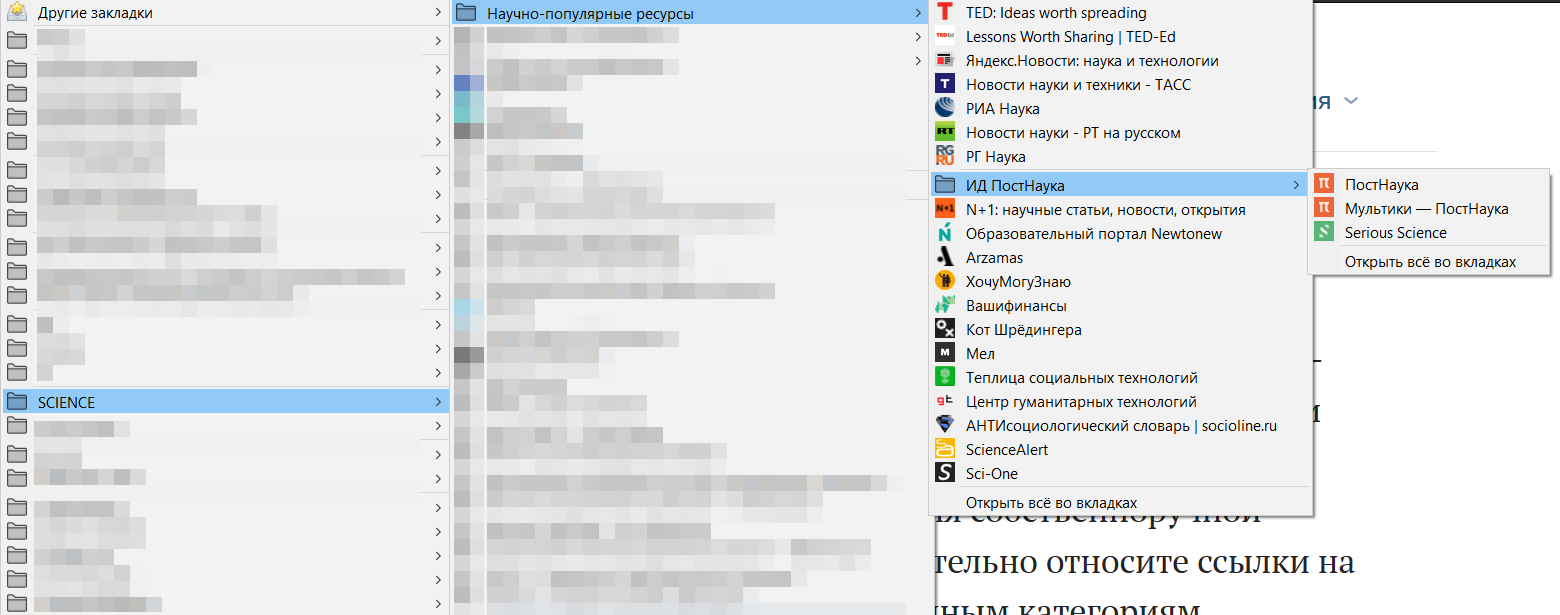
During the handwriting on the creation of a bookmark system, you unconsciously place links to web pages and meta-information about them to certain categories, categories to other categories, and as a result, a complete system with different levels is formed.
Firstly, when you click on the saved link in the address bar, an asterisk will be lit, which indicates that we have already visited this page (associations immediately pop up, when and for what).
Secondly, when we create a list with a certain number of elements, in fact everything can be translated into a plane of performance indicators (KPI).
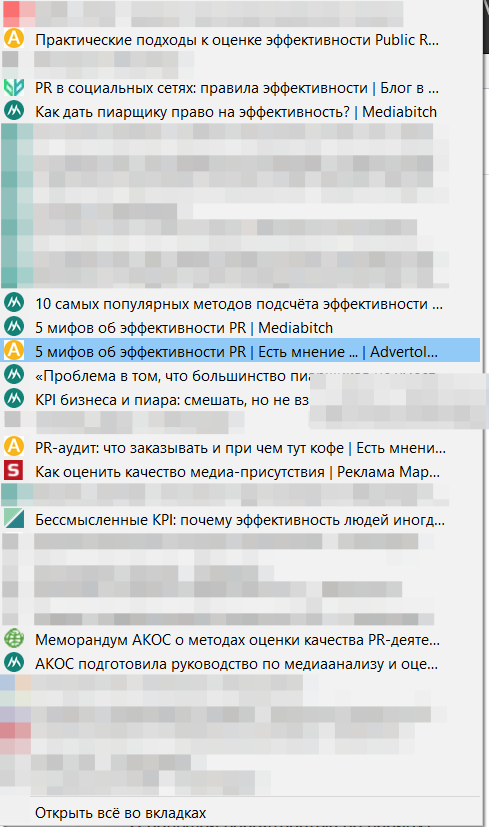
For example, you are preparing a scientific work and add all read articles and monographs to a separate folder (only after reading or knowing that the unread will soon be read accurately). In this case, the number of articles relevant to your work and read articles is one of the KPIs of your work (an example was taken from the ceiling, many others can be cited).
It is interesting sometimes to see how many bookmarks you have already saved (especially if the system has been running for years). To do this, you need to take a file with a backup of the bookmarks system and open it with a text editor (in this experiment I used Notepad ++).
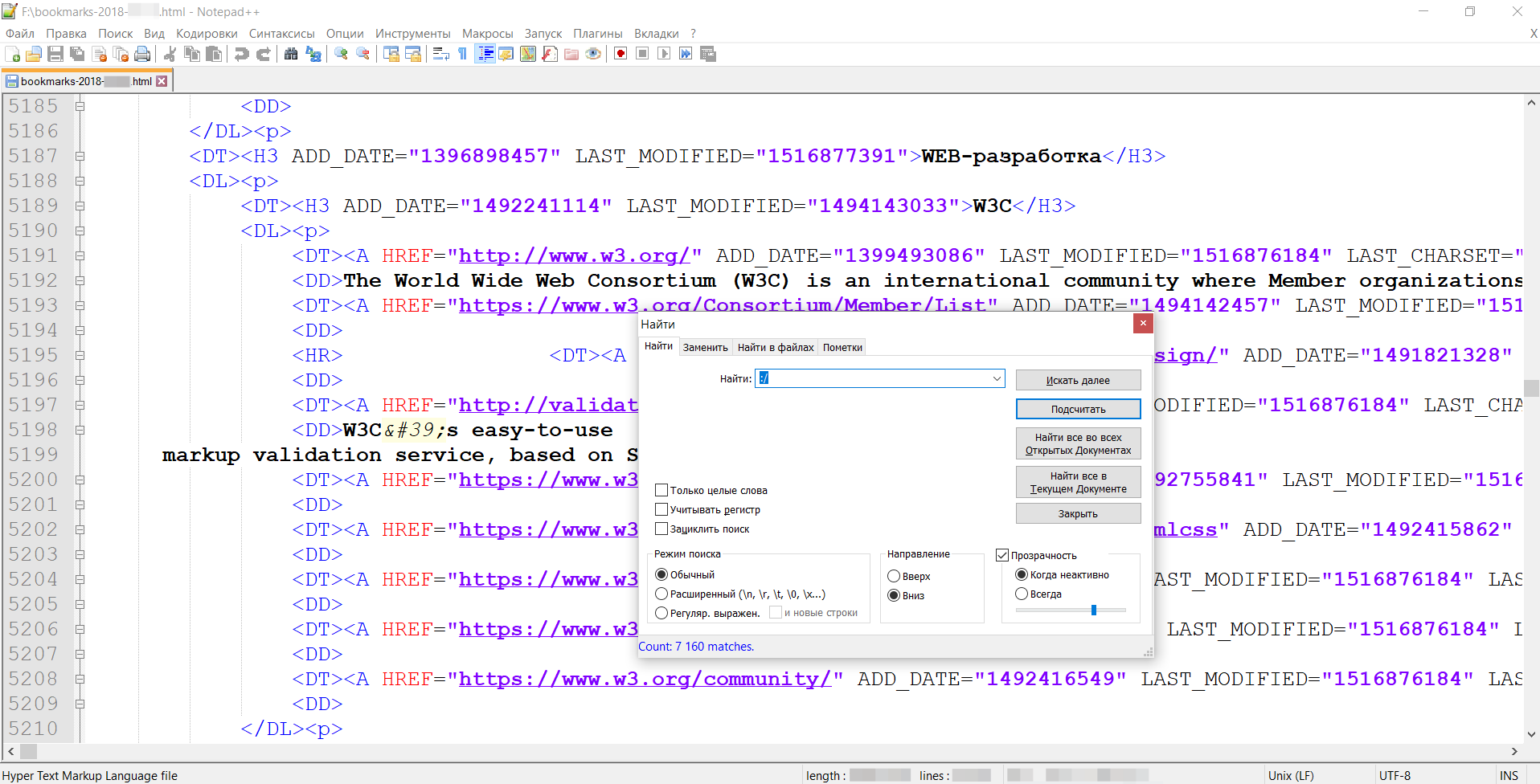
After opening, you will need to use the built-in search and count the number of mentions of the “http” or “: /” prefix (the number will indicate the number of saved links). By the way, the skill gives out more than 5 thousand. When comparing backups for different numbers there will be a positive trend.
Suppose you are working on a project in which you need to transfer a whole bookmark folder, without shining everything else.
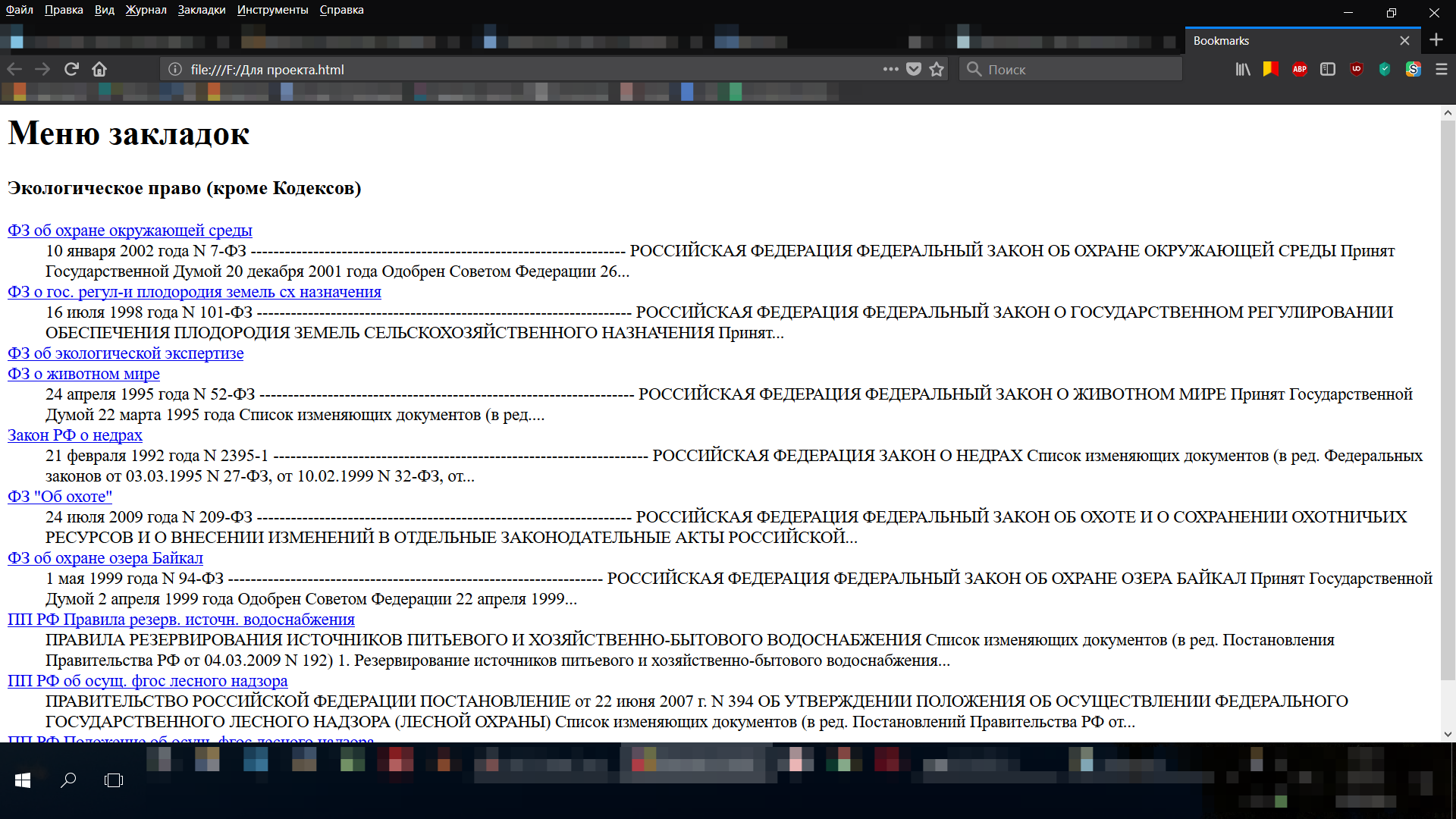
This can be easily achieved by making a backup of everything, and then opening Notepad ++ in the same folder and cutting out all other folders or inserting the necessary folder along with the sub-bookmarks into another file (for such purposes we have a search in the file).
I cite a few examples of online bookmark storage services. Suddenly, someone will access more browser-based ones.
And how do you work with bookmarks? Write below your ways of organizing digital memories (by the way, this is a new scientific direction for researching new media). Of course, many of these concerns about bookmarks will seem unnecessary, but here I would like to remind you that we are talking only about people who have to work with information not only a lot, but extremely much, and therefore their own "knowledge management systems" can not be avoided.
At some point I was surprised why many users do not pay attention to the obvious advantages that the “bookmark system” gives, because it allows not only to work faster, but also to remember more (remember, the main function of bookmarks is to remember )!
This article is devoted to the basics of creating your own system of browser bookmarks and will be useful to anyone who works a lot with information and is interested in improving personal efficiency and reducing the information load.
')
The material was collected based on an analysis of the Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Opera, Yandex.Browser, Opera Mobile and Chrome Mobile browsers, which cost me more to check the layout of sites, but also allowed me to compare browser-based browsing capabilities on their own (I know that Yandex.Browser and Chrome are somewhere nearby, but I wanted to specifically clarify).
Basic concepts
First we introduce a small glossary (in alphabetical order).
Association (eng. "Association") - a conceivable connection of one object with another for one reason or another.
Associative psychology - the direction of psychology, exploring the role of associations in the mental life of the individual.
Browser (English "browser") - a computer program for viewing web pages.
Bookmark (English “bookmark”) - a link to a web page saved in the browser by the user, as well as meta information about this link (nesting level, favicon, description, label).
Meta-information - information describing other, basic information.
Bookmarking system (English “bookmarks system”) - a set of bookmarks of an arbitrary number, stored in the browser according to user-defined principles.
Favicon (or "favicon"; the English. "Favicon") - a small image displayed in the browser next to the name of the site and its pages.
Basic principles
- Bookmarks must be classified.
- The bookmark system must have a design.
- In the bookmark system you need to implement other (child) bookmark systems.
- You can work with the bookmark system from several places (depending on the situation).
- You need to use the search for bookmarks.
- From time to time you need to make backups of bookmarks.
- Mobile devices must also have bookmarking systems.
Let us examine each of the principles in turn.
Bookmark classification
This principle means that all bookmarks should be in folders. If part of the bookmarks is outside the category, it should be in a special folder of the “Without category” type.
Folders must have multiple levels. They may not be all equally important, there are always folders of the 1st level, 2nd level, 3rd level and so on.
Bookmark Design
It has already been said about the meta-information. This topic is raised due to the need to work on the visual presentation of your bookmarks system.
It would seem that there is a visual? There is a long list of inscriptions, and in the near future they are unlikely to think of anything new.
Many (if not most) browsers now contain visual bookmarks and are able to present information in the form of large icons, but this does not solve all the problems.
The design principle contains the following rules:
- All bookmarks should have favicons (usually they are not found only in old bookmarks, if you transferred them from another operating system or if the information in the browser was completely erased). Graphic + text information is already multimedia, and therefore links with icons are easier to remember.

- If some of the links do not have favicons, it is better to go to these sites for at least 1 second (you can use the “batch approach” - a function like “open everything in new tabs”). The exception is the few sites that for some reason have no favicon at all.

- The most important thing should be in sight. The more important is on the list above, the less important is below. More authoritative resources and organizations are higher, less authoritative ones are lower. The organization itself is above the individual pages of your site and projects.
The most frequently used bookmarks should not be in the general menu, but on the panel below the address bar (when working with a link has become rare, it needs to be removed back to the menu, there are only up to 6 most necessary links on the panel).

- Often the names of the links will have to be rewritten. The fact is that many SEOs shove keywords into the page titles (it happens that among the keywords there is not even a place for the name of the portal itself). This works well for search engines (probably), but this is by no means a personable practice. When adding to bookmarks, it is advisable to leave only the name of the site (also suppose a slogan or 1 sentence with a brief description, if the words are not very many and they reflect the essence).
- The links themselves are also in many cases desirable to be rewritten in order to remove utm-tags (tags of digital-advertising) and redirects that arise after calling by reference (for example, language or region selector operators).
Introducing other bookmarking systems
Many sites contain their own functions for storing favorites (this is true for Vkontakte, Yandex.Kartinok and Yandex.Music, YouTube, Habra, Picaba and many others), so if you frequently use these portals you must have separate accounts.

As a rule, the function of bookmarks (no matter how it is called: “watch later”, “I like”, “saved posts”) allows you to create folders or playlists. Accordingly, the browser bookmark system in this case is freed from storing tons of posts and videos (it only remains to add the tab to the sites themselves).
Work from several places
All browsers have one or more of the following bookmarking capabilities:
- via the drop-down menu at the top (bookmarks menu; Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Opera, Yandex.Browser)

- via [top] bookmarks bar (bookmarks bar; Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Opera, Yandex.Browser)

- through the sidebar, which must be turned on as needed (fixed on the left or right edge of the screen, taking away space from the open page; Mozilla Firefox; Google Chrome - through the extension)

- via full-screen magazine / bookmark manager, which needs to be turned on as needed (Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Yandex.Browser)

- via the express panel / visual bookmarks panel when opening a new tab (Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Opera, Yandex.Browser)

As you can see, the functionality practically does not differ from different manufacturers, with the exception of the side panel.
Working with the log / dispatcher and in the sidebar is convenient when you need to climb on large levels of nesting (beyond the 2nd), and also if the drop-down menu is not provided or made uncomfortable, for the remaining cases you can use the menu and [top] panel.
Bookmark Search

All browsers have the ability to search in the saved. This is another way to reduce work time and an additional reason to rename the keyword-saturated links.
Bookmark backups
You can back up 2 ways (well, as always) - either as a local file or in the cloud.
I’m not a fan of bookmark synchronization services (both built-in browsers and third-party browsers), because experience shows that at times synchronization does not go according to plan and something can be lost or duplicated. In any case, separate files scattered in different secluded places, make saving more reliable.
There is another reason: synchronization services to render in the form of large icons, which takes more pixels than necessary (although I do not agitate for 10pt fonts at all, but more than 5-10 bookmarks should be placed on the screen, otherwise we are all sliding to clip thinking).
Backups can and should be saved at least once a month, and then it would be nice to copy them somewhere else (definitely not on the desktop). At worst, they can be sent by email to your own email.
Bookmarks can usually be saved in .html format (depending on the browser; Firefox also allows you to save to .json).
Mobile Bookmarks
Modern mobile browsers also allow you to organize a bookmark system. Although they are arranged differently, everywhere there is the possibility of categorization (it usually represents work not with folders, but with special forms that allow you to drag bookmarks to each other and thereby distinguish one category from another, as in the screenshot).

A big plus of mobile devices is that bookmarks can be dragged directly to the desktop.
Why the bookmark system allows you to memorize
Effective bookmarks work on the principles of associative psychology - you scatter links into folders that the brain considers categories. People think in categories (even if they don’t think about it), and categories (or, if you prefer, sets) include elements.

During the handwriting on the creation of a bookmark system, you unconsciously place links to web pages and meta-information about them to certain categories, categories to other categories, and as a result, a complete system with different levels is formed.
How else does the bookmark system improve efficiency
Firstly, when you click on the saved link in the address bar, an asterisk will be lit, which indicates that we have already visited this page (associations immediately pop up, when and for what).

Secondly, when we create a list with a certain number of elements, in fact everything can be translated into a plane of performance indicators (KPI).

For example, you are preparing a scientific work and add all read articles and monographs to a separate folder (only after reading or knowing that the unread will soon be read accurately). In this case, the number of articles relevant to your work and read articles is one of the KPIs of your work (an example was taken from the ceiling, many others can be cited).
How to find out how many of them
It is interesting sometimes to see how many bookmarks you have already saved (especially if the system has been running for years). To do this, you need to take a file with a backup of the bookmarks system and open it with a text editor (in this experiment I used Notepad ++).

After opening, you will need to use the built-in search and count the number of mentions of the “http” or “: /” prefix (the number will indicate the number of saved links). By the way, the skill gives out more than 5 thousand. When comparing backups for different numbers there will be a positive trend.
Bookmark Transfer
Suppose you are working on a project in which you need to transfer a whole bookmark folder, without shining everything else.

This can be easily achieved by making a backup of everything, and then opening Notepad ++ in the same folder and cutting out all other folders or inserting the necessary folder along with the sub-bookmarks into another file (for such purposes we have a search in the file).
A few more recommendations
- In Firefox, you can also insert separators between bookmarks that help visually separate link units, but other browsers have abandoned this practice. But if you use firelis, then do not forget about this feature.
- Do not forget about the ability to create entire folders on the [top] panel - this can speed up access speeds.
- You can also leave only favicons on the top panel - this will fit even more (thanks to this advice thanks to God_inSide ).
- In addition, you may encounter a situation where the same tab can be assigned to different categories. In this case, you will have to decide its fate, because you set up the system for yourself and in the end it will be clear only to you (although good categorization makes it in the main parts understandable for others).
- In Vkontakte, you can create your own private group to repost your favorite posts there. The advantages are that no one sees it (unlike your wall). Now many are doing this.
- In general, bookmarks should reflect your interests and your life.
- For scientific work it is better to start using bibliographic software like Zotero or Mendeley as early as possible - such programs have more opportunities to work with sources than browser bookmarks.
Links to online services
I cite a few examples of online bookmark storage services. Suddenly, someone will access more browser-based ones.
- Google bookmarks
- Pocket (not really bookmarking service, but still)
- Google Spreadsheets (custom application, as recommended by Doktor1962 )
- Saved.io (as recommended by Doktor1962 )
- Papaly (as recommended by AhJong )
- Booky
- Favoritus
findings
And how do you work with bookmarks? Write below your ways of organizing digital memories (by the way, this is a new scientific direction for researching new media). Of course, many of these concerns about bookmarks will seem unnecessary, but here I would like to remind you that we are talking only about people who have to work with information not only a lot, but extremely much, and therefore their own "knowledge management systems" can not be avoided.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/350390/
All Articles