How to organize parking for 5 hours on the method of determining the critical path CPM?
In the arsenal of any project manager has its reserves of management methods. Everyone strives for effective results based on his own intuition, practical experience, popular tools and well-known prioritization techniques. These results can be achieved if there is no chaos in the project life cycle, and the manager knows what to do at each stage, including determining the critical path of the project.
What role does the definition of the critical path play and why is a special CPM method necessary? In this material we learn to determine the critical path by the example of designing parking at the office. First, let's look at the terminology.

The critical path in project management is certain tasks that need to be performed in a clear order and for a certain period of time. If part of one task can be slowed down or postponed for a period, without leaving work on others, then this task is not critical. Tasks with a critical value cannot be delayed during the project implementation and are limited in time.
')

The Critical Path Method is an algorithm for planning, managing, and analyzing a project's timeline. The step-by-step CPM system helps to identify critical and non-critical tasks from start to finish the project and prevents temporary risks.
The method was developed by an American company in 1957. Its employees planned to shut down, repair and restart chemical plants. The tasks in this project were numerous and complex, and therefore there was a need for such a technique. After this, the critical path method quickly spread to projects in the agricultural and construction fields and wherever they wanted to learn how to cope with routine tasks .
Today, this method of identifying critical tasks is widely used in many industries, including software development.
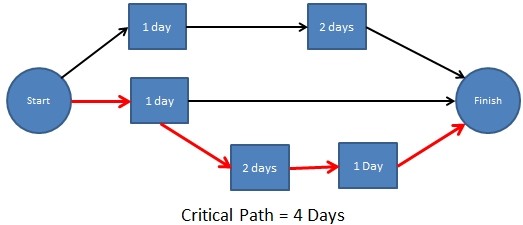
Project critical tasks have zero runtime reserve. If the duration of these tasks changes, the deadlines for the entire project will “move”. That is why in project management, critical tasks require special monitoring and timely identification of risks.
Analysis of the critical path is needed in order to predict the timing of the completion of the project.
Here are the 6 main benefits of critical path analysis:
However, ideal methodologies hardly exist, so some CPM “pitfalls” should be taken into account.
It is believed that the methodology was developed for routine and complex projects with the possibility of minimal changes in the time of completion of tasks. When applied to more chaotic projects, CPM will lose its utility. But there are alternatives, for example, PERT-diagrams that allow you to change the duration of each activity.
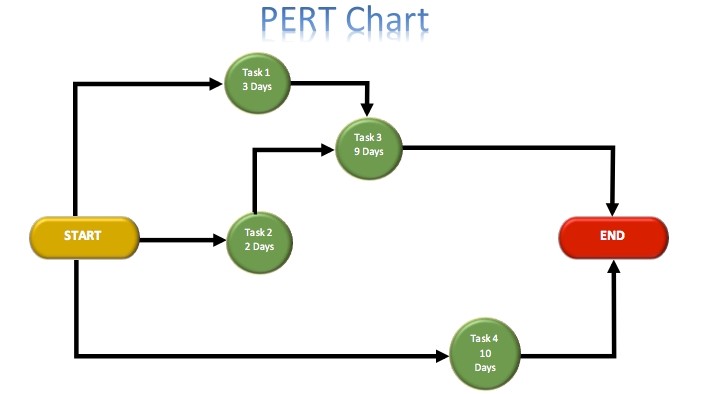
The critical path models events and actions in a project, representing them in an interconnected network. Actions are visualized as “nodes”, and the beginning and end of activities look like arches and lines between nodes.
The CPM method involves 5 consecutive steps:
Representing the scope of the project, you can break the work structure into a list of activities, give them names or codes. All activities in the project must have a duration and a specific date.
Refer to the project of parking near the office. This is a simple short-term project that can be completed in one day. Suppose our goal is to “break up” parking in an empty asphalt area near the office. To do this, it is necessary to plan and do certain stages so that the first car can park freely in a designated area.
For the successful implementation of the project, we plan 6 phased activities. It is necessary to determine the territory and clean it from debris, buy paint for marking, make all measurements, apply paint and, finally, install a barrier.
This is the most important step, as it gives a clear idea of the links between activities and helps to establish dependencies, since some actions will depend on the completion of others. To correctly assess the tasks and their priority, ask yourself three questions:
In our example of activity should be arranged in the following order:
Once you have determined which actions are dependent on each other, you can create a network or critical path analysis diagram. Using the arrows, you can easily connect the activity, based on their dependencies.
Assessing how much time will be spent on each action, you will be able to determine the time required to complete the entire project (small projects can be assessed in a few days, more complex ones require a long assessment).
Our illustrative project is the easiest, so one day is enough for evaluation. Based on the plan, you can determine the duration of the stages and the entire project:
Grouping actions will help create the longest sequence in a path or a critical path using the following parameters:
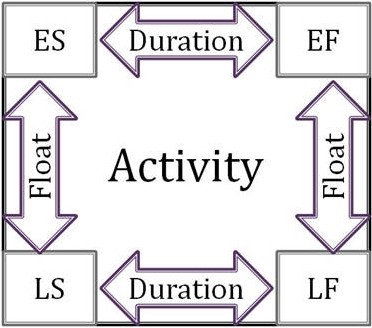
The time between the closest and the last start time, or between the closest and the last end time is called the reserve time of the project. This is the time by which the nearest start and finish can be postponed without changing the project deadlines.
Obviously, some steps in a parking project cannot start until others are completed. They are addicted. Stages 4,5,6 are sequential actions, because they must occur in a certain order. These stages are the most important critical tasks for resolving the issue. We will locate them on the critical path of the project, because we remember that it is impossible to begin any stages until others are completed.

Graphs, sections, columns, arrows, and columns are used in the graphical scheme of the critical path to get a complete picture of the project and individual tasks. With their help, it is easy to visualize activities and dependencies both on paper and use special programs and tools for these purposes. The simplest calculation of the critical path can be performed even in Excel using Gantt charts.
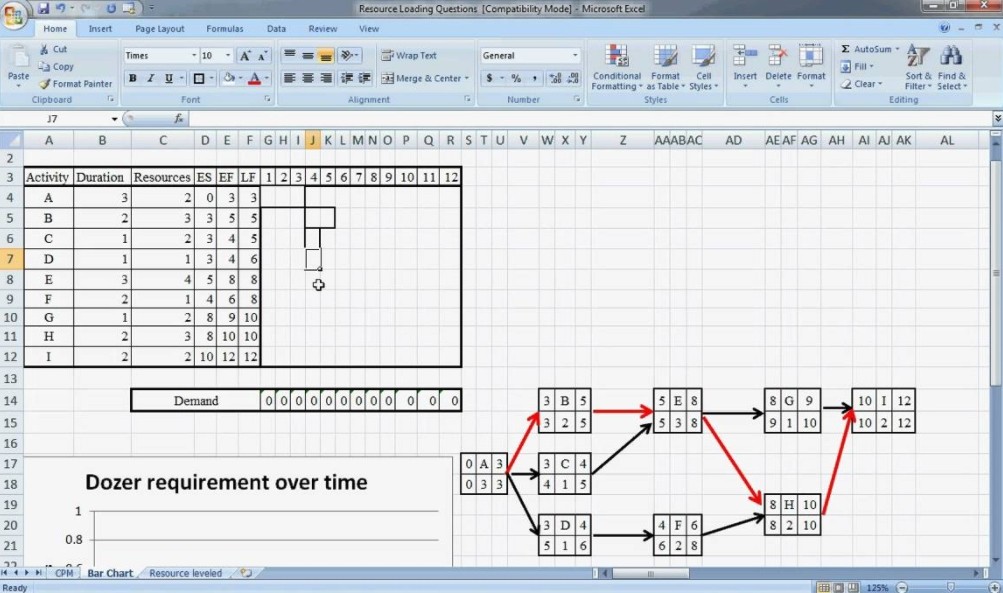
In an effort to maximize the benefits of the critical path method and ensure the continuous development of projects, we can still face some limitations that can affect projects and create new dependencies.
For example, if a team is suddenly reduced from 10 to 5 people, then you are faced with resource constraints.
Thus, the critical path becomes the “critical path of resources,” where resources associated with each activity become an integral part of the process.
This means that some tasks must be performed in a different order, which can lead to delays and, consequently, make the project longer than expected.
Although today the CPM critical path method is often criticized, its foundations continue to be sought after by project managers.
CPM has several advantages:
With the CPM method, you can shift less important tasks and focus your efforts on optimizing work.
Did you use the CPM method in your work? Share your experiences in the comments!
What role does the definition of the critical path play and why is a special CPM method necessary? In this material we learn to determine the critical path by the example of designing parking at the office. First, let's look at the terminology.

What is the critical path in project management?
The critical path in project management is certain tasks that need to be performed in a clear order and for a certain period of time. If part of one task can be slowed down or postponed for a period, without leaving work on others, then this task is not critical. Tasks with a critical value cannot be delayed during the project implementation and are limited in time.
')

The Critical Path Method is an algorithm for planning, managing, and analyzing a project's timeline. The step-by-step CPM system helps to identify critical and non-critical tasks from start to finish the project and prevents temporary risks.
The method was developed by an American company in 1957. Its employees planned to shut down, repair and restart chemical plants. The tasks in this project were numerous and complex, and therefore there was a need for such a technique. After this, the critical path method quickly spread to projects in the agricultural and construction fields and wherever they wanted to learn how to cope with routine tasks .
Today, this method of identifying critical tasks is widely used in many industries, including software development.

Project critical tasks have zero runtime reserve. If the duration of these tasks changes, the deadlines for the entire project will “move”. That is why in project management, critical tasks require special monitoring and timely identification of risks.
Benefits of Critical Path Analysis
Analysis of the critical path is needed in order to predict the timing of the completion of the project.
Here are the 6 main benefits of critical path analysis:
- The CPM method visualizes the project graphically.
- Identifies the most important tasks.
- Saves time and helps in managing deadlines.
- It helps to compare the planned with the real status.
- Identifies all critical activities that should be addressed.
- Makes dependencies clear and transparent.
However, ideal methodologies hardly exist, so some CPM “pitfalls” should be taken into account.
Limitations of the critical path method
It is believed that the methodology was developed for routine and complex projects with the possibility of minimal changes in the time of completion of tasks. When applied to more chaotic projects, CPM will lose its utility. But there are alternatives, for example, PERT-diagrams that allow you to change the duration of each activity.

The critical path models events and actions in a project, representing them in an interconnected network. Actions are visualized as “nodes”, and the beginning and end of activities look like arches and lines between nodes.
Stages of the critical path method
The CPM method involves 5 consecutive steps:
1. Definition of activities / tasks
Representing the scope of the project, you can break the work structure into a list of activities, give them names or codes. All activities in the project must have a duration and a specific date.
Refer to the project of parking near the office. This is a simple short-term project that can be completed in one day. Suppose our goal is to “break up” parking in an empty asphalt area near the office. To do this, it is necessary to plan and do certain stages so that the first car can park freely in a designated area.
For the successful implementation of the project, we plan 6 phased activities. It is necessary to determine the territory and clean it from debris, buy paint for marking, make all measurements, apply paint and, finally, install a barrier.
2. Determination of the sequence
This is the most important step, as it gives a clear idea of the links between activities and helps to establish dependencies, since some actions will depend on the completion of others. To correctly assess the tasks and their priority, ask yourself three questions:
- What task should be performed before this task is completed?
- What tasks should be performed simultaneously with this task?
- What tasks should be performed immediately after this task?
In our example of activity should be arranged in the following order:
- Choose a place.
- Clear the area of debris.
- Buy paint for marking.
- Measure the site for a certain number of cars.
- Apply markings and pointing elements for parking.
- Install the barrier.
3. Creating Activity Groups / Networks
Once you have determined which actions are dependent on each other, you can create a network or critical path analysis diagram. Using the arrows, you can easily connect the activity, based on their dependencies.
4. Definition of time periods for the completion of each activity
Assessing how much time will be spent on each action, you will be able to determine the time required to complete the entire project (small projects can be assessed in a few days, more complex ones require a long assessment).
Our illustrative project is the easiest, so one day is enough for evaluation. Based on the plan, you can determine the duration of the stages and the entire project:
- 15 minutes to choose a place
- 90 minutes to clear the ground
- 30 minutes to buy paint for marking
- 45 minutes to measure the site
- 60 minutes to markup
- 60 minutes to install the barrier
- The total time cost of the project is 5 hours.
5. Search for a critical path
Grouping actions will help create the longest sequence in a path or a critical path using the following parameters:
- The early start time (Early Start) is the moment when all previous tasks are completed.
- The nearest time to finish (Early Finish) - the near time to start and the time required to complete the task.
- The last time of the end (Late Finish) - the final moment - all activities are completed without postponement.
- Last start time (Late Start) - the last end time minus the time it takes to complete a task.

The time between the closest and the last start time, or between the closest and the last end time is called the reserve time of the project. This is the time by which the nearest start and finish can be postponed without changing the project deadlines.
Obviously, some steps in a parking project cannot start until others are completed. They are addicted. Stages 4,5,6 are sequential actions, because they must occur in a certain order. These stages are the most important critical tasks for resolving the issue. We will locate them on the critical path of the project, because we remember that it is impossible to begin any stages until others are completed.

How to build a critical path diagram?
Graphs, sections, columns, arrows, and columns are used in the graphical scheme of the critical path to get a complete picture of the project and individual tasks. With their help, it is easy to visualize activities and dependencies both on paper and use special programs and tools for these purposes. The simplest calculation of the critical path can be performed even in Excel using Gantt charts.

How does resource limiting affect a method?
In an effort to maximize the benefits of the critical path method and ensure the continuous development of projects, we can still face some limitations that can affect projects and create new dependencies.
For example, if a team is suddenly reduced from 10 to 5 people, then you are faced with resource constraints.
Thus, the critical path becomes the “critical path of resources,” where resources associated with each activity become an integral part of the process.
This means that some tasks must be performed in a different order, which can lead to delays and, consequently, make the project longer than expected.
As a conclusion
Although today the CPM critical path method is often criticized, its foundations continue to be sought after by project managers.
CPM has several advantages:
- Determines the priority of tasks.
- Gives a clear understanding of the project time intervals. This helps to reduce the time required to complete the project.
- Allows you to compare planned and actual progress.
- Evaluates risks.
- Helps in the distribution of team members.
- Helps the team stay focused on the essentials.
With the CPM method, you can shift less important tasks and focus your efforts on optimizing work.
Did you use the CPM method in your work? Share your experiences in the comments!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/350080/
All Articles