iPaaS - cloud ESB ... or not?
Everyone has become accustomed to cloud infrastructure and cloud services, but there is not a single article on the subject of iPaaS, just a few mentions.
With the growing number of cloud services and applications, the number of various APIs has grown, and here the mobile platforms have been pulled up, and all this should somehow exchange data. As a result, a lot of resources of developers began to go away on the integration of this diversity, and to support all this is necessary. And the logs to disassemble, if they have not forgotten to implement. The market responded to the problem with the advent of the iPaaS.
iPaaS by gartner is a set of cloud services that allow you to develop, execute, and maintain integration flows that connect any combination of local and cloud services, processes, applications, and data within one or more organizations.
The main pillars of the iPaaS:
')
Users create integrations using the REST API. After that, the Agents receive a command from the created integration processes using the REST API. Data is transferred between connectors using agents. Agents can be both cloud and local, depending on the integrable entities:
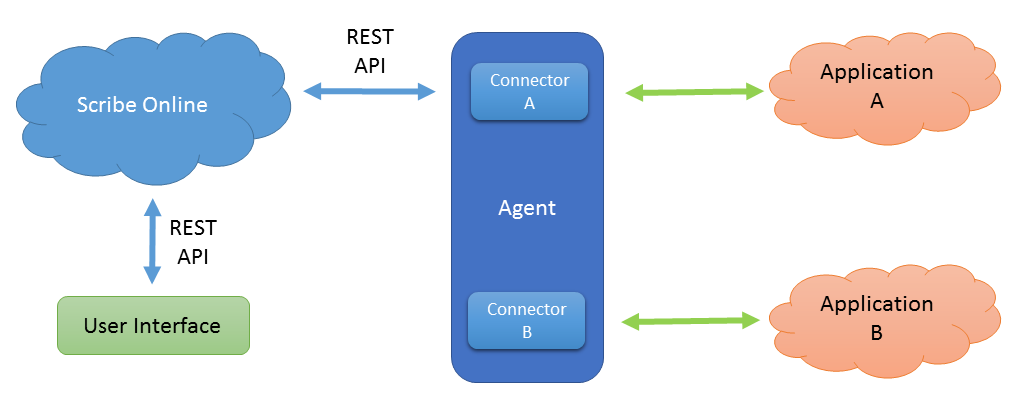
In fact, there are a lot of pictures with architecture, from each manufacturer .
Plus SDK to develop your connectors. All transmitted data is encrypted, business data is not stored inside the platform - but in case of erroneous records, you can see the transmitted record fields.
The entire integration development process is carried out in a browser client, where you install the necessary connectors, agents, connections. Developing integration. Connections are configured based on the installed agent and the connector, if you configure integration between local and cloud applications / services, then both systems will be accessed from the local agent, and, as described above, you will need to set the appropriate permissions in the firewall.
When the application / service is first accessed, all metadata is requested, due to which interaction is carried out later, the metadata is cached on the server side and is not requested every time.
The main thing in the setup is an integration card / cards - a set of consecutively connected logic blocks reflecting the integration workflow. There are standard blocks - responsible for typical operations "if / else", "for each", etc. and a set of commands derived from connections. Comparison of fields between systems is carried out by the drag & drop method, and in order to implement the logic of data transformation, the platforms support many extra-like functions.
Compared with the ESB, then support and development of integration for the ESB often became a separate project and required specialists with specific knowledge, becoming the center of all integration flows within the enterprise. iPaaS, on the other hand, aims to streamline the entire integration lifecycle with cloud applications and services — from creation to maintenance — to the maximum.
PS The article contains a general description of the iPaaS. Companies do not provide a backend description of their products.
With the growing number of cloud services and applications, the number of various APIs has grown, and here the mobile platforms have been pulled up, and all this should somehow exchange data. As a result, a lot of resources of developers began to go away on the integration of this diversity, and to support all this is necessary. And the logs to disassemble, if they have not forgotten to implement. The market responded to the problem with the advent of the iPaaS.
Definition and main features
iPaaS by gartner is a set of cloud services that allow you to develop, execute, and maintain integration flows that connect any combination of local and cloud services, processes, applications, and data within one or more organizations.
The main pillars of the iPaaS:
')
- Easy system deployment - if you integrate cloud instances you don’t need to install anything. If you integrate with a local application, the entire installation will consist in downloading and installing the agent and defining firewall rules for it.
- Ready connectors - developers are concerned
that you do not have to code anything(of course not). Included with the platform is a wide range of ready-made connectors to popular applications and services. But if you want to integrate with some kind of a netlenka, and there is no suitable connector, then you will be able to cut it yourself - a bundle often includes a package for quick development. - Graphic “code-free” interface - the whole process of building integration consists in assembling blocks of logic, both general and individual for systems (like children's programming under adruino).
- Error handling - convenient logs, with a detailed system error response, with the ability to re-send one / several / all erroneous entries. Email notifications.
IPaaS Architecture
Users create integrations using the REST API. After that, the Agents receive a command from the created integration processes using the REST API. Data is transferred between connectors using agents. Agents can be both cloud and local, depending on the integrable entities:

In fact, there are a lot of pictures with architecture, from each manufacturer .
Plus SDK to develop your connectors. All transmitted data is encrypted, business data is not stored inside the platform - but in case of erroneous records, you can see the transmitted record fields.
Development process
The entire integration development process is carried out in a browser client, where you install the necessary connectors, agents, connections. Developing integration. Connections are configured based on the installed agent and the connector, if you configure integration between local and cloud applications / services, then both systems will be accessed from the local agent, and, as described above, you will need to set the appropriate permissions in the firewall.
When the application / service is first accessed, all metadata is requested, due to which interaction is carried out later, the metadata is cached on the server side and is not requested every time.
The main thing in the setup is an integration card / cards - a set of consecutively connected logic blocks reflecting the integration workflow. There are standard blocks - responsible for typical operations "if / else", "for each", etc. and a set of commands derived from connections. Comparison of fields between systems is carried out by the drag & drop method, and in order to implement the logic of data transformation, the platforms support many extra-like functions.
So this is ESB
Compared with the ESB, then support and development of integration for the ESB often became a separate project and required specialists with specific knowledge, becoming the center of all integration flows within the enterprise. iPaaS, on the other hand, aims to streamline the entire integration lifecycle with cloud applications and services — from creation to maintenance — to the maximum.
PS The article contains a general description of the iPaaS. Companies do not provide a backend description of their products.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/349840/
All Articles