Remote work robots: technical details and application
Currently, about 15 thousand remote workers in the world are present at work virtually through remote presence robots. The article describes the scenarios for their use and some technical details.
In total, more than 30 varieties of such robots have been developed, almost all of them are presented on telepresencerobots.com , but only four of them are in actual demand and are being actively sold (on telepresencerobots.com, amazon.com, eBay.com and alibaba.com): Double, Beam , PadBot and BotEyes.
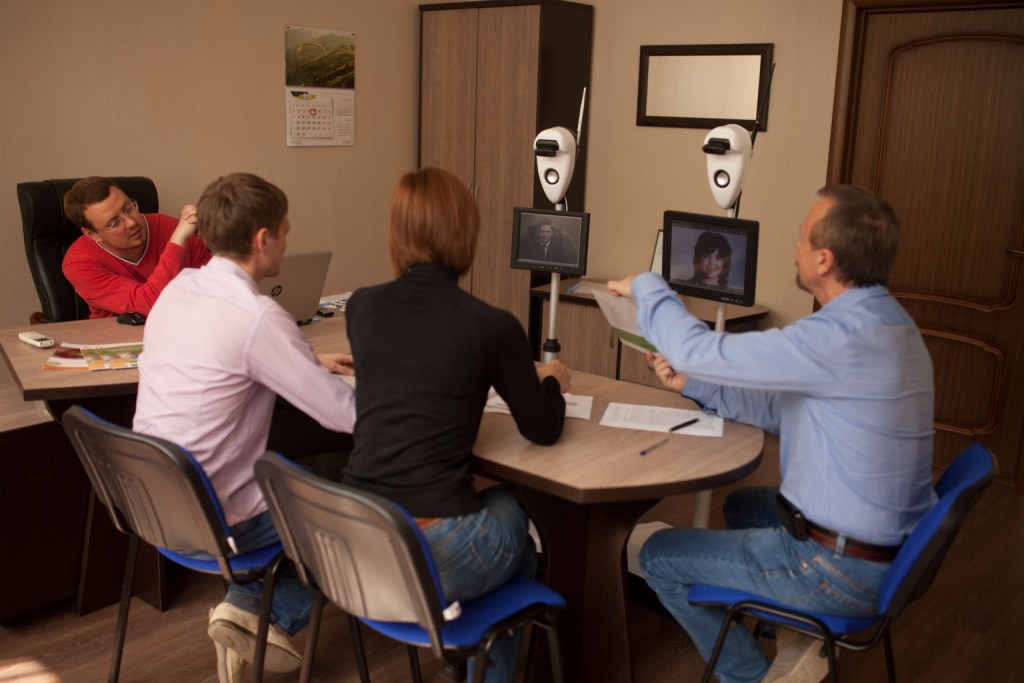

The idea of telepresence is very difficult to get used to, as to everything unusual and not yet found massive use. Most consumers view such robots as a toy. Nevertheless, around the world, 15,000 such robots have already been sold, which really help companies in solving the problems listed below and provide a tremendous economic effect with a payback period of several months. In Fig.1. presents a graph of the growth of this market.
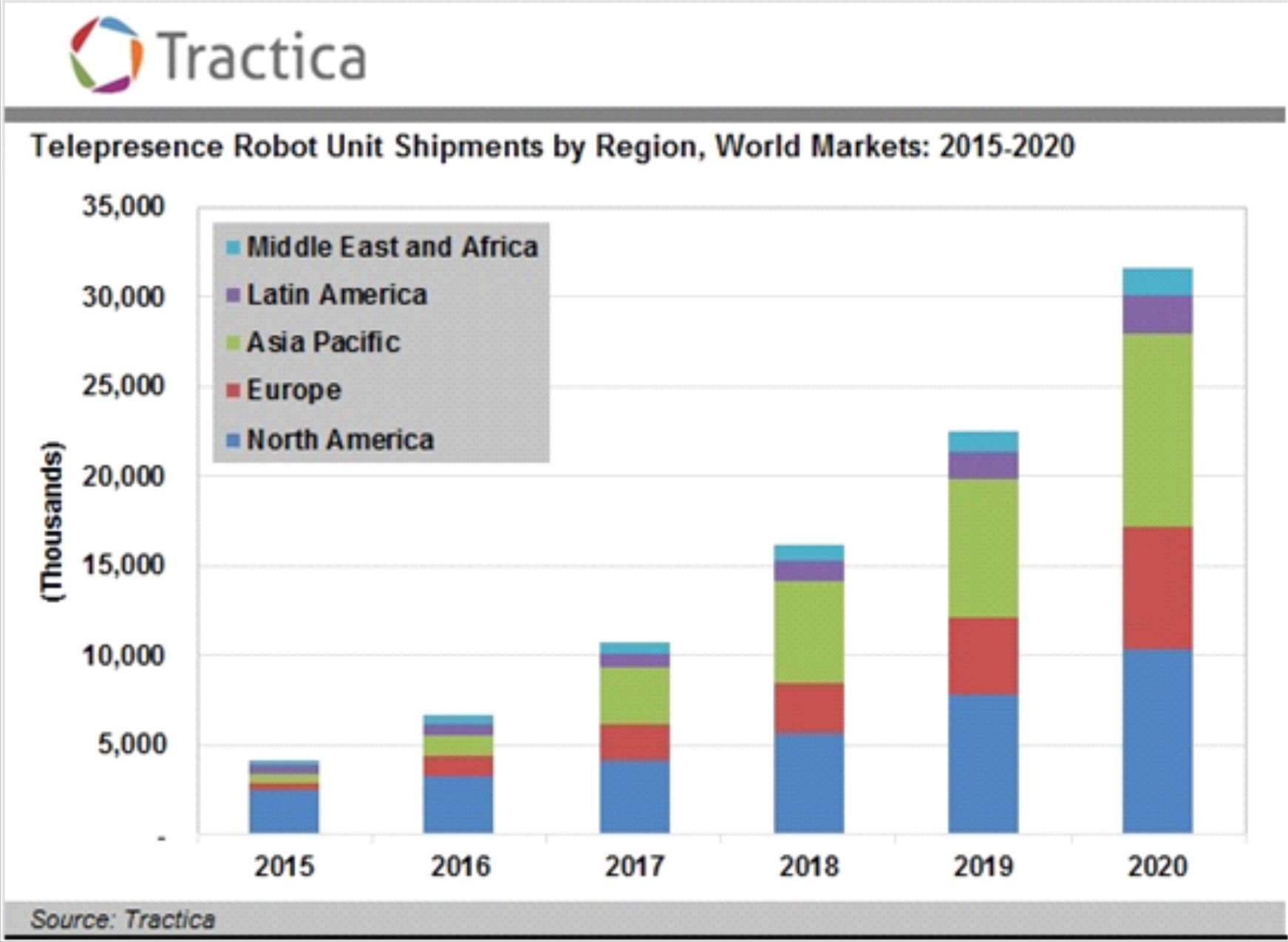
Fig. 1. Data site tractica.com
Application scenarios
Telepresence teleworking is the main application of this type of robots. Two scenarios are most in demand by the market:
a) the worker, being at home or on a business trip, participates in the life of the company and works exactly as if he were in the office, among his colleagues;
b) the head of a company with several offices performs its functions, communicating with staff or other managers remotely using a robot.
The use of robots by remote workers
Remote work should be used in the following cases:
- when it is impossible to find an employee in your city with the required narrow specialization, with unique abilities or a certified expert. For example, you found it in China, in the USA or in Novosibirsk, but your company is located in Moscow;
- when the employee himself cannot go to the office every day due to illness or due to illness, or it takes an extremely long time;
- when the employee is forced to spend a long time on a business trip, but his presence in the office is also necessary;
- when the worker must be in several places in one day. For example, a lecturer must read several lectures in different cities in one day; the head of the personnel department should conduct an interview with candidates for work in several employment bureaus; the general customer wants to visit several co-contractors in one day;
- when it is urgent to “appear” at the customer in order to understand the reasons for the failure of the equipment installed by you or adjust it by the hands of the customer’s personnel;
- when the presence of "live" is not economically feasible: only one trip can cost several tens of rubles and exceed the cost of the robot.
Let us give more specific examples.
Suppose you are a CNC programmer working at home. Before you mill a part, you usually first track the cutter's trajectory visually, “through the air”, before putting the workpiece on the machine. If you are working at home, then with the help of a robot you can remotely view the cutter's trajectory before installing the part and then during the milling process, even if the machine is located in China and you are in Fryazino. The presence of the robot wheels allows you to drive up to the machine and consider the process from the right angle. Similarly, you can see how the installer soldered your printed circuit board, how to cut a part on a CNC laser machine, what accessories and fixtures the assembler uses when making the product for your project.
Another example
You ordered a mold in Novosibirsk, inserted it into an automatic thermoplastic, which is located in Taganrog, and the part was cast. The detail turned out with defects. If you have a telepresence robot, the mold designer can remotely determine the nature of the defect, view the casting modes on the machine dashboard, remotely perform (with your help) the selection of more suitable modes or make changes to the size and location of the sprues by redesigning the mold .
Third example
Suppose you are a homeworker programmer on a team working on a common project. Every day there are held checkouts on which you need to be present, co-contractors during the working day have ideas that require discussion. If your telepresence robot is turned on all the time and the image from its camera is output via the HDMI interface to your home TV, then you have the full feeling that you are sitting in the same room with the other programmers, you can hear replicas concerning everyone and you can drive up "on the robot" to anyone and discuss the subtle places in the project. Your face is always visible on the monitor of the robot. During the planning meeting, you see not only the person who speaks, but also the facial expression of the others present, their facial expressions, you hear their statements. Further, in such events they usually use a blackboard on which they draw charts, diagrams, graphs, etc., with the chalk. The robot allows you to turn to the blackboard, drive closer if you need to look at something. It creates the effect of full presence, not reproduced by fixed monitors of traditional video conferencing.
The use of robots heads
For managers, the need for a telepresence robot arises in the following cases:
- if the company has several offices in different cities or countries. There are tasks of communication of the director of the company with the heads of remote offices (tasks of the teleconference);
- if the head of the company lives in another city or in another country (it is not uncommon abroad);
- if the owner of the company or the manager wants to control what the employees in the remote office do, how often they smoke and whether they form “groups for informal communication”;
- if the manager wants to show the company to the customer (remotely);
- if the manager wants to see how counterparties fulfill an order (for example, assembling a wardrobe of complete automation or assembling a milling machine by special order, which is also carried out in China);
- if the buyer wants to inspect a large-sized machine, room or technological process, production;
- If the firm builds a new office or workshop, the director may at any time observe the construction process instead of spending time on trips.
Other applications:
- remote participation in scientific, economic, political forums;
- remote visit to the exhibition;
- if the office is in one place and the warehouse is in another, then the robot can control how the goods are laid in the warehouse, how the storekeepers let it go, whether they are politely communicating with visitors.
The essence of telepresence and alternatives
The essence of telepresence is very vividly described in Avatar. This is a complete remote presence, with all the sensations and emotions associated with it, with the transmission of signals from all the senses. The robot, which provides only remote-controlled video and audio communication, physically transmits only sound and video, but psychologically, a much stronger effect is achieved - the robot allows you to see facial expressions, gestures, eye expression, change of surroundings, movement of people in the room and feel the movement of yourself. This is much more than a videoconference. This creates a sense of your presence in the team. Psychologically, this is a completely different level of communication, rather than by telephone or video link.
The following alternative means of implementing remote presence exist:
- robots that do not have wheels, but allow you to change the direction of the screen and webcam;
- teleconferencing systems, when large fixed video screens are installed in the room on which the image of remote persons is displayed;
- small-sized robots with telepresence;
- PTZ video cameras (their rotation in two planes can be controlled via the Internet);
- a regular computer with Skype installed.
The common difference between these options is the inability to move the point of presence in space or the inconvenience of communication (as in the case of toys).
Technical nuances
Consider the features of commercially available telepresence robots (Figure 2)

Fig.2. The most common telepresence robots
Double robot has only two wheels. This made it easy and stable in the longitudinal direction due to the electronic stabilization system, but the price for this is the lack of stability in the transverse direction. The robot has a small distance between the wheels, so it falls as soon as it hooks its side against an obstacle or drives one wheel over a hill. In practice, he can only move the wire lying on the floor. Therefore, although it allows you to adjust the height and at its maximum is the highest robot in the table, it must be borne in mind that increasing the height reduces the already poor stability. Fortunately, the high and not very hard sides of the tablet holder allow the tablet not to break when dropped.
Other robots do not use the principle of segway and their stability is determined by the weight of the robot, which is concentrated mainly in its chassis, and the distance between the wheels.
Most robots have a fixed screen and a fixed camera. This leads to the need to use a camera with a wide viewing angle, which is much more expensive than conventional cameras, and a second camera aimed at the wheels, which is necessary to avoid obstacles. The fixed screen and camera reduce the effect of presence, because when talking “face to face”, the “look” of the robot is not aimed at the speaker. This problem is fundamentally solved in the BotEyes-Pad robot, which allows you to change the angle of inclination of the tablet and camera to 120 degrees. and through the same camera "look under your feet."
The software for controlling the wheels of most robots is installed on the same computer (usually a tablet) that is used for video communication. To reduce the number of wires that fit the tablet and spoil the design, the control signals for the wheel part are transmitted from the computer to the wheel controller via Bluetooth.
Video communication is usually performed using WebRTC technology. It also transmits wheel control signals. In contrast, the BotEyes-Pad robot uses Skype for video calling and a WCF service to transmit wheel control signals over the Internet. This principle provides a number of advantages: more than half a billion people are familiar with Skype, Skype’s reliability and quality of communication has grown significantly after its acquisition by Microsoft, which made significant investments in Skype’s infrastructure (in particular, super sites were transferred to Microsoft’s servers). In addition, Skype is by default available in many modern TVs and can also be used to communicate with the robot.
As a computer that controls the movement, the robots usually use the same tablet as the software for video communication. Only the BotEyes-Pad robot uses the separate computer running the Windows 10 IoT Core to manage the wheelbase and using the WCF service to manage user accounts and redirect information from the operator to the robot and back. Selecting a separate computer for motion control allowed us to isolate tablet functions exclusively for video communications and use not only any tablet, but even a smartphone. For the mechanical attachment of the gadget uses a special design holder with adjustable grippers. The separation of functions between computers also allows you to independently install in the robot any video messenger that you like, for example, Google Hangout.
Remote control of robots is usually performed either from a special application or from a web browser. The browser option is convenient because it does not depend on the platform and type of gadget on which the browser is installed, and a separate application is more convenient because you do not need to type the address of the management site. Robots that use WebRTC are limited to browsers that support it (they only work stably with Google Chrome).
The price paid for using Skype in the BotEyes-Pad robot is to restrict the class of gadgets from which the robot can be controlled: they must have a split screen function so that Skype is open in one part of the screen, and the wheel part control program in another. This condition is satisfied by all desktop computers, iPads (but not iPhones), gadgets with Android 7 and higher.
In cases where the gadget does not support screen sharing, you can use "floating" browsers that run on top of Skype, have a transparency setting and there are quite a lot of them in the Play Market. As an example, in Figure 3, the lower right shows a view of the “control circle” of the robot, which is open over Skype in a floating browser with adjustable transparency installed on the Samsung Galaxy S6. The distance of the touch point of the screen from the center of the circle is proportional to the speed of movement of the robot, the deviation of the touch point from the vertical line causes the robot to turn, touching on a yellow background causes a reversal in place.
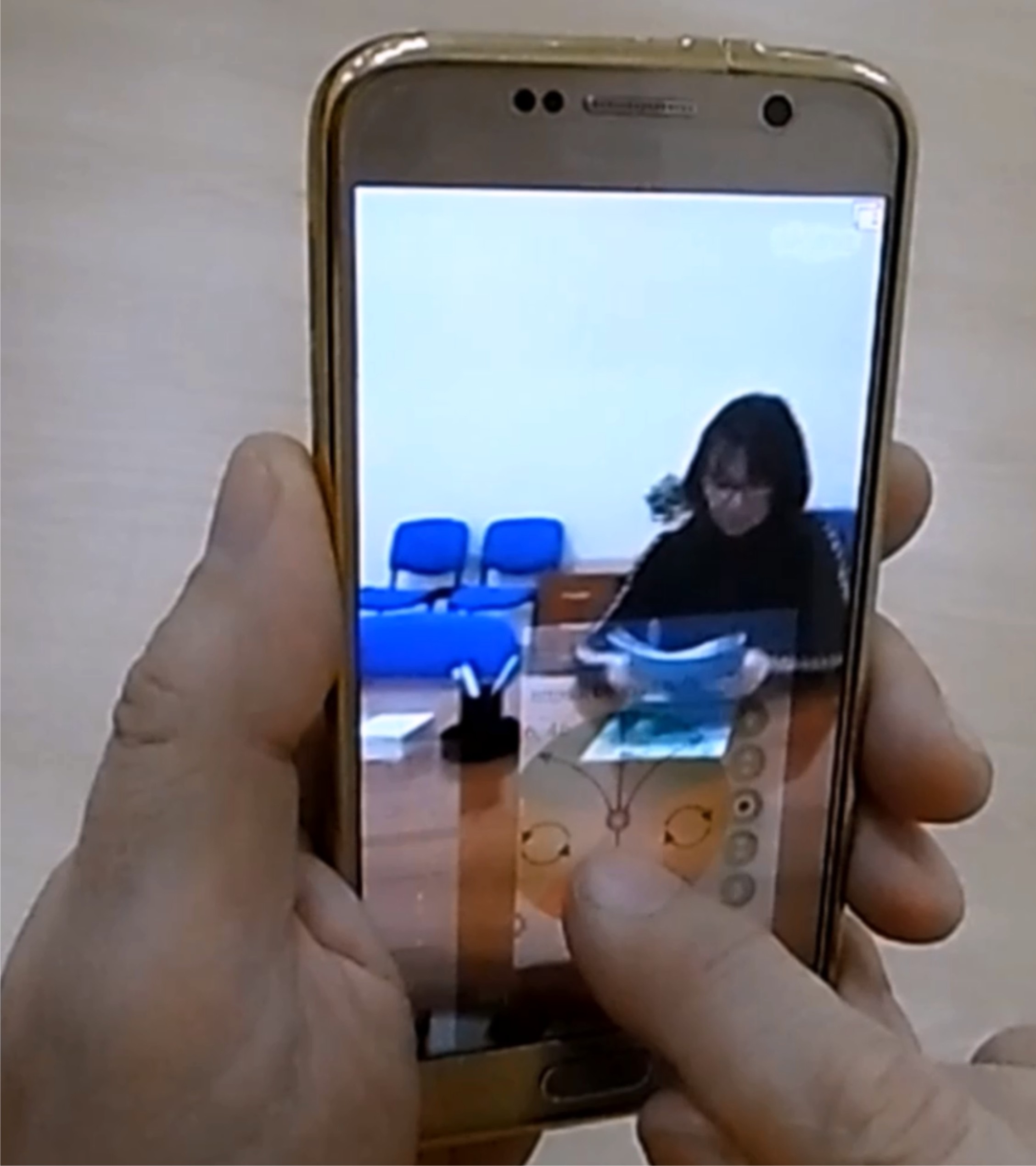

- Fig. 3. Robot control circle, open over Skype in a floating browser *
Table 1. Key Features of Telepresence Robots

Robots' computers sometimes install additional software (face recognition, text-to-speech, chatbot functions), but software with these functions has no direct relation to telepresence and can be installed on any robot tablet.
All robots have charging stations (docking stations), but not all are sold with them. Installing a robot docking station usually does not cause any difficulties. However, a number of robots have the function of automatic installation on the docking station.
findings
Telepresence robots that allow the market to grow were not immediately found. They tried to use robots to engage people in wheelchairs, as baby monitors, to monitor children in kindergarten, on the school playground or at home in the absence of their parents, to look after the house or cottage during the owners' departure, to communicate with patients. , for distance learning, for visiting exhibitions, for video surveillance, etc. However, the market has made its choice and now the vast majority of telepresence robots are used for remote work. This is probably due to the relatively high price of robots, which is feasible only for firms, but is not available for the average consumer.
The future of this industry is seen as follows: employees are at home, and their avatars (with arms and legs) are in the office of the company. Firms staff the state regardless of the country or city in which their employees live. The language barrier is overcome by an artificial intelligence translator gadget.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/349548/
All Articles