WIP: Product Design

I want to tell you about the cycle of work on the design of the finished product, based on my own experience in beepcar.ru . This is a service that helps one to get from point A to point B, another - to save on gasoline, and sometimes even to earn money. In short, driving drivers
and passengers. We have a web version and two apps for Android and iOS.
The cycle itself is divided into three modules: Before Design, Design and After Design. Below I will tell about each in detail.
')
Before Design
Before embarking on design, we need to know: what exactly we are doing and why . Understanding the causes of tasks and their goals is necessary for the whole team - the product manager is responsible for this. But in reality, the product manager is full of other tasks, meetings, research, and various concerns. Because of this, it is not always possible to convey the causes and goals of the tasks. Therefore, we will take the initiative and see for ourselves where the tasks come from.
Since the project is launched, we already have an audience - large or still small. These are people who have chosen our product for solving their problems (works on JTBD ). These people we need to be able to hear and understand their needs. Our metrics depend on satisfied needs, by which we evaluate the success of a product. How can you identify needs:
Reviews
They need to be read regularly and by the whole team. There are three easy ways. First, people leave them on Google Play and the App Store. Secondly, it is necessary to foresee the possibility of sending feedback directly from the application or website. Thirdly, they should be searched in our groups in social networks.
Friends / acquaintances and personal experiences
Most likely, the people around us will use our product, do not hesitate to ask once again whether they like everything or not. We put questions open, we try to talk to the person. Often with such interviews interesting cases pop up. Well, do not forget to get yourself in the place of people who use our service.
Experiments on "live"
“Live” in the team we call the current versions of the product: they are right now people are using. To conduct experiments, special training is required - during initial development, you need to spend time installing meters for different events. Thanks to this, we can measure the funnels, put forward hypotheses, and then test them. Below is a simple funnel example:
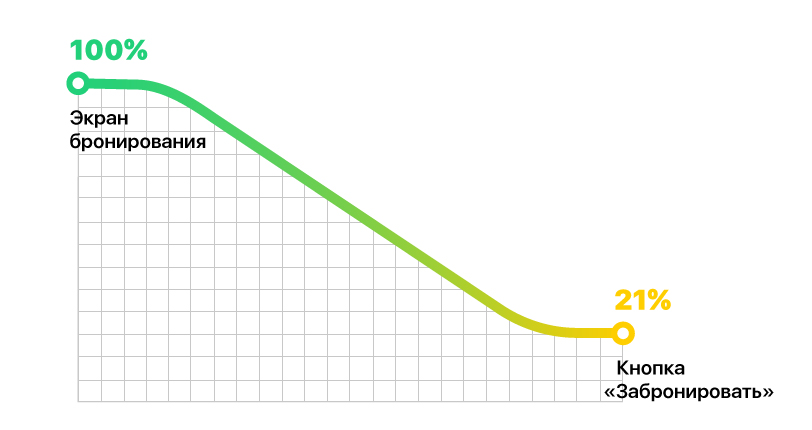
Why out of 100% of people who got on the booking screen, click on the "Book" button only 21%? The most obvious conclusion would be: people do not find the button. Then our hypothesis will be this: if you put the button on a more prominent place, you can increase the amount of armor.
Ux testing
In Mail.Ru, as in many large companies, there is a UX-lab. This is a special department that invites third-party people, shows our products, conducts interviews, records the reaction, and then, based on the results of these studies, they prepare a report on the product. Smaller companies without access to laboratories can independently conduct UX testing and interviews with acquaintances. It can also be done through online services — for example, through Fabuza .
Competitors
And of course, spying on our neighbors. We should be interested in both direct competitors and indirect ones. With straight lines everything is clear, but indirect ones can be completely different companies. For example, our indirect competitor is Russian Post, because in our service, people can send parcels with drivers. And when one of the competitors releases a feature, you need to study it and decide how much it is needed in our product. Nothing personal, it's just business.
After identifying the needs they need to be turned into features.
In half the cases, everything will be rather stupid, for example: passengers want to pay by card - let's make payment online, brilliant! With other needs, it is worth digging deeper. One of the last: people want to leave comments on the trip. It was possible not to think here, but simply to give them comments (spoiler, in the end we did so). But! At first we went the other way and discussed the topic: what exactly do they want to ask? Maybe you can warn these questions? Why comments on the trip? Maybe it should be a general chat? Or private messages? Etc. Why complicate your life with these questions? Because it is right, it is interesting, and it often brings interesting observations and thoughts.
Next we have a list of features that we want to do. And at first everything will be fine, it will be small and neat, but then the number of “hotelok” will grow like a snowball. Here we need to set priorities so that we end up with a smooth backlog with tasks. In general, you can prioritize tasks based on two things:
The model “Aah, it burns!” - very often we have tasks that need to be solved yesterday. For example, the metric important for us after rolling out the latest version. Or competitors have released a very important feature that we do not yet have. And still can accept the new law,
for example, the “Law on the Agreement on the processing of personal data”, in order to fulfill it, it also takes time for design and development. Here you can add marketing activities for holidays and various events. In most cases, all these tasks take the first place.
Model Kano - when the fire is extinguished, we can move on. To do this, we take our backlog and run it through the Kano model. This method helps to understand what percentage of people will like the new feature, what will be all the same, and what will be upset at all. In conjunction with the assessment of the development of this allows you to see the ratio of our work on the feature and the benefits of it. After that, our backlog will take on the list of priorities. About the model itself can be found here .
Design
Now we start to draw. Unlike the first module for which the product manager was responsible, here we play the main role - product designers. Since responsibility is entirely on us, we must not disappear. Therefore, we periodically coordinate intermediate decisions with the manager. The design process is divided into three parts:
- We draw
Before the first approach it is useful to meet in a narrow circle of managers / designers and speak the main points. We start drawing at this meeting, so at the exit we will have mock-up sketches and a clearer understanding of what everyone expects. Next, we work through all the ideas, transfer them to Sketch and think it through again in more detail. For every potential question we must have an answer. - Check
To test simple features, it is enough to show the design on the device; for more complex, clickable prototypes are needed. We demonstrate to our team and other colleagues, remember the reaction, draw conclusions. At this stage we try to ask more questions, the answers to them will be very useful to us. Why do you think so? How would you do? What confuses? Immediately figured out? Etc. - Three questions
What well? In our solutions, there will almost always be pluses (we thought well of them, right?), The main thing is to be able to notice and fix them: aha, I liked the cat on the screen and liked everything.
What is wrong? But there will be drawbacks, we also notice and remember them: the cat, of course, is cool, but what is being downloaded is not at all clear.
What ideas? On this question, you need to figure out how to preserve and increase the pros, as well as how to remove the minuses: try to add animation, let the cat rolls the ball, it will be clear that the application is not frozen.
Now we have ideas for further work, so we finish the first cycle and start drawing again. Yes Yes.

As a result, we have a vicious circle, from which we can exit as soon as the result will be fully arranged.
Solution protection
In fact, this is a huge part of the work of the designer and you can discuss it for a very long time. But I will try to bring the main idea.
At the design stage discussions always arise, and this is normal - it’s bad when there are no disputes. But many disputes can be resolved quite simply, the main thing is to "talk" in numbers. Unfortunately, not all experienced designers can do this.
Every small "taste" is solved by testing Side By Side. This is the younger brother of the A / B tests, when a person is shown two static pictures, and he should choose the one that he likes the most. I emphasize that serious things cannot be checked in this way. Free to test this method can be a regular distribution, for this you only need a database of addresses and time. It is possible and faster, but then for the money, for this there are special services: Amazon Turk or Yandex.Toloka . We use Toloka in the team, because there is a Russian-speaking audience for which we are doing our product.
We solve major issues with full-fledged A / B tests on "live". I told about this briefly above - we set a hypothesis, measure the funnels, we get a figure for a conversation.
Well, no one has canceled corridor testing. We take a prototype in our hands and go to show our colleagues and acquaintances, if the upbringing allows, you can even go out into the street and make fun of the passers-by. We ask everyone the same questions, according to the results of such testing, we will have response statistics, which will be our argument for protecting the design.
I use this approach to work, we will always have a number with which we can “talk”:
- 67% of people answered that this icon is clearer
- 7 people out of 10 immediately performed the right action
- 41% of people fell off on this option of issuing results
Design Principles
At the same time, the uncontrolled method of working with numbers can turn our product into a vinaigrette. Advance should take care of the principles of design in our team, register them and approve the whole team. You can even print it and hang it in a prominent place. A classic example is the principles of Dieter Rams that he promoted to Braun. There is also such a selection of the principles of younger companies , you can learn and be inspired. A resolution bonus will be the resolution of disputes - when we do not have the opportunity to test different solutions, then the one that follows our design principles is worth taking. We remove unnecessary disputes, thereby saving working time.
Of course, these tips on protecting solutions will not help us in all situations, but following them will make design simpler.
After design
After approval of the design begins development. The product designer is closely associated with the developers. In the Beepcar team, designers are sitting together with the developers, this speeds up the solution of minor issues and increases mutual understanding between us.
The entire last module is crucial for the designer. Who needs our beautiful layouts, if at the exit people see a frankly treshovy product. Then most of our efforts will be empty. Therefore, we follow the correct implementation of our design - after all, they will ask us if something looks or works not according to the approved design.
Training
Before giving layouts, you need to make sure that we have calculated all the states for all screens. In order not to forget anything, it is good to make yourself a check of the status sheet, for each project it will be individual, but you can start with standard things:
- How the screen will look if there is no content;
- What will happen if the Internet disappears or is slow;
- What it looks like for a logged in user;
- The maximum and minimum length of text fields;
- How long names are abbreviated;
- The names on the buttons fit in all languages that we support;
- Where errors may occur and how they should look;
- What elements may be inactive.
In addition, we need to be sure that our design will be displayed on all available platform screens equally well. It happens that it is difficult to please everyone, then you can look at the analytics and sacrifice the display quality at unpopular resolutions. And on the contrary, those permissions that we have in the first places should be worked out to the smallest details.
How to transfer layouts
To transfer layouts we use the well-known Zeplin and the lesser-known Sympli . If there are a lot of people in the team who should have access to the layouts, you should pay attention to the second one, it will be cheaper, because of the unlimited number of seats for a fixed price.
If there is an animation, we show it on GIF or video and make a description with changes of each parameter:
animation: easy in-out
time: 0.2
opacity: 100% → 90%
During the development we always stay in touch, any question on the design slows down the development. We try to immediately respond to mail and other channels of communication.
The final stage is testing and Design Review. In Beepcar, these processes are structured as follows:
- If we are talking about mobile applications, the developer rolls the feature into a test build via HockeyApp . If about Web, then the feature is sent to our test server.
- Testers are looking at all the devices, and compare the designer's layouts with what happened. Frank shoals, they immediately comment on the task and send back to the developers for revision. In controversial points, the designer is attracted to the discussion.
- After testers are completely satisfied with the quality of the features, the task returns to the designer. He must conduct a design review. Now almost the final version of the feature comes into our hands. For the most part, the designer is required to check all the indents, pins, colors, icons, etc., so that everything looks exactly and clean. It all depends on the developer, if he is attentive to the details, then you don’t need to check anything yourself. As soon as the designer finally confirmed that everything suits him, the feature is sent to the final assembly.
Epilogue
Of course, not always follow the cycle clearly. There are deviations: rethinking of tasks, kickbacks and everything that is inherent in our work. But for a year of use inside Beepcar, this principle of operation has borne fruit - in terms of design has become more predictable, and the designers themselves are more immersed in the product.
Thanks for attention.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/349092/
All Articles