Internet people and non-people

“Nonsense - to seek a solution, if it is already there.
It's about how to deal with a task that has no solution. ”
(Strugatsky brothers "Monday begins on Saturday")
It is difficult to seem original, paying attention to how progressive humanity can inflate any trend to universal scale. Take at least another rapidly inflating in the consolidated ICT sector the “bubble” of the so-called “Internet of Things” (IoT - Internet of Things). No, do not think anything bad, the Internet of things is a good thing, quite understandable, well-known and useful up to certain limits. But when what used to be called “hype” develops into what is now called “hype”, and from each, I’m sorry, coffee makers immediately after switching on the story about IoT, it becomes necessary to understand some aspects of IoT development, so to speak , of a strategic nature, in order to warn about the possible (that there is a “possible”, everyone thinks of himself).
IoT is looking for a place
So, quite recently, the telecom sector successfully “sold” the concept that a semi-autonomous IoT physical and logical domain should emerge within the “Internet of Everything” (Internet of Everything - IoE), developing according to its own logic and having its own infrastructure directed solely on the identification, interaction and manipulation in real time of billions (and in the future trillions) of inanimate objects: radio tags (RFID), various drones, unmanned cars, trains, airplanes, nuclear reactors, turbines, as well as Intellectual toasters, microwaves, refrigerators, washing machines, and everything else.
It is assumed that the future telecom infrastructure will be provided for this with appropriate technical means, and in its wireless / mobile / cellular segment - with physically dedicated RAN (Radio Access Network) subsystems that use either individual frequency resources specially allocated for this (mainly low frequency range - from 400 to 900 MHz), or frequency resources of cellular networks of general purpose, but according to their own special data transfer and communication protocols with IoT objects. The names of the corresponding IoT substandards are NB-IoT, LoRAWAN, LP-WAN, etc. - they say nothing to the Shirnarussam, but they are the secret elite jargon of the club of business neophytes, a la the North American "carpetbaggers", rushing to master the new, tasty morsel that has already opened up to the well-known telecom sector.
If you carefully read a psalm called Release 14 3GPP in Mobile Gospel, it is easy to see how much attention is paid in it to the description and specification of the parameters of the RAN 5G radio interface, which ensures the most accurate spatial positioning and real-time broadband communication (less than 1 ms) from mobile objects - cars, aircraft, etc. In general, there is a feeling that the IoT was created specifically for 5G technology (how else can you sell 5G at the global level?), and those 5G technologies are under IoT, but now this is not the case.
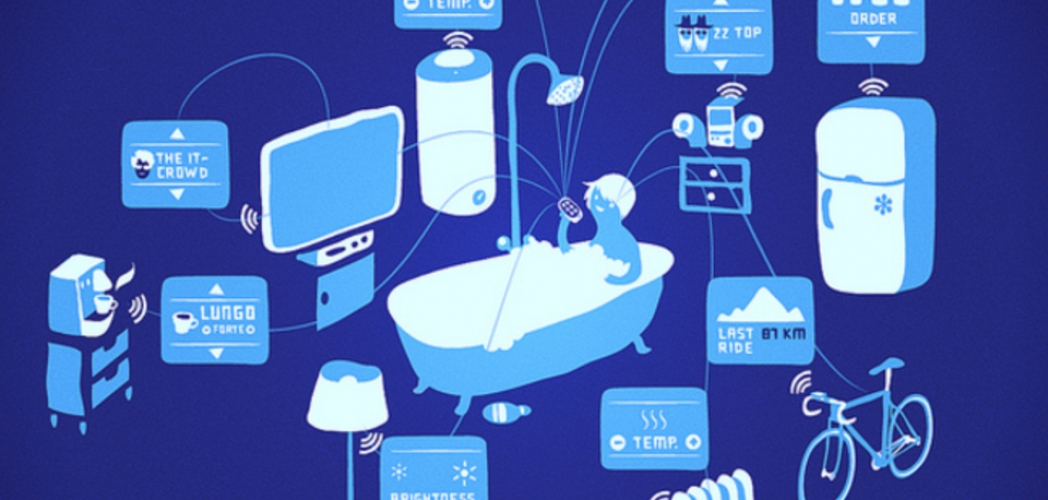
Living = non-living?
In the professional literature, the attention is rightly drawn to the fact that the “human” subscriber devices themselves (smartphones, communicators, tablets, etc.) are also IoT objects, and how they function there - with the knowledge or without the owner / user / subscriber - the case is dark, the tenth, and it is not so important. If only the traffic flowed, but there was money on the subscriber account. It turns out that the human subscriber base, which consists of “only” several billion individuals, globally (even taking into account the multiplicity factor of SIM cards - from 1 to 3-4, depending on the specific local cellular market) in the perspective of cellular networks 5 generation is just a small subset in the coming myriad of inanimate IoT subscribers.
No matter how humiliating or not, for a proud representative of the human race, sober awareness of the fact that from the point of view of the network operator, he, Homo Sapiens, although it sounds proud, is equal in its network rights with its own (or neighbor) “intellectual” from the technical point of view, the electric kettle is the carrier of the “unique attributes” (UA) and “unique identifiers” (UI) of the subscriber is not the subscriber himself, but his device (for example, via IMEI code) or SIM / e-SIM card in his device (through own MDs). Therefore, assigning to the IoT a subset of live subscribers to a huge number of non-living subscribers is, alas, quite logical and correct.
Every network consists of holes
On the one hand, in the field of mobile and fixed Internet access, almost from the very beginning of its operation, the developers paid great attention to network security and crypto-protection of traffic, subscriber data, content, etc., despite the formula - “the projectile is always stronger than armor”. On the other hand, the world is filled with chilling stories about hacking into other people's databases, followed by the abduction of them with naked photos on a grand public scandal, sometimes Bitcoins for millions of dollars, then subscriber bases for several billion accounts, and similar horrors. And this is despite the fact that anyone who has little sense in modern cryptographic systems is well aware that such systems that provide a symmetric exchange of crypto-keys with a sufficiently high duty cycle, practically make senseless attempts to break the communication link (and even more so in real time) for non-compliance of requirements to the use of expensive computer technical resources and the expected practical result. But since in the modern technical world, the weakest and most unreliable link is the same person, carried out by insiders "fraud" of the relevant resources ensures the success of attempts to hack the absolute majority of protected confidential data.

From the foregoing, we can conclude that, despite all the desperate attempts to protect valuable data and their confidentiality of storage, transfer and use, both UAs and UIs used in IoT do not provide an adequate degree of safety and protection. In other words, everything that is generated, stored or transmitted can be stolen either by storage space / system or in the process of transferring an information packet. Even a hundred-gigabyte (per second) optical data transmission channel over optical fiber can be easily intercepted, read and recorded in real time (assuming no overlay of cryptographic protection) without compromising the integrity of the optical fiber itself and almost imperceptibly to the optical transport network operator using an easily accessible device that costs about 2 thousand euros. When they talk about fundamentally un intercepted optical data networks using the so-called. “Quantum cryptography” (in the manner of a recent Chinese experiment to bring such a satellite network into space), it should be noted that, firstly, due to the low bandwidth, quantum cryptography is not used to encrypt the data channel itself, but only to send crypto keys to it, and, secondly, no matter how well protected such lines are, they are always protected on a point-to-point basis, leaving network nodes vulnerable to fraud. And, although we live in an incredible world, in which until recently seemed the purely speculative and physically impossible effect of "quantum teleportation" based on the "EPR Paradox (Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen)", it turned out not only physically realizable, but also technically and practically applicable in the field of quantum cryptography, the participants of awesome orgies, who discover their spicy photos in all corners of the world wide web, in all possible charms and angles, this does not get any easier.
This begs the sad conclusion that modern computer and telecommunication networks operating with multiple IoT objects, neither now nor in the foreseeable future, can provide adequate and moreover absolute protection of UA and UI of the above objects in exact correspondence with the lapidary statement of one literary hero that "in the end, every network consists of holes." And even if the networks approaching the ideal of confidentiality and cryptographic protection are ever built, the presence of an unavoidable human factor in them will reduce the strength of the whole chain to the strength of the weakest link in it, i.e. - man, and, therefore, - to zero. In any case, this will be the case while there are still living subscribers on the planet, not yet replaced by artificial intelligence, which, as smart people have already noticed, will be able to destroy fraud along with its source. Any references to saving technologies, such as “blockchain” or “smart contracts”, which theoretically make impossible situations with a gap in information security, are easily nullified with real stories about missing or stolen bitcoins and other glorious cryptocurrency representatives.
The high degree of vulnerability of IoT facilities to the facility today and tomorrow itself is undoubtedly an aggravating factor in the further development of IoT. But since, as one philosopher used to say, “man is the measure of all things” (and, by the way, the “helm” of the entire Internet), i.e. self-valuable basic subject of commodity-money relations (it seems the classics taught us so), then a reasonable question arises - what about the safety and security of the UA and UI of this very subject?
Get under the rink of mass grazing
Here, very opportunely, the Russian government came up with a refreshing initiative — for the five-year period, the entire commodity turnover in the Russian Federation was completely transparent in logistics, financial and fiscal relations at the expense of these UA and UI of each commodity object crossing the border or shipped on the national territory. Obviously, for this purpose, the idea of merging the Federal Tax Service and the Federal Customs Service has already been conveyed to the media in a single fiscal super-body for full end-to-end control and taxation of all material and financial transactions in the country, which is generally a global innovation. To this end, interested organizations to participate and shake the fruits of future success organizations are already preparing for the development and production of relevant components and technological equipment of this fascinating, of course, profitable and timeless process. It is obvious that, since the NFC, RFID technologies, their complementary readers, software, and other elements of this entire ecosystem are already well known, available and run in other markets, there are no sad surprises other than the standard Russian “maybe”.
However, even if you “dump” everything and everything, namely all inanimate and living objects (dogs, cats, sheep, cows, hamsters, etc.), the question arises - what about the “owner of the (electronic) signature” - directly the owner , owner, person, simply speaking? After all, it is precisely in the answer to the question - whether it is he or not - that the enormous amount of problems and collisions of property, financial, legal and biological plans comes up. The turbid wave of fraud, which is now rolling across Russia with fake credit agreements concluded on photocopies or simply the passports of their legal owners without their knowledge, clearly demonstrates that the existing system of identification of a person / citizen on his passport with a 3x4 cm photo is absolutely archaic, unreliable and dangerous for the holder of such a passport, and for the state and society as a whole.

All the fine-mindedness in terms of the turnover of subjects on the Internet ends as soon as it encounters a fundamental problem: - unlike a pack of cigarettes or a bottle of imported whiskey, you will not stick RFID to a person and you will not stick it inside. Of course, there were and continue the heroic attempts of enthusiasts to cross themselves with a computer, such as one American professor who, having chopped his hand, turned into a caricature of cyborg, or rather, the “thing” of IoT. Of course, there are still regular customers of the network of London pubs who voluntarily agree to chip themselves, loved ones, for the sake of being able to pay or take a drink in a bar at a loan, without having any wallet or NFC-tagged device. There are even willing to introduce RFID to all citizens without exception. But…
Any technical devices, be it RFID in general, and NFC, in particular, by definition, as well as SIM cards, can be hacked, compromised, duplicated, or simply withdrawn or disabled. Moreover, many of these devices can be read, rewritten, or destroyed remotely using mechanical or electromagnetic interference.
The question arises - what about the systems of biometric identification of actually “human” users?
Fluctuation biometric accuracy
Indeed, after the first fingerprint sensors, which ten years ago still worked “one time” and created some problems and troubles for users, in the form of blocking access to their own phones, computers, cars and apartments, high-speed devices appeared (with a response time of less than 0.2 sec ) with the probability of correct fingerprint recognition more than 95%. However, a recent successful attempt by a group of American experts to crack the biometric protection system of the iPhone of a criminal who was killed in a shootout by making a three-dimensional plastic copy of a fingerprint of a corpse and completely imitating its electrical and capacitive parameters using the selective deposition of metal layers showed that relatively "primitive" systems of this kind and everyday The levels can be cracked with all the sad consequences.
This led to the fact that the biometric fingerprint identification system, for the first time in history on a state scale, was introduced by the US immigration service against mass illegal entry into the country using foreign passports of citizens from Asia in general, and the Chinese, in particular, was fundamentally compromised due to the inability American immigration control officers distinguish the face of one Chinese from another.
Another similar fiasco is happening on a global scale right now in front of the entire venerable world public - Face ID, installed on the latest iPhone X, as it turned out, does not work on children under the age of 13, does not distinguish between twins and even sisters, easily deceived with penny plastic overlays on the face and makeup. It turns out that a three-dimensional face scan and the calculation of key parameters of its 3D model at critical points still does not give the required accuracy of identification.
There are also such, yet more exotic and rare, ways of establishing unique attributes and identifiers, such as scanning the iris and / or retina of the human eye, as in some models of smartphones or in systems of automatic biometric identification at immigration control at some European and American airports. But also to this technique there are questions about the convenience and versatility of use, the reliability of the identification of the individual and the possibility of circumventing the perfect technical means. In any case, Hollywood film production has already managed to show how this is done.
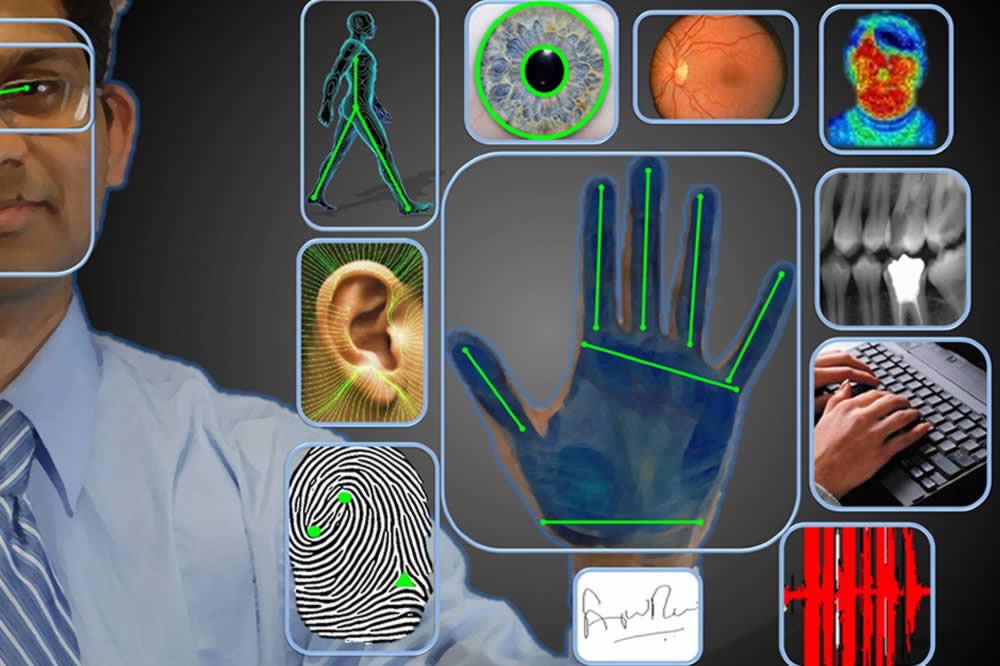
Thus, against the background of the global request for the establishment of the most reliable unique attributes and personality identifiers, allowing to lay the foundation for all the now fashionable and already built-up “digital state” with a “digital economy” and the ubiquitous IoT, working on the “Internet of People”, the whole multiplicity of possible solutions disappears, faced with the technical requirements for determining the identity of the personal identity, integral to it (the person) at a fundamental biological level, and, preferably, are unique and unchangeable parts her (personality) at the immanent cellular level.
Well, such a single fundamental, non-falsified procedure for establishing the authenticity of an individual is, at present, the so-called. "Gene fingerprinting" (or "Jeffreys test"), which provides identification at the cellular level by the unique individual structure of the characteristic nucleotide sequences of human DNA. Indeed, the fact of the presence of unique genetic information in every cell of the human body and the accuracy of identifying it at the level of 1 error per 10 billion people make gene fingerprinting the only possible method of absolute identification of a person adequate to the requirements of the Internet of People, the “digital state”, etc.
At the beginning of the tenths, the well-known Japanese company NEC (Nippon Electric Corporation) proposed two personal identification systems in Moscow - one based on the analysis of the image of people in the crowd video, and the second - in the form of a portable automatic DNA analyzer that, according to NEC, carried out the basic express genetic fingerprinting at a speed of 25 minutes per sample. The first system, which allowed “on the fly” to identify a person in a crowd with indication of his / her sex and exact age (up to a year) and was initially accepted for testing with great enthusiasm, was later rejected, in particular, by the then leadership of the Moscow Metro and representatives of competent organizations, because it turned out to be easily deceived by simple tricks such as a long visor of a headdress, dark glasses, whiskers, beards, make-up, and so on. The fate of the rapid DNA test system, however, remained unknown.
People Genocode Internet
Summarizing all the above, it is not difficult to come to the logical conclusion that the “Internet of Things” currently under construction needs a parallel (and perhaps advanced) construction of the Internet of People (IoP), which is completely focused on ensuring security and respecting fundamental rights and freedoms of an individual in civil, legal, financial and property terms. The basic level of such an IoP should be a system of absolute identification of the person, the only technical possibility for the realization of which is today the so-called. "Gene fingerprinting". It is her data stored in state registries of the passport system in an extremely protected, repeatedly reserved, unchangeable and non-rewritable form, additionally enhanced by the blockchain technology, and should become the basis of the entire system of guarantees of the rights of a citizen from any legal or financial encroachment or offenses, as well as the foundation and reference level for less reliable, but more easily readable in express or field conditions, secondary parameters of biometric identification (fingerprints, hands, feet, auricles, three-dimensional contour of the face, drawing of the iris or retina). Do you think that's all?
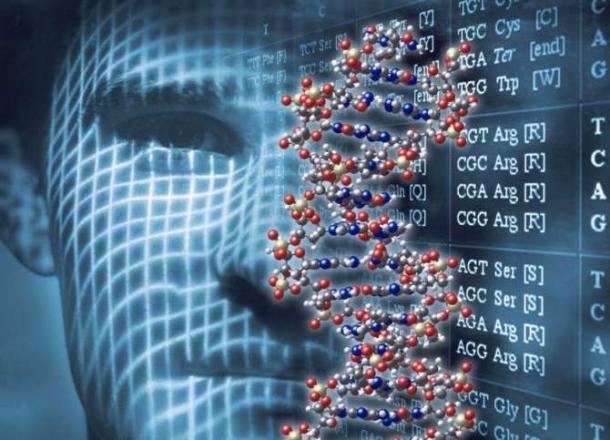

The fantastic time in which we are all fortunate enough to live is characterized by the “slug of dreams” that until recently were considered absolutely impossible in the scientific community. These include the transfer of information through mountain ranges by neutrino flows, and the registration of gravitational waves - the “ripples” of space-time, and the above-mentioned experimental confirmation and practical implementation in ICT in the form of quantum cryptography, which seemed to be absolutely abstract and physically impossible for the EPR paradox.
The idea of the in vivo correction of the genocode of an already formed organism at the level of its every single cell can also be referred to as such an “impossible, made possible”. This heresy — the lifetime rewriting of the genetic sequence in each individual cell — was relatively recently implemented using the newly developed CRISPR method (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats). To date, CRISPR is considered the most important technological innovation in the life sciences since the invention of the so-called. polymerase chain reaction (PCR), opened three decades earlier and allowed to implement the so-called. DNA sequencing, and on its basis to create a method of gene fingerprinting.
Currently, CRISPR technology is being investigated for the treatment of genetic diseases both in the pre-natal phase (at the stage of embryonic intra-placental development) and in the post-natal phase, i.e. in adult organisms and people, including first. This means, at least in theory, that it can allow an individual to change the DNA code to be registered, bypassing the system of gene fingerprinting. Time will show whether this is so, as well as future scientific and criminal practices of the “digital state”. So life goes on, and the shell still wins armor. Therefore, do not say later that you were not warned ...
Authors publication:
Alexander GOLYSHKO, systems analyst at Technoserv Group of Companies,
Vitaly SHUB, Deputy General Director, Telecom business area, IPG Photonics Russia (IRE-Polyus)
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/348594/
All Articles